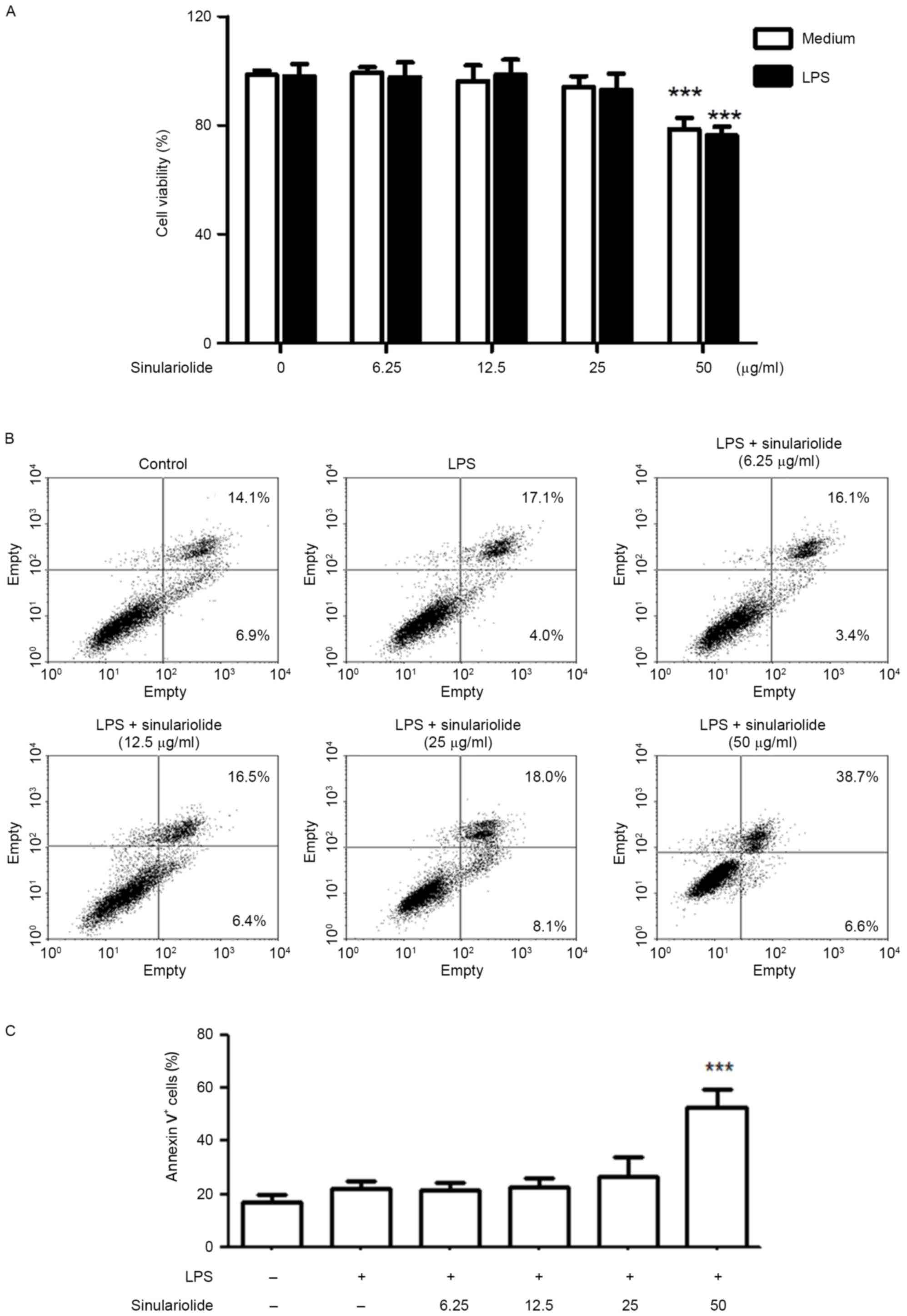
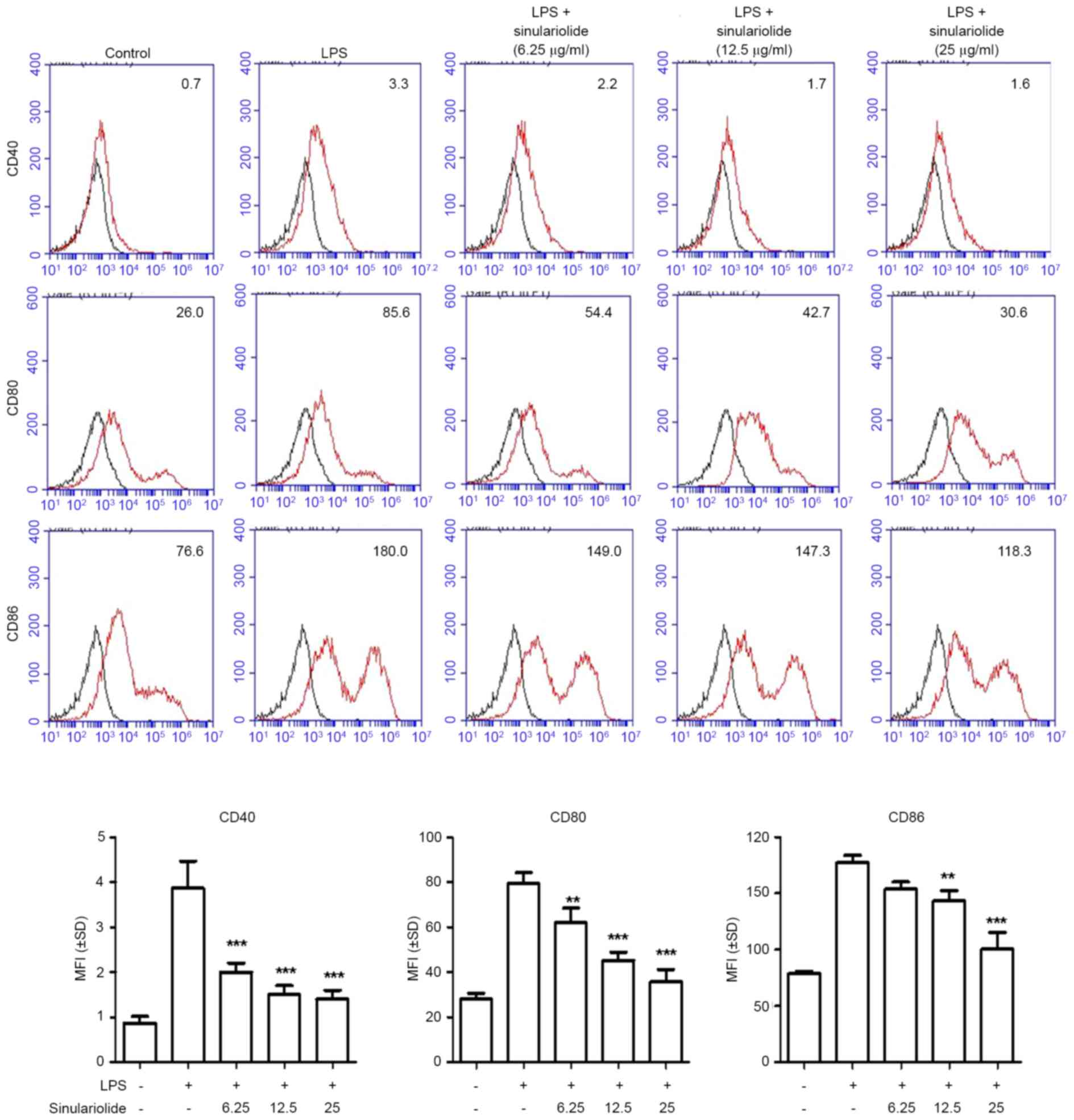
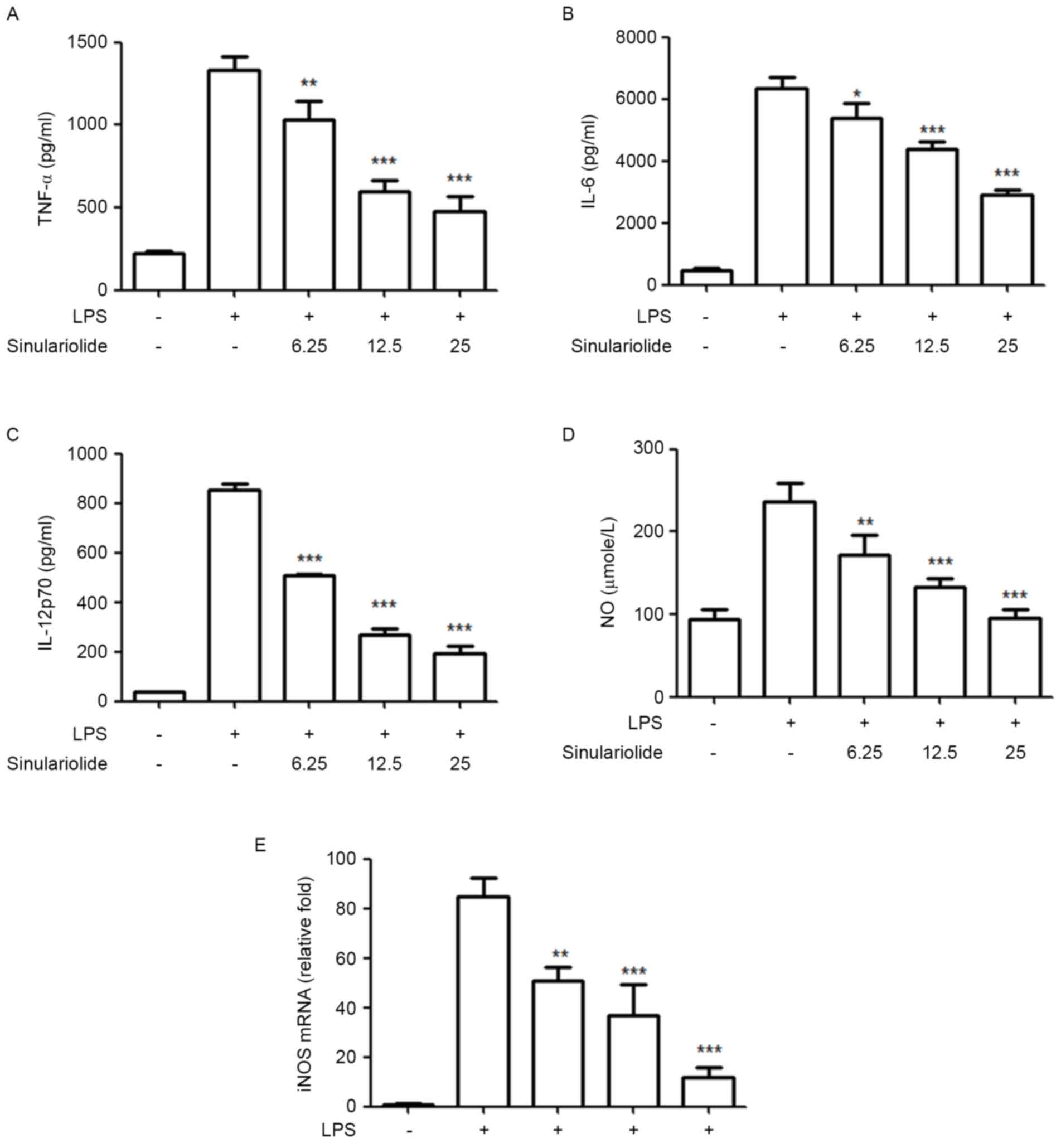
