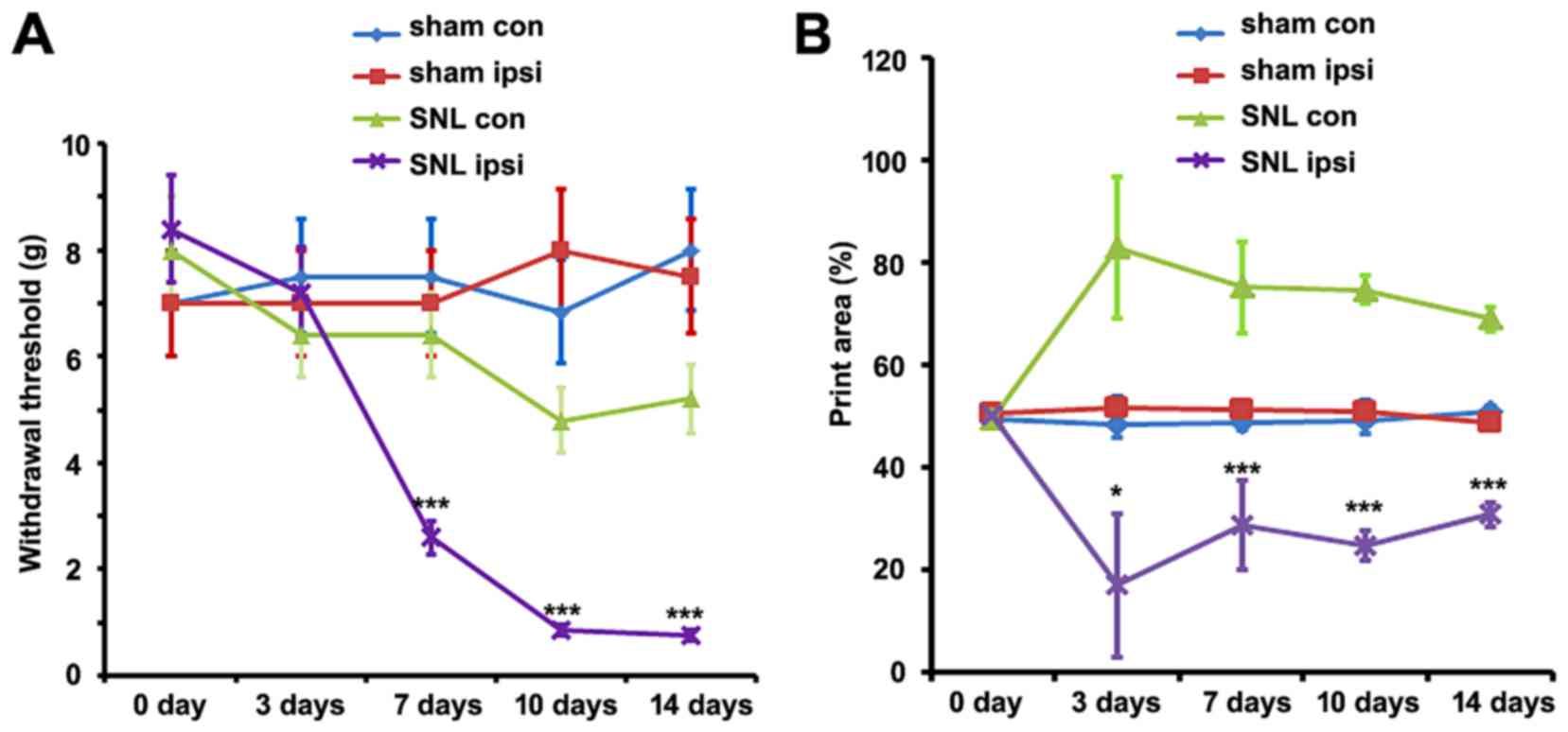
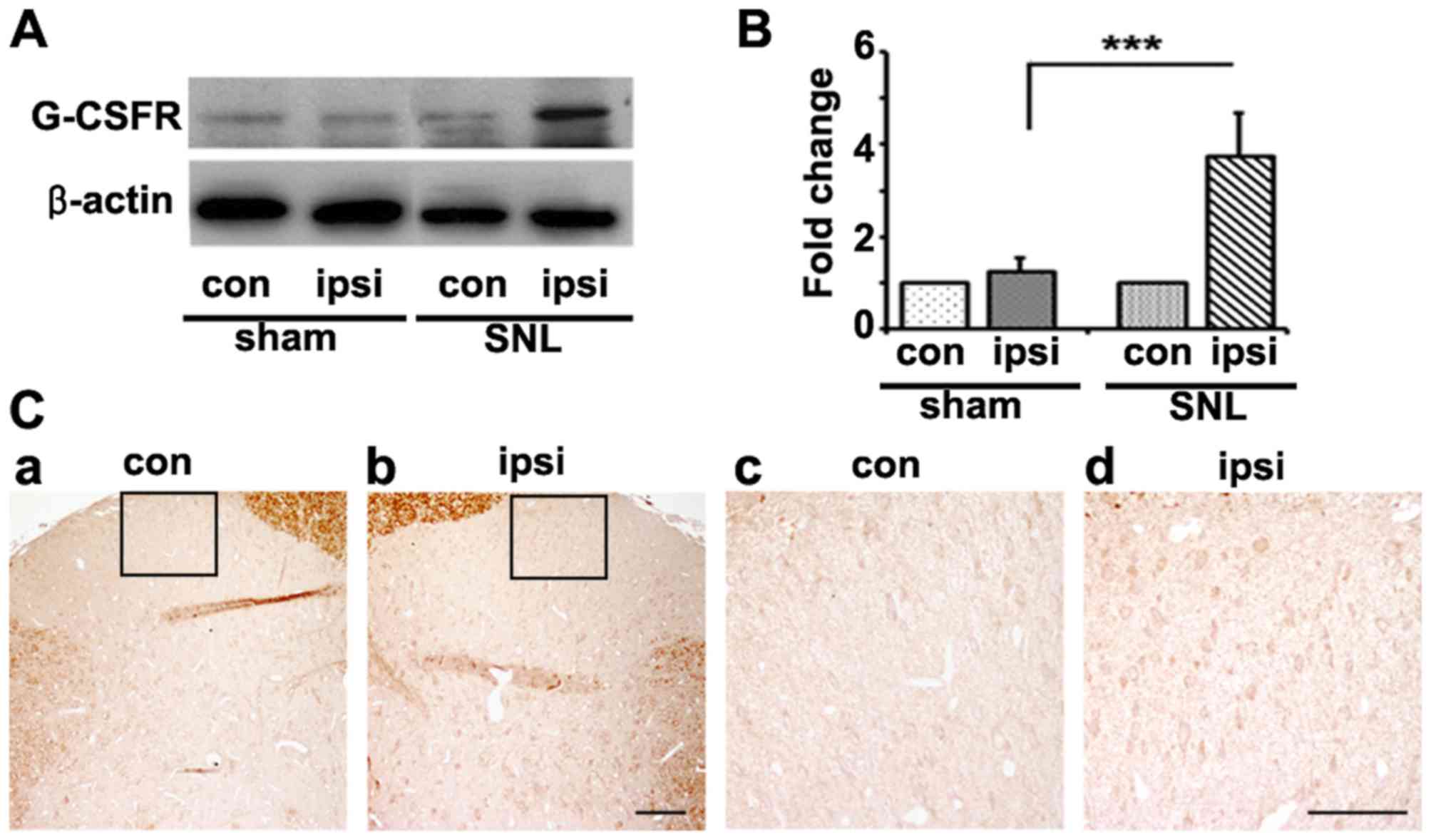
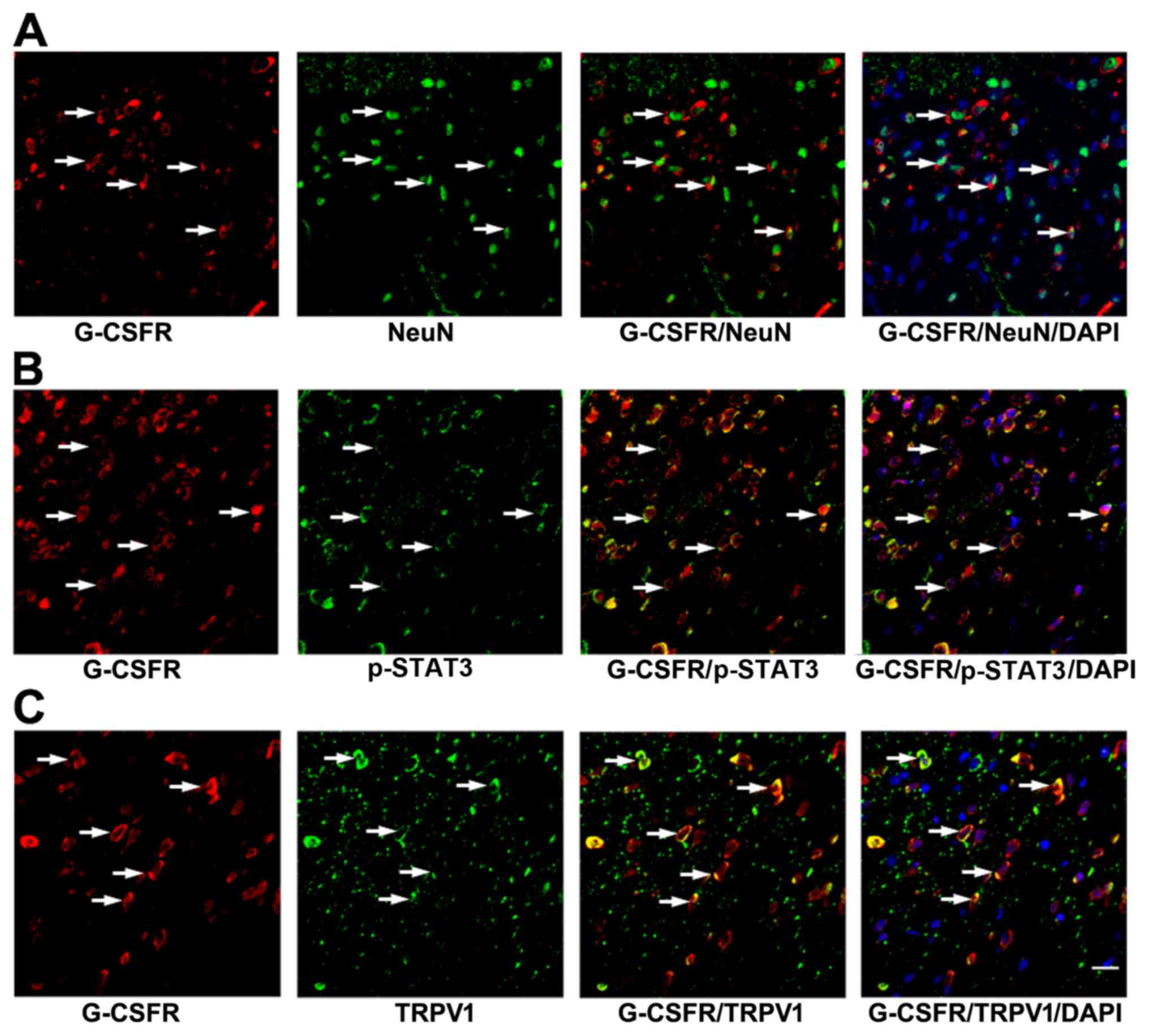
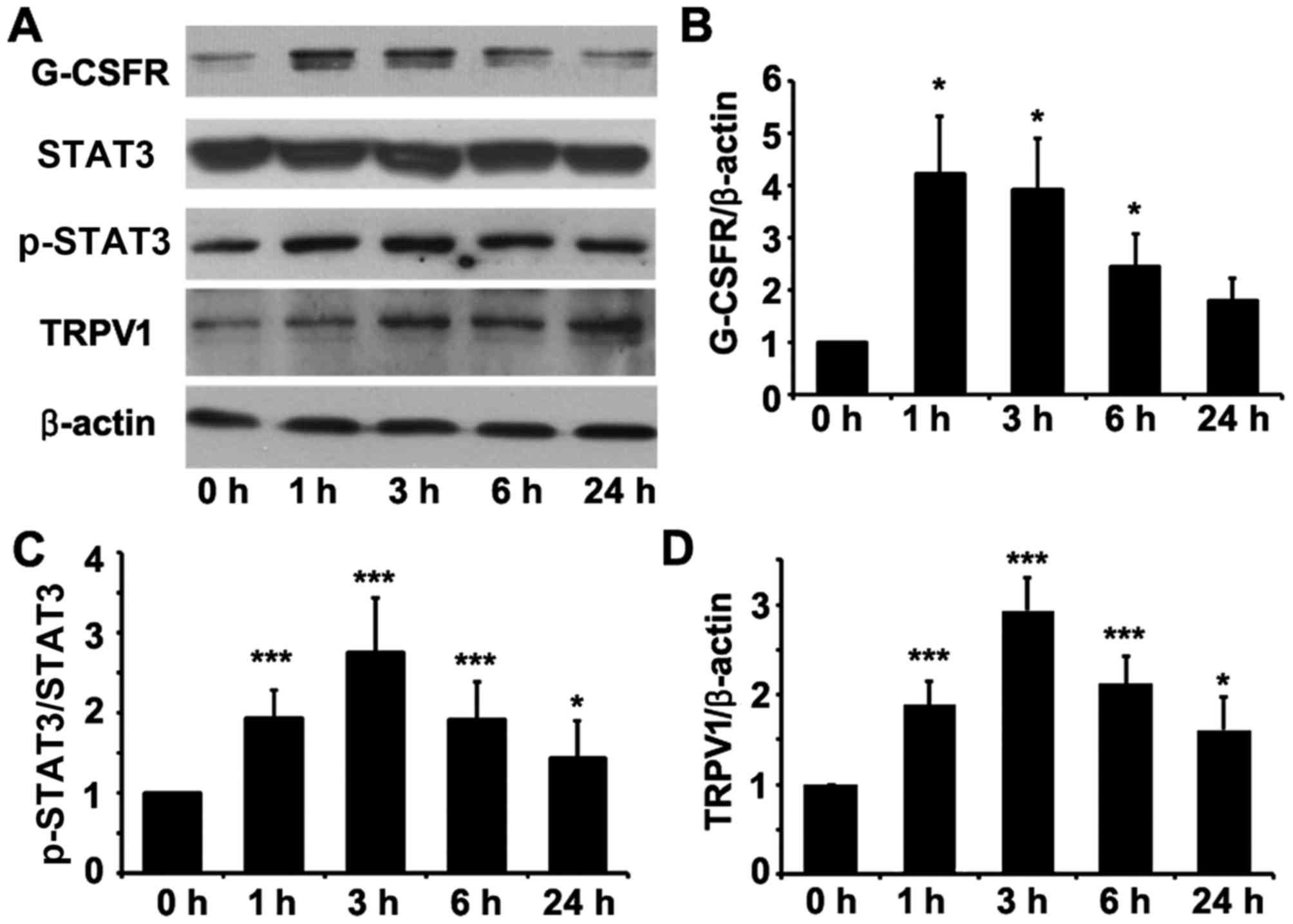
|
1
|
Nagata S, Tsuchiya M, Asano S, Kaziro Y,
Yamazaki T, Yamamoto O, Hirata Y, Kubota N, Oheda M, Nomura H, et
al: Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA for human granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor. Nature. 319:415–418. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fukunaga R, Ishizaka-Ikeda E, Seto Y and
Nagata S: Expression cloning of a receptor for murine granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor. Cell. 61:341–350. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mine S, Koshiba T, Honjo E, Okamoto T,
Tamada T, Maeda Y, Matsukura Y, Horie A, Ishibashi M, Sato M, et
al: Thermodynamic analysis of the activation mechanism of the GCSF
receptor induced by ligand binding. Biochemistry. 43:2458–2464.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marino VJ and Roguin LP: The granulocyte
colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) activates Jak/STAT and MAPK
pathways in a trophoblastic cell line. J Cell Biochem.
103:1512–1523. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shimoda K, Feng J, Murakami H, Nagata S,
Watling D, Rogers NC, Stark GR, Kerr IM and Ihle JN: Jak1 plays an
essential role for receptor phosphorylation and Stat activation in
response to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood.
90:597–604. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Würfel W: Treatment with granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor in patients with repetitive implantation
failures and/or recurrent spontaneous abortions. J Reprod Immunol.
108:123–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kirsch F, Krüger C and Schneider A: The
receptor for granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) is
expressed in radial glia during development of the nervous system.
