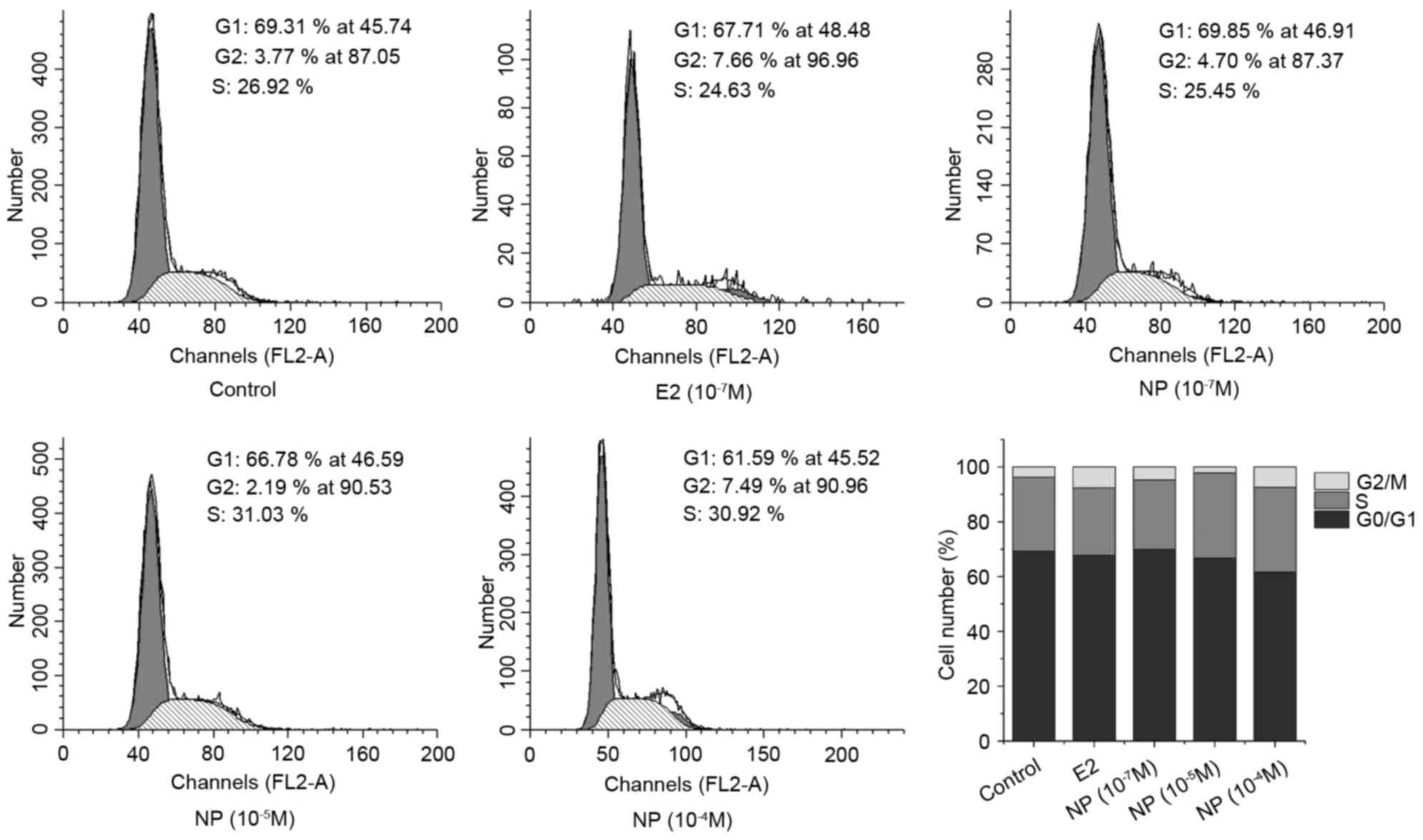
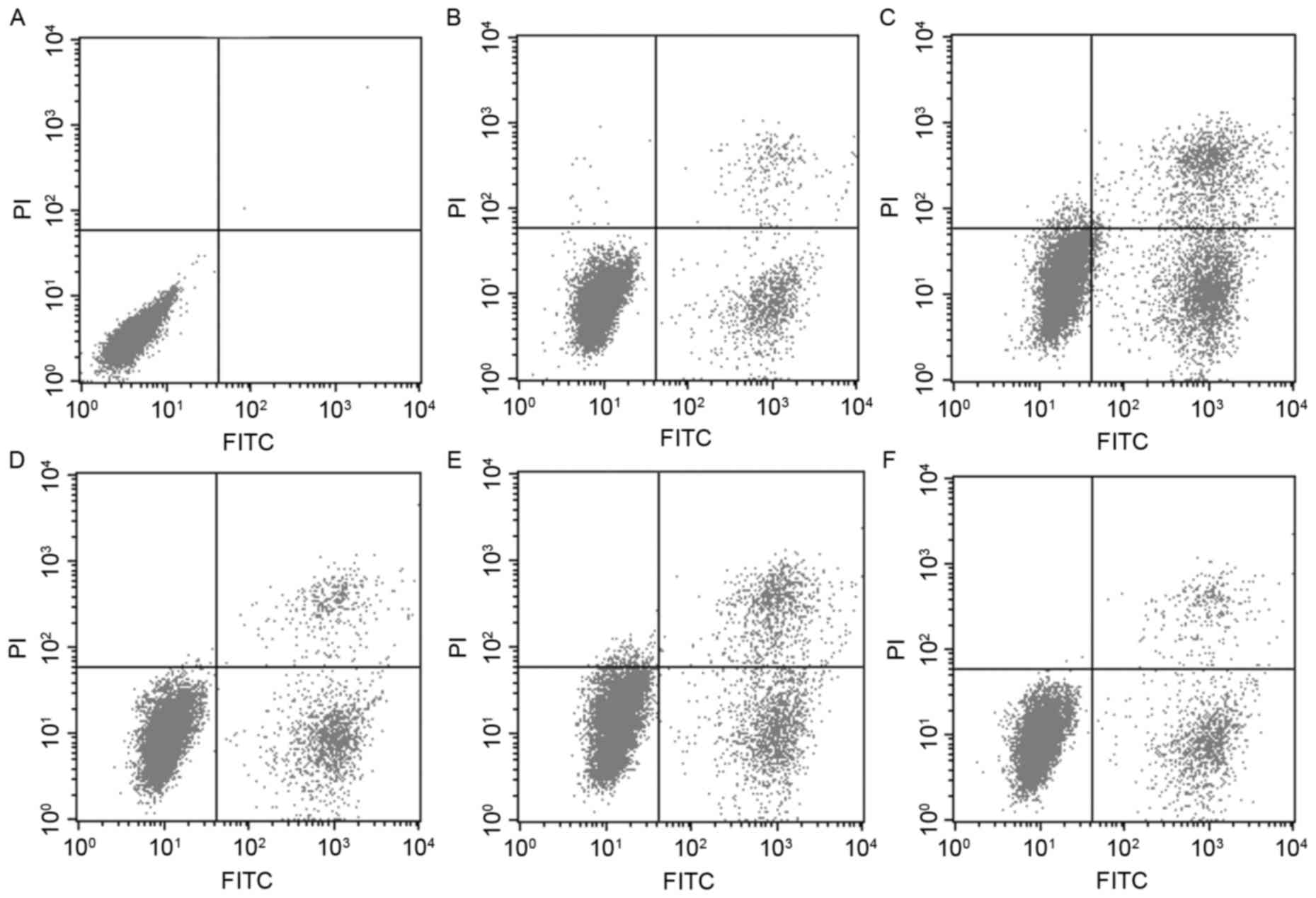
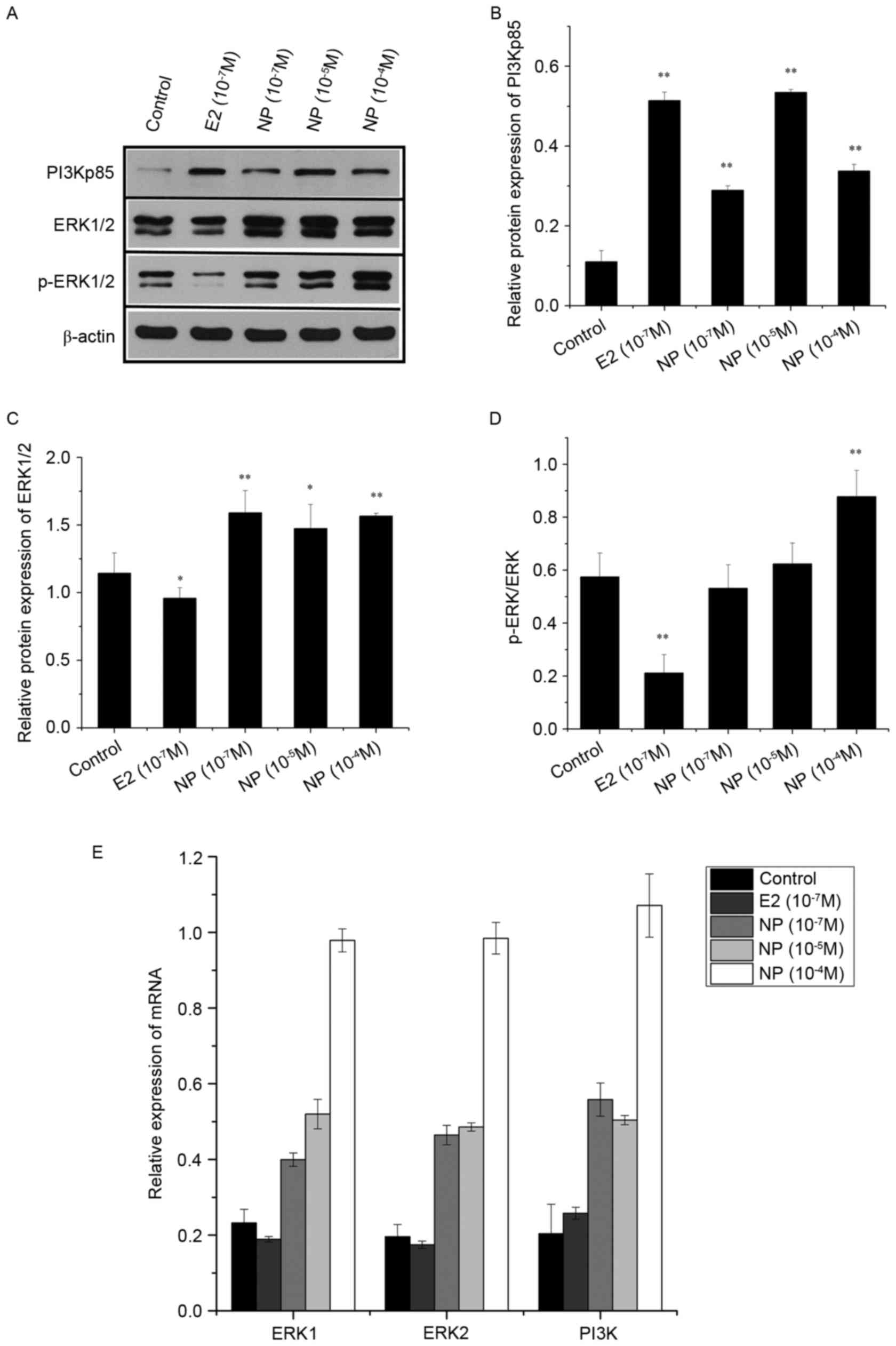
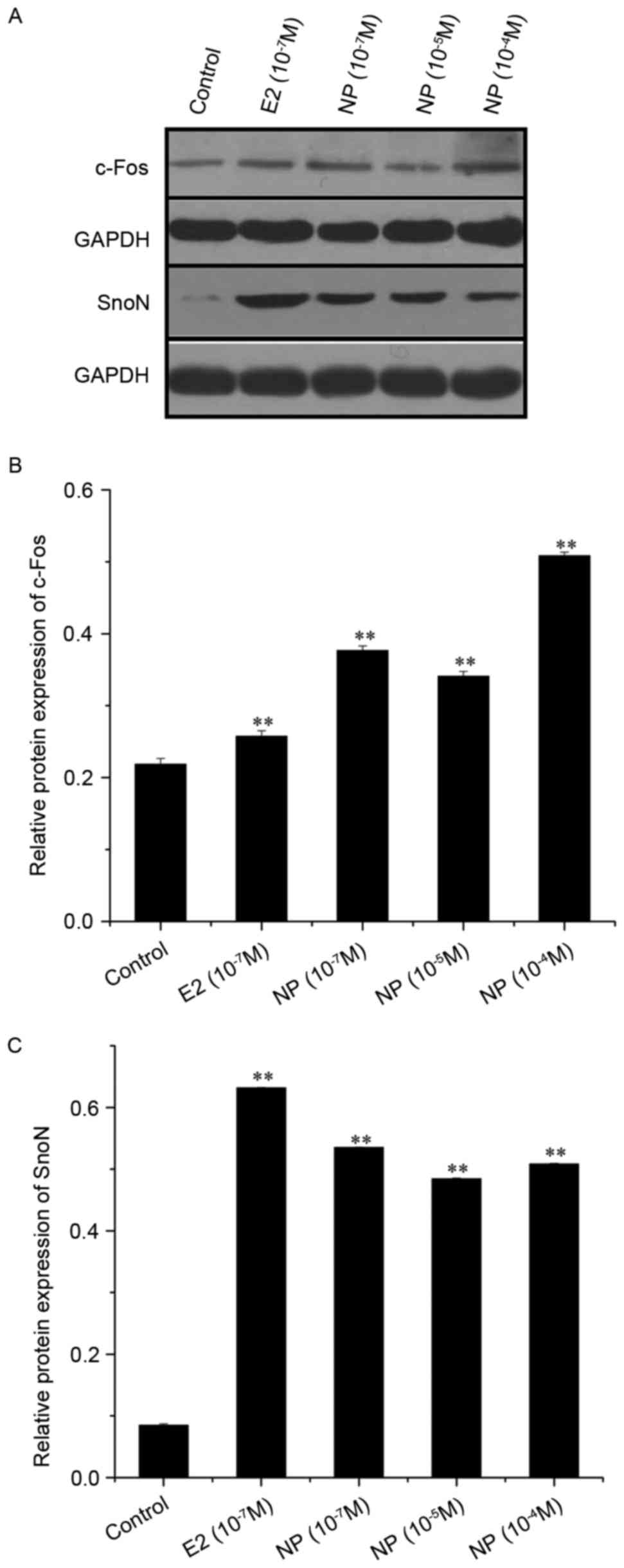
|
1
|
Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Bourguignon JP,
Giudice LC, Hauser R, Prins GS, Soto AM, Zoeller RT and Gore AC:
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: An endocrine society scientific
statement. Endocr Rev. 30:293–342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Palioura E,
Kandarakis SA and Koutsilieris M: The impact of endocrine
disruptors on endocrine targets. Horm Metab Res. 42:543–552. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yoon K, Kwack SJ, Kim HS and Lee BM:
