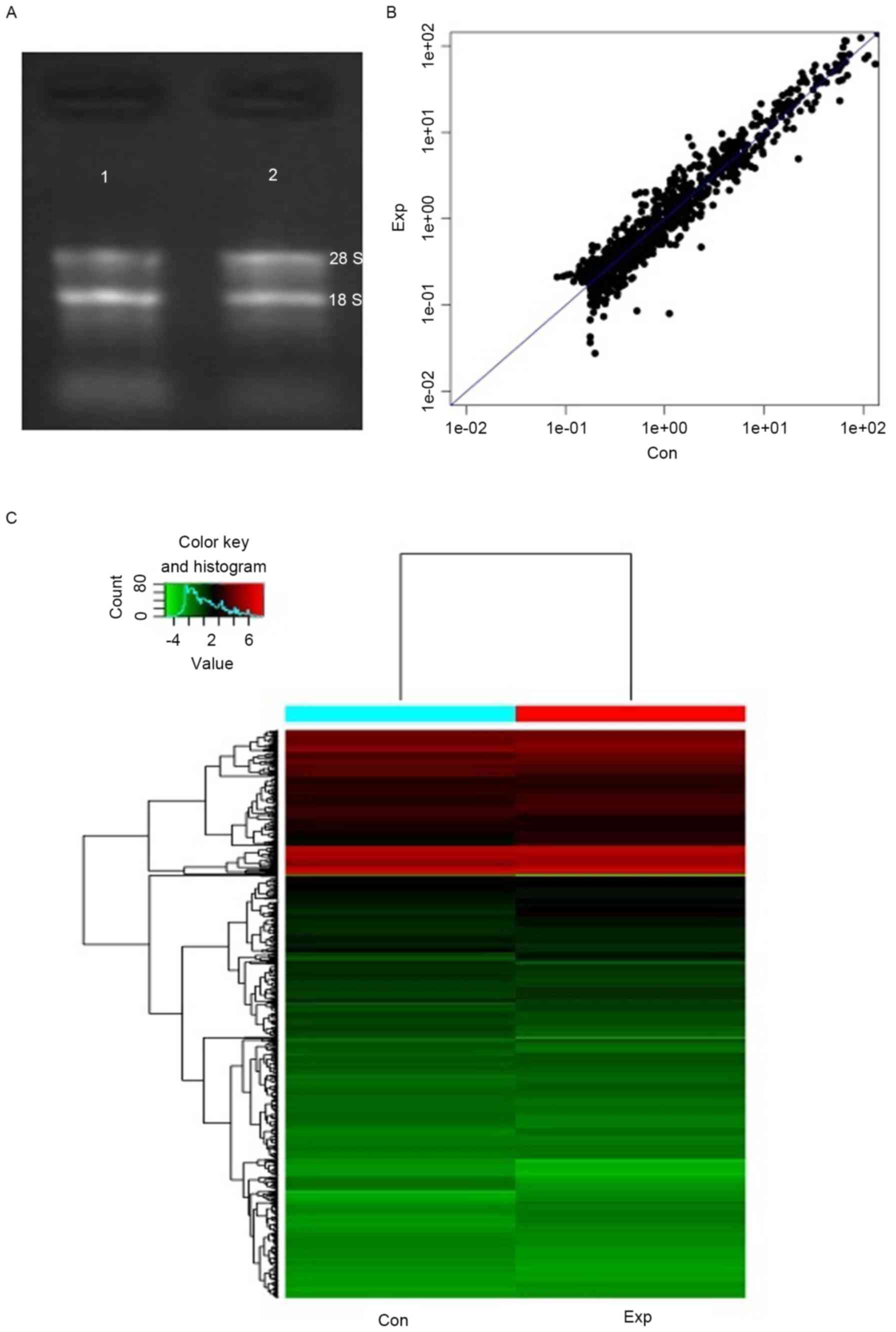
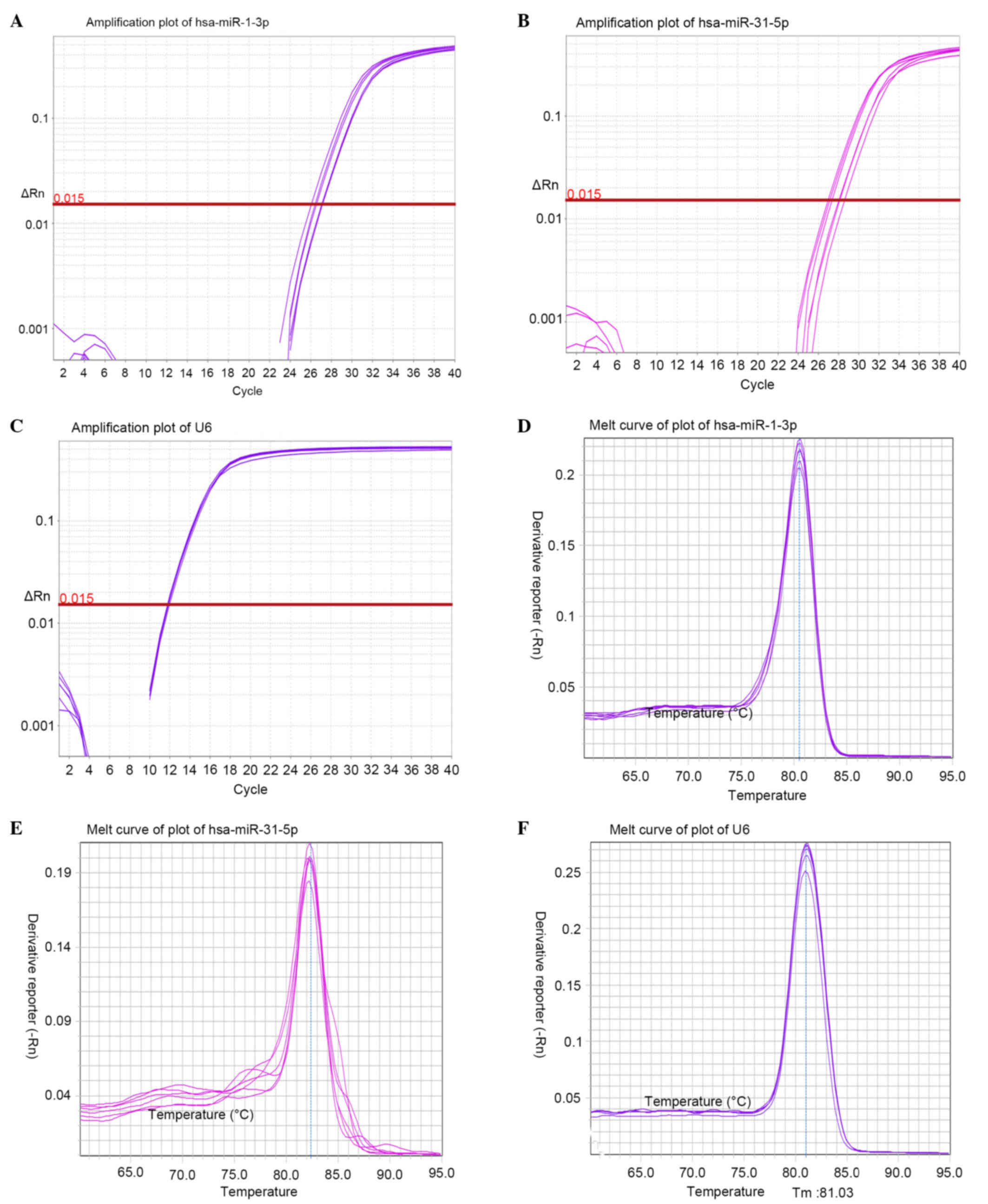
|
1
|
Moreno-Moya JM, Vilella F and Simón C:
MicroRNA: Key gene expression regulators. Fertil Steril.
101:1516–1523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Suzuki HI: Dissecting microRNA biogenesis
and microRNA-mediated regulation of gene network. Seikagaku.
87:413–421. 2015.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He L and Sedwick C: Lin He: ‘Junk’ DNA
isn't. J Cell Biol. 211:4–5. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martin EC, Qureshi AT, Dasa V, Freitas MA,
Gimble JM and Davis TA: MicroRNA regulation of stem cell
differentiation and diseases of the bone and adipose tissue:
Perspectives on miRNA biogenesis and cellular transcriptome.
Biochimie. 124:98–111. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yao S: MicroRNA biogenesis and their
functions in regulating stem cell potency and differentiation. Biol
Proced Online. 18:82016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Song Z, Liu D, Peng Y, Li J, Zhang Z and
Ning P: Differential microRNA expression profile comparison between
epidermal stem cells and differentiated keratinocytes. Mol Med Rep.
