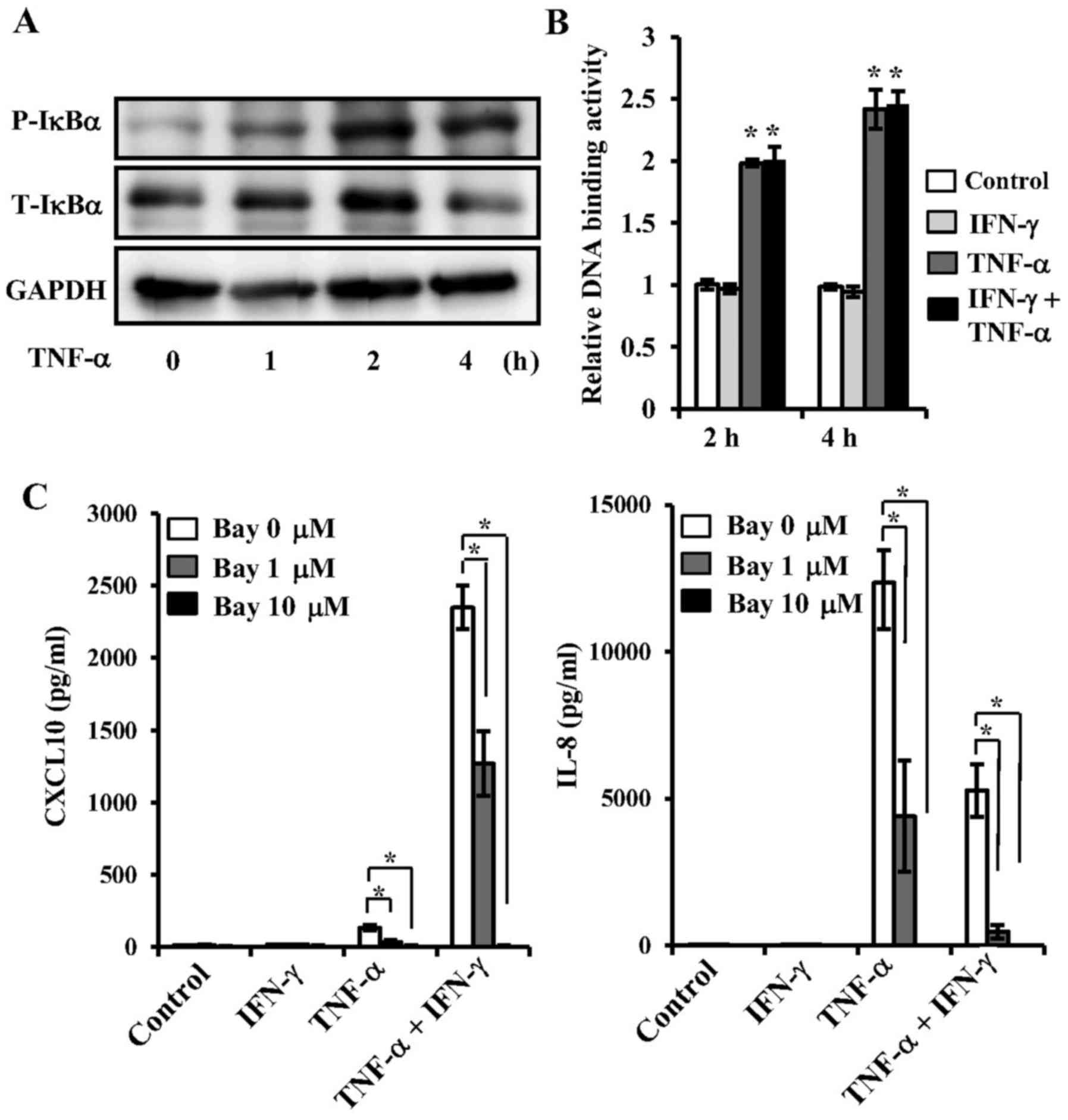
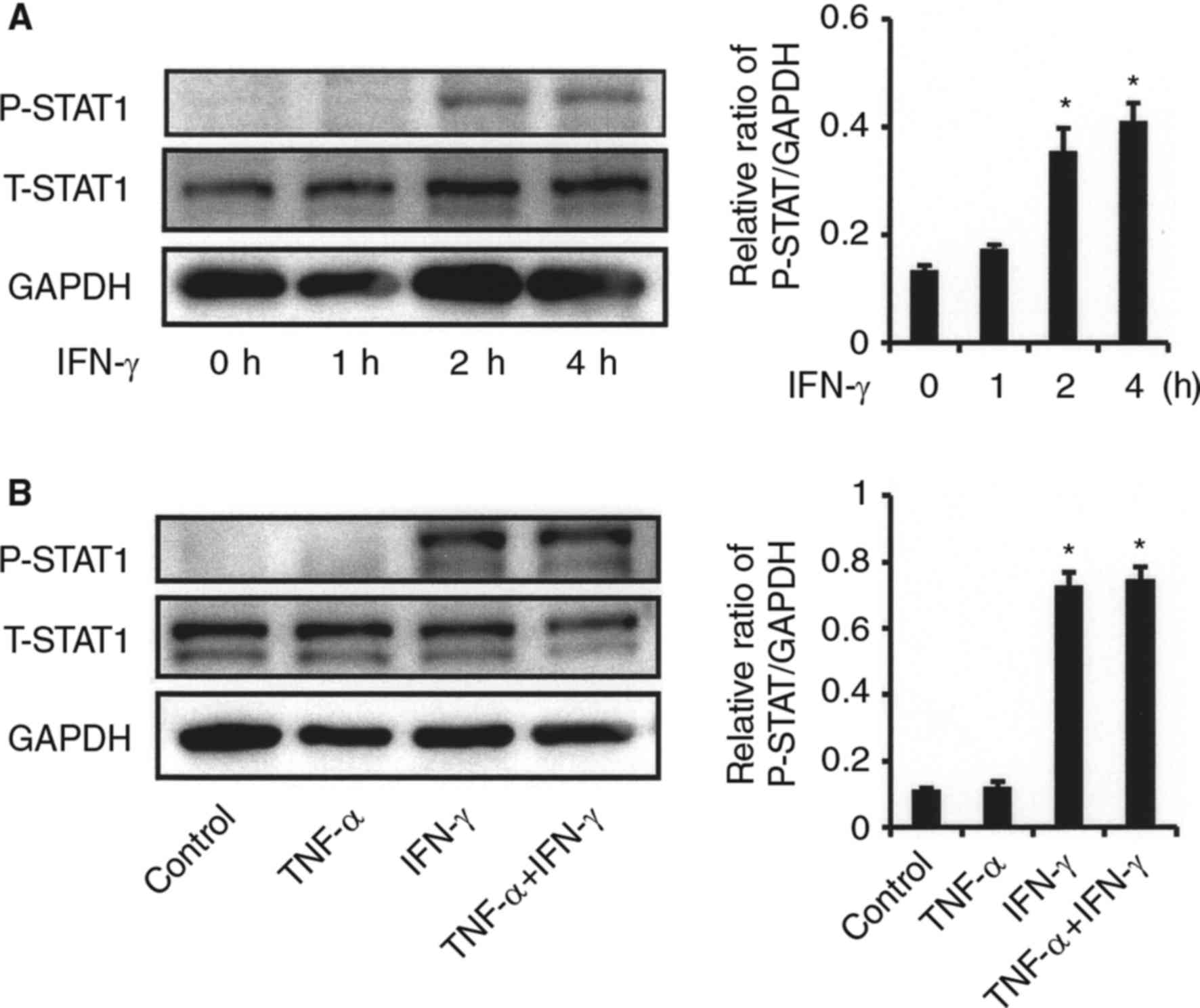
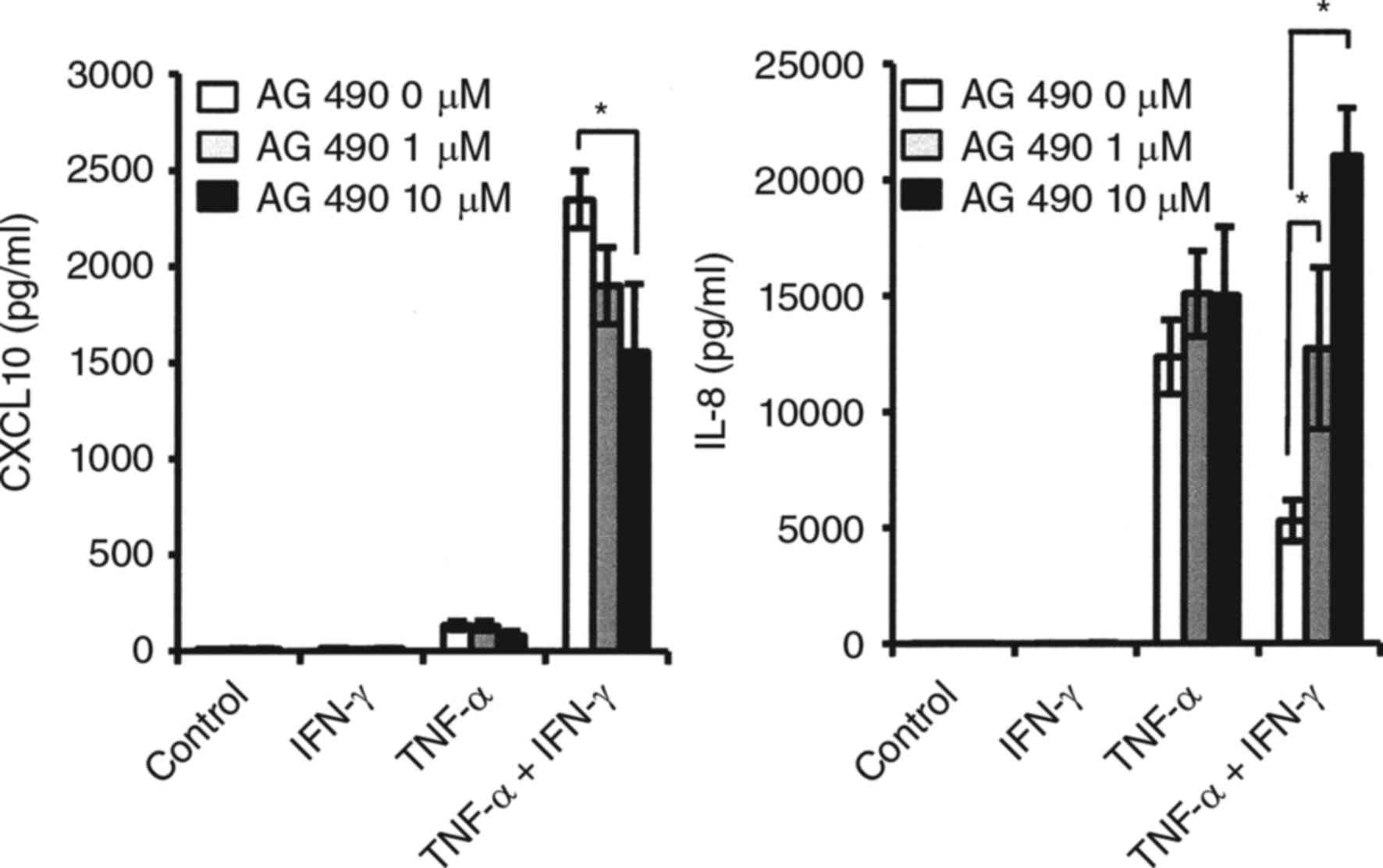
|
1
|
Dijkgraaf LC, de Bont LG, Boering G and
Liem RS: Structure of the normal synovial membrane of the
temporomandibular joint: A review of the literature. J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 54:332–338. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Israel HA, Langevin CJ, Singer MD and
Behrman DA: The relationship between temporomandibular joint
synovitis and adhesions: pathogenic mechanisms and
rheumatoidarthritis:aclinical, arthroscopic, histologic and
immunohistochemical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 26:10–16.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Israel HA, Diamond B, Saed-Nejad F and
Ratcliffe A: Osteoarthritis and synovitis as major pa arthroscopic
morphology. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 56:1023–1027. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takahashi T, Kondoh T, Fukuda M, Yamazaki