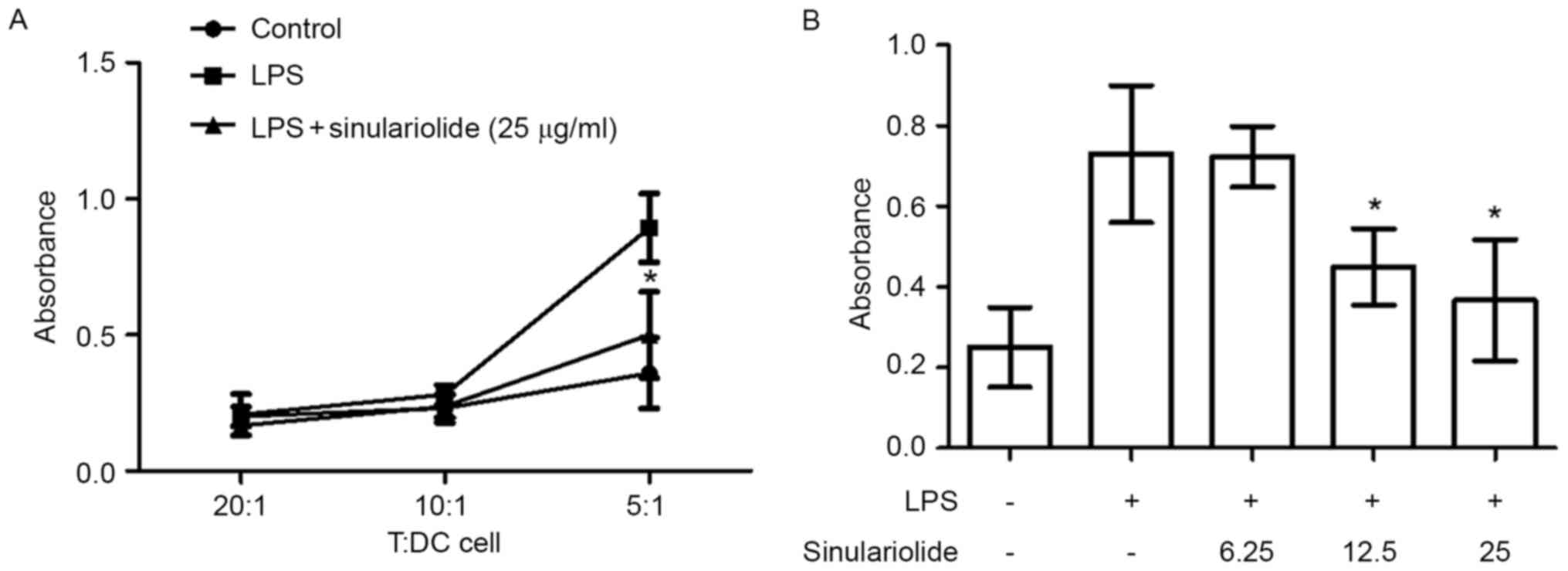
|
1
|
Li X, He X, Liu B, Xu L, Lu C, Zhao H, Niu
X, Chen S and Lu A: Maturation of murine bone marrow-derived
dendritic cells induced by Radix Glycyrrhizae polysaccharide.
