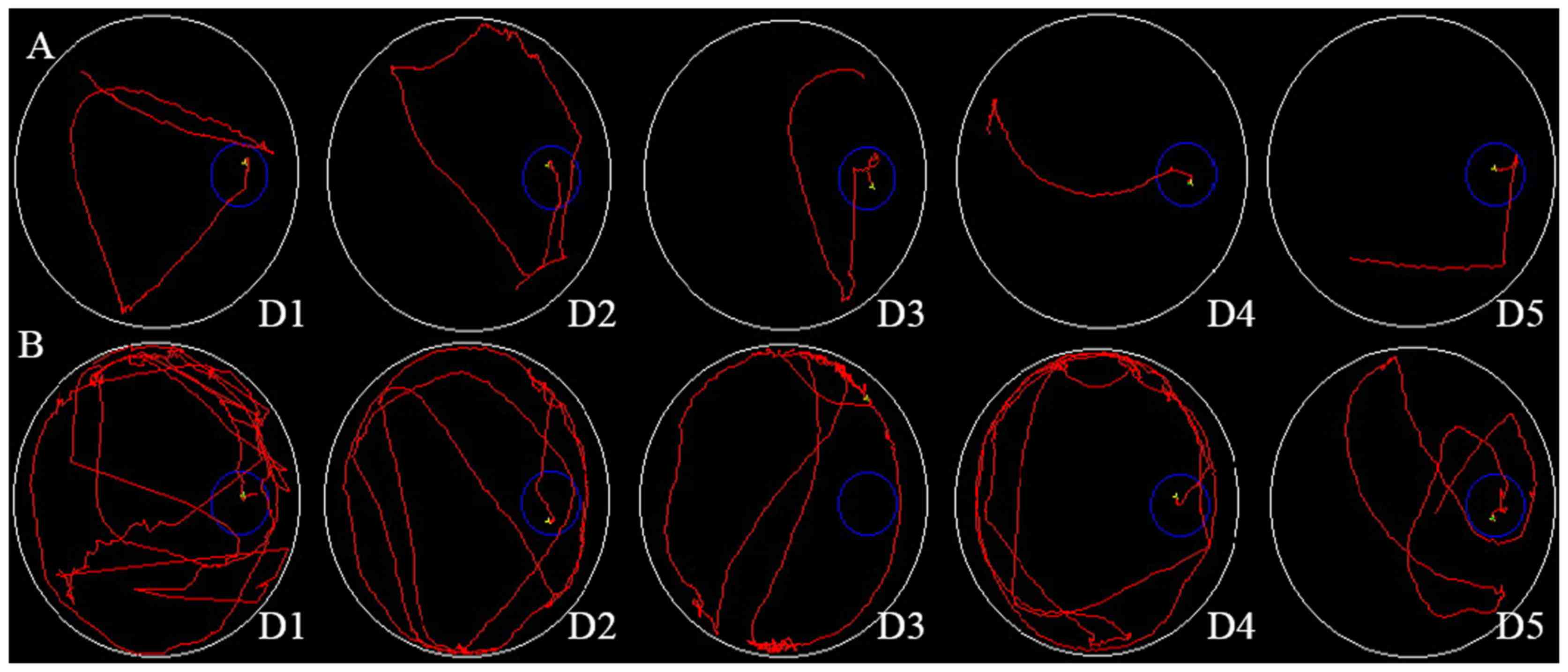
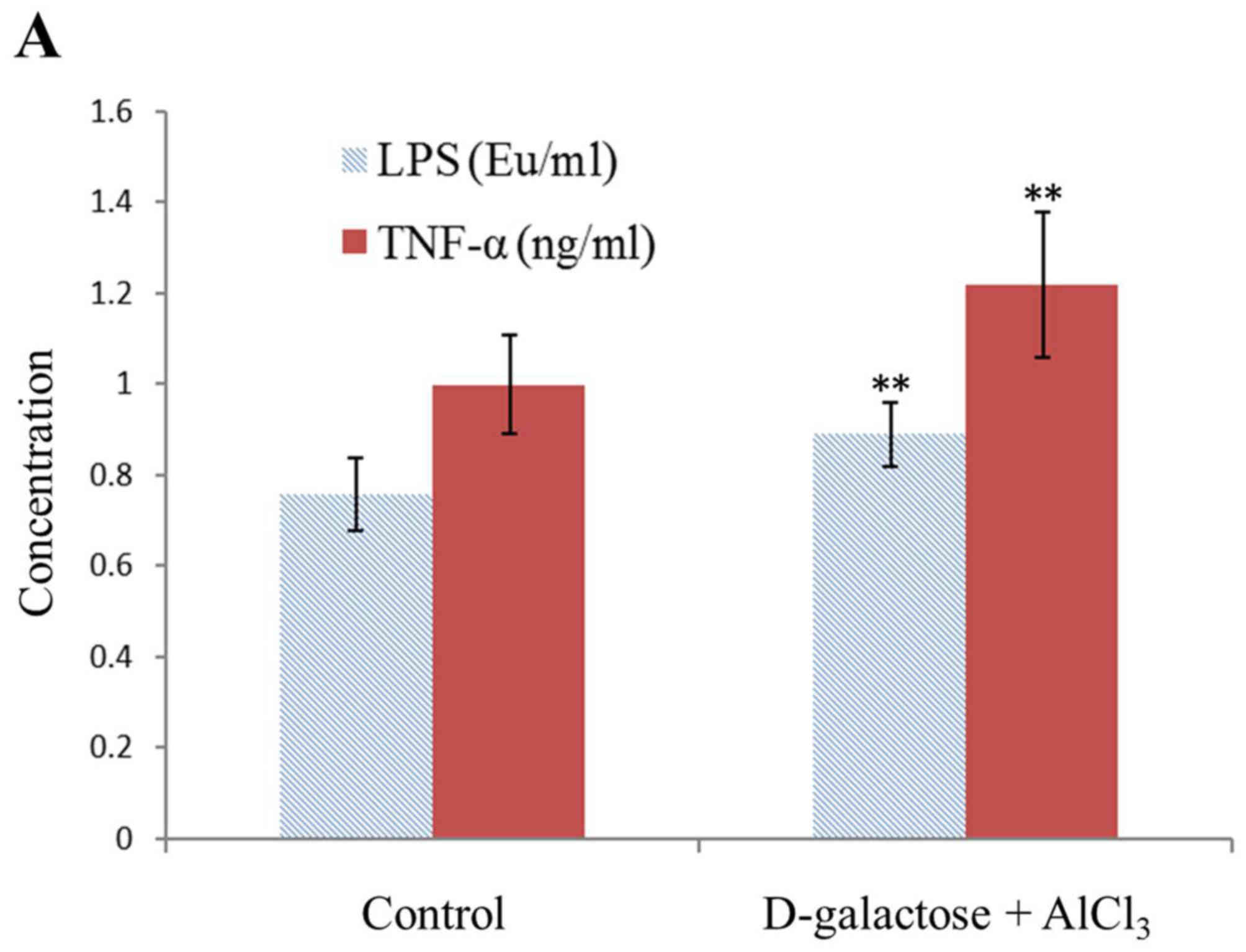
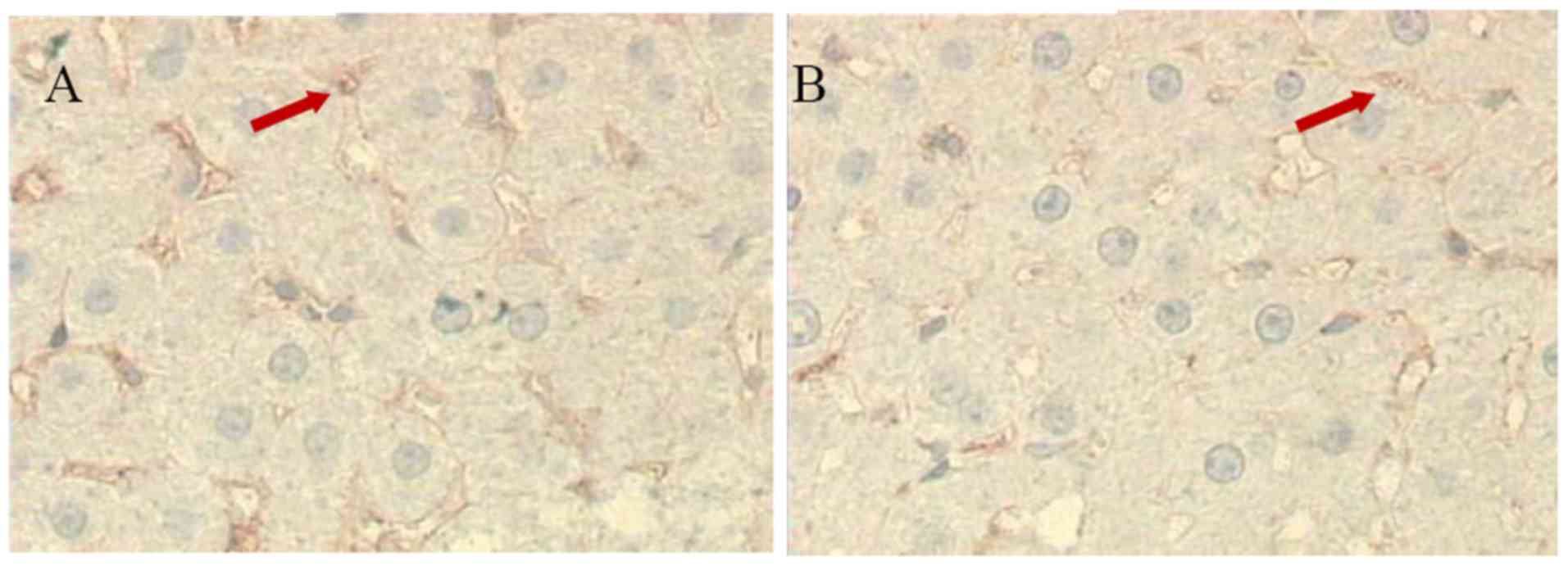
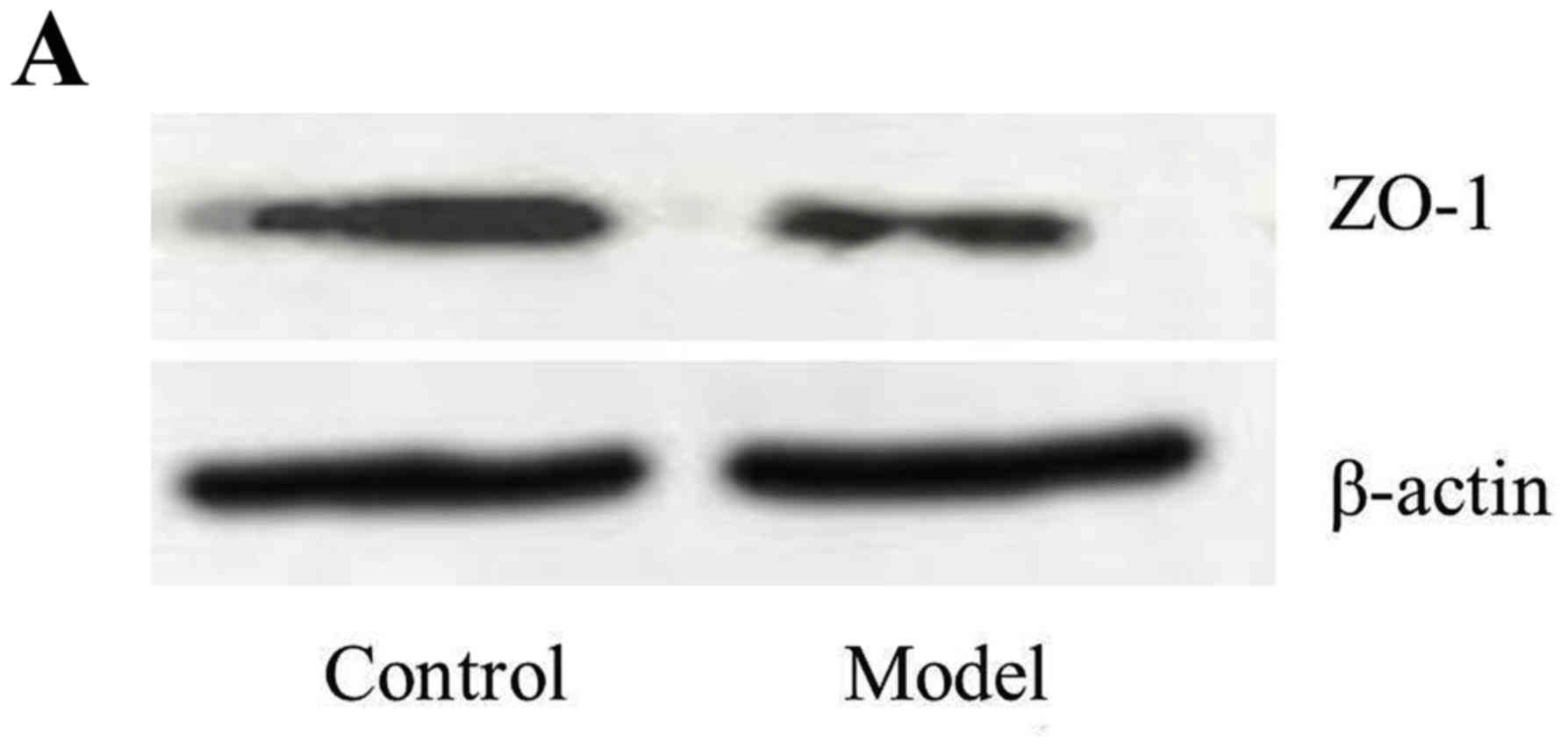
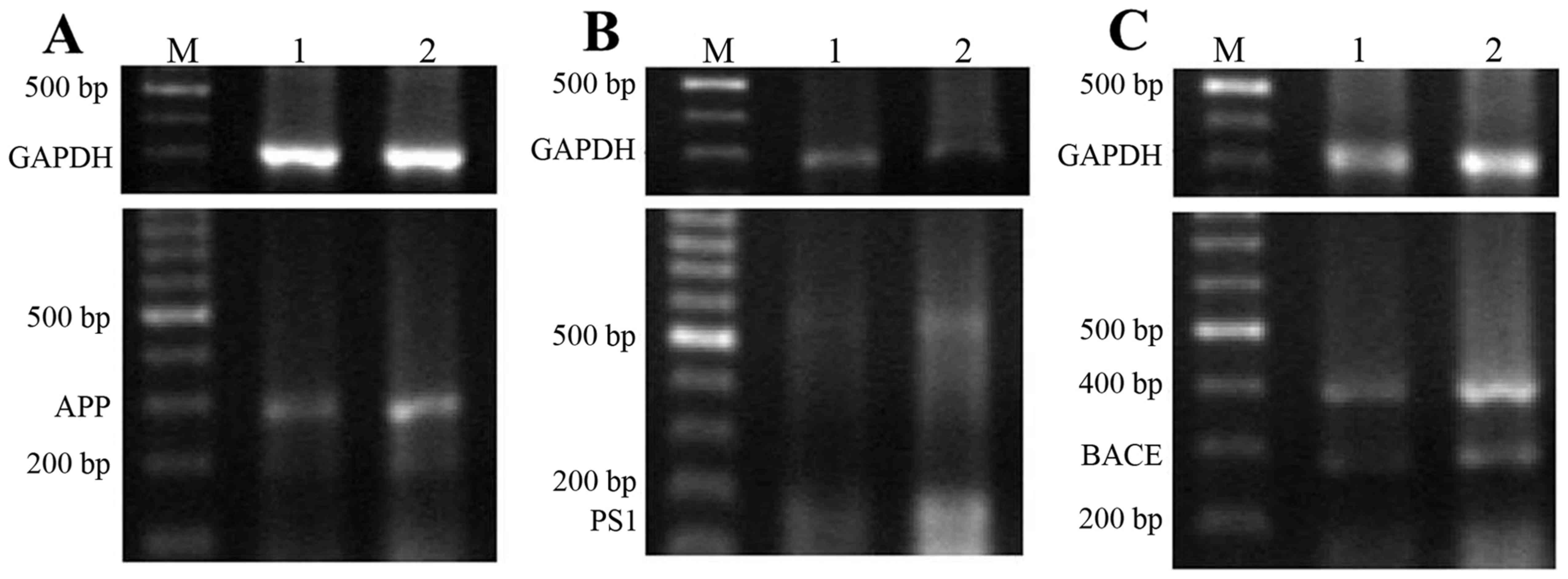
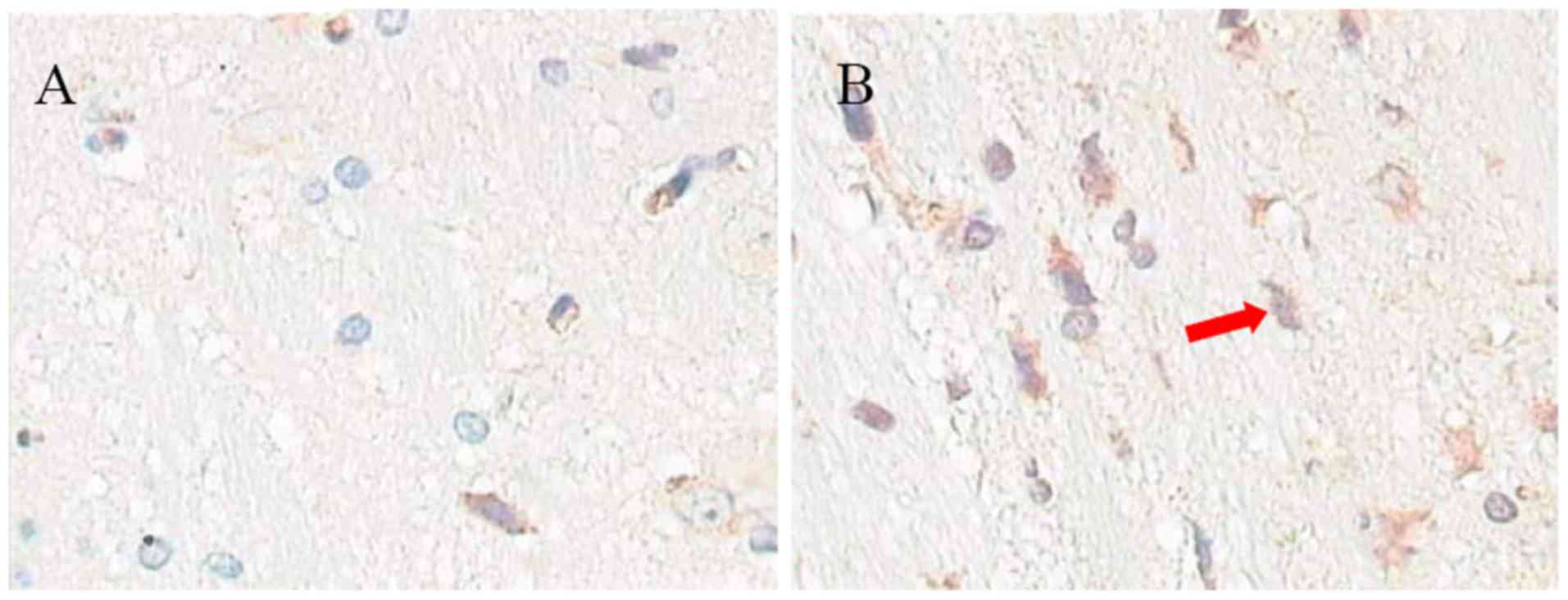
|
1
|
Zhang Q, Li N, Jiao X, Qin X, Kaur R, Lu
X, Song J, Wang L, Wang J and Niu Q: Caspase-3 short hairpin RNAs:
A potential therapeutic agent in neurodegeneration of
