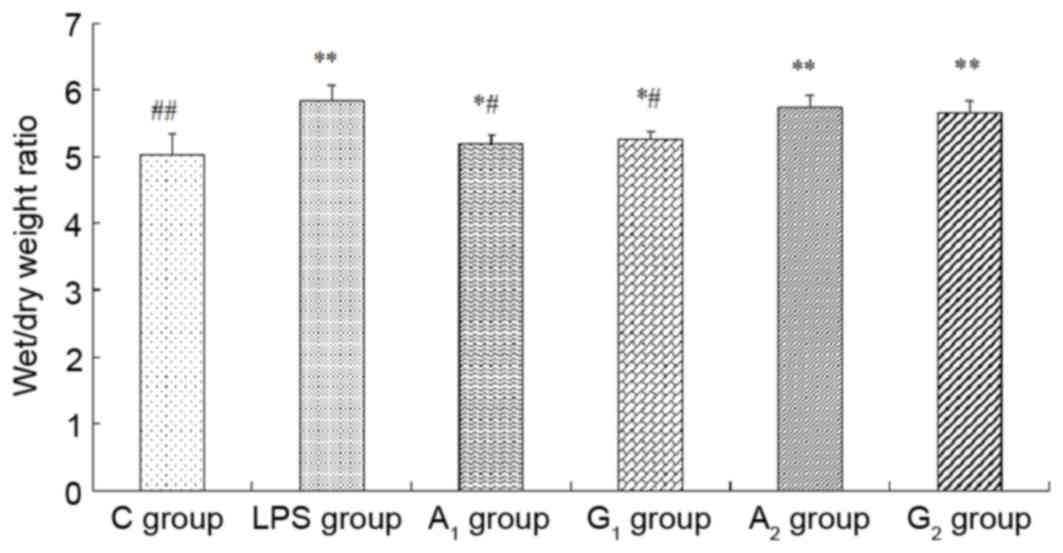
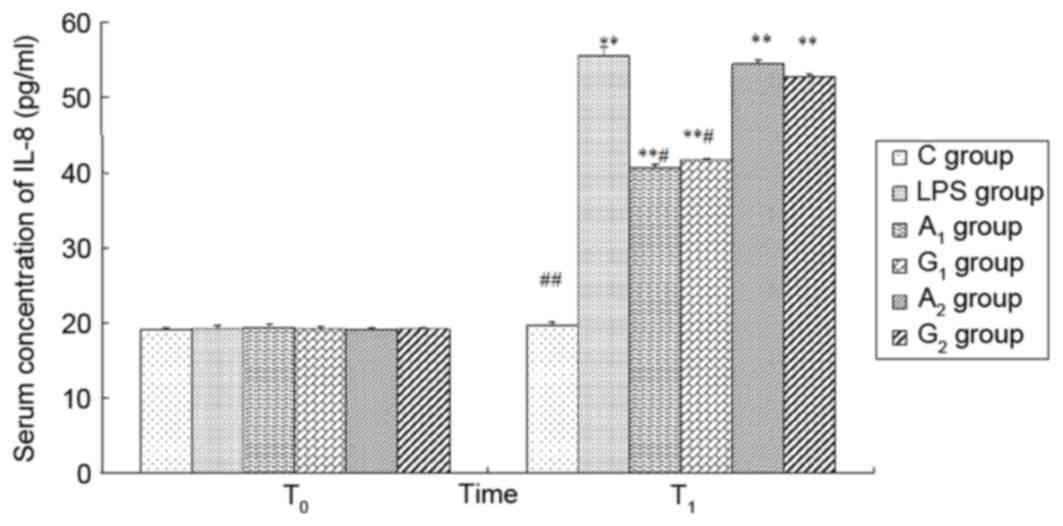
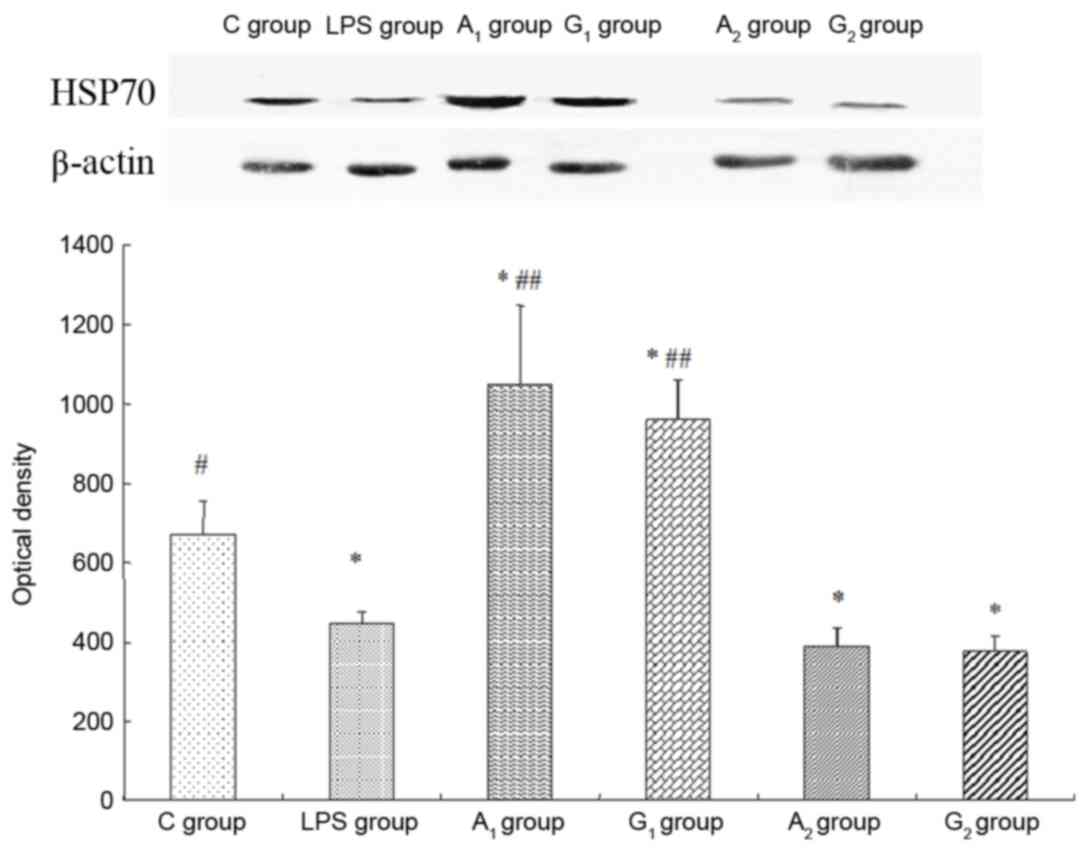
|
1
|
Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet
J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, Legall JR, Morris A and Spragg R: The
American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions,
mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am
J Respir Crit Care Med. 149:818–824. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Margulis BA, Sandler S, Eizirik DL, Welsh
N and Welsh M: Liposomal delivery of purified heat shock protein
hsp70 into rat pancreatic islets as protection against interleukin
1 beta-induced impaired beta-cell function. Diabetes. 40:1418–1422.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
White DJ, Carlson D, Ordway GA and Horton
JW: Protective role of heat stress in burn trauma. Crit Care Med.
32:1338–1345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wischmeyer PE, Kahana M, Wolfson R, Ren H,
Musch MM and Chang EB: Glutamine induces heat shock protein and
protects against endotoxin shock in the rat. J Appl Physiol (1985).
90:2403–2410. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jing L, Wu Q and Wang F: Glutamine induces
heat-shock protein and protects against Escherichia coli
lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular hyporeactivity in rats. Crit
Care. 11:R342007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oliveira GP, Oliveira MB, Santos RS, Lima
LD, Dias CM, Saber AM Ab', Teodoro WR, Capelozzi VL, Gomes RN,
Bozza PT, et al: Intravenous glutamine decreases lung and distal
organ injury in an experimental model of abdominal sepsis. Crit
Care. 13:R742009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Singleton KD, Beckey VE and Wischmeyer PE:
Glutamine prevents activation of NF-kappaB and stress kinase
pathways, attenuates inflammatory cytokine release, and prevents
acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) following sepsis. Shock.