Molecules. 17:6557–6568. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim GY, Lee MY, Lee HJ, Moon DO, Lee CM,
Jin CY, Choi YH, Jeong YK, Chung KT, Lee JY, et al: Effect of
water-soluble proteoglycan isolated from Agaricus blazei on the
maturation of murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Int
Immunopharmacol. 5:1523–1532. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
English K, Barry FP and Mahon BP: Murine
mesenchymal stem cells suppress dendritic cell migration,
maturation and antigen presentation. Immunol Lett. 115:50–58. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hackstein H and Thomson AW: Dendritic
cells: Emerging pharmacological targets of immunosuppressive drugs.
Nat Rev Immunol. 4:24–34. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li G, Zhang Y, Deng Z, van Ofwegen L,
Proksch P and Lin W: Cytotoxic cembranoid diterpenes from a soft
coral Sinularia gibberosa. J Nat Prod. 68:649–652. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang B, Zhou XF, Lin XP, Liu J, Peng Y,
Yang XW and Liu YH: Cembrane diterpenes chemistry and biological
properties. Curr Org Chem. 16:1512–1539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chao CH, Chou KJ, Huang CY, Wen ZH, Hsu
CH, Wu YC, Dai CF and Sheu JH: Bioactive cembranoids from the soft
coral Sinularia crassa. Mar Drugs. 9:1955–1968. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Gao AH, Huang H, Li J, Mollo E,
Gavagnin M, Cimino G, Gu YC and Guo YW: Diterpenoids from the
hainan soft coral sinularia parva. Helvetica Chim Acta.
92:1341–1348. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Coll JC, Price IR, Konig GM and Bowden BF:
Algal overgrowth of alcyonacean soft corals. Mar Biol. 96:129–135.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lu Y, Huang CY, Lin YF, Wen ZH, Su JH, Kuo
YH, Chiang MY and Sheu JH: Anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the
soft corals Sinularia querciformis and Sinularia granosa. J Nat
Prod. 71:1754–1759. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu Y, Su JH, Huang CY, Liu YC, Kuo YH, Wen
ZH, Hsu CH and Sheu JH: Cembranoids from the soft corals Sinularia
granosa and Sinularia querciformis. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
58:464–466. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu CI, Chen CC, Chen JC, Su JH, Huang HH,
Chen JY and Wu YJ: Proteomic analysis of anti-tumor effects of
11-dehydrosinulariolide on CAL-27 cells. Mar Drugs. 9:1254–1272.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin YS, Chen CH, Liaw CC, Chen YC, Kuo YH
and Shen YC: Cembrane diterpenoids from the Taiwanese soft coral
Sinularia flexibilis. Tetrahedron. 65:9157–9164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Aceret TL, Coll JC, Uchio Y and Sammarco
PW: Antimicrobial activity of the diterpenes flexibilide and
sinulariolide derived from Sinularia flexibilis Quoy and Gaimard
1833 (Coelenterata: Alcyonacea, Octocorallia). Comp Biochem Physiol
C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol. 120:121–126. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu YJ, Neoh CA, Tsao CY, Su JH and Li HH:
Sinulariolide suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma cell
migration and invasion by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9
through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci.
16:16469–16482. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen YJ, Su JH, Tsao CY, Hung CT, Chao HH,
Lin JJ, Liao MH, Yang ZY, Huang HH, Tsai FJ, et al: Sinulariolide
induced hepatocellular carcinoma apoptosis through activation of
mitochondrial-related apoptotic and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP pathway.
