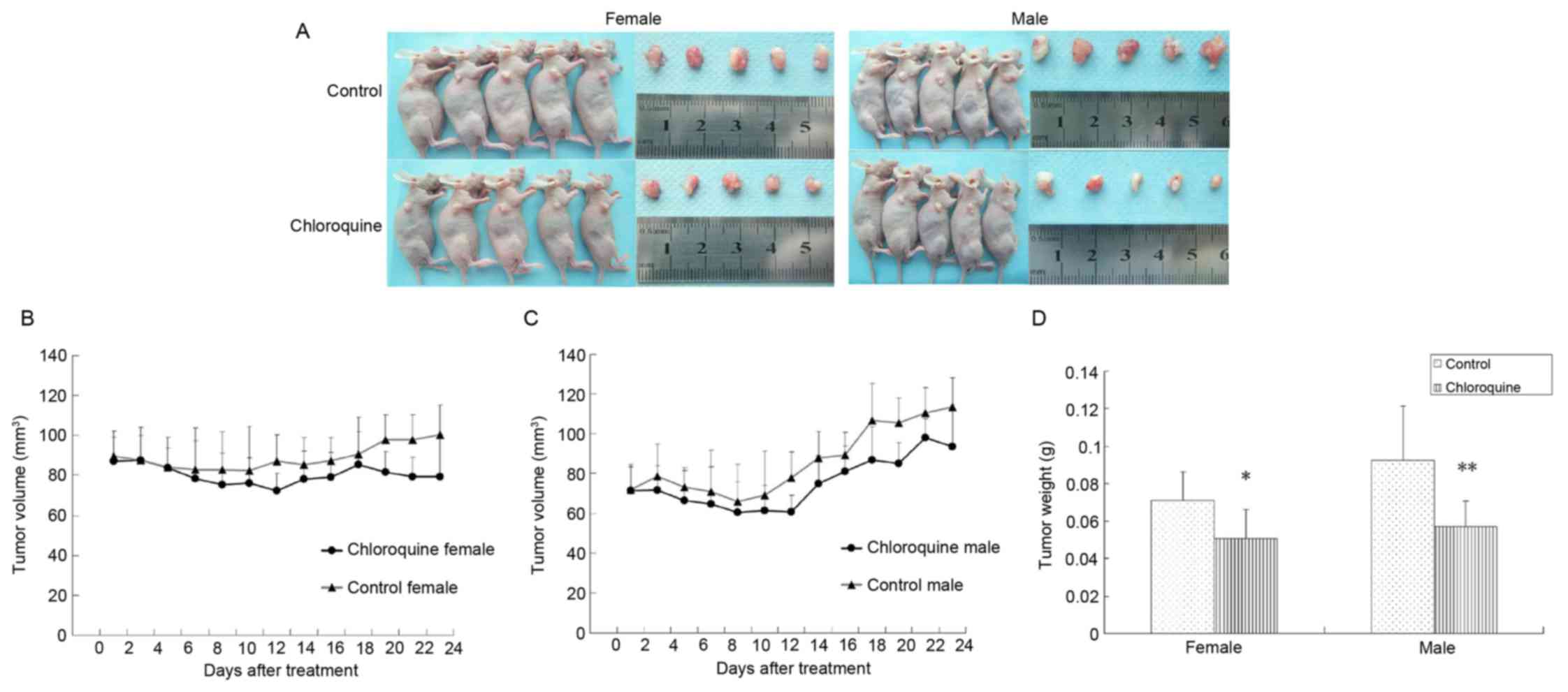
|
1
|
Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A and
Isaka Y: Chloroquine in cancer therapy: A double-edged sword of
autophagy. Cancer Res. 73:3–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Al-Bari MA: Chloroquine analogues in drug
discovery: New directions of uses, mechanisms of actions and toxic
manifestations from malaria to multifarious diseases. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 70:1608–1621. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang ZJ, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A and
Isaka Y: The role of autophagy in cancer: Therapeutic implications.