aluminum-exposed animal model. Curr Alzheimer Res. 11:961–970.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Campbell A: The role of aluminum and
copper on neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers
Dis. 10:165–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Castorina A, Tiralongo A, Giunta S,
Carnazza ML, Scapagnini G and D'Agata V: Early effects of aluminum
chloride on beta-secretase mRNA expression in a neuronal model of
beta-amyloid toxicity. Cell Biol Toxicol. 26:367–377. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sethi P, Jyoti A, Hussain E and Sharma D:
Curcumin attenuates aluminium-induced functional neurotoxicity in
rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 93:31–39. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Han DW: Intestinal endotoxemia and liver
disease-IETM theory of liver failure. Chin J Hepatol. 3:134–137.
1995.
|
|
6
|
Han DW: Intestinal endotoxemia as a
pathogenetic mechanism in liver failure. World J Gaotroenteral.
8:961–965. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhao LF and Han DW: Clinical significance
of endotoxemia in liver diseases. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi.
7:391–393. 1999.
|
|
8
|
Zhou X, Han D, Xu R, Li S, Wu H, Qu C,
Wang F, Wang X and Zhao Y: A model of metabolic syndrome and
related diseases with intestinal endotoxemia in rats fed a high fat
and high sucrose diet. PLoS One. 9:e1151482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang W, Shi L, Chen L, Zhang B, Ma K, Liu
Y and Qian Y: Protective effects of perindopril on d-galactose and
aluminum trichloride induced neurotoxicity via the apoptosis of
mitochondria-mediated intrinsic pathway in the hippocampus of mice.
