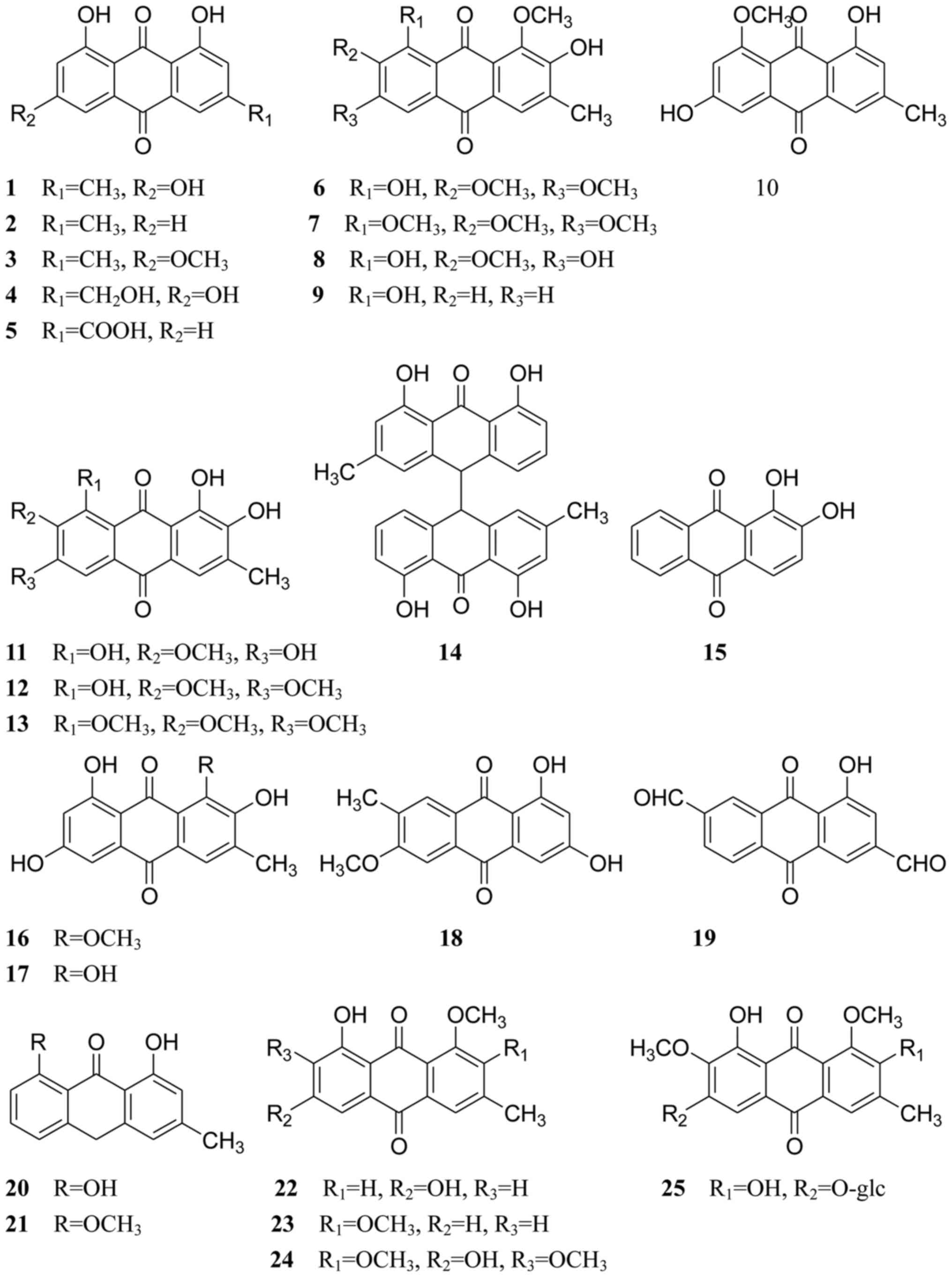
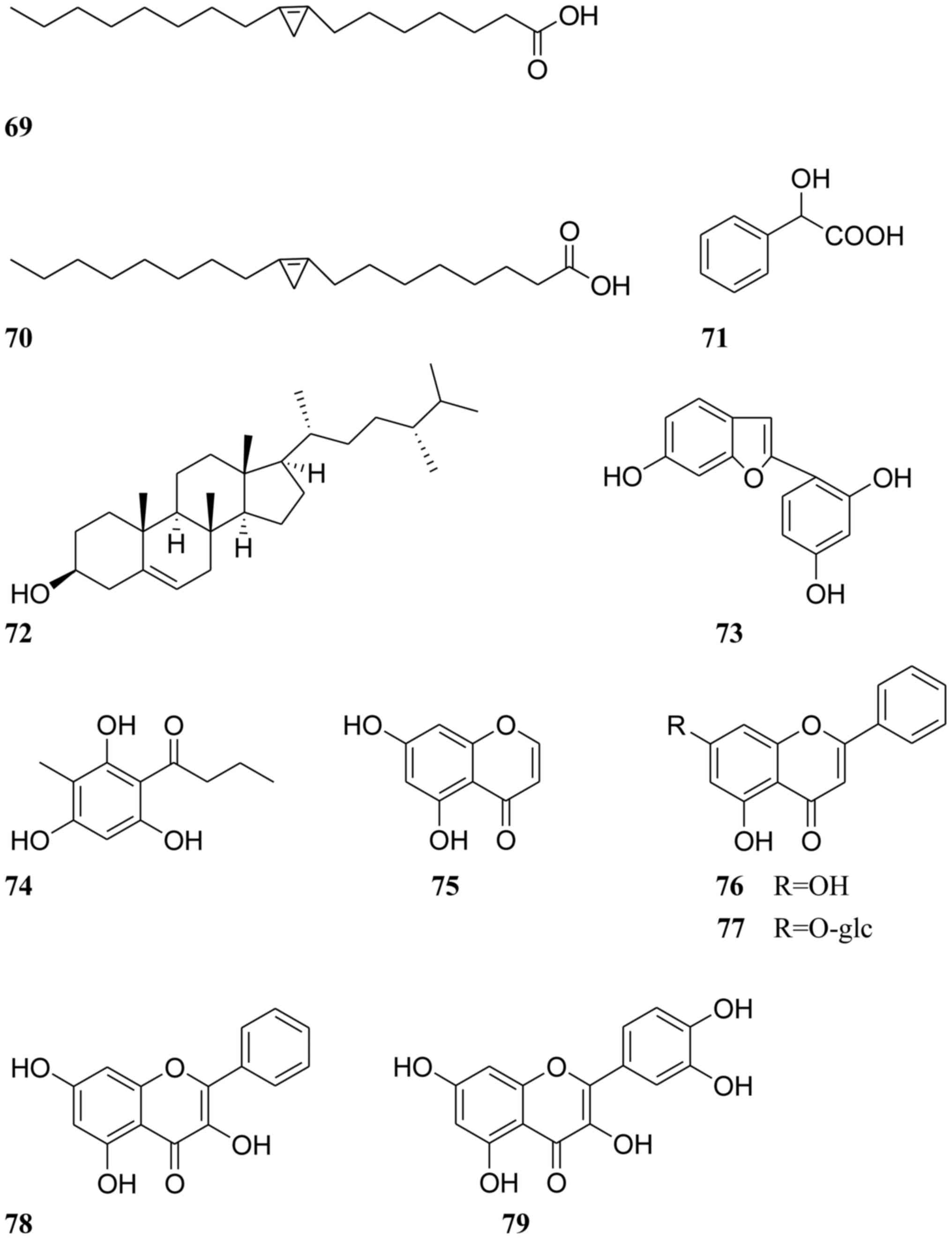
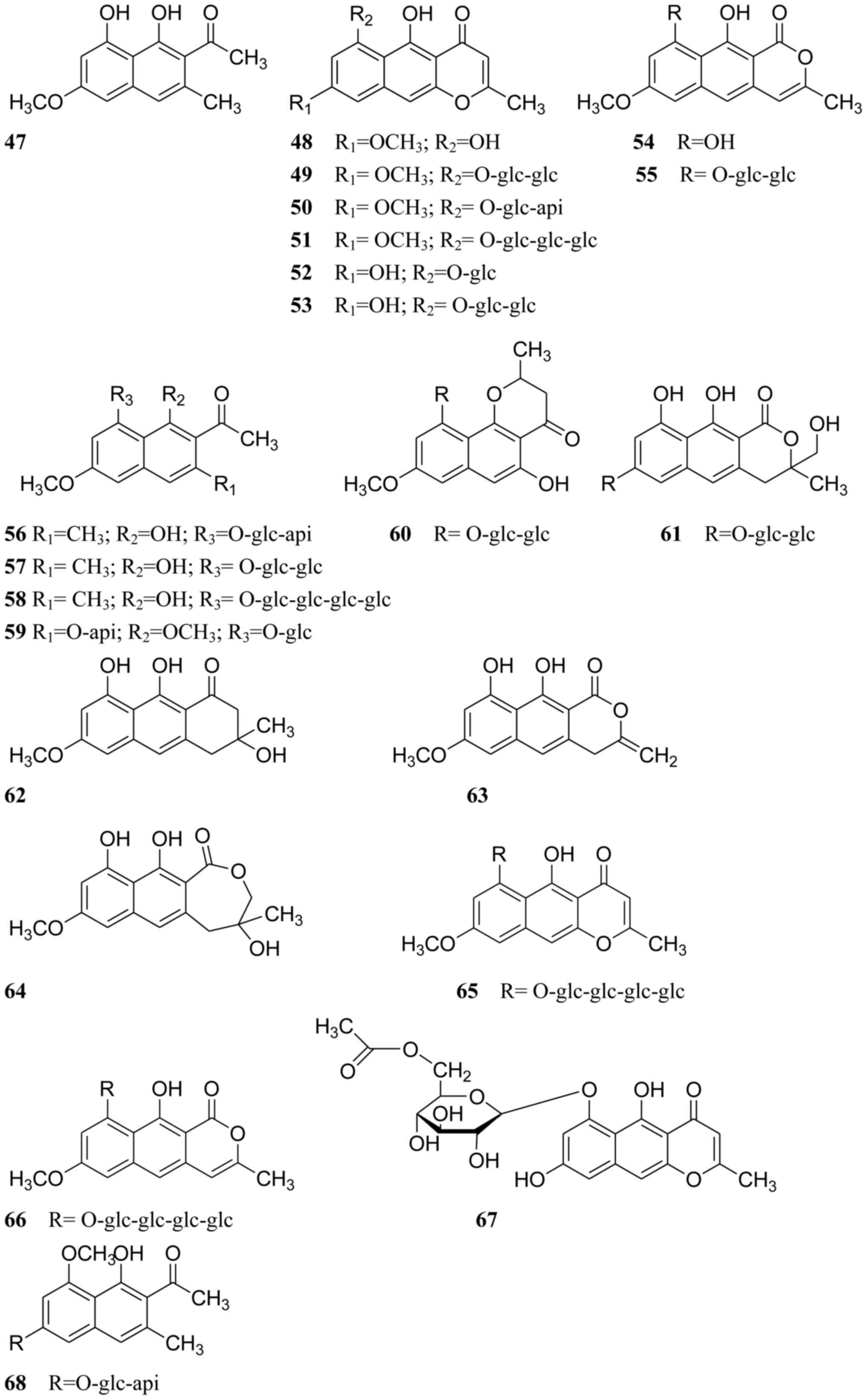
|
1
|
Editorial Committee of Chinese
PharmacopoeiaChinese Pharmacopoeia. 2015. Medical Science and
Technology Press; Beijing, China: pp. 1452015
|
|
2
|
Cho SH, Kim TH, Lee NH, Son HS, Cho IJ and
Ha TY: Effects of Cassia tora fiber supplement on serum lipids in
Korean diabetic patients. J Med Food. 8:311–318. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang W, Wang Y, Wang Q, Yang WJ, Gu Y,
Wang R, Song XM and Wang XJ: Quality evaluation of Semen Cassiae
(Cassia obtusifolia L.) by using ultra-high performance liquid
chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci.
35:2054–2062. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen JK and Chen TT: Chinese Medical
Herbology and Pharmacology. CA: Art of Medicine Press; pp.
8032001
|
|
5
|
Hao YJ, Sang YL and Zhao YQ: The
advancement of the studies on the seeds of Cassia obtusifolia.
Chinese Tradit Herb Drugs. 32:858–859. 2001.
|
|
6
|
Kim DH, Yoon BH, Kim YW, Lee S, Shin BY,
Jung JW, Kim HJ, Lee YS, Choi JS, Kim SY, et al: The seed extract
of Cassia obtusifolia ameliorates learning and memory impairments
induced by scopolamine or transient cerebral hypoperfusion in mice.
J Pharmacol Sci. 105:82–93. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kitanaka S, Kimura F and Takido M: Studies
on the Constituents of seeds of Cassia obusifolia LINN. The
structures of two new anthraquinone glycosides. Chem Pharm Bull.
