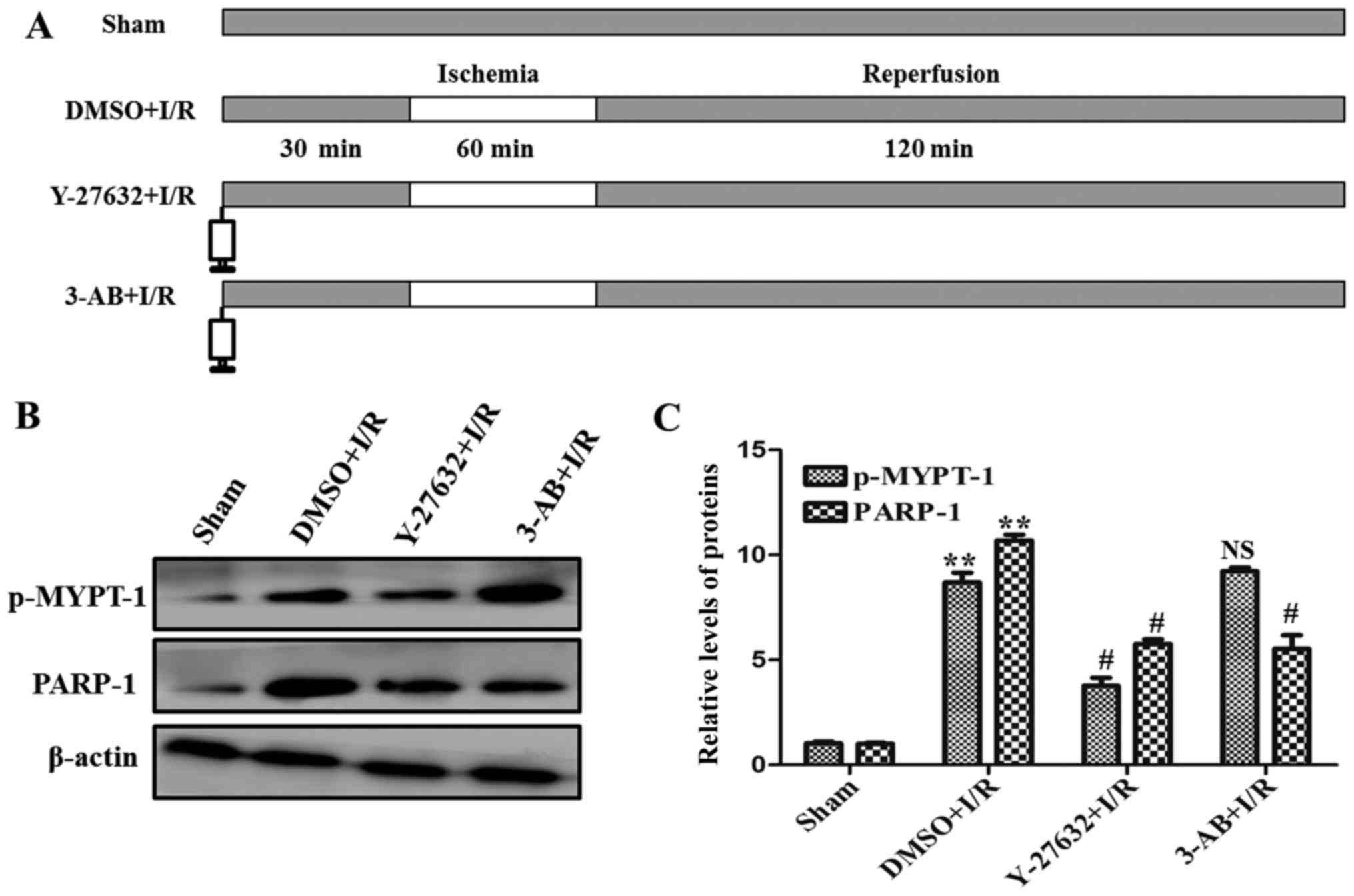
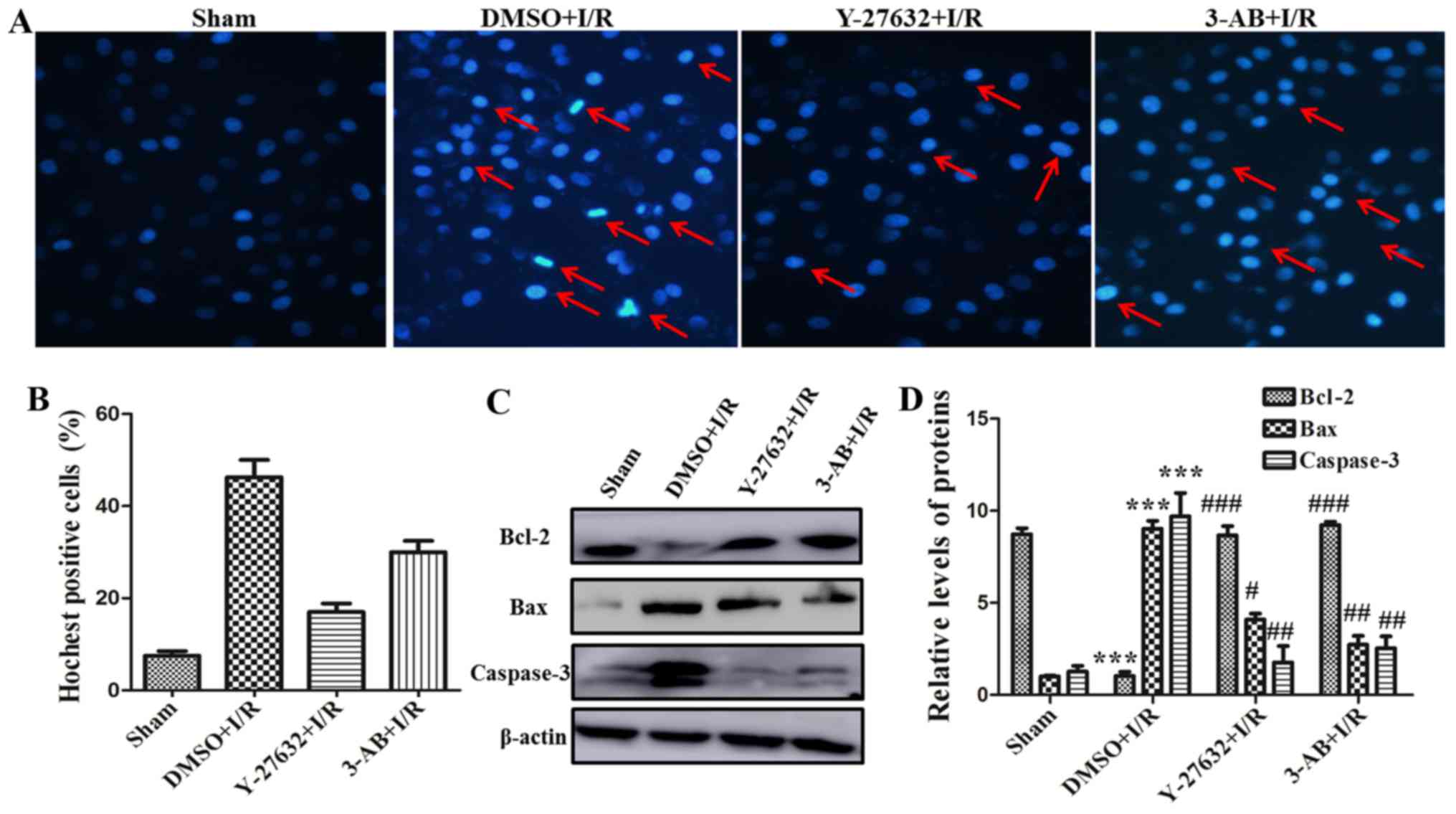
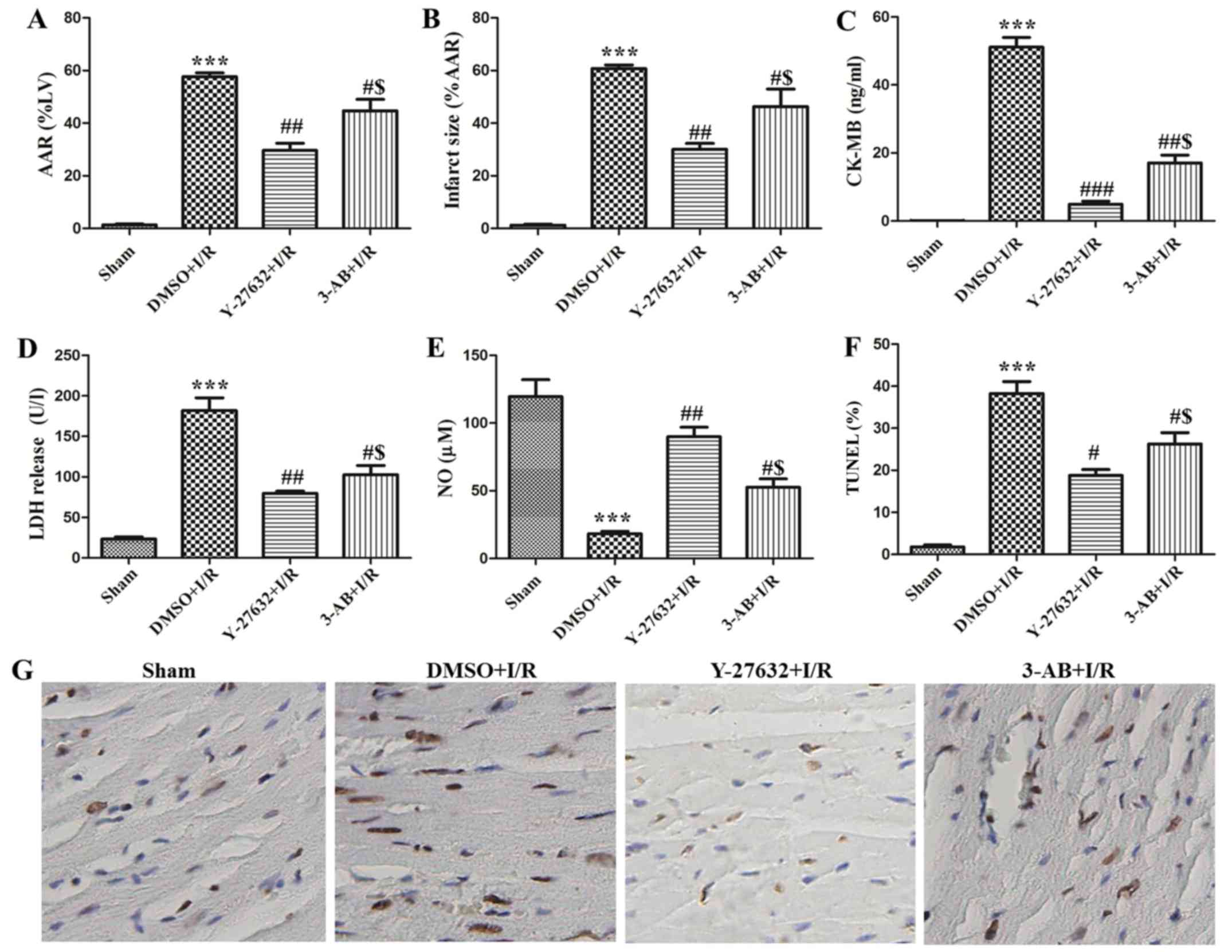
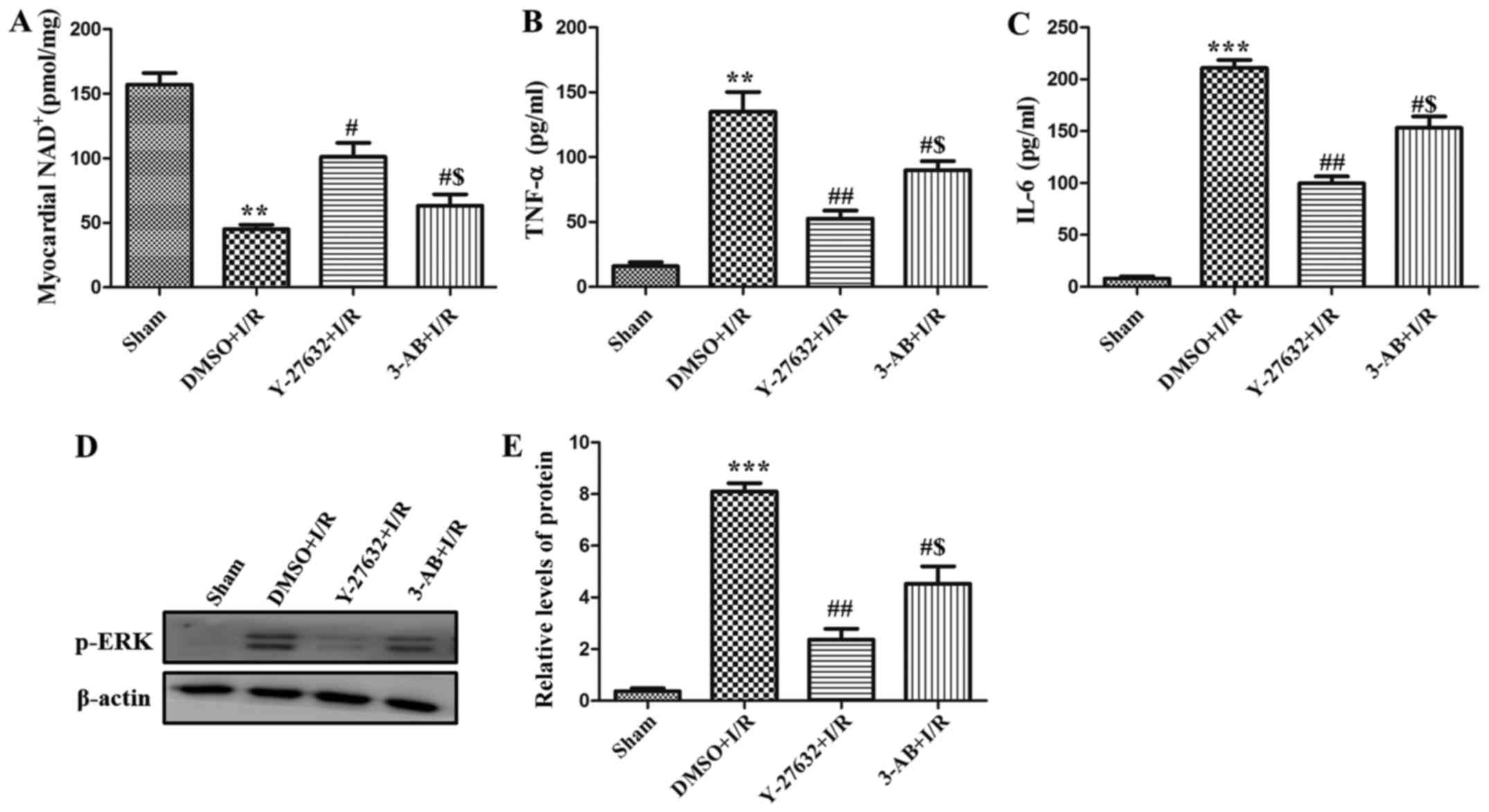
|
1
|
Peuhkurinen K: Myocardial reperfusion-a
double-edged sword? Duodecim. 105:822–830. 1989.(In Finnish).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kurian GA, Rajagopal R, Vedantham S and
Rajesh M: The role of oxidative stress in myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury and remodeling: Revisited. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:16564502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Patil KD, Halperin HR and Becker LB:
Cardiac arrest: Resuscitation and reperfusion. Circ Res.