Brain Res Bull. 109:46–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Navarrete M, Núñez H, Ruiz S, Soto-Moyano
R, Valladares L, White A and Pérez H: Prenatal undernutrition
decreases the sensitivity of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis
in rat, as revealed by subcutaneous and intra-paraventricular
dexamethasone challenges. Neurosci Lett. 419:99–103. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Coria F, Castaño EM and Frangione B: Brain
amyloid in normal aging and cerebral amyloid angiopathy is
antigenically related Alzheimer's disease beta-protein. Am J
Pathol. 129:422–428. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Davies L, Wolska B, Hilbich C, Multhaup G,
Martins R, Simms G, Beyreuther K and Masters CL: A4 amyloid protein
deposition and the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: Prevalence in
aged brains determined by immunocytochemistry compared with
conventional neuropathologic techniques. Neurology. 38:1688–1693.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kitamoto T, Ogomori K, Tateishi J and
Prusiner SB: Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of
cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest. 57:230–236.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Philippens IH, Ormel PR, Baarends G,
Johansson M, Remarque EJ and Doverskog M: Acceleration of
amyloidosis by inflammation in the amyloid-beta marmoset monkey
model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 55:101–113. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Perl DP and Pendlebury WW: Aluminum
neurotoxicity-potential role in the pathogenesis of neurofibrillary
tangle formation. Can J Neurol Sci. 13 4 Suppl:S441–S445. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kawahara M, Muramoto K, Kobayashi K, Mori
H and Kuroda Y: Aluminum promotes the aggregation of Alzheimer's
amyloid beta-protein in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
198:531–535. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prakash D, Gopinath K and Sudhandiran G:
Fisetin enhances behavioral performances and attenuates reactive
gliosis and inflammation during aluminum chloride-induced
neurotoxicity. Neuromolecular Med. 15:192–208. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Andreasen AS, Krabbe KS, Krogh-Madsen R,
Taudorf S, Pedersen BK and Møller K: Human endotoxemia as a model
of systemic inflammation. Curr Med Chem. 15:1697–1705. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu C, Cui Z, Wang S and Zhang D: CD93 and
GIPC expression and localization during central nervous system
inflammation. Neural Regen Res. 9:1995–2001. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mandrekar-Colucci S and Landreth GE:
Microglia and inflammation in Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurol
Disord Drug Targets. 9:156–167. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Skelly DT, Hennessy E, Dansereau MA and
Cunningham C: A systematic analysis of the peripheral and CNS
effects of systemic LPS, IL-1β, [corrected] TNF-α and IL-6
challenges in C57BL/6 mice. PLoS One. 8:e691232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kang YH, Lee CH, Monroy RL, Dwivedi RS,
Odeyale C and Newball HH: Uptake, distribution and fate of
bacterial lipopolysaccharides in monocytes and macrophages: An
ultrastructural and functional correlation. Electron Microsc Rev.
5:381–419. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Y, Walter S, Stagi M, Cherny D,
Letiembre M, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Heine H, Penke B, Neumann H and
Fassbender K: LPS receptor (CD14): A receptor for phagocytosis of
Alzheimer's amyloid peptide. Brain. 128:1778–1789. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jaeger LB, Dohgu S, Sultana R, Lynch JL,
Owen JB, Erickson MA, Shah GN, Price TO, Fleegal-Demotta MA,
Butterfield DA and Banks WA: Lipopolysaccharide alters the
blood-brain barrier transport of amyloid beta protein: A mechanism
for inflammation in the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Brain
Behav Immun. 23:507–517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu L, Zhang K, Hu G, Yan H, Xie C and Wu
X: Inflammatory response and neuronal necrosis in rats with
cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res. 9:1753–1762. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zaky A, Mohammad B, Moftah M, Kandeel KM
and Bassiouny AR: Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 is a key
modulator of aluminum-induced neuroinflammation. BMC Neurosci.
14:262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nedzvetsky VS, Tuzcu M, Yasar A,
Tikhomirov AA and Baydas G: Effects of vitamin E against aluminum
neurotoxicity in rats. Biochemistry (Mosc). 71:239–244. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsunoda M and Sharma RP: Modulation of
tumor necrosis factor alpha expression in mouse brain after
exposure to aluminum in drinking water. Arch Toxicol. 73:419–426.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mackenzie IR: Anti-inflammatory drugs and
Alzheimer-type pathology in aging. Neurology. 54:732–734. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Samy AS and Igwe OJ: Regulation of
IL-1β-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression by interactions of Aβ
peptide, apolipoprotein E and nitric oxide in human neuroglioma. J
Mol Neurosci. 47:533–545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gutteridge JM, Quinlan GJ, Clark I and
Halliwell B: Aluminium salts accelerate peroxidation of membrane
lipids stimulated by iron salts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 835:441–447.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu CH, Wen CY, Shieh JY and Ling EA:
Remodeling of membrane-bound glycoproteins containing
alpha-D-galactose in the cerebral endothelial cells of rats during
blood-brain barrier maturation and alteration. J Hirnforsch.
38:541–552. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|