33:1274–1276. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang C, Li GL, Xiao YQ and Pang LZ: Two
new glycosides from the seeds of Cassia obtusifolia. Chinese Chem
Lett. 20:1097–1099. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Deng ZY, Zhang JW, Li J, Fan YW, Cao SW,
Huang RL, Yin YL, Zhong HY and Li TJ: Effect of polysaccharides of
cassiae seeds on the intestinal microflora of piglets. Asia Pac J
Clin Nutr. 16:(Suppl 1). 143–147. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Luo X, Xu X, Huang C, Wu X, Liu J, Lan B
and Xu J: Experiment study of total anthraquinone in Cassiae Semen
on lipid peroxidation and PPAR-gamma expression in liver tissues of
rats with alcoholic fatty liver. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
36:1654–1658. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Su H, Wang Z and Tang L: Simultaneous
determination of 4 major components in Cassiae Semen obtusifoline
by HPLC. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 36:1327–1329. 2011.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yen GC, Chen HW and Duh PD: Extraction and
identification of an antioxidative component from Jue Ming Zi
(Cassia tora L.). J Agr Food Chem. 46:820–824. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Patil UK, Saraf S and Dixit VK:
Hypolipidemic activity of seeds of Cassia tora Linn. J
Ethnopharmacol. 90:249–252. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi JS, Lee HJ, Park KY, Ha JO and Kang
SS: In vitro antimutagenic effects of anthraquinone aglycones and
naphthopyrone glycosides from Cassia tora. Planta Med. 63:11–14.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee GY, Jang DS, Lee YM, Kim JM and Kim
JS: Naphthopyrone glucosides from the seeds of Cassia tora with
inhibitory activity on advanced glycation end products (AGEs)
formation. Arch Pharm Res. 29:587–590. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jung DH, Kim YS, Kim NH, Lee J, Jang DS
and Kim JS: Extract of Cassiae semen and its major compound inhibit
S100b-induced TGF-beta1 and fibronectin expression in mouse
glomerular mesangial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 641:7–14. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hatano T, Uebayashi H, Ito H, Shiota S,
Tsuchiya T and Yoshida T: Phenolic constituents of Cassia seeds and
antibacterial effect of some naphthalenes and anthraquinones on
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Chem Pharm Bull
(Tokyo). 47:1121–1127. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Das C, Dash S, Sahoo DC, Mohanty A and
Rout D: Cassia tora: A phyto-pharmacological overview. Int J Res
Ayurveda Pharm. 2:1162–1174. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Kitanaka S, Nakayama T, Shibano T, Ohkoshi
E and Takido M: Antiallergic agent from natural sources. Structures
and inhibitory effect of histamine release of naphthopyrone
glycosides from seeds of Cassia obtusifolia L. Chem Pharm Bull
(Tokyo). 46:1650–1652. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Deore SL, Khadabadi SS, Kamdi KS, Ingle
VP, Kawalkar NG, Sawarkar PS, Patil UA and Vyas AJ: In vitro
Anthelmintic activity of Cassia tora. Int J Chem Tech Res.
1:177–179. 2009.
|
|
21
|
Editorial Board of Flora of China. Science
Publishing House Press; pp. 1261988
|
|
22
|
Du ZX: Comparative identification of
Cassiae Semen and Sesbania aculeata Pers. Chinese Pharm J.
30:204–205. 1995.
|
|
23
|
Zhu SY, Xv HJ and Xv MG: Comparative
identification of Semen Cassiae and Cassia sophera. Chin Tradit
Herb Drugs. 34:379–380. 2003.
|
|
24
|
Liu J, Zou CC and Sun ZF: Comparative
identification of Cassiae Semen and Cassia occidentalis L.
Heilongjiang Med Pharm. 29:63–64. 2006.
|
|
25
|
Hu YJ, Wan L, Zhang JX, et al:
Identification of Cassia obtusifolia L. by TLC. Lishizhen Med Mater
Med Res. 17:21292006.
|
|
26
|
Sun GF: Identification of Cassia
obtusifolia L., Cassia tora. and Cassia occidentalis L. by
SDS-Polyacrylamide gelelectrophoresis. Tianjin Pharm. 8:69–71.
1996.
|
|
27
|
Wang JB, Zhou X and Hu ZF: Quality
evaluation of Cassiae Semen by both indicated component
determination and HPLC fingerprint. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs.
39:917–919. 2008.
|
|
28
|
Luo Y, Zhang L, Wang WH and Li B:
Components identification in Cassiae Semen by HPLC-IT-TOF MS. Chin
J Pharm Anal. 35:1408–1516. 2015.
|
|
29
|
Lee HJ, Choi JS, Jung JH and Kang SS:
Alaternin glucoside isomer from Cassia tora. Phytochemistry.
49:1403–1404. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chen QD, Xv R, Xv ZN, et al: Progress in
studies of active coustituents of anthraquinones and their
biological activities from Cassiae Semen. Chins J Mod Appl Pharm.
20:120–123. 2003.
|
|
31
|
DiGiovanni J and Boutwell RK: Tumor
promoting activity of 1, 8-dihydroxy-3-methyl-9-anthrone
(chrysarobin) in female SENCAR mice. Carcinogenesis. 4:281–284.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jia ZB, Chen WW, Jiang JX and DING XL:
Study on anthraquinone constituents in the seed of Cassia tora L.
