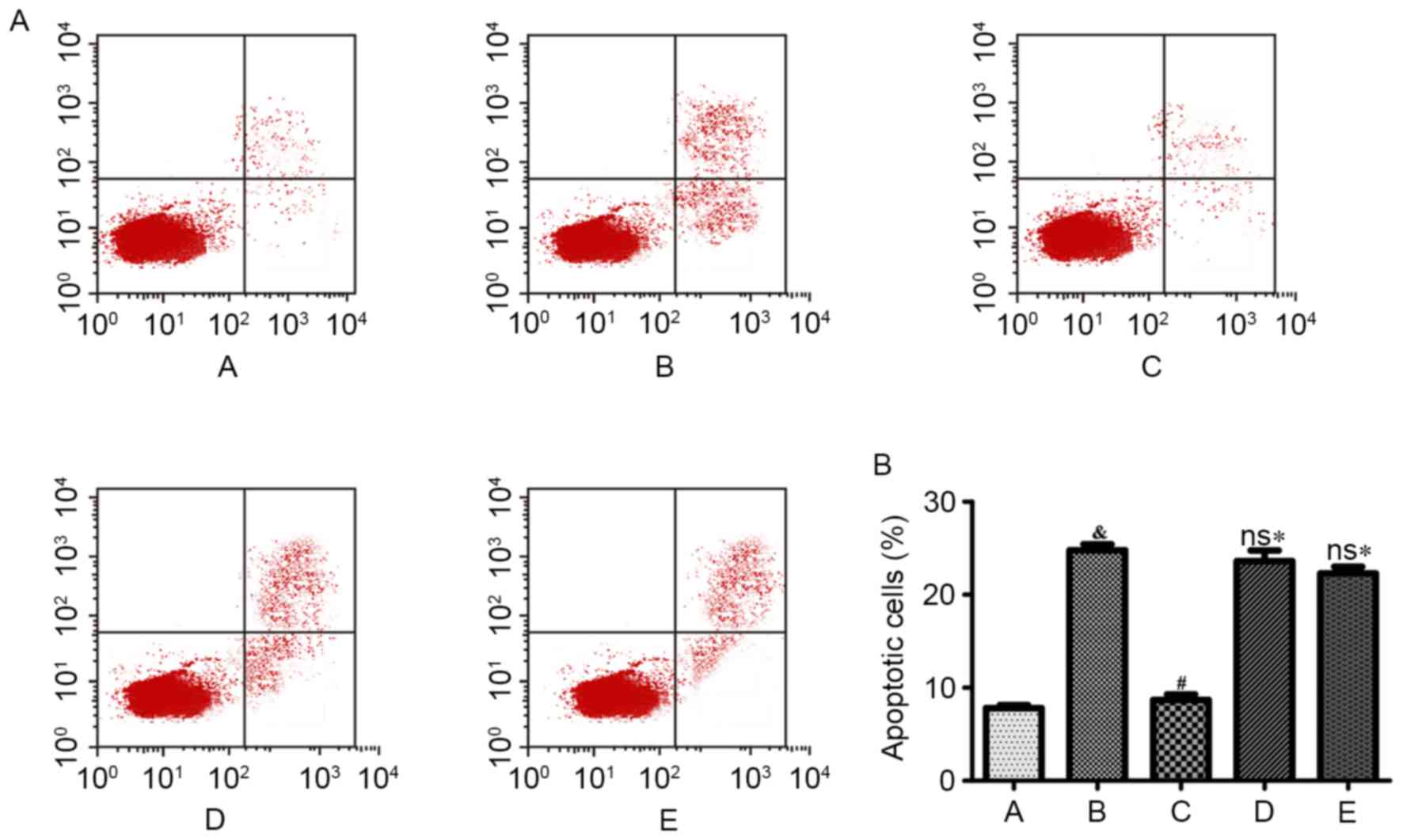
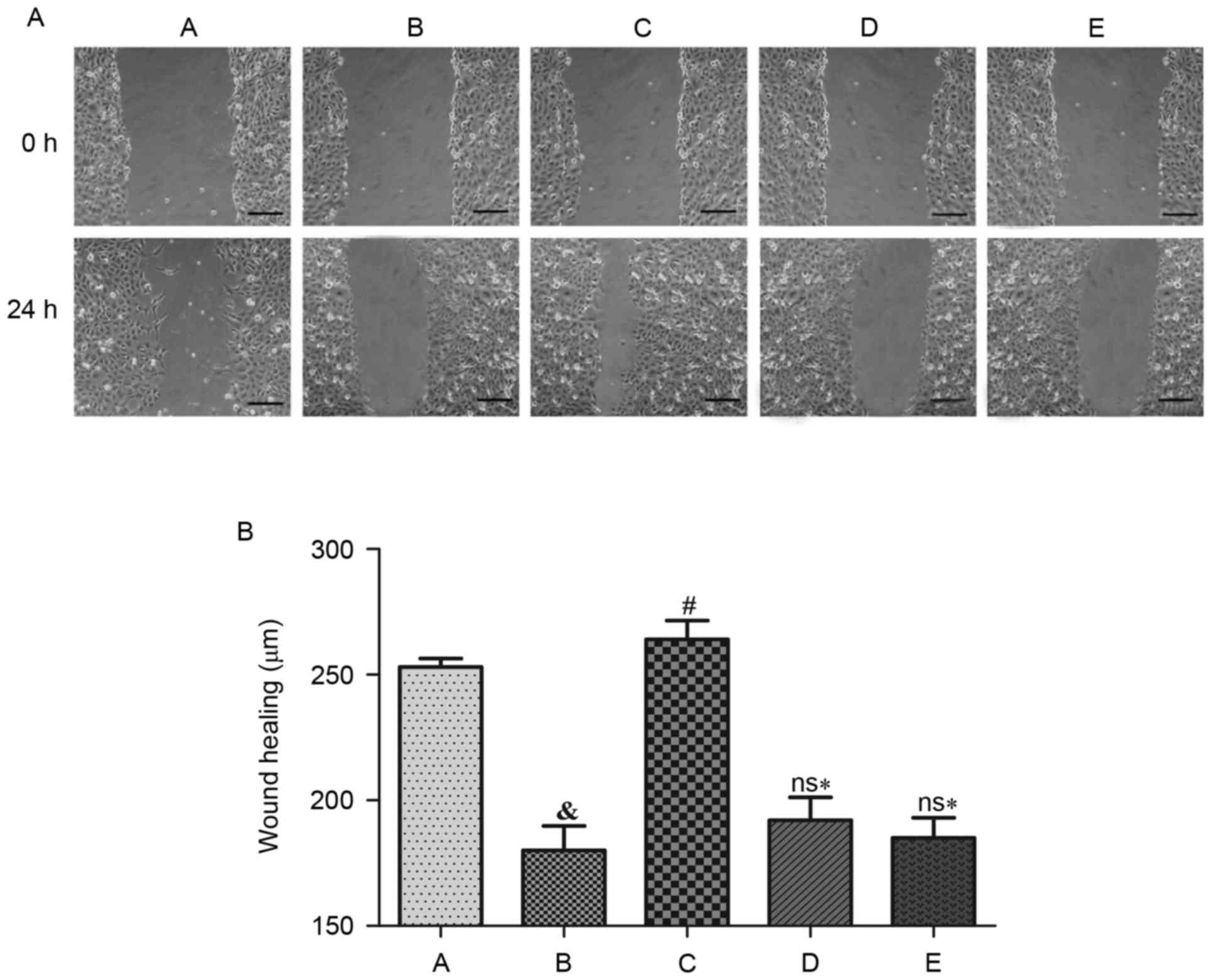
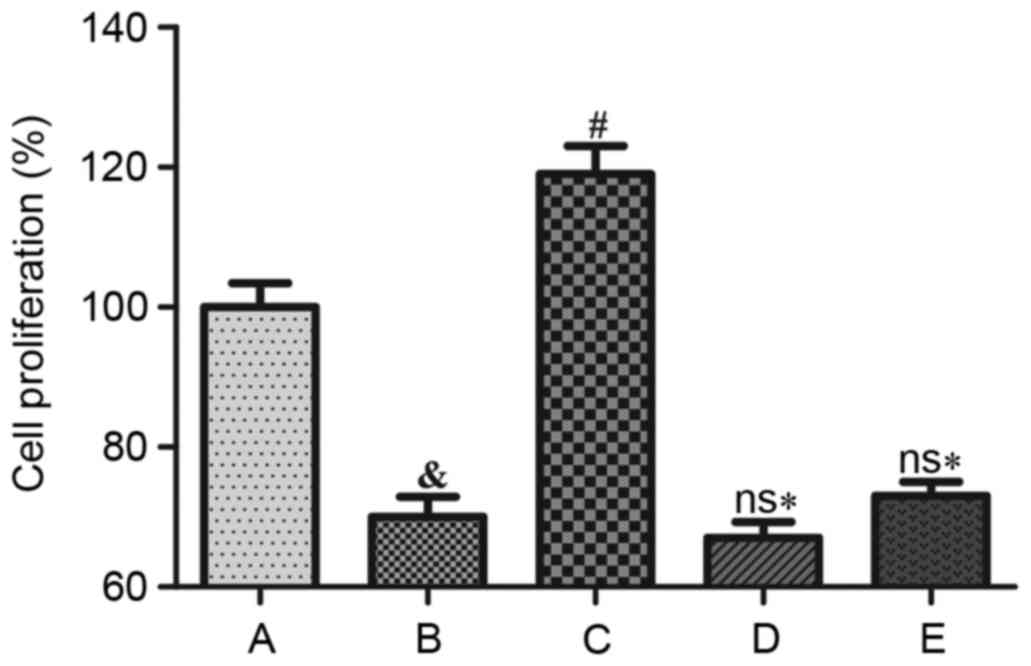