11:2285–2291. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu YF, Ding M, Liu DW, Liu Y, Mao YG and
Peng Y: MicroRNA profiling in cutaneous wounds of diabetic rats.
Genet Mol Res. 14:9614–9625. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sonkoly E, Wei T, Loriè E Pavez, Suzuki H,
Kato M, Törmä H, Ståhle M and Pivarcsi A: Protein kinase
C-dependent upregulation of miR-203 induces the differentiation of
human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 130:124–134. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gutcher I, Webb PR and Anderson NG: The
isoform-specific regulation of apoptosis by protein kinase C. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 60:1061–1070. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Diaz-Meco MT and Moscat J: The atypical
PKCs in inflammation: NF-κB and beyond. Immunol Rev. 246:154–167.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mitev V and Miteva L: Signal transduction
in keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 8:96–108. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Le Panse R, Coulomb B, Mitev V, Bouchard
B, Lebreton C and Dubertret L: Differential modulation of human
fibroblast and keratinocyte growth by the protein kinase C
inhibitor GF 109203X. Mol Pharmacol. 46:445–451. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee YS, Yuspa SH and Dlugosz AA:
Differentiation of cultured human epidermal keratinocytes at high
cell densities is mediated by endogenous activation of the protein
kinase C signaling pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 111:762–766. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
You HL, Eng HL, Hsu SF, Chen CM, Ye TC,
Liao WT, Huang MY, Baer R and Cheng JT: A PKC-Sp1 signaling pathway
induces early differentiation of human keratinocytes through
upregulation of TSG101. Cell Signal. 19:1201–1211. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tibudan SS, Wang Y and Denning MF:
Activation of protein kinase C triggers irreversible cell cycle
withdrawal in human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol.
119:1282–1289. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park YK and Jang BC: UVB-induced
anti-survival and pro-apoptotic effects on HaCaT human
keratinocytes via caspase- and PKC-dependent downregulation of PKB
HIAP-1, Mcl-1, XIAP andER stress. Int J Mol Med. 33:695–702. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2. 0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kormos B, Belso N, Bebes A, Szabad G,
Bacsa S, Széll M, Kemény L and Bata-Csörgo Z: In vitro
dedifferentiation of melanocytes from adult epidermis. PLoS One.
6:e171972011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Poloni A, Maurizi G, Anastasi S, Mondini
E, Mattiucci D, Discepoli G, Tiberi F, Mancini S, Partelli S,
Maurizi A, et al: Plasticity of human dedifferentiated adipocytes
toward endothelial cells. Exp Hematol. 43:137–146. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun X, Fu X, Han W, Zhao Y, Liu H and
Sheng Z: Dedifferentiation of human terminally differentiating
keratinocytes into their precursor cells induced by basic
fibroblast growth factor. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1037–1045. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li JF, Duan HF, Wu CT, Zhang DJ, Deng Y,
Yin HL, Han B, Gong HC, Wang HW and Wang YL: HGF accelerates wound
healing by promoting the dedifferentiation of epidermal cells
through beta1-integrin/ILK pathway. Biomed Res Int.
2013:4704182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao Z, Zhang C, Fu X, Yang R, Peng C, Gu
T, Sui Z, Wang C and Liu C: Differentiated epidermal cells regain
the ability to regenerate a skin equivalent by increasing the level
of β-catenin in the cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 196:353–361. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Eming SA, Martin P and Tomic-Canic M:
Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and
translation. Sci Transl Med. 6:265sr62014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hay RJ, Johns NE, Williams HC, Bolliger
IW, Dellavalle RP, Margolis DJ, Marks R, Naldi L, Weinstock MA,
Wulf SK, et al: The global burden of skin disease in 2010: An
analysis of the prevalence and impact of skin conditions. J Invest
Dermatol. 134:1527–1534. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun BK, Siprashvili Z and Khavari PA:
Advances in skin grafting and treatment of cutaneous wounds.
Science. 346:941–945. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boštjančič E, Jerše M, Glavač D and Zidar
N: miR-1, miR-133a/b and miR-208a in human fetal hearts correlate
to the apoptotic and proliferation markers. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
240:211–219. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Minetti GC, Feige JN, Bombard F, Heier A,
Morvan F, Nürnberg B, Leiss V, Birnbaumer L, Glass DJ and Fornaro
M: Gαi2 signaling is required for skeletal muscle growth,
regeneration, and satellite cell proliferation and differentiation.