Chem Ind Forest Prod. 29:100–102. 2009.
|
|
33
|
Xv YL: Studies on the chemical
constituents from Semen Cassiae and the influence of processing.
Beijing: Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. 1:152014.
|
|
34
|
Takido M: Studies on the constituents of
the seeds of Cassia obtusifolia L. I. The Structure of Obtusifolin.
Chem Pharm Bull. 6:397–400. 1958. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Takido M: Studies on the constituents of
seeds of Cassia obusifolia L. II. The structure of Obtusin,
Chryso-obutsin and Aurantio-obyusin. Chem Pharm Bull. 8:2461960.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kitanaka S and Takido M: Studies on the
constituents of the seeds of Cassia obusifolia: The structures of
three new anthraquinones. Chem Pharm Bull. 32:860–864. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tang LY, Wang ZJ, Fu HM, et al: Study on
anthraquinones constituents from Semen Cassiae. J Chinese Med
Mater. 32:717–719. 2009a.
|
|
38
|
Zhang ZX and Liang YF: Isolation and
identification of chemical constituents from seeds of Cassia
obtusifolia. China Pharm. 23:1782–1783. 2012.
|
|
39
|
Yun-Choi HS, Kim JH and Takido M:
Potential inhibitors of platelet aggregation from plant sources, V.
Anthraquinones from seeds of Cassia obtusifolia and related
compounds. J Nat Prod. 53:630–633. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hao YJ, Sang YL and Zhao YQ: Study on
anthraquinone constituents in Cassiae Semen. Chinese Tradit Herb
Drugs. 34:18–19. 2003.
|
|
41
|
Li CH, Wei XY and Li XE: A new
anthraquinone glycoside from the seed of Cassia obtusifolia.
Chinese Chem Lett. 15:1448–1450. 2004.
|
|
42
|
Wong SM, Wong MM, Seligmann O and Wagner
H: Anthraquinone glycosides from the seeds of Cassia tora.
Phytochemistry. 28:211–214. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tang LY, Wang ZJ, Fu MH, He Y, Wu HW and
Huang LQ: A new anthraquinone glycoside from seeds of Cassia
obtusifolia. Chinese Chem Lett. 19:1083–1085. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Li G, Xiao Y, Li L, Zhang C and Pang Z:
Studies on chemical constituents of roasted seeds of Cassia
obtusifolia. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 34:54–56. 2009.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tang LY, Wang ZJ, He Y, et al: Glycosides
from seeds of Cassia obtusifolia. Chinese J Exp Tradit Med
Formulae. 15:35–37. 2009b.
|
|
46
|
Jia ZB and Ding XL: Anthraquinone
constituents from seeds of Cassia tora L. J Chinese Med Mater.
29:28–29. 2006.
|
|
47
|
Miyuki K, Eisaku M and Shoji S: Chemical
Studies on the Oriental Plant Drugs. XXI. The Constituents of
Cassia tora L. (2). A Glycoside of Rubrofusarin. Chem Pharm Bull.
17:458–461. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shibata S, Morishita E and Kaneda M:
Chemical Studies on the Oriental Plant Drugs. XX. The Constituents
of Cassia tora L. (1). The Structure of Torachrysone. Chem Pharm
Bull. 17:454–457. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Takahashi S and Takido M: Studies on the
constituents of the seeds of Cassia tora L. II. (On the purgative
crude drugs. VII). The structure of the new naphthopyrone
derivative, toralactone. Yakugaku Zasshi. 93:2611973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wong SM, Wong MM, Seligmann O and Wagner
H: New antihepatotoxic naphthopyrone glycosides from the seeds of
Cassia tora. Planta Med. 55:276–280. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Choi JS, Jung JH, Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Lee JH
and Kang SS: A naphthalene glycoside from Cassia tora.
Phytochemistry. 40:997–999. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Tianaka S and Takido M: Studies on the
constituents of the seeds of Cassia obtusifolia L. The structures
of two naphthopyrone glycosides. Chem Pharm Bull. 36:3980–3984.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kitanaka S and Miehio T: Studies on the
constituents of the seeds of Cassia obtusifolia: The structures of
two new lactones, isotoralactone and cassialactone. Phytochemistry.
20:1951–1953. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li L, Zhang C, Xiao YQ, Li W, Yin X, Chen
D, Tian G and Wang Y: Glycosides of roasted seeds of Cassia
obtusifolia. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 35:1566–1568.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang ZJ, Wu QP, Tang LY, Fu MH, He Y, Gong
QF and Hung LQ: Two new glycosides from the genus of Cassia.
