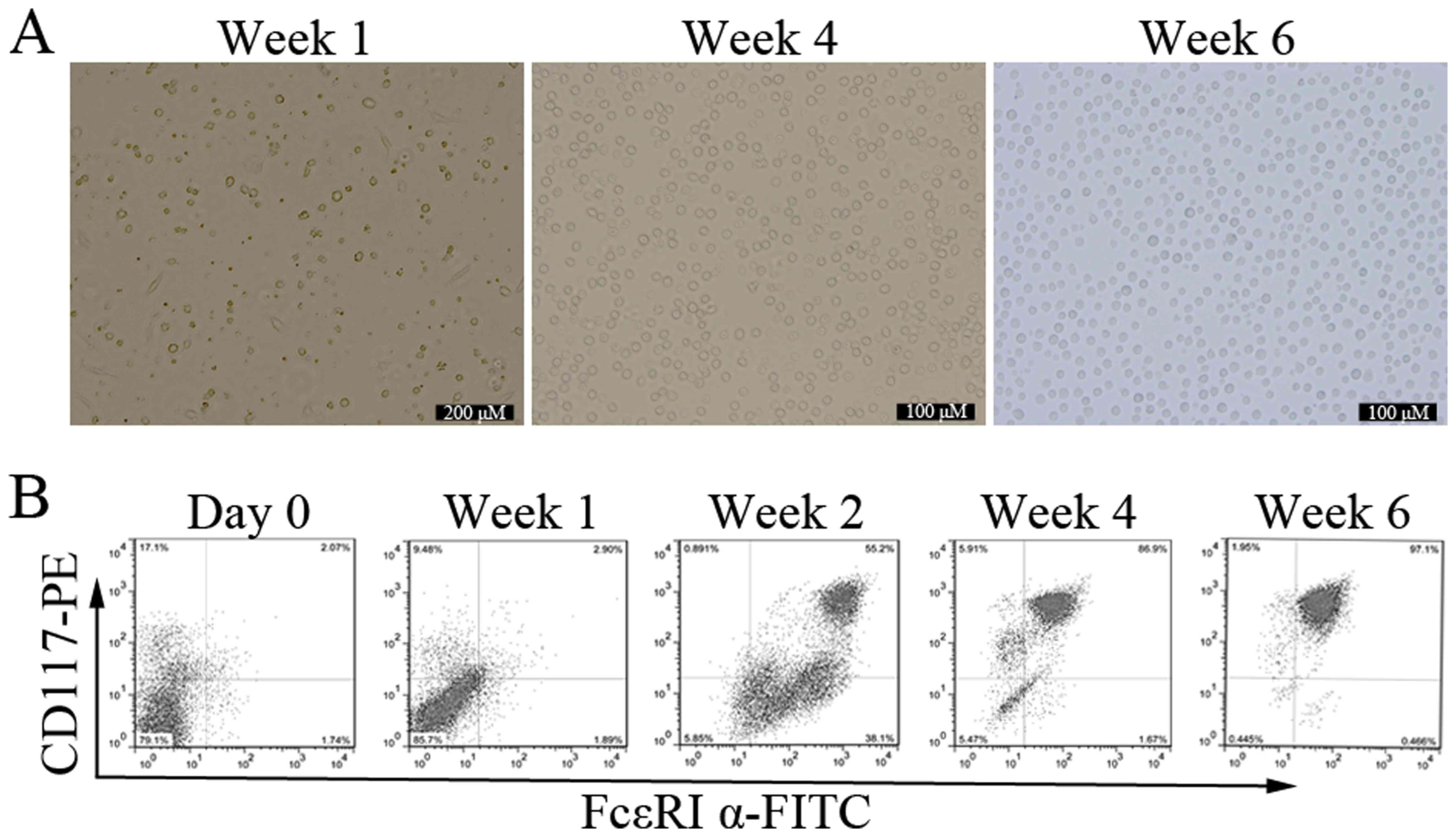
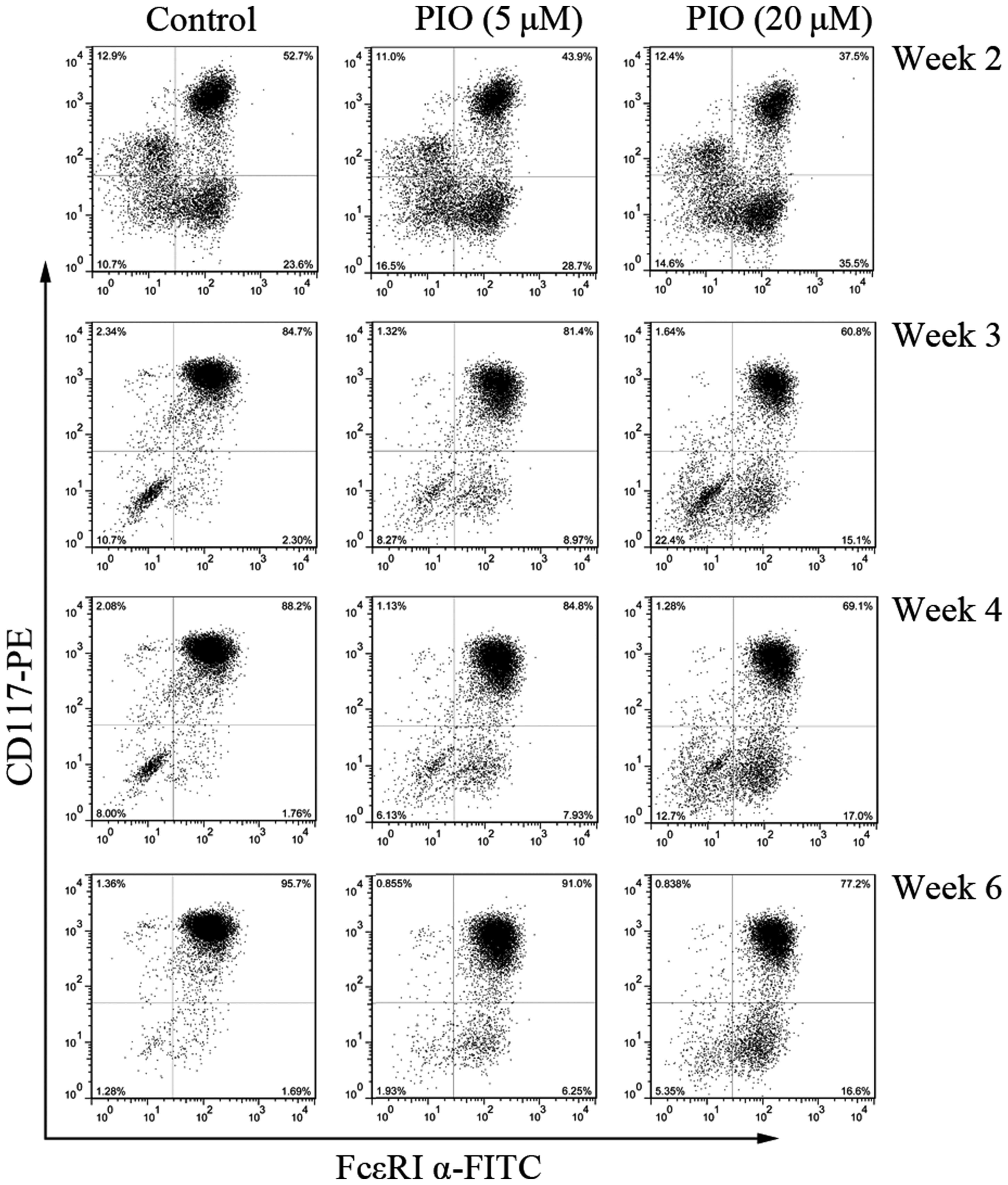
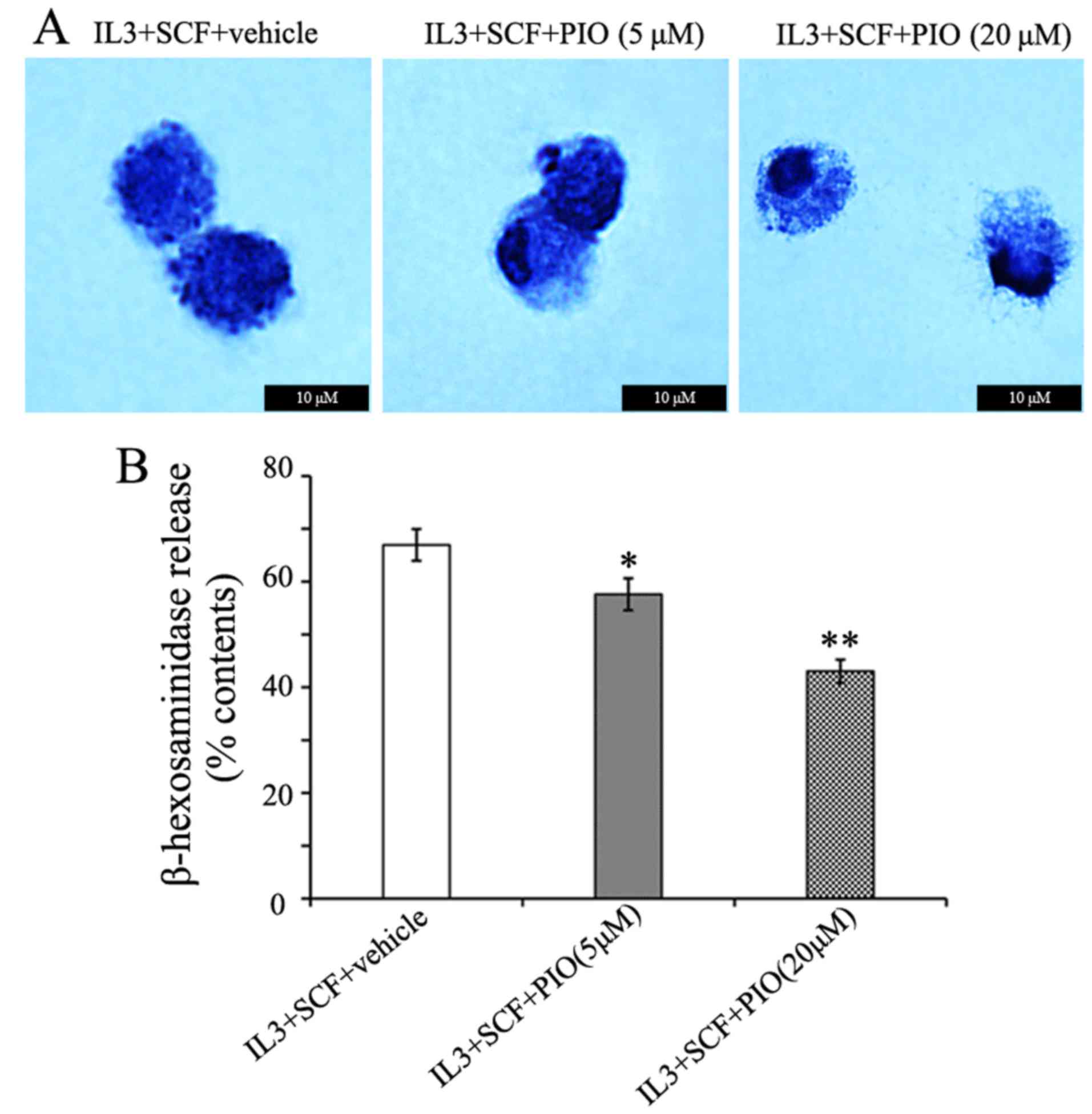
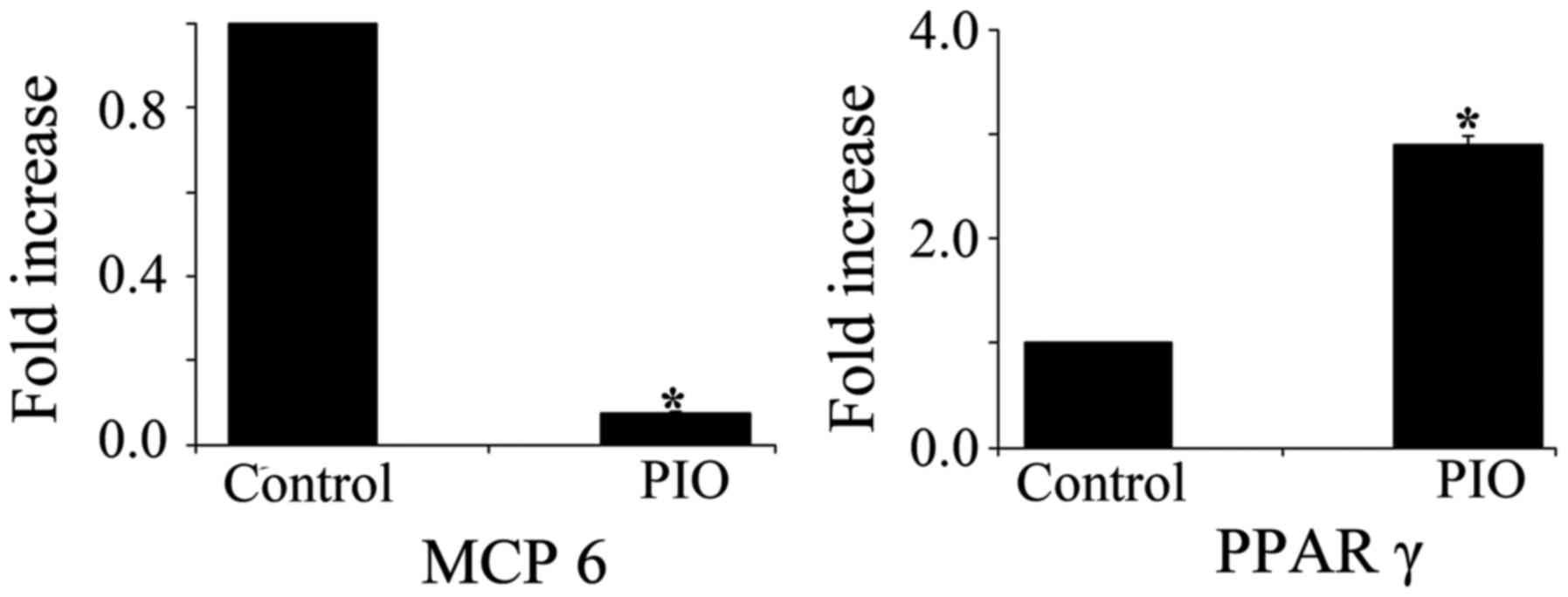
|
1
|
Kersten S, Desvergne B and Wahli W: Roles
of PPARs in health and disease. Nature. 405:421–424. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tachibana M, Wada K, Katayama K, Kamisaki
Y, Maeyama K, Kadowaki T, Blumberg RS and Nakajima A: Activation of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma suppresses mast
cell maturation involved in allergic diseases. Allergy.
63:1136–1147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao Y, Huang Y, He J, Li C, Deng W, Ran X
and Wang D: Rosiglitazone, a peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-γ agonist, attenuates airway inflammation by inhibiting
the proliferation of effector T cells in a murine model of
neutrophilic asthma. Immunol Lett. 157:9–15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marcone S, Haughton K, Simpson PJ, Belton
O and Fitzgerald DJ: Milk-derived bioactive peptides inhibit human