Mol Cell Biol. 34:619–630. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Peng H, Kaplan N, Hamanaka RB, Katsnelson
J, Blatt H, Yang W, Hao L, Bryar PJ, Johnson RS, Getsios S, et al:
microRNA-31/factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 nexus
regulates keratinocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:14030–14034. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan S, Xu Z, Lou F, Zhang L, Ke F, Bai J,
Liu Z, Liu J, Wang H, Zhu H, et al: NF-κB-induced microRNA-31
promotes epidermal hyperplasia by repressing protein phosphatase 6
in psoriasis. Nat Commun. 6:76522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang A, Landén NX, Meisgen F,
Lohcharoenkal W, Ståhle M, Sonkoly E and Pivarcsi A: MicroRNA-31 is
overexpressed in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and regulates
cell motility and colony formation ability of tumor cells. PLoS
One. 9:e1032062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sanchez-Diaz PC, Hsiao TH, Chang JC, Yue
D, Tan MC, Chen HI, Tomlinson GE, Huang Y, Chen Y and Hung JY:
De-regulated microRNAs in pediatric cancer stem cells target
pathways involved in cell proliferation, cell cycle and
development. PLoS One. 8:e616222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu T, Zhang C, Chai MX, An YB and Jia JL:
miR-374a promotes the proliferation of osteosarcoma cell
proliferation by targeting Axin2. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:10776–10783. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mishra S, Tripathi A, Chaudhari BP,
Dwivedi PD, Pandey HP and Das M: Deoxynivalenol induced mouse skin
cell proliferation and inflammation via MAPK pathway. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 279:186–197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Pesakhov S, Weng A, Kafka M, Gocek
E, Nguyen M, Harrison JS, Danilenko M and Studzinski GP: ERK 5/MAPK
pathway has a major role in 1α, 25-(OH)2 vitamin D3-induced
terminal differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 144:223–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saha K, Adhikary G, Kanade SR, Rorke EA
and Eckert RL: p38δ Regulates p53 to Control p21Cip1 expression in
human epidermal keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 289:11443–11453. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saha K and Eckert RL: Methylosome protein
50 and PKCδ/p38δ protein signaling control keratinocyte
proliferation via opposing effects on p21Cip1 Gene Expression. J
Biol Chem. 290:13521–13530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiao X, He Y, Li C, Zhang X, Xu H and Wang
B: Nicastrin mutations in familial acne inversa impact keratinocyte
proliferation and differentiation through Notch and
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathways. Br J Dermatol.
174:522–532. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Patruno A, Pesce M, Grilli A, Speranza L,
Franceschelli S, De Lutiis MA, Vianale G, Costantini E, Amerio P,
Muraro R, et al: mTOR Activation by PI3K/Akt and ERK signaling in
short ELF-EMF exposed human keratinocytes. PLoS One.
10:e01396442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiao Y, Thoresen DT, Williams JS, Wang C,
Perna J, Petrova R and Brownell I: Neural Hedgehog signaling
maintains stem cell renewal in the sensory touch dome epithelium.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:7195–7200. 2015; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nakamura Y, Ishikawa H, Kawai K, Tabata Y
and Suzuki S: Enhanced wound healing by topical administration of
mesenchymal stem cells transfected with stromal cell-derived
factor-1. Biomaterials. 34:9393–9400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tao R, Sun TJ, Han YQ, Xu G, Liu J and Han
YF: Optimization of in vitro cell labeling methods for human
umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 18:1127–1134. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC,
Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, Waldvogel B, Vannier C, Darling D,
zur Hausen A, et al: The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity
by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol.
11:1487–1495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B and
Rigoutsos I: MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions
modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature.
455:1124–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lauschke VM, Vorrink SU, Moro SM, Rezayee
F, Nordling Å, Hendriks DF, Bell CC, Sison-Young R, Park BK,
Goldring CE, et al: Massive rearrangements of cellular miRNA
signatures are key drivers of hepatocyte dedifferentiation.
Hepatology. 64:1743–1756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sethupathy P: The promise and challenge of
therapeutic MicroRNA silencing in diabetes and metabolic diseases.
Curr Diab Rep. 16:522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|