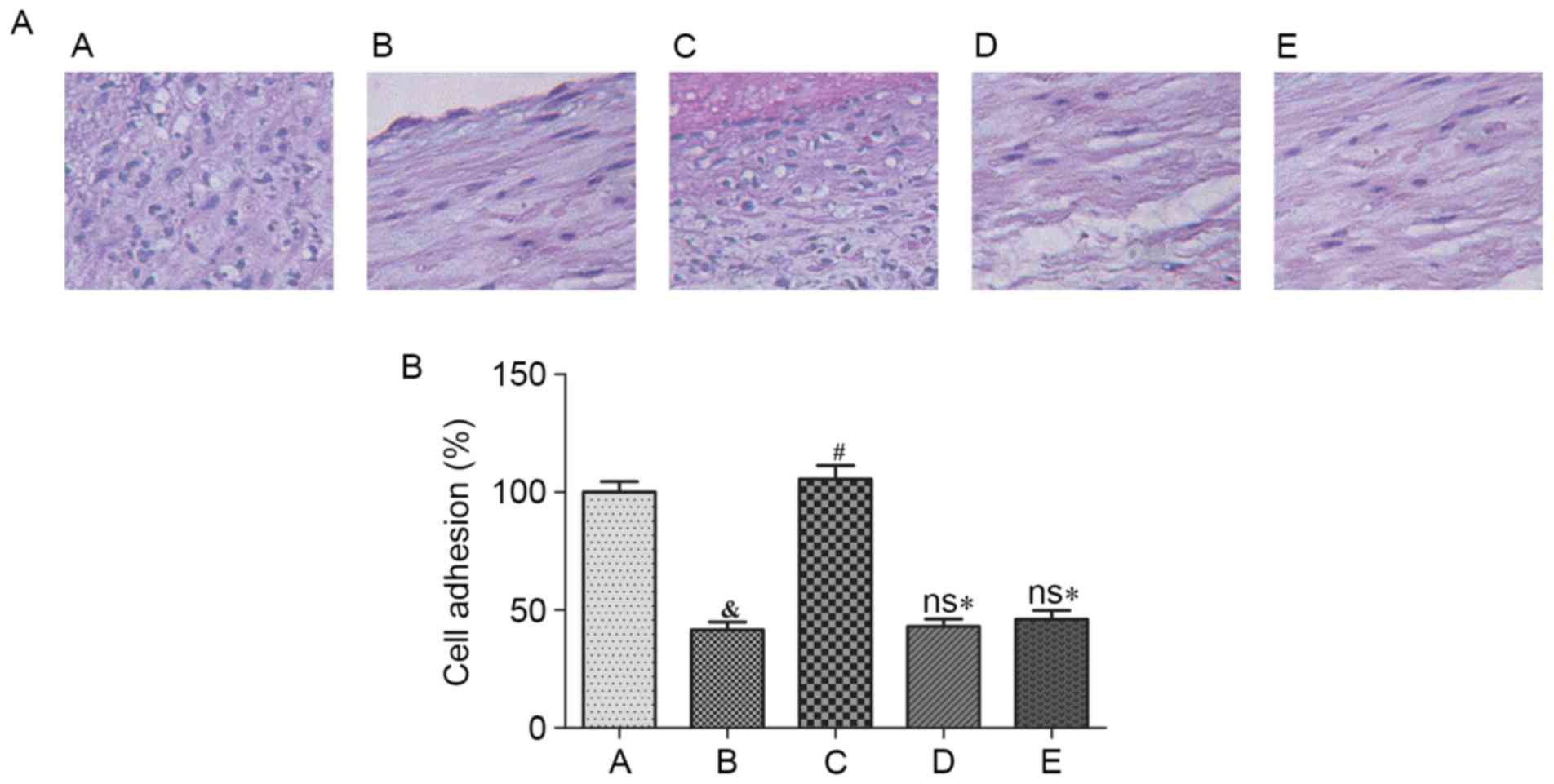
|
1
|
Li B, Zani A, Martin Z, Lee C,
Zani-Ruttenstock E, Eaton S and Pierro A: Intestinal epithelial
cell injury is rescued by hydrogen sulfide. J Pediatr Surg.
