|
1
|
Thielecke F and Boschmann M: The potential
role of green tea catechins in the prevention of the metabolic
syndrome-a review. Phytochemistry. 70:11–24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shimizu M, Adachi S, Masuda M, Kozawa O
and Moriwaki H: Cancer chemoprevention with green tea catechins by
targeting receptor tyrosine kinases. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:832–843.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Higdon JV and Frei B: Coffee and health: A
review of recent human research. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr.
46:101–123. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Harborne JB and Williams CA: Advances in
flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry. 55:481–504. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
George SE, Ramalakshmi K and Rao LJ Mohan:
A perception on health benefits of coffee. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr.
48:464–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shen CL, Yeh JK, Cao JJ and Wang JS: Green
tea and bone metabolism. Nutr Res. 29:437–456. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Karsenty G and Oury F: Biology without
walls: The novel endocrinology of bone. Annu Rev Physiol.
74:87–105. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Parfitt AM: Targeted and nontargeted bone
remodeling: Relationship to basic multicellular unit origination
and progression. Bone. 30:5–7. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kwak SC, Lee C, Kim JY, Oh HM, So HS, Lee
MS, Rho MC and Oh J: Chlorogenic acid inhibits osteoclast
differentiation and bone resorption by down-regulation of receptor
activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand-induced nuclear factor
of activated T cells c1 expression. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:1779–1786.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Folwarczna J, Pytlik M, Zych M, Cegiela U,
Nowinska B, Kaczmarczyk-Sedlak L, Sliwinski L, Trzeciak H and
Trzeciak HI: Effects of caffeic and chlorogenic acids on the rat
skeletal system. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:682–693.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takai S, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Adachi S,
Natsume H, Minamitani C, Mizutani J, Otsuka T, Tokuda H and Kozawa
O: (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate reduces platelet-derived growth
factor-BB-stimulated interleukin-6 synthesis in osteoblasts:
Suppression of SAPK/JNK. Mediators Inflamm. 2008:2918082008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tokuda H, Takai S, Hanai Y,
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Yamauchi J, Harada A, Hosoi T, Ohta T and
Kozawa O: (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits basic fibroblast
growth factor-stimulated interleukin-6 synthesis in osteoblasts.
Horm Metab Res. 40:674–678. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tokuda H, Takai S, Hanai Y,
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Hosoi T, Harada A, Ohta T and Kozawa O:
