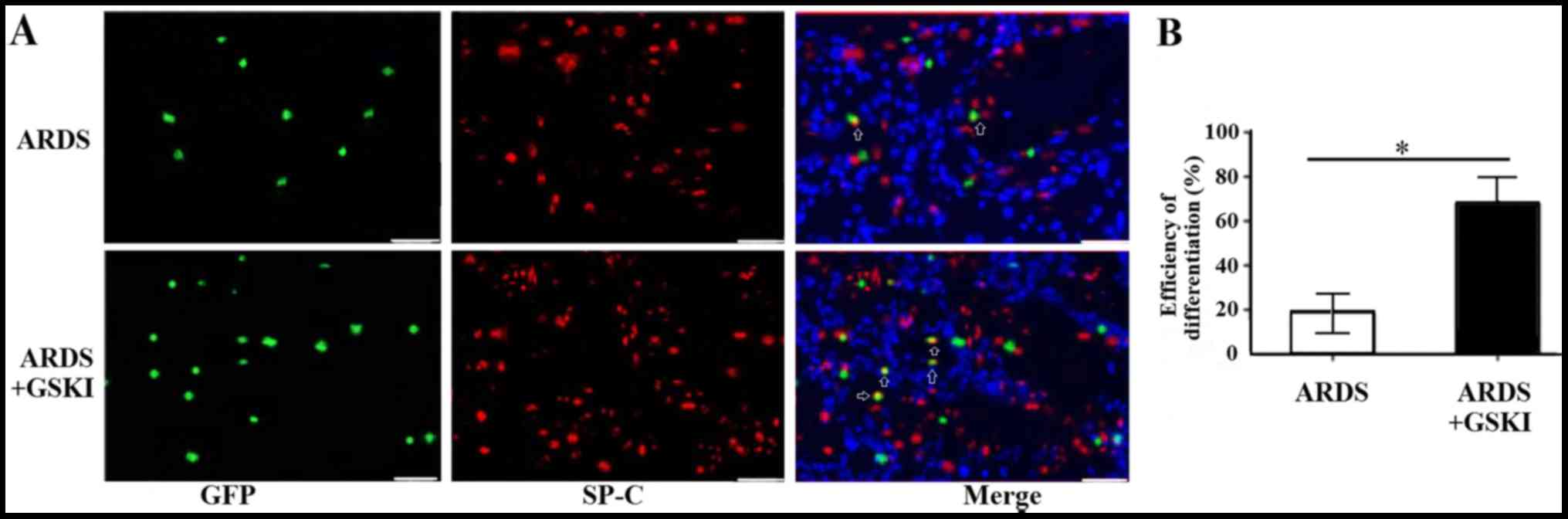
|
1
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goss CH, Brower RG, Hudson LD and
Rubenfeld GD: ARDS Network: Incidence of acute lung injury in the
United States. Crit Care Med. 31:1607–1611. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mendez JL and Hubmayr RD: New insights
into the pathology of acute respiratory failure. Curr Opin Crit
Care. 11:29–36. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E,
Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, Stern EJ and Hudson LD: Incidence and
outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 353:1685–1693. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Quílez ME, López-Aguilar J and Blanch L:
Organ crosstalk during acute lung injury, acute respiratory
distress syndrome, and mechanical ventilation. Curr Opin Crit Care.
18:23–28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Middelveld RJ and Alving K: Synergistic
septicemic action of the gram-positive bacterial cell wall
components peptidoglycan and lipoteichonic acid in the pig in vivo.
Shock. 13:297–306. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoshinari D, Takeyoshi I, Koibuchi Y,
Matsumoto K, Kawashima Y, Koyama T, Ohwada S and Morishita Y:
Effects of a dual inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and
interleukin-1 on lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in rats:
Involvement of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.
Crit Care Med. 29:628–634. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tanaka S, Nishiumi S, Nishida M, Mizushina
Y, Kobayashi K, Masuda A, Fujita T, Morita Y, Mizuno S, Kutsumi H,
et al: Vitamin K3 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury through inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activationce.
Clin Exp Immunol. 160:283–292. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ranieri VM, Thompson BT, Barie PS,
Dhainaut JF, Douglas IS, Finfer S, Gårdlund B, Marshall JC, Rhodes
A, Artigas A, et al: Drotrecogin alfa (activated) in adults with
septic shock. N Engl J Med. 366:2055–2064. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huber-Lang MS, Younkin EM, Sarma JV,
McGuire SR, Lu KT, Guo RF, Padgaonkar VA, Curnutte JT, Erickson R
and Ward PA: Complement-induced impairment of innate immunity
during sepsis. J Immunol. 169:3223–3231. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Neff TA, Laudes IJ,
Keller KA, Sarma VJ, Markiewski MM, Mastellos D, Strey CW, Pierson
CL, et al: Increased C5a receptor expression in sepsis. J Clin
Invest. 110:101–108. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lehmann LE, Novender U, Schroeder S,
Pietsch T, von Spiegel T, Putensen C, Hoeft A and Stüber F: Plasma
levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor are elevated in
patients with severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 27:1412–1415.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ulloa L, Ochani M, Yang H, Tanovic M,
Halperin D, Yang R, Czura CJ, Fink MP and Tracey KJ: Ethyl pyruvate
prevents lethality in mice with established lethal sepsis and
systemic inflammationProc Natl Acad Sci. USA: 99. pp. 12351–12356.