Chinese Chem Lett. 18:1218–1220. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Li YM: Comparison of volatile components
of Cassiae Semen and semen seeds tea. J Med Plants Res.
6:3865–3869. 2012.
|
|
57
|
Jiao SF and Han HD: Studies on chemical
constituents of Cassiae Semen. Chinese J Clin Ration Drug Use.
3:81–82. 2010.
|
|
58
|
Wu XH: Study on the chemical constituents,
quality control and metabolism of Cassia obtusifolia. Wuhan:
Huazhong University of Science and Technology. 1:11–12. 2010.
|
|
59
|
Guan Y and Zhao S: Yishou jiangzhi
(de-blood-lipid) tablets in the treatment of hyperlipidemia. J
Tradit Chin Med. 15:178–179. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yang Y, Liu J and Lai XH: Observation on
cassia seed tea combined with walking exercise on weight loss in
the elderly. Modern Prev Med. 40:2468–2474. 2013.
|
|
61
|
Lai XH: Double intervention of cassia seed
tea and sports on older women weight loss. Chinese J Gerontol.
31:2402–2404. 2011.
|
|
62
|
Zhang R, Feng ML and Wu YP: Experimental
study on the active situs of fetid cassia seed to reduce blood
lipid and their dose-effect relation. China Remedies Clin.
5:183–185. 2005b.
|
|
63
|
Zhang JX, Wan L, Hu YJ, Qu OL and Shi JY:
Study on the effective part of reducing blood lipid in Semen
Cassiae. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res. 17:904–905. 2006.
|
|
64
|
Li CH, Li XE and Guo BJ: The effects of
Cassia obtusifolia seeds extracts on reducing blood lipid. J South
China Normal Univ. 98:29–32. 2002.
|
|
65
|
Wang YH, Gao L, Zhou WJ and Ma WJ: Effects
of ethanol extraction from Cassiae Semen on Serum IL-6 and TNF-α in
hyperlipidemia rats. Chinese J Exp Tradit Med Formulae. 20:178–181.
2014.
|
|
66
|
He JY, Liu SQ, Peng YF, et al: Study of
the Mechanism of Cassia Obtusifolia L in decreasing blood -lipid.
China Pharm. 14:202–203. 2003.
|
|
67
|
Cho IJ, Lee C and Ha TY: Hypolipidemic
effect of soluble fiber isolated from seeds of Cassia tora Linn. In
rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. J Agric Food Chem. 55:1592–1596.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu SM, Sun C and Xie WH: Effect of Semen
Cassiae extracts on expression of lipogenesis genes in
hyperlipidemia model mice. Chinese Tradit Herb Drugs. 40:583–587.
2009.
|
|
69
|
Wei N, Lv HR and Liu MF: Study on the
chemical constitutions of reducing blood lipid in Cassiae Semen.
Guangdong Chem Ind. 39:99–100. 2012.
|
|
70
|
Li BL: The active ingredients of reducing
blood lipid in Semen Cassia. China Prac Med. 7:172–173. 2012.
|
|
71
|
Guo CY, Horn W and Pin DD: Extraction and
identification of an antioxidative component from Jue Ming Zi
(Cassia tora L.). J Agric Food Chem. 46:820–824. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Li XE and Guo BJ: Effects of protein and
anthraquinone glucosides from Cassia seed on serum lipid of
hyperlipidemia rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 27:374–376.
2002.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Li CH, Li XE, Fang KY and Guo BJ: Effects
of anthraquinones from Cassia obtusifolia L. on cholesterol
biosynthesis in cells. J Clin Rehabilit Tissue Eng Res.
12:6593–6596. 2008.
|
|
74
|
Huang YL, Chow CJ and Tsai YH:
Composition, characteristics, and in-vitro physiological effects of
the water-soluble polysaccharides from Cassia seed. Food Chem.
134:1967–1972. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kim YS, Jung DH, Sohn E, Lee YM, Kim CS
and Kim JS: Extract of Cassiae semen attenuates diabetic
nephropathy via inhibition of advanced glycation end products
accumulation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Phytomedicine. 21:734–739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Jung DH, Kim YS, Sohn EJ, et al: Effects
of CS, a BuOH-Soluble Fraction of Cassiae Semen Methanolic Extract,
on COX-2 Expression in Renal Cortex of STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats
and Cultured Glomerular Mesangial Cells. Diabetes. 56:pA155.