24:583–589. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Singleton KD and Wischmeyer PE:
Glutamine's protection against sepsis and lung injury is dependent
on heat shock protein 70 expression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol. 292:R1839–R1845. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singleton KD, Serkova N, Beckey VE and
Wischmeyer PE: Glutamine attenuates lung injury and improves
survival after sepsis: Role of enhanced heat shock protein
expression. Crit Care Med. 33:1206–1213. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singleton KD and Wischmeyer PE: Oral
glutamine enhances heat shock protein expression and improves
survival following hyperthermia. Shock. 25:295–299. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hayashi Y, Sawa Y, Fukuyama N, Nakazawa H
and Matsuda H: Preoperative glutamine administration induces
heat-shock protein 70 expression and attenuates cardiopulmonary
bypass-induced inflammatory response by regulating nitric oxide
synthase activity. Circulation. 106:2601–2607. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Heyland D, Muscedere J, Wischmeyer PE,
Cook D, Jones G, Albert M, Elke G, Berger MM, Day AG, et al:
Canadian Critical Care Trials Group: A randomized trial of
glutamine and antioxidants in critically ill patients. N Engl J
Med. 368:1489–1497. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kristof AS, Goldberg P, Laubach V and
Hussain SN: Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
158:1883–1889. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun D, Chen D, Du B and Pan J: Heat shock
response inhibits NF-kappaB activation and cytokine production in
murine Kupffer cells. J Surg Res. 129:114–121. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Malhotra V and Wong HR: Interactions
between the heat shock response and the nuclear factor-kappaB
signaling pathway. Crit Care Med. 30:(1 Supp). S89–S95. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chu EK, Ribeiro SP and Slutsky AS: Heat
stress increases survival rates in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
rats. Crit Care Med. 25:1727–1732. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
DeMeester SL, Buchman TG and Cobb JP: The
heat shock paradox: Does NF-kappaB determine cell fate? FASEB J.
15:270–274. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bai T, Sun YH and Wang JK: Effect of
glutamine administered at different times on endotoxin-induced
acute lung injury in rats. J China Med Univ. 36:418–420. 2007.
|
|
19
|
Kaplan J, Nowell M, Chima R and Zingarelli
B: Pioglitazone reduces inflammation through inhibition of NF-κB in
polymicrobial sepsis. Innate Immun. 20:519–528. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Scharte M, Baba HA, Van Aken H, Schulzki
C, Meyer J, Goeters C and Bone HG: Alanyl-glutamine dipeptide does
not affect hemodynamics despite a greater increase in myocardial
heat shock protein 72 immunoreactivity in endotoxemic sheep. J
Nutr. 131:1433–1437. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bonet A and Grau T: Glutamine, an almost
essential amino acid in critically ill patient. Med Intensiva.
31:402–406. 2007.(In Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL,
Cho SK, Li CY, Sasaki T, Elia AJ, Cheng HY, Ravagnan L, et al:
Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in
programmed cell death. Nature. 410:549–554. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ahmad S, White CW, Chang LY, Schneider BK
and Allen CB: Glutamine protects mitochondrial structure and
function in oxygen toxicity. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
280:L779–L791. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roth E, Oehler R, Manhart N, Exner R,
Wessner B, Strasser E and Spittler A: Regulative potential of
glutamine-relation to glutathione metabolism. Nutrition.
18:217–221. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Armeni T, Ghiselli R, Balercia G, Goffi L,
Jassem W, Saba V and Principato G: Glutathione and ultrastructural
changes in inflow occlusion of rat liver. J Surg Res. 88:207–214.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tritsch GL and More GE: Spontaneous
decomposition of glutamine in cell culture media. Exp Cell Res.
28:360–364. 1962. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamamoto Y, Kume M and Yamaoka Y:
Implications of heat shock proteins during liver surgery and liver
perfusion. Recent Results Cancer Res. 147:157–172. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|