endothelial-monocyte interactions via PPAR-γ dependent regulation
of NF-κB. J Inflamm (Lond). 12:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Housley WJ, Adams CO, Vang AG, Brocke S,
Nichols FC, LaCombe M, Rajan TV and Clark RB: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma is required for
CD4+ T cell-mediated lymphopenia-associated
autoimmunity. J Immunol. 187:4161–4169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim SH, Hong JH and Lee YC: Ursolic acid,
a potential PPARγ agonist, suppresses ovalbumin-induced airway
inflammation and Penh by down-regulating IL-5, IL-13 and IL-17 in a
mouse model of allergic asthma. Eur J Pharmacol. 701:131–143. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang W, Zhu Z, Zhu B and Ma Z: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist induces regulatory T
cells in a murine model of allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 144:506–513. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meng Y, Chen C, Tian C, Du J and Li HH:
Angiotensin II-induced Egr-1 expression is suppressed by peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ ligand 15d-PGJ2 in macrophages.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:689–698. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Maeyama K, Emi M and Tachibana M: Nuclear
receptors as targets for drug development: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma in mast cells: Its roles in
proliferation and differentiation. J Pharmacol Sci. 97:190–194.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sugiyama H, Nonaka T, Kishimoto T,
Komoriya K, Tsuji K and Nakahata T: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors are expressed in mouse bone
marrow-derived mast cells. FEBS Lett. 467:259–262. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Spencer M, Yang L, Adu A, Finlin BS, Zhu
B, Shipp LR, Rasouli N, Peterson CA and Kern PA: Pioglitazone
treatment reduces adipose tissue inflammation through reduction of
mast cell and macrophage number and by improving vascularity. PLoS
One. 9:e1021902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sly LM, Kalesnikoff J, Lam V, Wong D, Song
C, Omeis S, Chan K, Lee CW, Siraganian RP, Rivera J and Krystal G:
IgE-induced mast cell survival requires the prolonged generation of
reactive oxygen species. J Immunol. 181:3850–3860. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Okayama Y and Kawakami T: Development,
migration, and survival of mast cells. Immunol Res. 34:97–115.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma P, Mali RS, Munugalavadla V, Krishnan
S, Ramdas B, Sims E, Martin H, Ghosh J, Li S, Chan RJ, et al: The
PI3K pathway drives the maturation of mast cells via microphthalmia
transcription factor. Blood. 118:3459–3469. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wada K, Nakajima A, Katayama K, Kudo C,
Shibuya A, Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Tachibana M, Miyoshi H, Kamisaki
Y, et al: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated
regulation of neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation. J
Biol Chem. 281:12673–12681. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki K and Verma IM: Phosphorylation of
SNAP-23 by IkappaB kinase 2 regulates mast cell degranulation.
