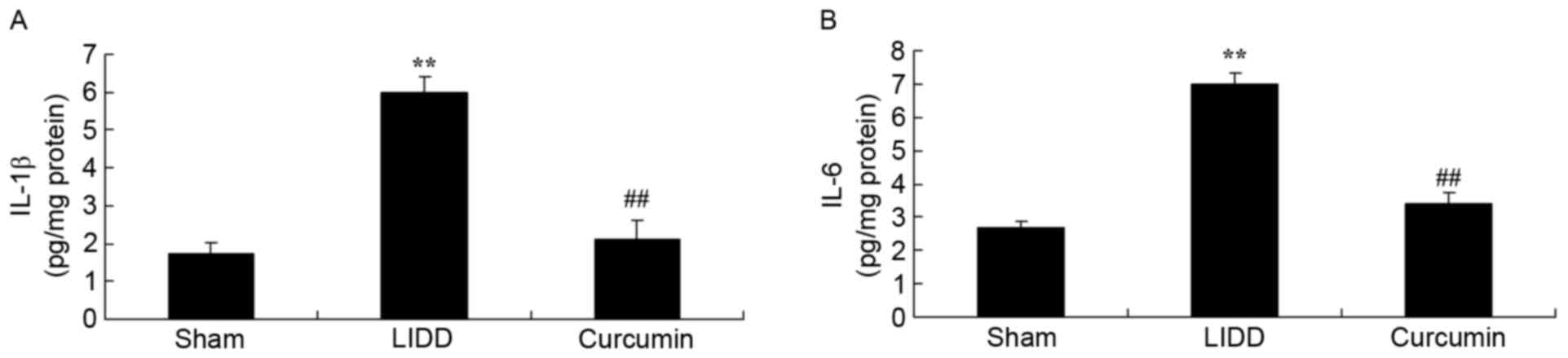
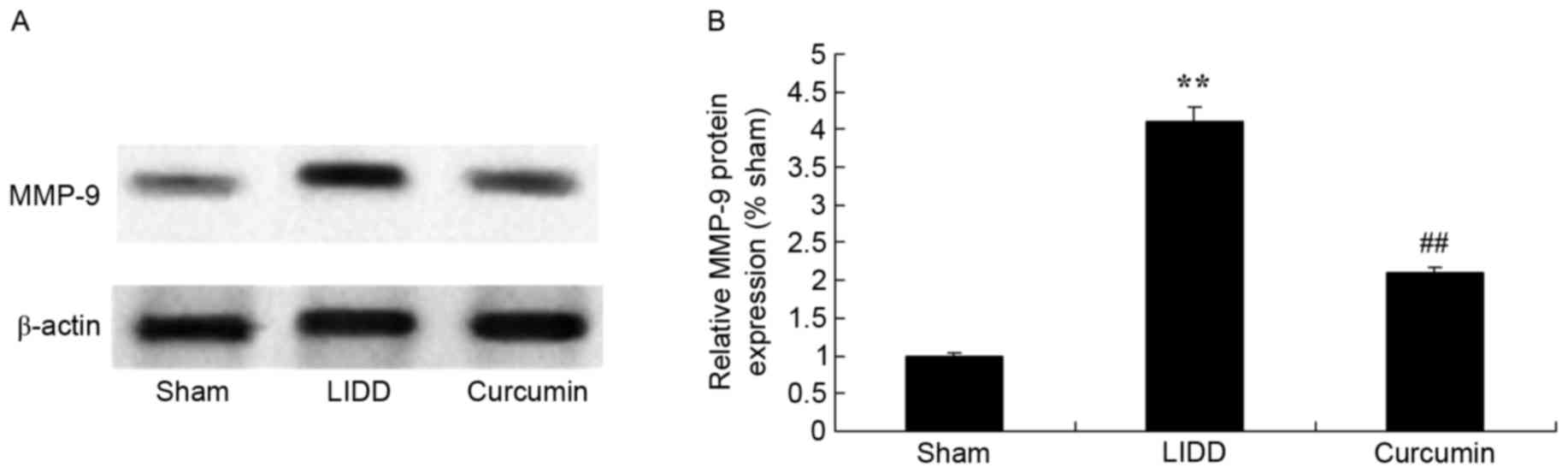
|
1
|
Vieira LA, De Marchi PL, dos Santos AA,
Christofolini DM, Barbosa CP, Fonseca FL, Bianco B and Rodrigues
LM: Analysis of FokI polymorphism of vitamin D receptor gene in
intervertebral disc degeneration. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers.
18:625–629. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Høy K, Bunger C, Niederman B, Helmig P,
Hansen ES, Li H and Andersen T: Transforaminal lumbar interbody
fusion (TLIF) versus posterolateral instrumented fusion (PLF) in
degenerative lumbar disorders: A randomized clinical trial with
2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 22:2022–2029. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brox JI, SØrensen R, Friis A, Nygaard Ø,
Indahl A, Keller A, Ingebrigtsen T, Eriksen HR, Holm I, Koller AK,
et al: Randomized clinical trial of lumbar instrumented fusion and
cognitive intervention and exercises in patients with chronic low
back pain and disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
28:1913–1921. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Delecrin J, Allain J, Beaurain J, Steib
JP, Huppert J, Chataigner H, Ameil M, Aubourg L and Nguyen JM:
Effects of lumbar artificial disc design on intervertebral
mobility: In vivo comparison between mobile-core and fixed-core.