BMC Dev Biol. 8:322008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ridwan S, Bauer H, Frauenknecht K, Hefti
K, von Pein H and Sommer CJ: Distribution of the hematopoietic
growth factor G-CSF and its receptor in the adult human brain with
specific reference to Alzheimer's disease. J Anat. 224:377–391.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schneider A, Krüger C, Steigleder T, Weber
D, Pitzer C, Laage R, Aronowski J, Maurer MH, Gassler N, Mier W, et
al: The hematopoietic factor G-CSF is a neuronal ligand that
counteracts programmed cell death and drives neurogenesis. J Clin
Invest. 115:2083–2098. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin EH, Zhang E, Ko Y, Sim WS, Moon DE,
Yoon KJ, Hong JH and Lee WH: Genome-wide expression profiling of
complex regional pain syndrome. PLoS One. 8:e794352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schweizerhof M, Stösser S, Kurejova M,
Njoo C, Gangadharan V, Agarwal N, Schmelz M, Bali KK, Michalski CW,
Brugger S, et al: Hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors mediate
tumor-nerve interactions and bone cancer pain. Nat Med. 15:802–807.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baron R: Neuropathic pain: A clinical
perspective. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 3–30. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim SH and Chung JM: An experimental model
for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve
ligation in the rat. Pain. 50:355–363. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jänig W and Baron R: Complex regional pain
syndrome is a disease of the central nervous system. Clin Auton
Res. 12:150–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chung JM, Kim HK and Chung K: Segmental
spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain. Methods Mol Med.
99:35–45. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang SP and Tsai RK: Efficacy of
granulocyte-colony stimulating factor treatment in a rat model of
anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Neural Regen Res. 9:1502–1505.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liou JT, Lui PW, Liu FC, Lai YS and Day
YJ: Exogenous granulocyte colony-stimulating factor exacerbate
pain-related behaviors after peripheral nerve injury. J
Neuroimmunol. 232:83–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lima CK, Silva RM, Lacerda RB, Santos BL,
Silva RV, Amaral LS, Quintas LE, Fraga CA, Barreiro EJ, Guimaraes
MZ and Miranda AL: LASSBio-1135: A dual TRPV1 antagonist and
anti-TNF-alpha compound orally effective in models of inflammatory
and neuropathic pain. PLoS One. 9:e995102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen NF, Huang SY, Lu CH, Chen CL, Feng
CW, Chen CH, Hung HC, Lin YY, Sung PJ, Sung CS, et al: Flexibilide
obtained from cultured soft coral has anti-neuroinflammatory and
analgesic effects through the upregulation of spinal transforming
growth factor-β1 in neuropathic rats. Mar Drugs. 12:3792–3817.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Walters ET: Neuroinflammatory
contributions to pain after SCI: Roles for central glial mechanisms
and nociceptor-mediated host defense. Exp Neurol. 258:48–61. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shao Q, Li Y, Wang Q and Zhao J: IL-10 and
IL-1β mediate neuropathic-pain like behavior in the ventrolateral
orbital cortex. Neurochem Res. 40:733–739. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma W and Quirion R: Inflammatory mediators
modulating the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 receptor:
Therapeutic targets to treat inflammatory and neuropathic pain.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 11:307–320. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szallasi A, Cortright DN, Blum CA and Eid
SR: The vanilloid receptor TRPV1: 10 years from channel cloning to
antagonist proof-of-concept. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:357–372. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kanai Y, Nakazato E, Fujiuchi A, Hara T
and Imai A: Involvement of an increased spinal TRPV1 sensitization
through its up-regulation in mechanical allodynia of CCI rats.
Neuropharmacology. 49:977–984. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Puttfarcken PS, Han P, Joshi SK, Neelands
TR, Gauvin DM, Baker SJ, Lewis LG, Bianchi BR, Mikusa JP, Koenig
JR, et al: A-995662
[(R)-8-(4-methyl-5-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)oxazol-2-ylamino)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol],
a novel, selective TRPV1 receptor antagonist, reduces spinal
release of glutamate and CGRP in a rat knee joint pain model. Pain.
150:319–326. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Honore P, Chandran P, Hernandez G, Gauvin
DM, Mikusa JP, Zhong C, Joshi SK, Ghilardi JR, Sevcik MA, Fryer RM,
et al: Repeated dosing of ABT-102, a potent and selective TRPV1
antagonist, enhances TRPV1-mediated analgesic activity in rodents,
but attenuates antagonist-induced hyperthermia. Pain. 142:27–35.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|