Cell. 134:485–495. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kashyap M, Bailey DP, Gomez G, Rivera J,
Huff TF and Ryan JJ: TGF-beta1 inhibits late-stage mast cell
maturation. Exp Hematol. 33:1281–1291. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lantz CS and Huff TF: Murine
KIT+ lineage- bone marrow progenitors express Fc
gamma-RII but do not express Fc epsilon-RI until mast cell granule
formation. J Immunol. 154:355–362. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cui Y, Dahlin JS, Feinstein R, Bankova LG,
Xing W, Shin K, Gurish MF and Hallgren J: Mouse mast cell
protease-6 and MHC are involved in the development of experimental
asthma. J Immunol. 193:4783–4789. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vangansewinkel T, Geurts N, Quanten K,
Nelissen S, Lemmens S, Geboes L, Dooley D, Vidal PM, Pejler G and
Hendrix S: Mast cells promote scar remodeling and functional
recovery after spinal cord injury via mouse mast cell protease 6.
FASEB J. 30:2040–2057. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang W, Zhu Z, Zhu B and Ma Z:
Pioglitazone attenuates allergic inflammation and induces
production of regulatory T lymphocytes. Am J Rhinol Allergy.
24:454–458. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gurish MF and Austen KF: Developmental
origin and functional specialization of mast cell subsets.
Immunity. 37:25–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rao KN and Brown MA: Mast cells:
Multifaceted immune cells with diverse roles in health and disease.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1143:83–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen CC, Grimbaldeston MA, Tsai M,
Weissman IL and Galli SJ: Identification of mast cell progenitors
in adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:11408–11413. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kitamura Y, Oboki K and Ito A: Molecular
mechanisms of mast cell development. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am.
26:387–405; v. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Saito H: Culture of human mast cells from
hemopoietic progenitors. Methods Mol Biol. 315:113–122.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Succar J, Douaiher J, Lancerotto L, Li Q,
Yamaguchi R, Younan G, Pejler G and Orgill DP: The role of mouse
mast cell proteases in the proliferative phase of wound healing in
microdeformational wound therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 134:459–467.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Metcalfe DD, Baram D and Mekori YA: Mast
cells. Physiol Rev. 77:1033–1079. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakazawa S, Sakanaka M, Furuta K,
Natsuhara M, Takano H, Tsuchiya S, Okuno Y, Ohtsu H, Nishibori M,
Thurmond RL, et al: Histamine synthesis is required for granule
maturation in murine mast cells. Eur J Immunol. 44:204–214. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hirai S, Ohyane C, Kim YI, Lin S, Goto T,
Takahashi N, Kim CS, Kang J, Yu R and Kawada T: Involvement of mast
cells in adipose tissue fibrosis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
306:E247–E255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu ZQ, Song JP, Liu X, Jiang J, Chen X,
Yang L, Hu T, Zheng PY, Liu ZG and Yang PC: Mast cell-derived
serine proteinase regulates T helper 2 polarization. Sci Rep.
4:46492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McNeil HP, Shin K, Campbell IK, Wicks IP,
Adachi R, Lee DM and Stevens RL: The mouse mast cell-restricted
tetramer-forming tryptases mouse mast cell protease 6 and mouse
mast cell protease 7 are critical mediators in inflammatory
arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 58:2338–2346. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shin K, Nigrovic PA, Crish J, Boilard E,
McNeil HP, Larabee KS, Adachi R, Gurish MF, Gobezie R, Stevens RL
and Lee DM: Mast cells contribute to autoimmune inflammatory
arthritis via their tryptase/heparin complexes. J Immunol.
182:647–656. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hamilton MJ, Sinnamon MJ, Lyng GD,
Glickman JN, Wang X, Xing W, Krilis SA, Blumberg RS, Adachi R, Lee
DM and Stevens RL: Essential role for mast cell tryptase in acute
experimental colitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:290–295. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|