Estrogenic endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Molecular mechanisms of
actions on putative human diseases. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit
Rev. 17:127–174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Safe SH, Pallaroni L, Yoon K, Gaido K,
Ross S, Saville B and McDonnellc D: Toxicology of environmental
estrogens. Reprod Fertil Dev. 13:307–315. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi SM, Yoo SD and Lee BM: Toxicological
characteristics of endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Developmental
toxicity, carcinogenicity, and mutagenicity. J Toxicol Environ
Health B Crit Rev. 7:1–24. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bonefeld-Jørgensen EC, Long M, Hofmeister
MV and Vinggaard AM: Endocrine-disrupting potential of bisphenol A,
bisphenol A dimethacrylate, 4-n-nonylphenol, and 4-n-octylphenol in
vitro: New data and a brief review. Environ Health Perspect. 115
Suppl 1:S69–S76. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kim YS, Hwang KA, Hyun SH, Nam KH, Lee CK
and Choi KC: Bisphenol A and nonylphenol have the potential to
stimulate the migration of ovarian cancer cells by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via an estrogen receptor
dependent pathway. Chem Res Toxicol. 28:662–671. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park MA and Choi KC: Effects of
4-nonylphenol and bisphenol A on stimulation of cell growth via
disruption of the transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway in
ovarian cancer models. Chem Res Toxicol. 27:119–128. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim SH, Nam KH, Hwang KA and Choi KC:
Influence of hexabromocyclododecane and 4-nonylphenol on the
regulation of cell growth, apoptosis and migration in prostatic
cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 32:240–247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
In SJ, Kim SH, Go RE, Hwang KA and Choi
KC: Benzophenone-1 and nonylphenol stimulated MCF-7 breast cancer
growth by regulating cell cycle and metastasis-related genes via an
estrogen receptor α-dependent pathway. J Toxicol Environ Health A.