51:775–778. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nakashima H, Suzuki H, Ohtsu H, Chao JY,
Utsunomiya H, Frank GD and Eguchi S: Angiotensin II regulates
vascular and endothelial dysfunction: Recent topics of Angiotensin
II type-1 receptor signaling in the vasculature. Curr Vasc
Pharmacol. 4:67–78. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhi Z, Pengfei Z, Xiaoyi T and Genshan M:
Adiponectin ameliorates angiotensin II-induced vascular endothelial
damage. Cell Stress Chaperones. 19:705–713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo P, Zhang WF, Qian ZX, Xiao LF, Wang H,
Zhu TT, Li F, Hu CP and Zhang Z: MiR-590-5p-meidated LOX-1
upregulation promotes Angiotensin II-induced endothelial cell
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 471:402–408. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cai WJ, Wang MJ, Moore PK, Jin HM, Yao T
and Zhu YC: The novel proangiogenic effect of hydrogen sulfide is
dependent on Akt phosphorylation. Cardiovasc Res. 76:29–40. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Altaany Z, Yang G and Wang R: Crosstalk
between hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in endothelial cells. J
Cell Mol Med. 17:879–888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Osipov RM, Robich MP, Feng J, Liu Y,
Clements RT, Glazer HP, Sodha NR, Szabo C, Bianchi C and Sellke FW:
Effect of hydrogen sulfide in a porcine model of myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion: Comparison of different administration
regimens and characterization of the cellular mechanisms of
protection. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 54:287–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marampon F, Gravina GL, Scarsella L,
Festuccia C, Lovat F, Ciccarelli C, Zani BM, Polidoro L, Grassi D,
Desideri G, et al: Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition
counteracts angiotensin II-mediated endothelial cell dysfunction by
modulating the p38/SirT1 axis. J Hypertens. 31:1972–1983. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Altaany Z, Moccia F, Munaron L, Mancardi D
and Wang R: Hydrogen sulfide and endothelial dysfunction:
Relationship with nitric oxide. Curr Med Chem. 21:3646–3661. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang R, Szabo C, Ichinose F, Ahmed A,
Whiteman M and Papapetropoulos A: The role of H2S bioavailability
in endothelial dysfunction. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 36:568–578. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kanaide H, Ichiki T, Nishimura J and
Hirano K: Cellular mechanism of vasoconstriction induced by
angiotensin II: It remains to be determined. Circ Res.
93:1015–1017. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Desideri G, Bravi MC, Tucci M, Croce G,
Marinucci MC, Santucci A, Alesse E and Ferri C: Angiotensin II
inhibits endothelial cell motility through an AT1-dependent
oxidant-sensitive decrement of nitric oxide availability.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:1218–1223. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu Y, Wang RH, Guo BB and Jia YP:
Quercetin inhibits angiotensin II induced apoptosis via
mitochondrial pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:1609–1616. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jang H, Oh MY, Kim YJ, Choi IY, Yang HS,
Ryu WS, Lee SH and Yoon BW: Hydrogen sulfide treatment induces
angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res. 92:1520–1528.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang G and Wang R: H2S and blood vessels:
An overview. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 230:85–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang MJ, Cai WJ and Zhu YC: Mechanisms of
angiogenesis: Role of hydrogen sulphide. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 37:764–771. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shen Y, Guo W, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhong L
and Zhu Y: Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide in hypoxic human
umbilical vein endothelial cells: A possible mitochondria-dependent
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 14:13093–13108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Coletta C, Papapetropoulos A, Erdelyi K,
Olah G, Módis K, Panopoulos P, Asimakopoulou A, Gerö D, Sharina I,
Martin E and Szabo C: Hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide are
mutually dependent in the regulation of angiogenesis and
endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:9161–9166. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Go YM, Lee HR and Park H: H(2)S inhibits
oscillatory shear stress-induced monocyte binding to endothelial
cells via nitric oxide production. Mol Cells. 34:449–455. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Predmore BL, Julian D and Cardounel AJ:
Hydrogen sulfide increases nitric oxide production from endothelial
cells by an akt-dependent mechanism. Front Physiol. 2:1042011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu H, Chen T, Li N, Wang S and Bu P: Role
of SIRT3 in angiotensin II-induced human umbilical vein endothelial
cells dysfunction. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 15:812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|