Y, Toyosaki T and Suzuki R: Proinflammatory cytokines detectable in
synovial fluids from patients with temporomandibular disorders.
Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 85:135–141. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaneyama K, Segami N, Nishimura M, Suzuki
T and Sato J: Importance of proinflammatory cytokines in synovial
fluid from 121 joints with temporomandibular disorders. Br J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 40:418–423. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baud V and Karin M: Signal transduction by
tumor necrosis factor and its relativs. Trends Cell Biol.
11:372–377. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Puzas JE, Landeau JM, Tallents R, Albright
J, Schwarz EM and Landesberg R: Degradative pathways in tissues of
the temporomandibular joint. Use of in vitro and in vivo models to
characterize matrix metalloproteinase and cytokine activity. Cells
Tissues Organs. 169:248–256. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ogura N, Tobe M, Sakamaki H, Nagura H,
Abiko Y and Kondoh T: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases
chemokine gene expression and production in synovial fibroblasts
from human temporomandibular joint. J Oral Pathol Med. 34:357–363.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Akutsu M, Ogura N, Ito K, Kawashima M,
Kishida T and Kondoh T: Effects of interleukin-1β and tumor
necrosis factor-α on macrophage inflammatory protein-3α production
in synovial fibroblast-like cells from human temporomandibular
joints. J Oral Pathol Med. 42:491–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rodig S, Kaplan D, Shankaran V, Old L and
Schreiber RD: Signaling and signaling dysfunction through the
interferon gamma receptor. Eur Cytokine Netw. 9 3 Suppl:S49–S53.
1998.
|
|
11
|
Qin S, Rottman JB, Myers P, Kassam N,
Weinblatt M, Loetscher M, Koch AE, Moser B and Mackay CR: The
chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CCR5 mark subsets of T cells
associated with certain inflammatory reactions. J Clin Invest.