Molecules. 18:10146–10161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li HH, Su JH, Chiu CC, Lin JJ, Yang ZY,
Hwang WI, Chen YK, Lo YH and Wu YJ: Proteomic investigation of the
sinulariolide-treated melanoma cells A375: Effects on the cell
apoptosis through mitochondrial-related pathway and activation of
caspase cascade. Mar Drugs. 11:2625–2642. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Neoh CA, Wang RY, Din ZH, Su JH, Chen YK,
Tsai FJ, Weng SH and Wu YJ: Induction of apoptosis by sinulariolide
from soft coral through mitochondrial-related and p38MAPK pathways
on human bladder carcinoma cells. Mar Drugs. 10:2893–2911. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li S, Lin YC, Ho CT, Lin PY, Suzawa M,
Wang HC, Chu CL, Chen DY and Lin CC: Formulated extract from
multiple citrus peels impairs dendritic cell functions and
attenuates allergic contact hypersensitivity. Int Immunopharmacol.
20:12–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hsieh PW, Chang FR, McPhail AT, Lee KH and
Wu YC: New cembranolide analogues from the formosan soft coral
Sinularia flexibilis and their cytotoxicity. Nat Prod Res.
17:409–418. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin CC, Chu CL, Ng CS, Lin CY, Chen DY,
Pan IH and Huang KJ: Immunomodulation of phloretin by impairing
dendritic cell activation and function. Food Funct. 5:997–1006.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Caux C, Massacrier C, Vanbervliet B,
Dubois B, Van Kooten C, Durand I and Banchereau J: Activation of
human dendritic cells through CD40 cross-linking. J Exp Med.
180:1263–1272. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pinchuk LM, Polacino PS, Agy MB, Klaus SJ
and Clark EA: The role of CD40 and CD80 accessory cell molecules in
dendritic cell-dependent HIV-1 infection. Immunity. 1:317–325.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Diehl S and Rincón M: The two faces of
IL-6 on Th1/Th2 differentiation. Mol Immunol. 39:531–536. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heufler C, Koch F, Stanzl U, Topar G,
Wysocka M, Trinchieri G, Enk A, Steinman RM, Romani N and Schuler
G: Interleukin-12 is produced by dendritic cells and mediates T
helper 1 development as well as interferon-gamma production by T
helper 1 cells. Eur J Immunol. 26:659–668. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moncada S, Palmer RM and Higgs EA: Nitric
oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol
Rev. 43:109–142. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bonham CA, Lu L, Li Y, Hoffman RA, Simmons
RL and Thomson AW: Nitric oxide production by mouse bone
marrow-derived dendritic cells: Implications for the regulation of
allogeneic T cell responses. Transplantation. 62:1871–1877. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu L, Bonham CA, Chambers FG, Watkins SC,
Hoffman RA, Simmons RL and Thomson AW: Induction of nitric oxide
synthase in mouse dendritic cells by IFN-gamma, endotoxin, and
interaction with allogenic T cells: Nitric oxide production is
associated with dendritic cell apoptosis. J Immunol. 157:3577–3586.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Neves BM, Cruz MT, Francisco V,
Garcia-Rodriguez C, Silvestre R, Cordeiro-da-Silva A, Dinis AM,
Batista MT, Duarte CB and Lopes MC: Differential roles of
PI3-kinase, MAPKs and NF-kappaB on the manipulation of dendritic
cell T(h)1/T(h)2 cytokine/chemokine polarizing profile. Mol
Immunol. 46:2481–2492. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rescigno M, Martino M, Sutherland CL, Gold
MR and Ricciardi-Castagnoli P: Dendritic cell survival and
maturation are regulated by different signaling pathways. J Exp
Med. 188:2175–2180. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ardeshna KM, Pizzey AR, Devereux S and
Khwaja A: The PI3 kinase, p38 SAP kinase, and NF-kappaB signal
transduction pathways are involved in the survival and maturation
of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocyte-derived dendritic
cells. Blood. 96:1039–1046. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xie J, Qian J, Yang J, Wang S, Freeman ME
III and Yi Q: Critical roles of Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling
and inactivation of p38 MAP kinase in the differentiation and
survival of monocyte-derived immature dendritic cells. Exp Hematol.
33:564–572. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsiao KY, Wu YJ, Liu ZN, Chuang CW, Huang
HH and Kuo SM: Anticancer effects of sinulariolide-conjugated
hyaluronan nanoparticles on lung adenocarcinoma cells. Molecules.
21:2972016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|