(−)-Epigallocatechin gallate suppresses endothelin-1-induced
interleukin-6 synthesis in osteoblasts: inhibition of p44/p42 MAP
kinase activation. FEBS Lett. 581:1311–1316. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamamoto N, Tokuda H, Kuroyanagi G,
Kainuma S, Ohguchi R, Fujita K, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kozawa O
and Otsuka T: Amplification by (−)-epigallocatechin gallate and
chlorogenic acid of TNF-α-stimulated interleukin-6 synthesis in
osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 36:1707–1712. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kostenuik PJ and Shalhoub V:
Osteoprotegerin: A physiological and pharmacological inhibitor of
bone resorption. Curr Pharm Des. 7:613–635. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley
M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, et
al: Osteoprotegerin: A novel secreted protein involved in the
regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mizuno A, Amizuka N, Irie K, Murakami A,
Fujise N, Kanno T, Sato Y, Nakagawa N, Yasuda H, Mochizuki S, et
al: Severe osteoporosis in mice lacking osteoclastogenesis
inhibitory factor/osteoprotegerin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
247:610–615. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizuno A, Kanno T, Hoshi M, Shibata O,
Yano K, Fujise N, Kinosaki M, Yamaguchi K, Tsuda E, Murakami A, et
al: Transgenic mice overexpressing soluble osteoclast
differentiation factor (sODF) exhibit severe osteoporosis. J Bone
Miner Metab. 20:337–344. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tat S Kwan, Padrines M, Théoleyre S,