Eur Spine J. 21 Suppl 5:S630–S640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Omair A, Holden M, Lie BA, Reikeras O and
Brox JI: Treatment outcome of chronic low back pain and
radiographic lumbar disc degeneration are associated with
inflammatory and matrix degrading gene variants: A prospective
genetic association study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 14:1052013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sedighi M and Haghnegahdar A: Role of
vitamin D3 in treatment of lumbar disc herniation-pain and sensory
aspects: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials.
15:3732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mochida J, Sakai D, Nakamura Y, Watanabe
T, Yamamoto Y and Kato S: Intervertebral disc repair with activated
nucleus pulposus cell transplantation: A three-year, prospective
clinical study of its safety. Eur Cell Mater. 29:202–212. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu H, Wu W, Li Y, Liu J, Yang K and Chen
Y: Protective effects of preserving the posterior complex on the
development of adjacent-segment degeneration after lumbar fusion:
Clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 19:201–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng Y, Lu X, Wang L, Li T, Ding Y, Cao H,
Zhang Y, Guo X and Yu G: Curcumin inhibits the AKT/NF-kB signaling
via CpG demethylation of the promoter and restoration of NEP in the
N2a cell line. AAPS J. 16:649–657. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yuan J, Zou M, Xiang X, Zhu H, Chu W, Liu
W, Chen F and Lin J: Curcumin improves neural function after spinal
cord injury by the joint inhibition of the intracellular and
extracellular components of glial scar. J Surg Res. 195:235–245.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pu Y, Zhang H, Wang P, Zhao Y, Li Q, Wei
X, Cui Y, Sun J, Shang Q, Liu D and Zhu Z: Dietary curcumin
ameliorates aging-related cerebrovascular dysfunction through the
AMPK/uncoupling protein 2 pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem.
32:1167–1177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang M, Liang L, Li L, Han K, Li Q, Peng
Y, Peng X and Zeng K: Increased miR-424-5p expression in peripheral
blood mononuclear cells from patients with pemphigus. Mol Med Rep.
15:3479–3484. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Siepe CJ, Heider F, Haas E, Hitzl W,
Szeimies U, Stäbler A, Weiler C, Nerlich AG and Mayer MH: Influence
of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration on the outcome of total
lumbar disc replacement: A prospective clinical, histological,
X-ray and MRI investigation. Eur Spine J. 21:2287–2299. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Akeda K, Yamada T, Inoue N, Nishimura A
and Sudo A: Risk factors for lumbar intervertebral disc height
narrowing: A population-based longitudinal study in the elderly.
BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 16:3442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao B, Chang C, Zhou J, Zhao T, Wang C, Li
C and Gao G: Pycnogenol protects against rotenone-induced
neurotoxicity in PC12 cells through regulating NF-kB-iNOS signaling
pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 34:643–649. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xue Y, Wu J and Sun J: Four types of
inorganic nanoparticles stimulate the inflammatory reaction in
brain microglia and damage neurons in vitro. Toxicol Lett.
214:91–98. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jimbo K, Park JS, Yokosuka K, Sato K and
Nagata K: Positive feedback loop of interleukin-1beta upregulating
production of inflammatory mediators in human intervertebral disc
cells in vitro. J Neurosurg Spine. 2:589–595. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cabraja M, Endres M, Abbushi A, Zenclussen
M, Blechschmidt C, Lemke AJ, Kroppenstedt S, Kaps C and
Woiciechowsky C: Effect of degeneration on gene expression of
chondrogenic and inflammatory marker genes of intervertebral disc
cells: A preliminary study. J Neurosurg Sci. 57:307–316.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zigouris A, Alexiou GA, Batistatou A,
Voulgaris S and Kyritsis AP: The role of matrix metalloproteinase 9
in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Clin Neurosci. 18:1424–1425.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun ZM, Miao L, Zhang YG and Ming L:
Association between the −1562 C/T polymorphism of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 gene and lumbar disc disease in the young adult
population in North China. Connect Tissue Res. 50:181–185. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li X, Lu Y, Sun Y and Zhang Q: Effect of
curcumin on permeability of coronary artery and expression of
related proteins in rat coronary atherosclerosis heart disease
model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7247–7253. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhan Z, Shao Z, Xiong X, Yang S, Du J,
Zheng Q, Wang H, Guo X and Liu Y: Ad/CMV-hTGF-beta1 treats rabbit
intervertebral discs degeneration in vivo. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 24:599–601, 624. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kartha S, Zeeman ME, Baig HA, Guarino BB
and Winkelstein BA: Upregulation of BDNF and NGF in cervical
intervertebral discs exposed to painful whole-body vibration. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 39:1542–1548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Orita S, Eguchi Y, Kamoda H, Arai G,
Ishikawa T, Miyagi M, Inoue G, Suzuki M, Toyone T, Aoki Y, et al:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor inhibition at the punctured
intervertebral disc downregulates the production of calcitonin
gene-related peptide in dorsal root ganglia in rats. Spine (Phila
Pa 1976). 36:1737–1743. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fanaei H, Khayat S, Kasaeian A and
Javadimehr M: Effect of curcumin on serum brain-derived
neurotrophic factor levels in women with premenstrual syndrome: A
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuropeptides.
56:25–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|