2007.
|
|
77
|
Zhu TC: Inhibitory Effects of Cassia Seed
on the Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Rats. Chin J Exp Tradit Med
Formulae. 18:315–319. 2012.
|
|
78
|
Kim DH, Kim S, Jung WY, Park SJ, Park DH,
Kim JM, Cheong JH and Ryu JH: The neuroprotective effects of the
seeds of Cassia obtusifolia on transient cerebral global ischemia
in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:1473–1479. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Drever BD, Anderson WG, Riedel G, Kim DH,
Ryu JH, Choi DY and Platt B: The seed extract of Cassia obtusifolia
offers neuroprotection to mouse hippocampal cultures. J Pharmacol
Sci. 107:380–392. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yi JH, Park HJ, Lee S, Jung JW, Kim BC,
Lee YC, Ryu JH and Kim DH: Cassia obtusifolia seed ameliorates
amyloid β-induced synaptic dysfunction through anti-inflammatory
and Akt/GSK-3β pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 178:50–57. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ju MS, Kim HG, Choi JG, Ryu JH, Hur J, Kim
YJ and Oh MS: Cassiae semen, a seed of Cassia obtusifolia, has
neuroprotective effects in Parkinson's disease models. Food Chem
Toxicol. 48:2037–2044. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Liu JZ, Lin X, Li XE and Guo BJ: Effect of
protein and anthraquinone glucosides from Semen Cassiae on learning
and memory capacity and related substances of senile mice induced
by D-galactone. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 32:516–519. 2007.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Jiangsu New Medical College: Encyclopedia
of Chinese MateriaMedica, I. Shanghai Science and Technology Press;
Shanghai, China: pp. 949841975
|
|
84
|
Yun HS and Chang IM: Plants with liver
protective activities (I). Korean J Pharmacogn. 8:125–129.
1977.
|
|
85
|
Gao Q, Xu H and Chen J: Liver-protective
and bowel-lubricating and defecation-promoting effects of crude and
processed Semen Cassiae. Tradit Chinese Drug Res Clin Pharmacol.
18:194–196. 2007.
|
|
86
|
Lin DJ and Jin Z: Experimental Study on
Protective Effect of Semen Cassiae Extract Against Acute Liver
Injury. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res. 17:214–215. 2006.
|
|
87
|
Niu YF, Zhao T, Zeng T, et al: Study on
the protective effect of Cassiae Semen extract against
alcohol-induced acute liver injury in mice. J Toxicol. 24:58–61.
2010.
|
|
88
|
Kim YM, Lee CH, Kim HG and Lee HS:
Anthraquinones isolated from Cassia tora (Leguminosae) seed show an
antifungal property against phytopathogenic fungi. J Agr Food Chem.
52:6096–6100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Li Y, Xu C, Zhang Q, Liu JY and Tan RX: In
vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori action of 30 Chinese herbal
medicines used to treat ulcer diseases. J Ethnopharmacol.
98:329–333. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Sung BK, Kim MK, Lee WH, Lee DH and Lee
HS: Growth responses of Cassia obtusifolia toward human intestinal
bacteria. Fitoterapia. 75:505–509. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Li XH, Gong CR, Cao H, et al: Primary
study on inhabiting of the extracts from Cassia obtusifolia seeds
against Fusarium oxysporum and Botrytis cinerea. J Shanxi Agric
Univ. 26:348–350. 2006.
|
|
92
|
Yen GC and Chung DY: Antioxidant Effects
of Extracts from Cassia tora L. Prepared under different degrees of
roasting on the oxidative damage to biomolecules. J Agr Food Chem.
47:1326–1332. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Yen GC and Chuang DY: Antioxidant
properties of water extracts from Cassia tora L. In relation to the
degree of roasting. J Agr Food Chem. 48:2760–2765. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Xv JG and Hu QP: Study on Free Radical
Scavenging Capacity by Cassia Seed Water Extract in vitro. Food
Sci. 27:73–75. 2006.
|
|
95
|
Guo CQ, Yan J, Wu XY, Xu GY, Fan CH and
Gou XJ: Study on purification and antioxidation of water-soluble
polysaccharide isolated from semen cassia. Food Sci. 28:205–208.
2007.
|
|
96
|
Liu J, Deng ZY and Yu HH: Antioxidation
Study on Water-soluble Polysaccharide Isolated from Semen Cassiae.
