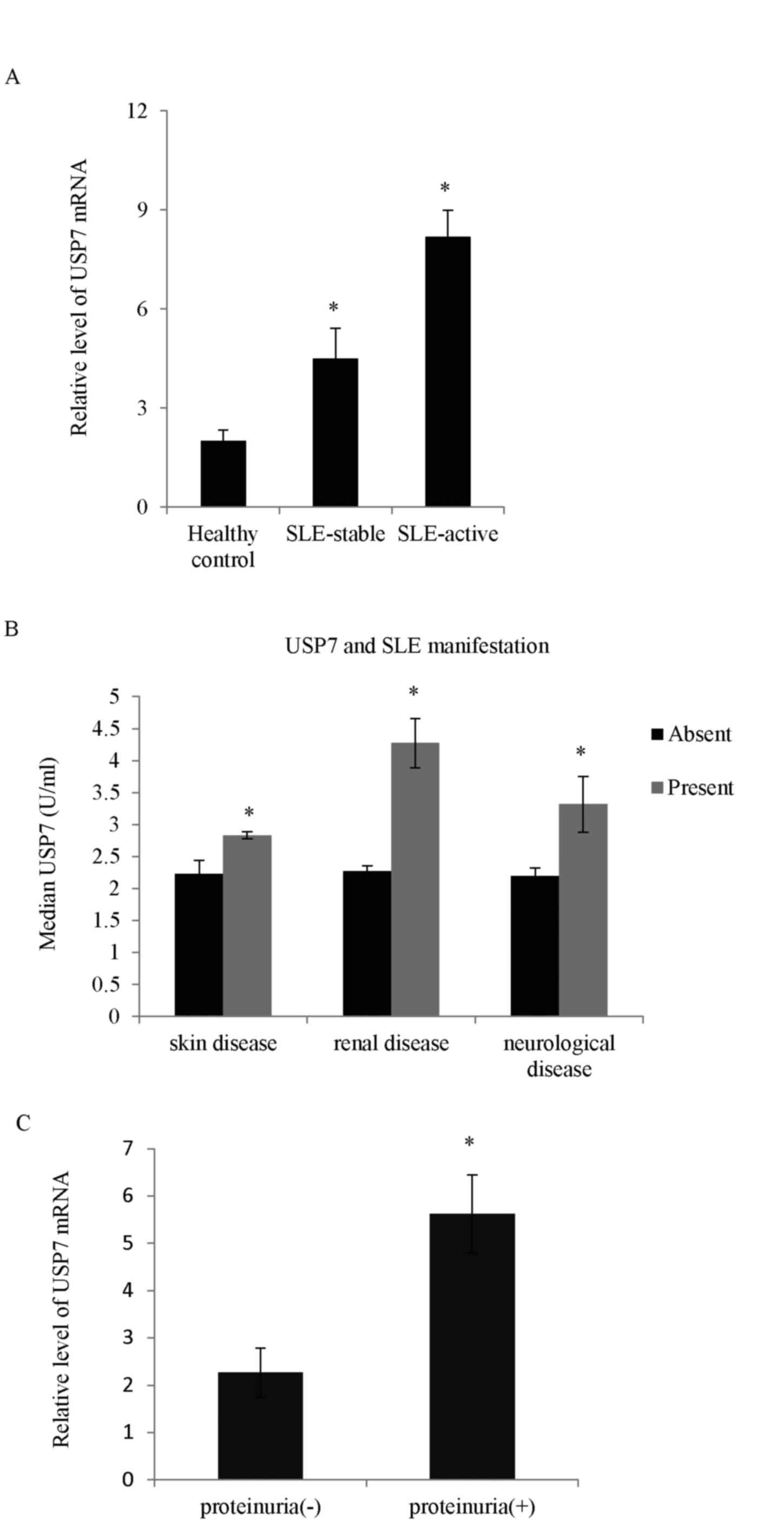
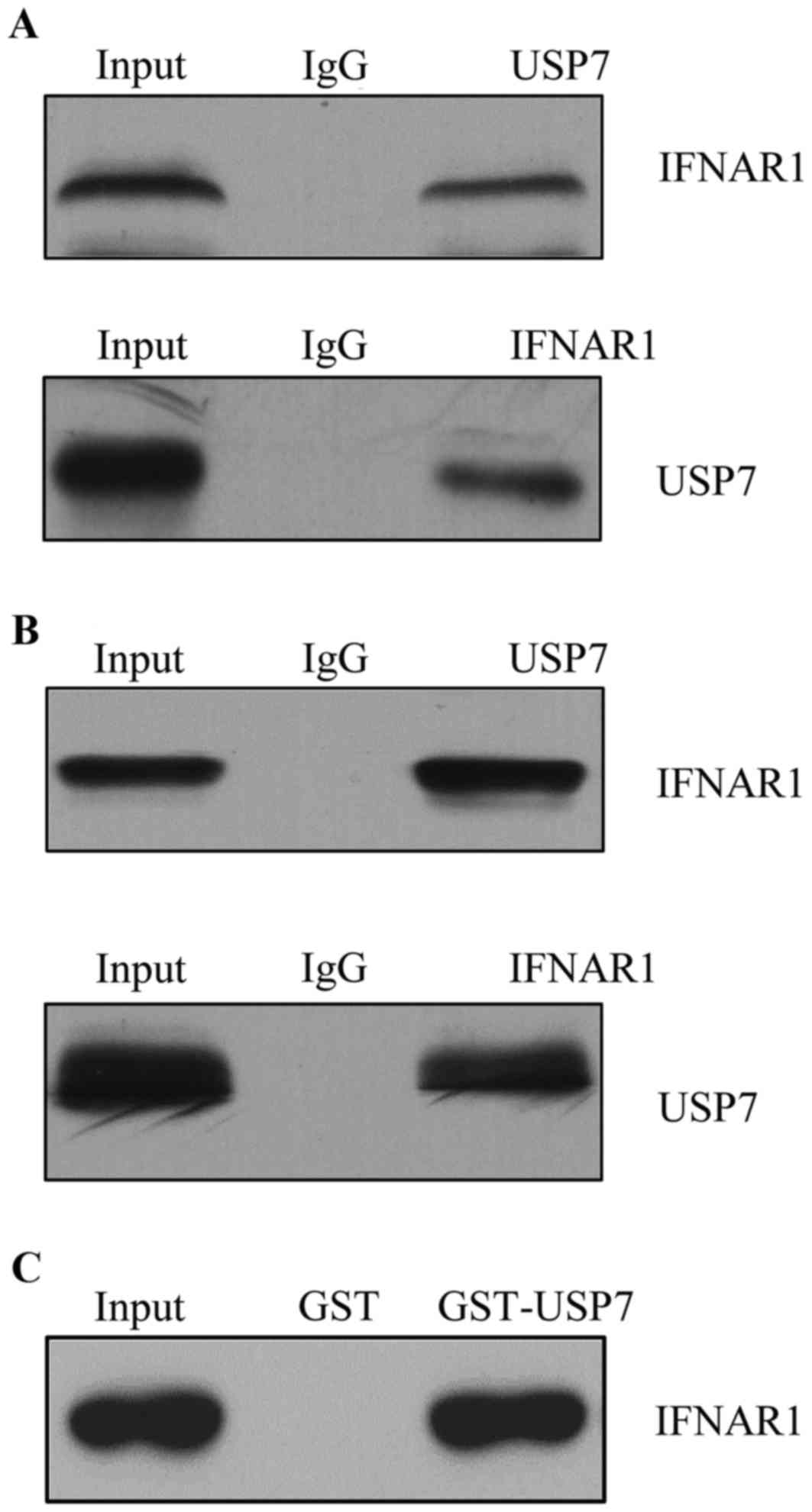
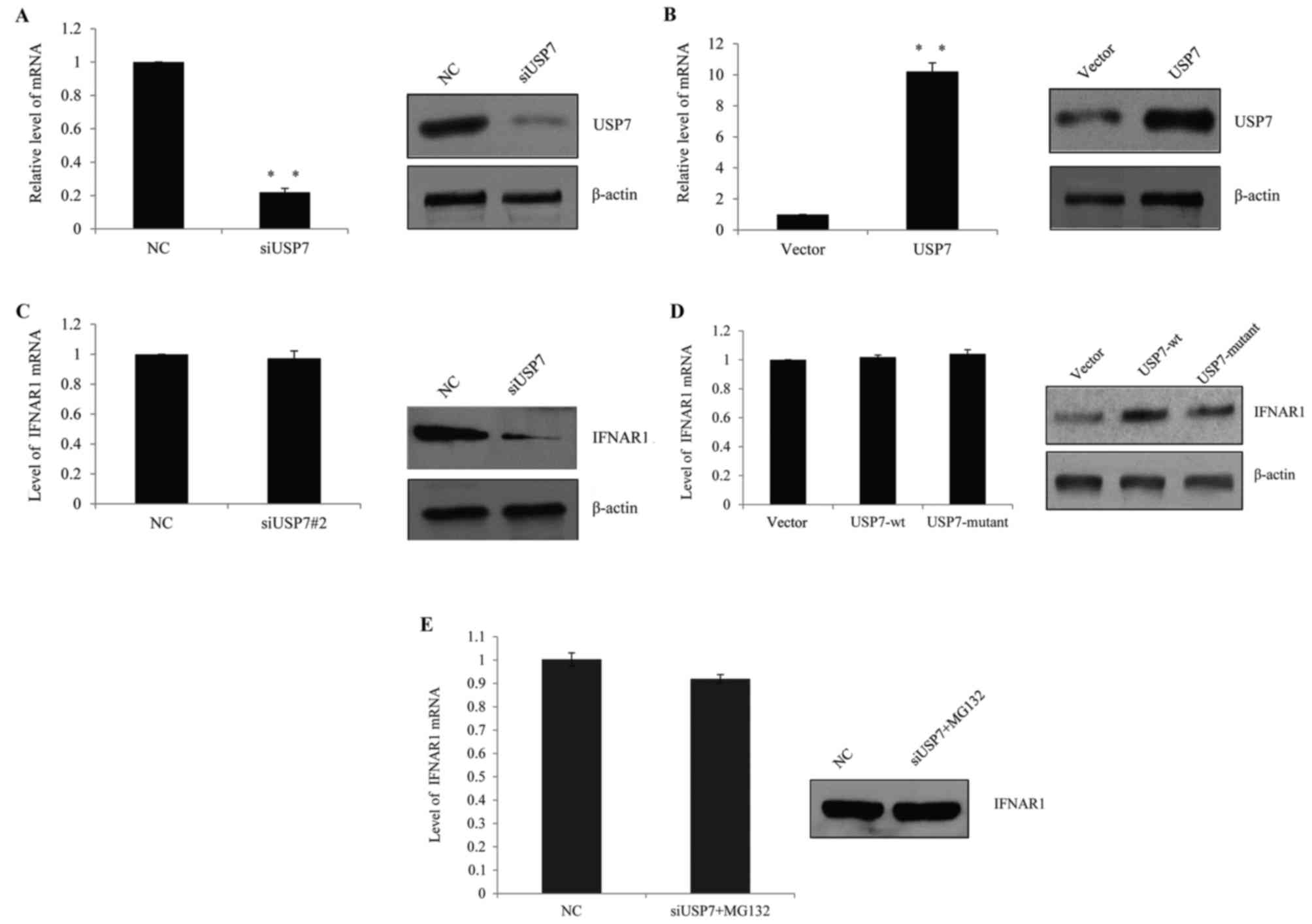
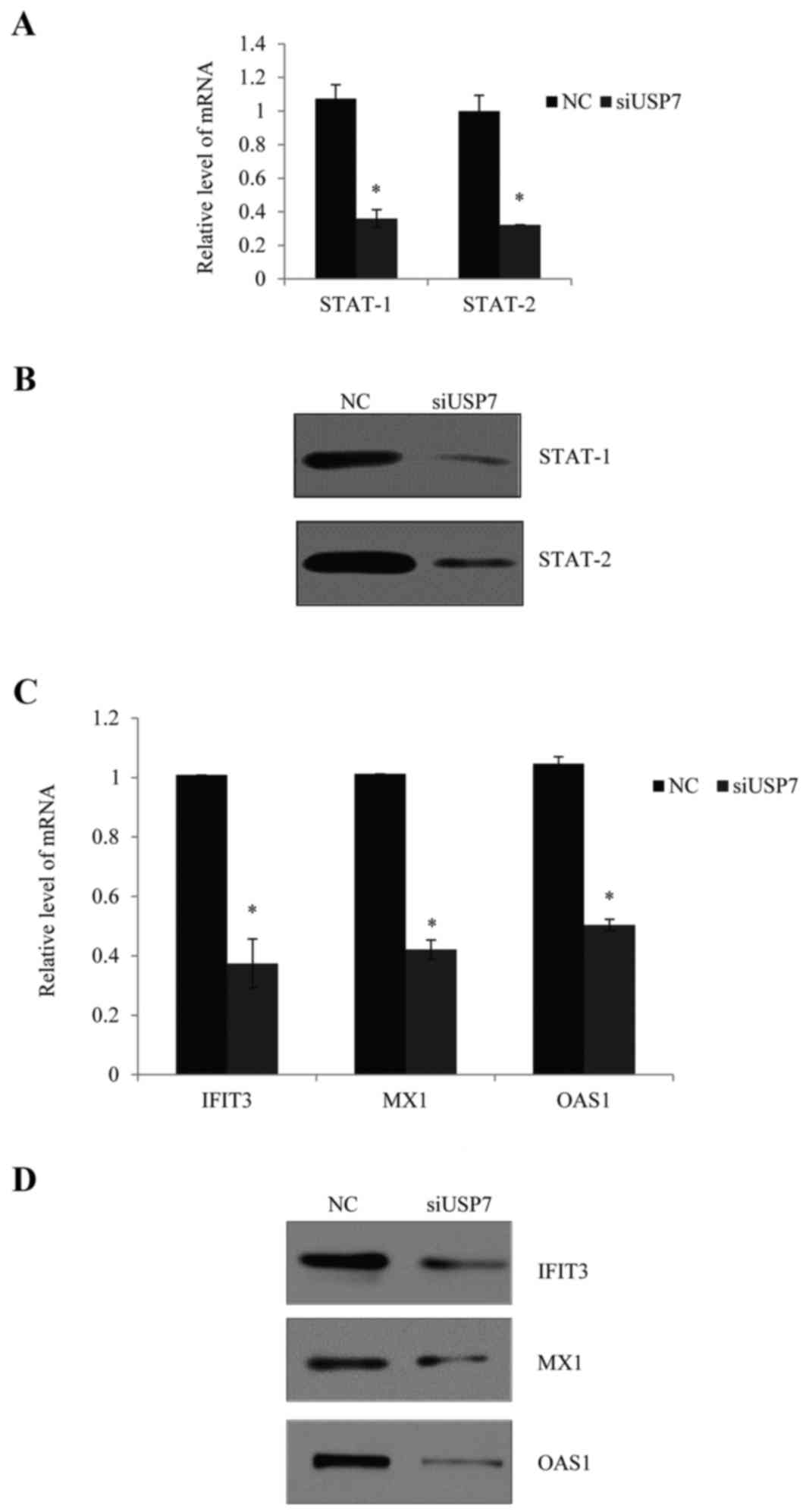
|
1
|
Tsokos GC: Systemic lupus erythematosus. N
Engl J Med. 365:2110–2121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gillis JZ, Panopalis P, Schmajuk G,
Ramsey-Goldman R and Yazdany J: Systematic review of the literature
informing the systemic lupus erythematosus indicators project:
Reproductive health care quality indicators. Arthritis Care Res
(Hoboken). 63:17–30. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hedrich CM and Tsokos GC: Epigenetic
mechanisms in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune
diseases. Trends Mol Med. 17:714–724. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qu B and Shen N: miRNAs in the
pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Sci.
