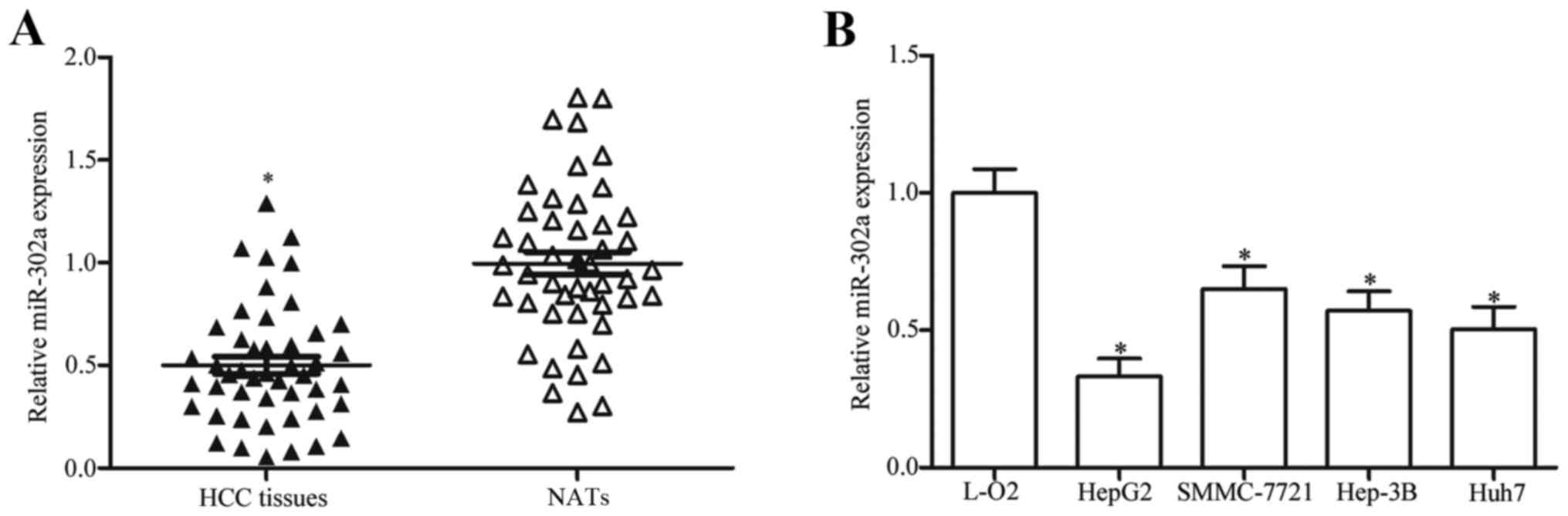
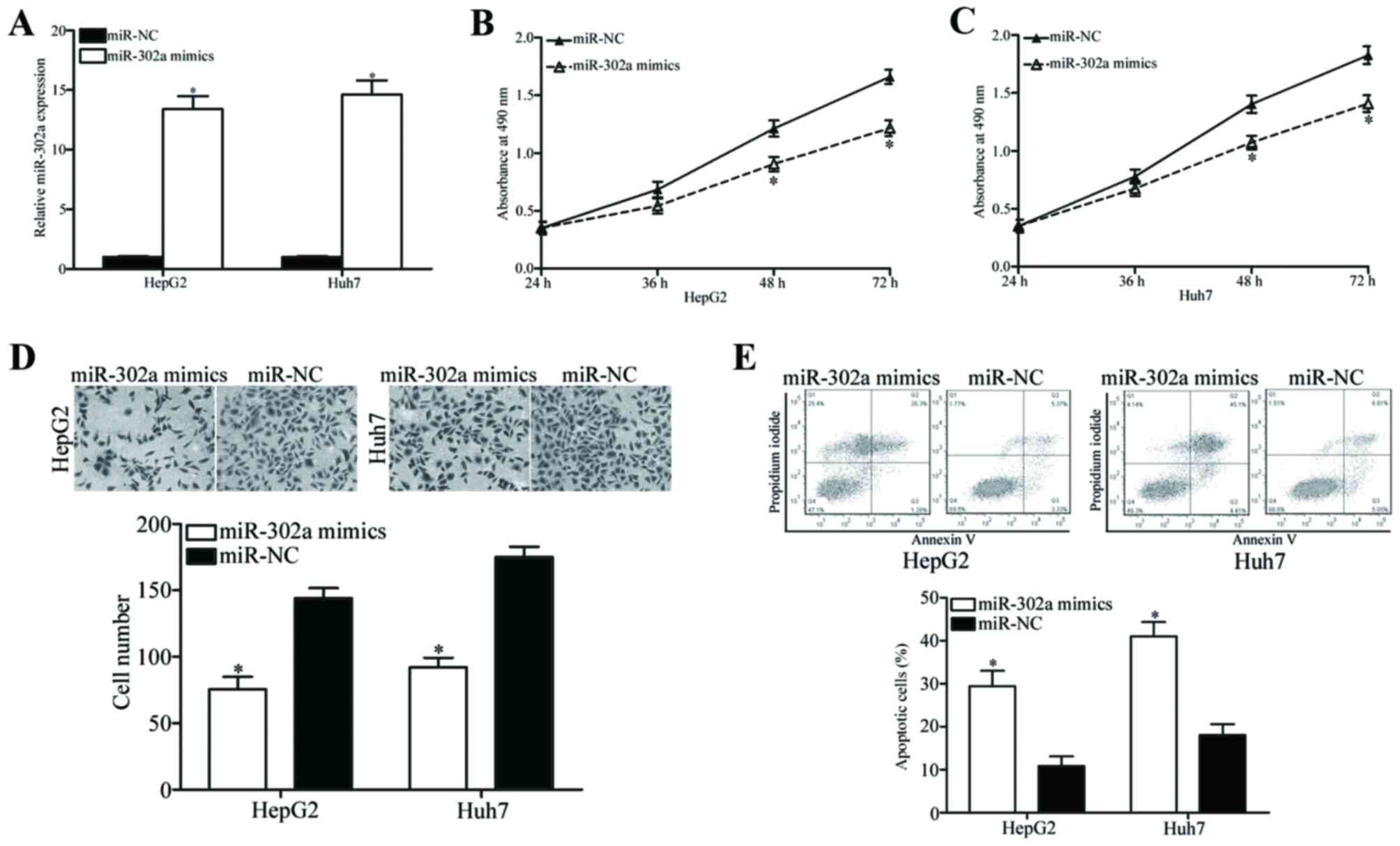
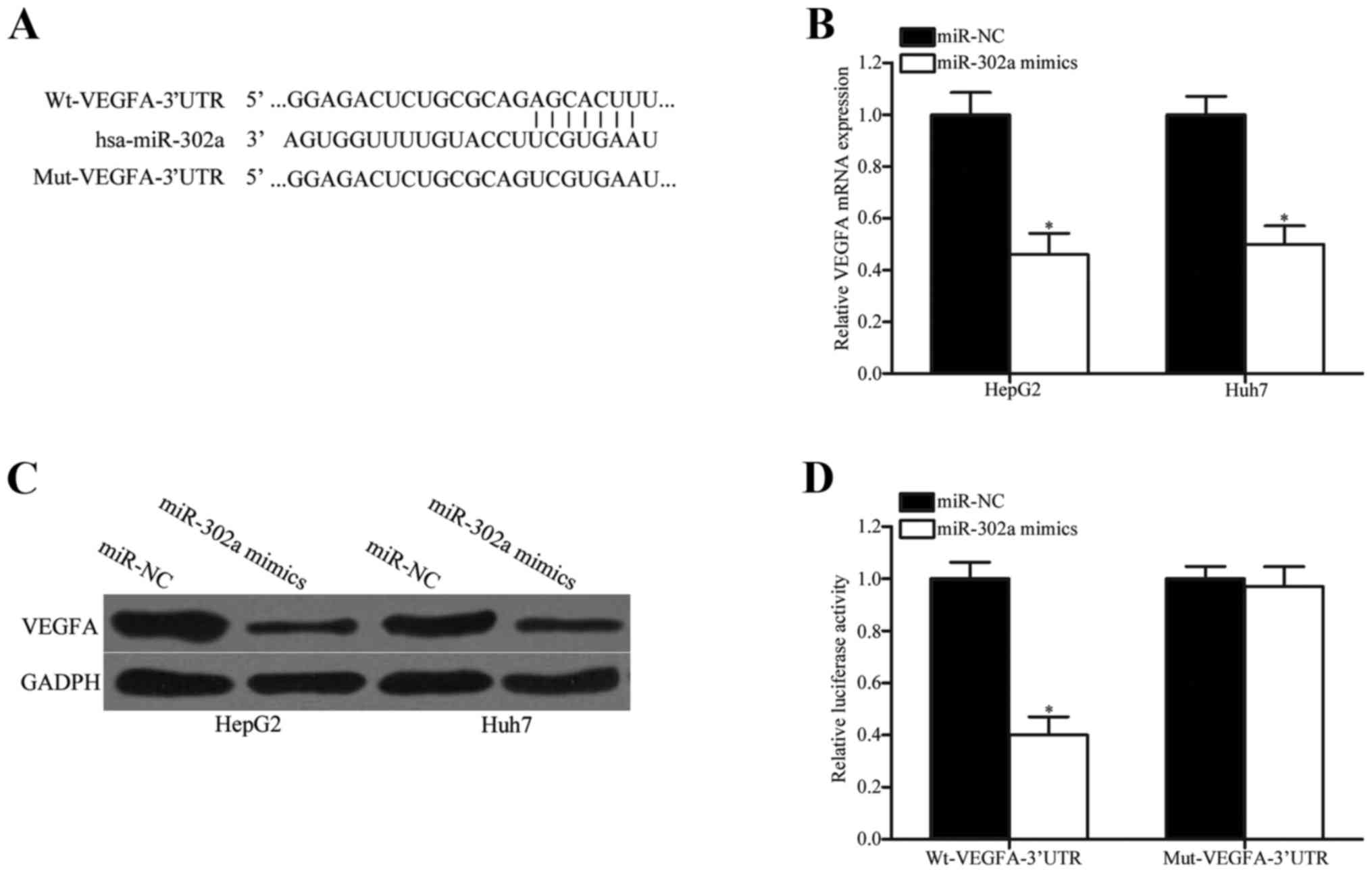
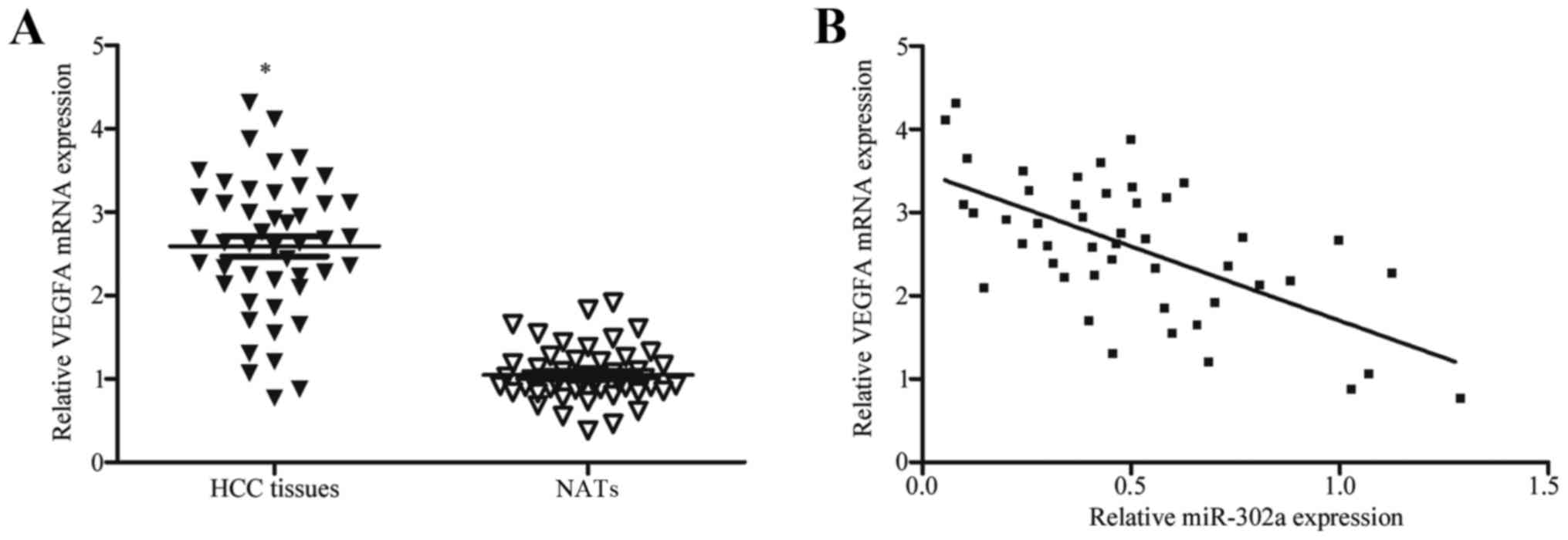
|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dhanasekaran R, Limaye A and Cabrera R:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current trends in worldwide epidemiology,
risk factors, diagnosism, and therapeutics. Hepat Med. 4:19–37.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu L, Zhang M, Zheng X, Yi P, Lan C and Xu
M: The circular RNA ciRS-7 (Cdr1as) acts as a risk factor of
hepatic microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 143:17–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hou B, Jian Z, Chen S, Ou Y, Li S and Ou
J: Expression of miR-216a in pancreatic cancer and its clinical
significance. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 32:1628–1631. 2012.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Choi E, Choi E and Hwang KC: MicroRNAs as
novel regulators of stem cell fate. World J Stem Cells. 5:172–187.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou W, Zou B, Liu L, Cui K, Gao J, Yuan S
and Cong N: MicroRNA-98 acts as a tumor suppressor in
hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting SALL4. Oncotarget.
7:74059–74073. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang CY, Zhang JJ, Hua L, Yao KH, Chen JT
and Ren XQ: MicroRNA-98 suppresses cell proliferation, migration
and invasion by targeting collagen triple helix repeat containing 1
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:2639–2644. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu S, Liu K, Zhang W, Wang Y, Jin Z, Jia
B and Liu Y: miR-449a inhibits proliferation and invasion by
regulating ADAM10 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res.
8:2609–2619. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang LL, Wang L, Wang XY, Shang D, Yin SJ,
Sun LL and Ji HB: MicroRNA-218 inhibits the proliferation,
migration, and invasion and promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer
cells by targeting LASP1. Tumour Biol. 37:15241–15252. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li H, Zhang H, Lu G, Li Q, Gu J, Song Y,
Gao S and Ding Y: Mechanism analysis of colorectal cancer according
to the microRNA expression profile. Oncol Lett. 12:2329–2336.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peng G, Liao Y and Shen C: miRNA-429
inhibits astrocytoma proliferation and invasion by targeting BMI1.
Pathol Oncol Res. 23:369–376. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu D, Niu X, Pan H, Zhou Y, Qu P and Zhou
J: MicroRNA-335 is downregulated in bladder cancer and inhibits
cell growth, migration and invasion via targeting ROCK1. Mol Med
Rep. 13:4379–4385. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Q, Huang Z, Guo W, Ni S, Xiao X, Wang
L, Huang D, Tan C, Xu Q, Zha R, et al: microRNA-202-3p inhibits
cell proliferation by targeting ADP-ribosylation factor-like 5A in
human colorectal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1146–1157. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Josson S, Gururajan M, Hu P, Shao C, Chu
GY, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lao K, Lu CL, Lu YT, et al: miR-409-3p/-5p
promotes tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and
bone metastasis of human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:4636–4646. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fan MQ, Huang CB, Gu Y, Xiao Y, Sheng JX
and Zhong L: Decrease expression of microRNA-20a promotes cancer
cell proliferation and predicts poor survival of hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 32:212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du C, Weng X, Hu W, Lv Z, Xiao H, Ding C,
Gyabaah OA, Xie H, Zhou L, Wu J and Zheng S: Hypoxia-inducible
MiR-182 promotes angiogenesis by targeting RASA1 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chuang KH, Whitney-Miller CL, Chu CY, Zhou
Z, Dokus MK, Schmit S and Barry CT: MicroRNA-494 is a master
epigenetic regulator of multiple invasion-suppressor microRNAs by
targeting ten eleven translocation 1 in invasive human
hepatocellular carcinoma tumors. Hepatology. 62:466–480. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang Z, Ahn J, Guo D, Votaw JR and Shim
H: MicroRNA-302 replacement therapy sensitizes breast cancer cells
to ionizing radiation. Pharm Res. 30:1008–1016. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liang Z, Bian X and Shim H: Inhibition of
breast cancer metastasis with microRNA-302a by downregulation of
CXCR4 expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 146:535–542. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu L, Lian J, Zhang H, Tian H, Liang M,
Yin M and Sun F: MicroRNA-302a sensitizes testicular embryonal
carcinoma cells to cisplatin-induced cell death. J Cell Physiol.