Mol Cancer Ther. 10:1533–1541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Johnson NW, Jayasekara P and Amarasinghe
AA: Squamous cell carcinoma and precursor lesions of the oral
cavity: Epidemiology and aetiology. Periodontol 2000. 57:19–37.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pignon JP, Bourhis J, Domenge C and
Designé L: Chemotherapy added to locoregional treatment for head
and neck squamous-cell carcinoma: Three meta-analyses of updated
individual data. MACH-NC collaborative group. Meta-analysis of
chemotherapy on head and neck cancer. Lancet. 355:949–955. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sturgis EM, Moore BA, Glisson BS, Kies MS,
Shin DM and Byers RM: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for squamous cell
carcinoma of the oral tongue in young adults: A case series. Head
Neck. 27:748–756. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Freier K, Engel M, Lindel K,
Flechtenmacher C, Mühling J, Hassfeld S and Hofele C: Neoadjuvant
concurrent radiochemotherapy followed by surgery in advanced oral
squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC): A retrospective analysis of 207
patients. Oral Oncol. 44:116–123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wedemeyer I, Kreppel M, Scheer M, Zöller
JE, Büttner R and Drebber U: Histopathological assessment of tumour
regression, nodal stage and status of resection margins determines
prognosis in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma treated
with neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy. Oral Dis. 20:e81–e89. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang PD, Zhao YL, Shi W, Deng XQ, Xie G,
Mao YQ, Li ZG, Zheng YZ, Yang SY and Wei YQ: Cell growth
inhibition, G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by
chloroquine in human breast cancer cell line Bcap-37. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 22:431–440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng Y, Zhao YL, Deng X, Yang S, Mao Y,
Li Z, Jiang P, Zhao X and Wei Y: Chloroquine inhibits colon cancer
cell growth in vitro and tumor growth in vivo via induction of
apoptosis. Cancer Invest. 27:286–292. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu T, Li P, Luo Z, Chen X, Zhang J, Wang
C, Chen P and Dong Z: Chloroquine inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma
cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 35:43–49. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan C, Wang W, Zhao B, Zhang S and Miao J:
Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549
lung cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 14:3218–3222. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Geng Y, Kohli L, Klocke BJ and Roth KA:
Chloroquine-induced autophagic vacuole accumulation and cell death
in glioma cells is p53 independent. Neuro Oncol. 12:473–481.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lakhter AJ, Sahu RP, Sun Y, Kaufmann WK,
Androphy EJ, Travers JB and Naidu SR: Chloroquine promotes
apoptosis in melanoma cells by inhibiting BH3 domain-mediated PUMA
degradation. J Invest Dermatol. 133:2247–2254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang J, Jia L, Kuang Z, Wu T, Hong Y, Chen
X, Leung WK, Xia J and Cheng B: The in vitro and in vivo antitumor
effects of clotrimazole on oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
9:e988852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: LC3
conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:2503–2518. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pascolo S: Time to use a dose of
Chloroquine as an adjuvant to anti-cancer chemotherapies. Eur J
Pharmacol. 771:139–144. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lefort S, Joffre C, Kieffer Y, Givel AM,
Bourachot B, Zago G, Bieche I, Dubois T, Meseure D, Vincent-Salomon
A, et al: Inhibition of autophagy as a new means of improving
chemotherapy efficiency in high-LC3B triple-negative breast
cancers. Autophagy. 10:2122–2142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liang DH, Choi DS, Ensor JE, Kaipparettu
BA, Bass BL and Chang JC: The autophagy inhibitor chloroquine
targets cancer stem cells in triple negative breast cancer by
inducing mitochondrial damage and impairing DNA break repair.
Cancer Lett. 376:249–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi DS, Blanco E, Kim YS, Rodriguez AA,
Zhao H, Huang TH, Chen CL, Jin G, Landis MD, Burey LA, et al:
Chloroquine eliminates cancer stem cells through deregulation of
Jak2 and DNMT1. Stem Cells. 32:2309–2323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Angadi PV and Krishnapillai R: Cyclin D1
expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma and verrucous carcinoma:
Correlation with histological differentiation. Oral Surg Oral Med
Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 103:e30–e35. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhong LP, Zhu DW, William WN Jr, Liu Y, Ma
J, Yang CZ, Yang X, Wang LZ, Li J, Myers JN, et al: Elevated cyclin
D1 expression is predictive for a benefit from TPF induction
chemotherapy in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients with advanced
nodal disease. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:1112–1121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao Y, Yu D, Li H, Nie P, Zhu Y, Liu S,
Zhu M and Fang B: Cyclin D1 overexpression is associated with poor
clinicopathological outcome and survival in oral squamous cell
carcinoma in Asian populations: Insights from a meta-analysis. PLoS
One. 9:e932102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Myo K, Uzawa N, Miyamoto R, Sonoda I, Yuki
Y and Amagasa T: Cyclin D1 gene numerical aberration is a
predictive marker for occult cervical lymph node metastasis in TNM
Stage I and II squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Cancer.
104:2709–2716. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao XG, Sun RJ, Yang XY, Liu DY, Lei DP,
Jin T and Pan XL: Chloroquine-enhanced efficacy of cisplatin in the
treatment of hypopharyngeal carcinoma in xenograft mice. PLoS One.
10:e01261472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Verschooten L, Barrette K, Van Kelst S,
Romero N Rubio, Proby C, De Vos R, Agostinis P and Garmyn M:
Autophagy inhibitor chloroquine enhanced the cell death inducing
effect of the flavonoid luteolin in metastatic squamous cell
carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 7:e482642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Quan HY, Quan HY, Zhou LJ, Li AD and Zhang
ZB: Mechanism of chloroquine in promoting sensitivity of
chemotherapeutics in oral squamous cell carcinoma CAL-27 cell line
to cisplatin. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 24:30–36. 2015.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amaravadi RK, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Yin
XM, Weiss WA, Takebe N, Timmer W, DiPaola RS, Lotze MT and White E:
Principles and current strategies for targeting autophagy for
cancer treatment. Clin Cancer Res. 17:654–666. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kapoor V, Paliwal D, Singh S Baskar,
Mohanti BK and Das SN: Deregulation of Beclin 1 in patients with
tobacco-related oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 422:764–769. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nomura H, Uzawa K, Yamano Y, Fushimi K,
Ishigami T, Kouzu Y, Koike H, Siiba M, Bukawa H, Yokoe H, et al:
Overexpression and altered subcellular localization of
autophagy-related 16-like 1 in human oral squamous-cell carcinoma:
Correlation with lymphovascular invasion and lymph-node metastasis.
Hum Pathol. 40:83–91. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|