101:746–754. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsumoto K, Honda K, Ohshima M, Yamaguchi
Y, Nakajima I, Micke P and Otsuka K: Cytokine profile in synovial
fluid from patients with internal derangement of the
temporomandibular joint: A preliminary study. Dentomaxillofac
Radiol. 35:432–441. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee EY, Lee ZH and Song YW: CXCL10 and
autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 8:379–383. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alaaeddine N, DiBattista JA, Pelletier JP,
Cloutier JM, Kiansa K, Dupuis M and Martel-Pelletier J:
Osteoarthritic synovial fibroblasts possess an increased level of
tumor necrosis factor-receptor 55 (TNF-R55) that mediates
biological activation by TNF-alpha. J Rheumatol. 24:1985–1994.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thanos D and Maniatis T: NF-kappa B: A
lesson in family values. Cell. 80:529–532. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gough DJ, Messina NL, Hii L, Gould JA,
Sabapathy K, Robertson AP, Trapani JA, Levy DE, Hertzog PJ, Clarke
CJ and Johnstone RW: Functional crosstalk between type I and II
interferon through the regulated expression of STAT1. PLoS Biol.
27:e10003612010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Suzuki T, Segami N, Nishimura M and Nojima
T: Co-expression of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor
alpha in synovial tissues and synovial fluids of temporomandibular
joint with internal derangement: Comparison with histological
grading of synovial inflammation. J Oral Pathol Med. 31:549–557.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ke J, Long X, Liu Y, Zhang YF, Li J, Fang
W and Meng QG: Role of NF-kappaB in TNF-alpha-induced COX-2
expression in synovial fibroblasts from human TMJ. J Dent Res.
86:363–367. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Patel DD, Zachariah JP and Whichard LP:
CXCR3 and CCR5 ligands in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Clin
Immunol. 98:39–45. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mohan K, Ding Z, Hanly J and Issekutz TB:
IFN-gamma-inducible T cell a chemoattractant is a potent stimulator
of normal human blood T lymphocyte transendothelial migration:
Differential regulation by IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. J Immunol.
168:6420–6428. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ueno A, Yamamura M, Iwahashi M, Okamoto A,
Aita T, Ogawa N and Makino H: The production of CXCR3-agonistic
chemokines by synovial fibroblasts from patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 25:361–367. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kuan WP, Tam LS, Wong CK, Ko FW, Li T, Zhu
T and Li EK: CXCL 9 and CXCL 10 as sensitive markers of disease
activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol.
37:257–264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gynther GW, Holmlund AB, Reinholt FP and
Lindblad S: Temporomandibular joint involvement in generalized
osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: A clinical, arthroscopic,
histologic, and immunohistochemical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 26:10–16. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Godiska R, Chantry D, Dietsch GN and Gray
PW: Chemokine expression in murine experimental allergic
encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 58:167–176. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Murphy PM: Neutrophil receptors for
interleukin-8 and related CXC chemokines. Semin Hematol.
34:311–318. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sukedai M, Tominaga K, Habu M, Matsukawa
A, Nishihara T and Fukuda J: Involvement of tumor necrosis
factor-alpha and interleukin-8 in antigen-induced arthritis of the
rabbit temporomandibular joint. J Oral Pathol Med. 33:102–110.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kohara H, Kitaura H, Fujimura Y,
Yoshimatsu M, Morita Y, Eguchi T, Masuyama R and Yoshida N: IFN-γ
directly inhibits TNF-α-induced osteoclastogenesis in vitro and in
vivo and induces apoptosis mediated by Fas/Fas ligand interactions.
Immunol Lett. 30:53–61. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Meyer FA, Yaron I and Yaron M:
Synergistic, additive, and antagonistic effects of
interleukin-1beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and gamma-interferon
on prostaglandin E, hyaluronic acid, and collagenase production by
cultured synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 33:1518–1525. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kristensen KD, Alstergren P, Stoustrup P,
Küseler A, Herlin T and Pedersen TK: Cytokines in healthy
temporomandibular joint synovial fluid. J Oral Rehabil. 41:250–256.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM and Stark GR:
Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to
IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science.
264:1415–1421. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bromberg J and Darnell JE Jr: The role of
STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular
function. Oncogene. 19:2468–2473. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
O'Shea JJ, Gadina M and Schreiber RD:
Cytokine signaling in 2002: New surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway.
Cell. 109 Suppl:S121–S131. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kasperkovitz PV, Verbeet NL, Smeets TJ,
van Rietschoten JG, Kraan MC, van der Pouw Kraan TC, Tak PP and
Verweij CL: Activation of the STAT1 pathway in rheumatoid
arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 63:233–239. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|