228:2294–2304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamaguchi R, Yano H, Iemura A, Ogasawara
S, Haramaki M and Kojiro M: Expression of vascular endothelial
growth factor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
28:68–77. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miura H, Miyazaki T, Kuroda M, Oka T,
Machinami R, Kodama T, Shibuya M, Makuuchi M, Yazaki Y and Ohnishi
S: Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 27:854–861. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mao B and Wang G: MicroRNAs involved with
hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol Rep. 34:2811–2820. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Giordano S and Columbano A: MicroRNAs: New
tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma? Hepatology. 57:840–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jin H, Yu M, Lin Y, Hou B, Wu Z, Li Z and
Sun J: MiR-502-3P suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SET. Onco Targets
Ther. 9:3281–3289. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo T, Yu W, Lv S, Zhang C and Tian Y:
MiR-302a inhibits the tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by
suppression of SDC1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4869–4880.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang GM, Bao CY, Wan FN, Cao DL, Qin XJ,
Zhang HL, Zhu Y, Dai B, Shi GH and Ye DW: MicroRNA-302a suppresses
tumor cell proliferation by inhibiting AKT in prostate cancer. PLoS
One. 10:e01244102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wei ZJ, Tao ML, Zhang W, Han GD, Zhu ZC,
Miao ZG, Li JY and Qiao ZB: Up-regulation of microRNA-302a
inhibited the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells
by regulation of the MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4481–4491. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fan L, Wu Q, Xing X, Wei Y and Shao Z:
MicroRNA-145 targets vascular endothelial growth factor and
inhibits invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 44:407–414. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ji YN, Wang Q, Li Y and Wang Z: Prognostic
value of vascular endothelial growth factor A expression in gastric
cancer: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 35:2787–2793. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang YJ, Qi WX, He AN, Sun YJ, Shen Z and
Yao Y: Prognostic value of tissue vascular endothelial growth
factor expression in bladder cancer: A meta-analysis. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 14:645–649. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Youssef NS and Said AM:
Immunohistochemical expression of CD117 and vascular endothelial
growth factor in retinoblastoma: Possible targets of new therapies.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:5725–5737. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wen L, Wang R, Lu X and You C: Expression
and clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor and
fms-related tyrosine kinase 1 in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett.
9:2414–2418. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhuang Y and Wei M: Impact of vascular
endothelial growth factor expression on overall survival in
patients with osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol.
35:1745–1749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu Y, Zheng Q, Wu H, Guo X, Li J and Hao
S: Rapamycin increases pCREB, Bcl-2, and VEGF-A through ERK under
normoxia. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:259–267. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wiszniak S, Mackenzie FE, Anderson P,
Kabbara S, Ruhrberg C and Schwarz Q: Neural crest cell-derived VEGF
promotes embryonic jaw extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:6086–6091. 2015; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu YY, Chen L, Wang GL, Zhang YX, Zhou JM,
He S, Qin J and Zhu YY: Inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma
growth and angiogenesis by dual silencing of NET-1 and VEGF. J Mol
Histol. 44:433–445. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|