116:2041–2049. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Matsushima S, Tsutsui H and Sadoshima J:
Physiological and pathological functions of NADPH oxidases during
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 24:202–205.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Julian L and Olson MF: Rho-associated
coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): Structure, regulation, and
functions. Small GTPases. 5:e298462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Minambres R, Guasch RM, Perez-Aragó A and
Guerri C: The RhoA/ROCK-I/MLC pathway is involved in the
ethanol-induced apoptosis by anoikis in astrocytes. J Cell Sci.
119:271–282. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chang J, Xie M, Shah VR, Schneider MD,
Entman ML, Wei L and Schwartz RJ: Activation of Rho-associated
coiled-coil protein kinase 1 (ROCK-1) by caspase-3 cleavage plays
an essential role in cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:14495–14500. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang J, Bian HJ, Li XX, Liu XB, Sun JP,
Li N, Zhang Y and Ji XP: ERK-MAPK signaling opposes rho-kinase to
reduce cardiomyocyte apoptosis in heart ischemic preconditioning.
Mol Med. 16:307–315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang J, Li XX, Bian HJ, Liu XB, Ji XP and
Zhang Y: Inhibition of the activity of Rho-kinase reduces
cardiomyocyte apoptosis in heart ischemia/reperfusion via
suppressing JNK-mediated AIF translocation. Clin Chim Acta.
401:76–80. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abe K, Shimokawa H, Morikawa K, Uwatoku T,
Oi K, Matsumoto Y, Hattori T, Nakashima Y, Kaibuchi K, Sueishi K
and Takeshit A: Long-term treatment with a Rho-kinase inhibitor
improves monocrotaline-induced fatal pulmonary hypertension in
rats. Circ Res. 94:385–393. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harris JL, Jakob B, Taucher-Scholz G,
Dianov GL, Becherel OJ and Lavin MF: Aprataxin, poly-ADP ribose
polymerase 1 (PARP-1) and apurinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) function
together to protect the genome against oxidative damage. Hum Mol
Genet. 18:4102–4117. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song ZF, Ji XP, Li XX, Wang SJ, Wang SH
and Zhang Y: Inhibition of the activity of poly (ADP-ribose)
polymerase reduces heart ischaemia/reperfusion injury via
suppressing JNK-mediated AIF translocation. J Cell Mol Med.
12:1220–1228. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li B, Li R, Zhang C, Bian HJ, Wang F, Xiao
J, Liu SW, Yi W, Zhang MX, Wang SX, et al: MicroRNA-7a/b protects
against cardiac myocyte injury in ischemia/reperfusion by targeting
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. PLoS One. 9:e900962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bolli R, Becker L, Gross G, Mentzer R Jr,
Balshaw D and Lathrop DA: NHLBI Working Group on the Translation of
Therapies for Protecting the Heart from Ischemia: Myocardial
protection at a cross roads: The need for translation into clinical
therapy. Circ Res. 95:125–134. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Erwig LP, McPhilips KA, Wynes MW, Ivetic
A, Ridley AJ and Henson PM: Differential regulation of phagosome
maturation in macrophages and dendritic cells mediated by Rho
GTPases and ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:12825–12830. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tosello-Trampont AC, Nakada-Tsukui K and
Ravichandran KS: Engulfment of apoptotic cells is negatively
regulated by Rho-mediated signaling. J Biol Chem. 278:49911–49919.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meng X, Song W, Deng B, Xing Z and Zhang
W: 3-aminobenzamide, one of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1
inhibitors, rescues apoptosis in rat models of spinal cord injury.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:12207–12215. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang SJ, Wang SH, Song ZF, Liu XW, Wang R
and Chi ZF: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor is
neuroprotective in epileptic rat via apoptosis-inducing factor and
Akt signaling. Neuroreport. 18:1285–1289. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meli E, Pangallo M, Picca R, Baronti R,
Moroni F and Pellegrini-Giampietro DE: Differential role of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in apoptotic and necrotic neuronal
death induced by mild or intense NMDA exposure in vitro. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 25:172–180. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang SI, Yuan Y, Jiao S, Luo QI and Yu J:
Calcitonin gene-related peptide protects rats from cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury via a mechanism of action in the MAPK
pathway. Biomed Rep. 4:699–703. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|