Food Sci. 27:61–63. 2006.
|
|
97
|
Liu C, Liu Q, Sun J, Jiang Bb and Yan J:
Extraction of water-soluble polysaccharide and the antioxidant
activity from Cassiae Semen. J Food Drug Anal. 22:492–499. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Zeng H, Liu Q, Wang M, Jiang S, Zhang L,
He X, Wang J and Chen X: Target-guided separation of antioxidants
from Semen cassia via off-line two-dimensional high-speed
counter-current chromatography combined with complexation and
extrusion elution mode. J Chromatogr B. 1001:58–65. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Kim SY, Kim JH, Kim SK, Oh MJ and Jung MY:
Antioxidant activities of selected oriental herb extracts. J Am Oil
Chem Soc. 71:633–640. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Choi JS, Lee HJ and Kang SS: Alatemin,
cassiaside and rubrofusarin gentiobioside, radical scavenging
principles from the seeds of Cassia tora on 1,
1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical. Arch Pharm Res.
17:462–466. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Koo A, Wang JC and Li KM: Extraction of
hypotensive principles from seeds of Cassia tora. Am J Chin Med
(Gard City N Y). 4:245–248. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Koo A, Chan WS and Li KM: A possible
reflex mechanism of hypotensive action of extract from Cassia tora
seeds. Am J Chin Med (Gard City N Y). 4:249–255. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Chan SH, Koo A and Li KM: The involvement
of medullary reticular formation in the hypotensive effect of
extracts from seeds of Cassia tora. Am J Chin Med (Gard City N Y).
4:383–389. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Mao WH, Shang QH, Liu AD, et al: Effects
of Cassiae Semen Extracts on Vasorelaxation and Its Mechanisms in
Rat Aorta. Chin J Hypertens. 18:60–63. 2010.
|
|
105
|
Zhang CZ, Wang SX, Zhang Y, Chen JP and
Liang XM: In vitro estrogenic activities of Chinese medicinal
plants traditionally used for the management of menopausal
symptoms. J Ethnopharmacol. 98:295–300. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Wu CH and Yen GC: Antigenotoxic properties
of Cassia tea (Cassia tora L.): Mechanism of action and the
influence of roasting process. Life Sci. 76:85–101. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Fu F, Tian F, Zhou H, Lv W, Tie R, Ji L,
Li R, Shi Z, Yu L, Liang X, et al: Semen cassiae attenuates
myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury in high-fat diet
streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Am J Chinese Med.
42:95–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Zhang P and Chen JW: HPLC Fingerprint of
Cassiae Semen. Chinese Tradit Herb Drugs. 38:372–375. 2007.
|
|
109
|
Luo W, Liu B, Wang W, et al: HPLC
fingerprint chromatogram of Cassiae Semen. J Beijing Univ Tradit
Chin Med. 32:115–117. 2009.
|
|
110
|
Wang WY, Zhao Q, Zhang TJ, et al: HPLC
Fingerprint and chemical pattern recognition of Cassiae Semen.
Chinese Tradit Herb Drugs. 40:1638–1641. 2009.
|
|
111
|
Tang YL, Liang TZ, Zhang HX and Xu JY:
Study on fingerprint of Cassiae Semen, ultramicro powder and powder
particle. Zhong Yao Cai. 34:1861–1866. 2011.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Wang N, Wu Y, Wu X, Liang S and Sun H: A
novel nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis method for effective
separation and simultaneous determination of aurantio-obtusin,
emodin and rhein in semen cassiae and cassia seed tea. Anal
Methods. 6:5133–5139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Yang C, Wang S, Guo X, Sun J, Liu L and Wu
L: Simultaneous determination of seven anthraquinones in rat plasma
by Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography-tandem Mass
Spectrometry and pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of
Semen Cassiae extract. J Ethnopharmacol. 169:305–313. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Hyun SK, Lee H, Kang SS, Chung HY and Choi
JS: Inhibitory activities of Cassia tora and its anthraquinone
constituents on angiotensin-converting enzyme. Phytother Res.
23:178–184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Dhanasekaran M, Ignacimuthu S and Agastian
P: Potential hepatoprotective activity of ononitol monohydrate
isolated from Cassia tora L. on carbon tetrachloride induced
hepatotoxicity in Wistar rats. Phytomedicine. 16:891–895. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Jung HA, Ali MY, Jung HJ, Jeong HO, Chung
HY and Choi JS: Inhibitory activities of major anthraquinones and
other constituents from Cassia obtusifolia against β-secretase and
cholinesterases. J Ethnopharmacol. 191:152–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wen CC, Shyur LF, Jan JT, Liang PH, Kuo
CJ, Arulselvan P, Wu JB, Kuo SC and Yang NS: Traditional Chinese
medicine herbal extracts of Cibotium barometz, Gentiana scabra,
Dioscorea batatas, Cassia tora and Taxillus chinensis inhibit
SARS-CoV replication. J Tradit Complement Med. 1:41–50. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|