2002; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Li M, Stadler S, Correll S, Li P,
Wang D, Hayama R, Leonelli L, Han H, Grigoryev SA, et al: Histone
hypercitrullination mediates chromatin decondensation and
neutrophil extracellular trap formation. J Cell Biol. 184:205–213.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bouldin CM, Manning AJ, Peng YH, Farr GH
III, Hung KL, Dong A and Kimelman D: Wnt signaling and tbx16 form a
bistable switch to commit bipotential progenitors to mesoderm.
Development. 142:2499–2507. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Etheridge SL, Spencer GJ, Heath DJ and
Genever PG: Expression profiling and functional analysis of wnt
signaling mechanisms in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells.
22:849–860. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, Gaupp D,
Baddoo M, Kaminski N and Phinney DG: Mesenchymal stem cell
engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin exposure
and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:8407–8411. 2003; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamada M, Kubo H, Kobayashi S, Ishizawa K,
Numasaki M, Ueda S, Suzuki T and Sasaki H: Bone marrow-derived
progenitor cells are important for lung repair after
lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. J Immunol. 172:1266–1272.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kotton DN, Ma BY, Cardoso WV, Sanderson
EA, Summer RS, Williams MC and Fine A: Bone marrow-derived cells as
progenitors of lung alveolar epithelium. Development.
128:5181–5188. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, Lee JW, Serikov V
and Matthay MA: Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol.
179:1855–1863. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Geburek F, Mundle K, Conrad S, Hellige M,
Walliser U, van Schie HT, van Weeren R, Skutella T and Stadler PM:
Tracking of autologous adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal
cells with in vivo magnetic resonance imaging and histology after
intralesional treatment of artificial equine tendon lesions - a
pilot study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 7:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takaoka Y, Goto S, Nakano T, Tseng HP,
Yang SM, Kawamoto S, Ono K and Chen CL: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase (GAPDH) prevents lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced,
sepsis-related severe acute lung injury in mice. Sci Rep.
4:52042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mei SH, McCarter SD, Deng Y, Parker CH,
Liles WC and Stewart DJ: Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing
angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med. 4:e2692007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fang WF, Cho JH, He Q, Lin MC, Wu CC,
Voelkel NF and Douglas IS: Lipid A fraction of LPS induces a
discrete MAPK activation in acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L336–L344. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong L, He HL, Lu XM, Yang Y and Qiu HB:
Modulation of FLT3 signaling targets conventional dendritic cells
to attenuate acute lung injury. APMIS. 120:808–818. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matute-Bello G, Winn RK, Jonas M, Chi EY,
Martin TR and Liles WC: Fas (CD95) induces alveolar epithelial cell
apoptosis in vivo: Implications for acute pulmonary inflammation.
Am J Pathol. 158:153–161. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gordon MD and Nusse R: Wnt signaling:
Multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription
factors. J Biol Chem. 281:22429–22433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Troussard AA, Tan C, Yoganathan TN and
Dedhar S: Cell-extracellular matrix interactions stimulate the AP-1
transcription factor in an integrin-linked kinase- and glycogen
synthase kinase 3-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 19:7420–7427.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jean D, Harbison M, McConkey DJ, Ronai Z
and Bar-Eli M: CREB and its associated proteins act as survival
factors for human melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 273:24884–24890.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Walton M, Woodgate AM, Muravlev A, Xu R,
During MJ and Dragunow M: CREB phosphorylation promotes nerve cell
survival. J Neurochem. 73:1836–1842. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kurosaki T: Checks and balances on
developing B cells. Nat Immunol. 4:13–15. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Masterson C, Jerkic M, Curley GF and
Laffey JG: Mesenchymal stromal cell therapies: Potential and
pitfalls for ARDS. Minerva Anestesiol. 81:179–194. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li J, Huang S, Wu Y, Gu C, Gao D, Feng C,
Wu X and Fu X: Paracrine factors from mesenchymal stem cells: A
proposed therapeutic tool for acute lung injury and acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Int Wound J. 11:114–121. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Simonson OE, Mougiakakos D, Heldring N,
Bassi G, Johansson HJ, Dalén M, Jitschin R, Rodin S, Corbascio M,
El Andaloussi S, et al: In vivo effects of mesenchymal stromal
cells in two patients with severe acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Stem Cells Transl Med. 4:1199–1213. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Grove JE, Lutzko C, Priller J, Henegariu
O, Theise ND, Kohn DB and Krause DS: Marrow-derived cells as
vehicles for delivery of gene therapy to pulmonary epithelium. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 27:645–651. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu AR, Liu L, Chen S, Yang Y, Zhao HJ,
Liu L, Guo FM, Lu XM and Qiu HB: Activation of canonical wnt
pathway promotes differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived MSCs
into type II alveolar epithelial cells, confers resistance to
oxidative stress, and promotes their migration to injured lung
tissue in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 228:1270–1283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|