16:9557–9572. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Crow MK: Advances in understanding the
role of type I interferons in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr
Opin Rheumatol. 26:467–474. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thacker SG, Zhao W, Smith CK, Luo W, Wang
H, Vivekanandan-Giri A, Rabquer BJ, Koch AE, Pennathur S, Davidson
A, et al: Type I interferons modulate vascular function, repair,
thrombosis, and plaque progression in murine models of lupus and
atherosclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 64:2975–2985. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee PY, Li Y, Richards HB, Chan FS, Zhuang
H, Narain S, Butfiloski EJ, Sobel ES, Reeves WH and Segal MS: Type
I interferon as a novel risk factor for endothelial progenitor cell
depletion and endothelial dysfunction in systemic lupus
erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 56:3759–3769. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Denny MF, Thacker S, Mehta H, Somers EC,
Dodick T, Barrat FJ, McCune WJ and Kaplan MJ: Interferon-alpha
promotes abnormal vasculogenesis in lupus: A potential pathway for
premature atherosclerosis. Blood. 110:2907–2915. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reynier F, Petit F, Paye M, Turrel-Davin
F, Imbert PE, Hot A, Mougin B and Miossec P: Importance of
correlation between gene expression levels: Application to the type
I interferon signature in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One.
6:e248282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Müller U, Steinhoff U, Reis LF, Hemmi S,
Pavlovic J, Zinkernagel RM and Aguet M: Functional role of type I
and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science.
264:1918–1921. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumar KG, Tang W, Ravindranath AK, Clark
WA, Croze E and Fuchs SY: SCF(HOS) ubiquitin ligase mediates the
ligand-induced down-regulation of the interferon-alpha receptor.
EMBO J. 22:5480–5490. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Everett RD, Meredith M, Orr A, Cross A,
Kathoria M and Parkinson J: A novel ubiquitin-specific protease is
dynamically associated with the PML nuclear domain and binds to a
herpesvirus regulatory protein. EMBO J. 16:1519–1530. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou Z, Yao X, Li S, Xiong Y, Dong X, Zhao
Y, Jiang J and Zhang Q: Deubiquitination of Ci/Gli by Usp7/HAUSP
regulates hedgehog signaling. Dev Cell. 34:58–72. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song MS, Salmena L, Carracedo A, Egia A,
Lo-Coco F, Teruya-Feldstein J and Pandolfi PP: The
deubiquitinylation and localization of PTEN are regulated by a
HAUSP-PML network. Nature. 455:813–817. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van der Horst A, de Vries-Smits AM,
Brenkman AB, van Triest MH, van den Broek N, Colland F, Maurice MM
and Burgering BM: FOXO4 transcriptional activity is regulated by
monoubiquitination and USP7/HAUSP. Nat Cell Biol. 8:1064–1073.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van der Knaap JA, Kumar BR, Moshkin YM,
Langenberg K, Krijgsveld J, Heck AJ, Karch F and Verrijzer CP: GMP
synthetase stimulates histone H2B deubiquitylation by the
epigenetic silencer USP7. Mol Cell. 17:695–707. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li M, Chen D, Shiloh A, Luo J, Nikolaev
AY, Qin J and Gu W: Deubiquitination of p53 by HAUSP is an
important pathway for p53 stabilization. Nature. 416:648–653. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hochberg MC: Updating the American College
of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic
lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 40:17251997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gladman DD, Ibañez D and Urowitz MB:
Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J
Rheumatol. 29:288–291. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Einarson MB, Pugacheva EN and Orlinick JR:
GST Pull-down. CSH Protoc. 2007:pdb prot47572007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang ZM, Rothbart SB, Allison DF, Cai Q,
Harrison JS, Li L, Wang Y, Strahl BD, Wang GG and Song J: An
allosteric interaction links USP7 to deubiquitination and chromatin
targeting of UHRF1. Cell Rep. 12:1400–1406. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dall'era MC, Cardarelli PM, Preston BT,
Witte A and Davis JC Jr: Type I interferon correlates with
serological and clinical manifestations of SLE. Ann Rheum Dis.
64:1692–1697. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|