78:492–505. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Van Cutsem E and Oliveira J; ESMO
Guidelines Working Group, : Advanced colorectal cancer: ESMO
clinical recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up.
Ann Oncol. 20 Suppl 4:S61–S63. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kennelly R, Kavanagh DO, Hogan AM and
Winter DC: Oestrogen and the colon: Potential mechanisms for cancer
prevention. Lancet Oncol. 9:385–391. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin JH and Giovannucci E: Sex hormones and
colorectal cancer: What have we learned so far? J Natl Cancer Inst.
102:1746–1747. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grodstein F, Newcomb PA and Stampfer MJ:
Postmenopausal hormone therapy and the risk of colorectal cancer: A
review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 106:574–582. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gunter MJ, Hoover DR, Yu H,
Wassertheil-Smoller S, Rohan TE, Manson JE, Howard BV, Wylie-Rosett
J, Anderson GL, Ho GY, et al: Insulin, insulin-like growth
factor-I, endogenous estradiol and risk of colorectal cancer in
postmenopausal women. Cancer Res. 68:329–337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Clendenen TV, Koenig KL, Shore RE, Levitz
M, Arslan AA and Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A: Postmenopausal levels of
endogenous sex hormones and risk of colorectal cancer. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:275–281. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu H, Xu L, Chen J, Hu J, Yu S, Hu G,
Huang L, Chen X, Yuan X and Li G: Association of estrogen receptor
beta variants and serum levels of estradiol with risk of colorectal
cancer: A case control study. BMC Cancer. 12:2762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sato R, Suzuki T, Katayose Y, Miura K,
Shiiba K, Tateno H, Miki Y, Akahira J, Kamogawa Y, Nagasaki S,
Yamamoto K, et al: Steroid sulfatase and estrogen sulfotransferase
in colon carcinoma: Regulators of intratumoral estrogen
concentrations and potent prognostic factors. Cancer Res.
69:914–922. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang O, Kim HL, Weon JI and Seo YR:
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Review of toxicological mechanisms
using molecular pathway analysis. J Cancer Prev. 20:12–24. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ariemma F, D'Esposito V, Liguoro D,
Oriente F, Cabaro S, Liotti A, Cimmino I, Longo M, Beguinot F,
Formisano P and Valentino R: Low-dose bisphenol-A impairs
adipogenesis and generates dysfunctional 3T3-L1 adipocytes. PloS
One. 11:e01507622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jambor T, Lukáčová J, Tvrdá E, Knážická Z,
Forgács Z and Lukáč N: The impact of 4-nonylphenol on the viability
and hormone production of mouse leydig cells. Folia Biol (Praha).
62:34–39. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee HR, Hwang KA, Park MA, Yi BR, Jeung EB
and Choi KC: Treatment with bisphenol A and methoxychlor results in
the growth of human breast cancer cells and alteration of the
expression of cell cycle-related genes, cyclin D1 and p21, via an
estrogen receptor-dependent signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
29:883–890. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong Y, Araki M, Hirane M, Tanabe E,
Fukushima N and Tsujiuchi T: Effects of bisphenol A and
4-nonylphenol on cellular responses through the different induction
of LPA receptors in liver epithelial WB-F344 cells. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 34:201–204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wei Z, Ma W, Qi X, Zhu X, Wang Y, Xu Z,
Luo J, Wang D, Guo W, Li X, et al: Pinin facilitated proliferation
and metastasis of colorectal cancer through activating EGFR/ERK
signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 7:29429–29439. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jeng YJ and Watson CS: Combinations of
physiologic estrogens with xenoestrogens alter ERK phosphorylation
profiles in rat pituitary cells. Environ Health Perspect.
119:104–112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Watson CS, Jeng YJ, Hu G, Wozniak A,
Bulayeva N and Guptarak J: Estrogen- and xenoestrogen-induced ERK
signaling in pituitary tumor cells involves estrogen receptor-α
interactions with G protein-αi and caveolin I. Steroids.
77:424–432. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A:
TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat
Genet. 29:117–129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Milde-Langosch K: The Fos family of
transcription factors and their role in tumourigenesis. Eur J
Cancer. 41:2449–2461. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Deheuninck J and Luo K: Ski and SnoN,
potent negative regulators of TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res.
19:47–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|