Heymann D and Fortun Y: IL-6, RANKL, TNF-α/IL-1: Interrelations in
bone resorption pathophysiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
15:49–60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hikiji H, Takato T, Shimizu T and Ishii S:
The roles of prostanoids, leukotrienes, and platelet-activating
factor in bone metabolism and disease. Prog Lipid Res. 47:107–126.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Agas D, Marchetti L, Hurley MM and
Sabbieti MG: Prostaglandin F2α: A bone remodeling mediator. J Cell
Physiol. 228:25–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kuroyanagi G, Tokuda H,
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kondo A, Mizutani J, Kozawa O and Otsuka T:
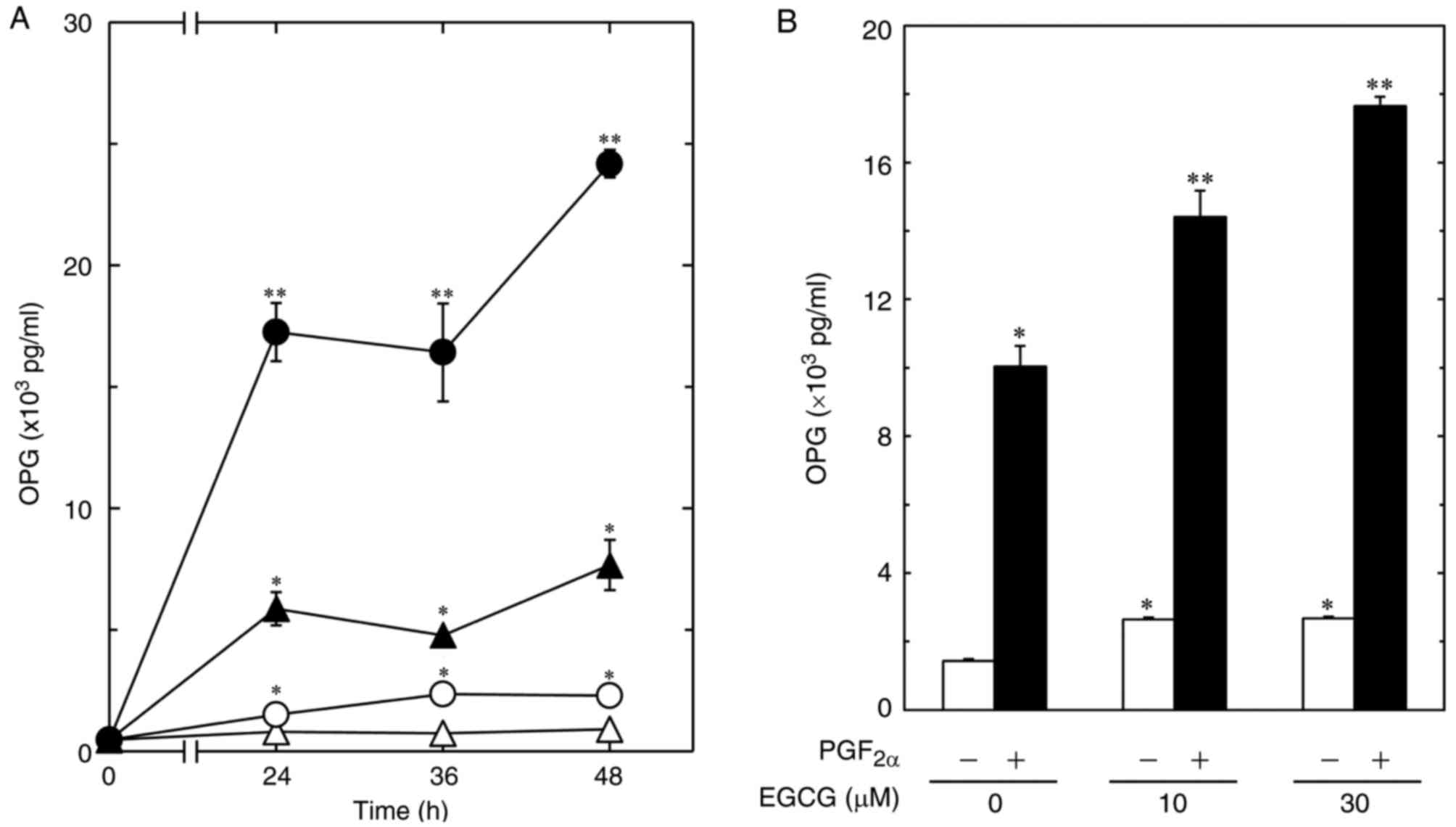
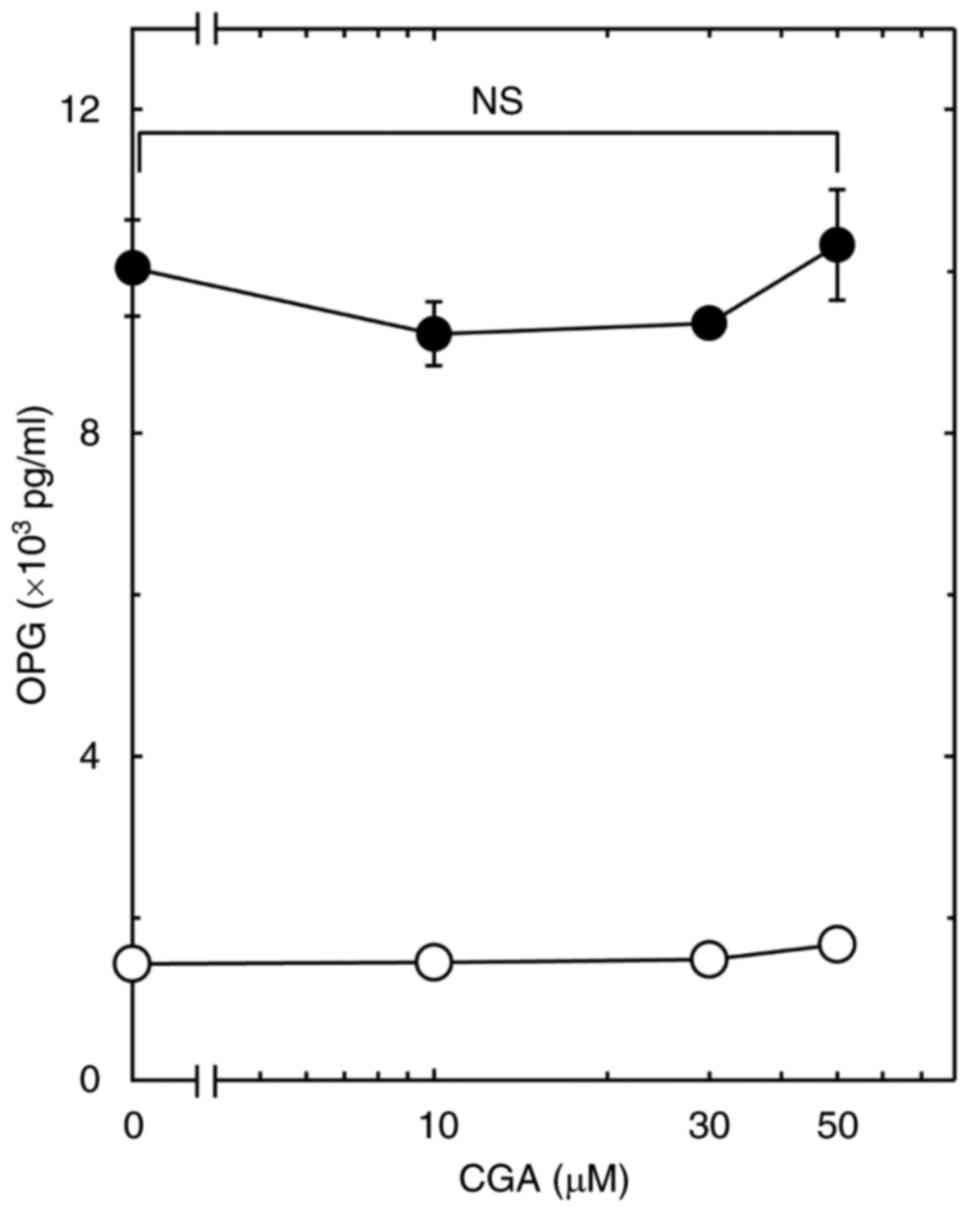
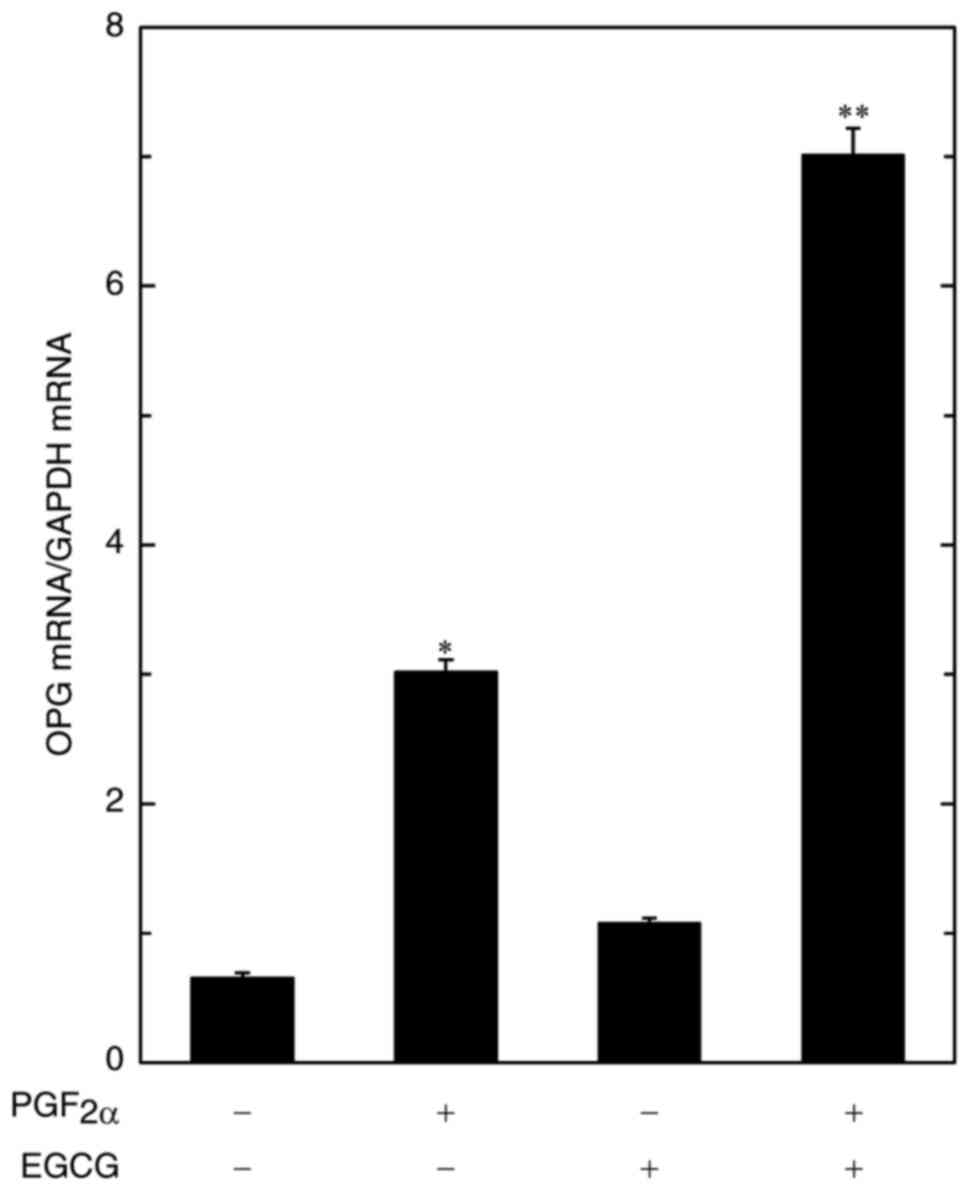
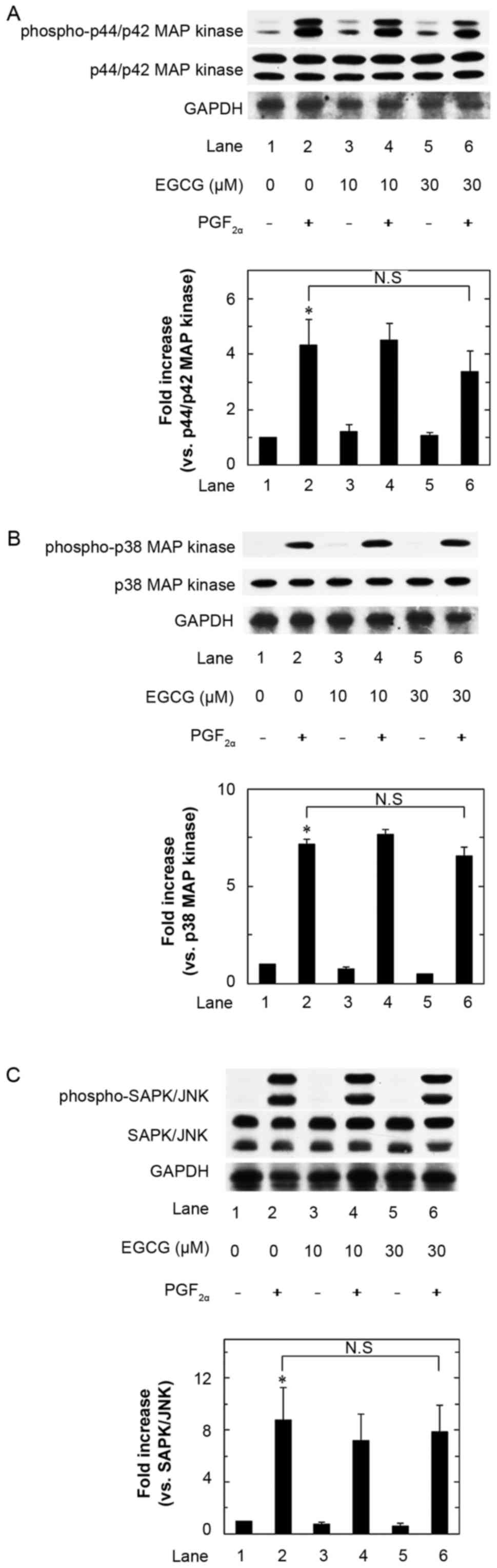
Resveratrol suppresses prostaglandin F2α-induced osteoprotegerin
synthesis in osteoblasts: Inhibition of the MAP kinase signaling.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 542:39–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sudo H, Kodama HA, Amagai Y, Yamamoto S
and Kasai S: In vivo differentiation and calcification in a new
clonal osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J
Cell Biol. 96:191–198. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kozawa O, Tokuda H, Miwa M, Kotoyori J and
Oiso Y: Cross-talk regulation between cyclic AMP production and
phosphoinositide hydrolysis induced by prostaglandin E2 in
osteoblast-like cells. Exp Cell Res. 198:130–134. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Simpson DA, Feeney S, Boyle C and Stitt
AW: Retinal VEGF mRNA measured by SYBR green I fluorescence: A
versatile approach to quantitative PCR. Mol Vis. 6:178–183.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kato K, Ito H, Hasegawa K, Inaguma Y,
Kozawa O and Asano T: Modulation of the stress-induced synthesis of
hsp27 and alpha B-crystallin by cyclic AMP in C6 rat glioma cells.
J Neurochem. 66:946–950. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Mammalian
mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways
activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev. 81:807–869.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Widmann C, Gibson S, Jarpe MB and Johnson
GL: Mitogen-activated protein kinase: Conservation of a
three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol Rev. 79:143–180.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dhanasekaran N and Reddy E Premkumar:
Signaling by dual specificity kinases. Oncogene. 17:1447–1455.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin A, Minden A, Martinetto H, Claret FX,
Lange-Carter C, Mercurio F, Johnson GL and Karin M: Identification
of a dual specificity kinase that activates the Jun kinases and
p38-Mpk2. Science. 14:286–290. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Greenfield EM, Bi Y and Miyauchi A:
Regulation of osteoclast activity. Life Sci. 65:1087–1102. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|