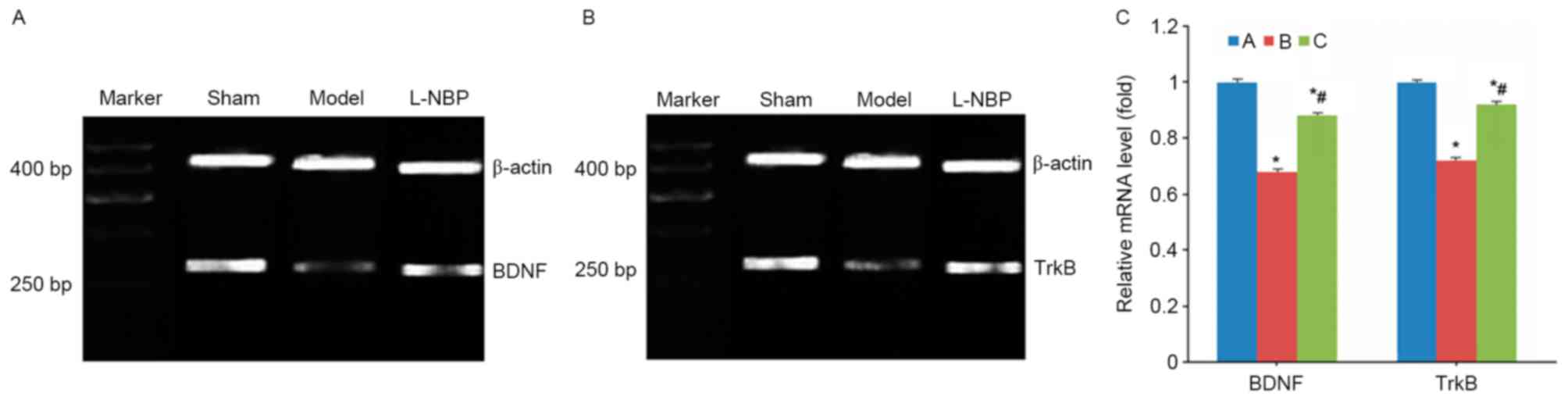
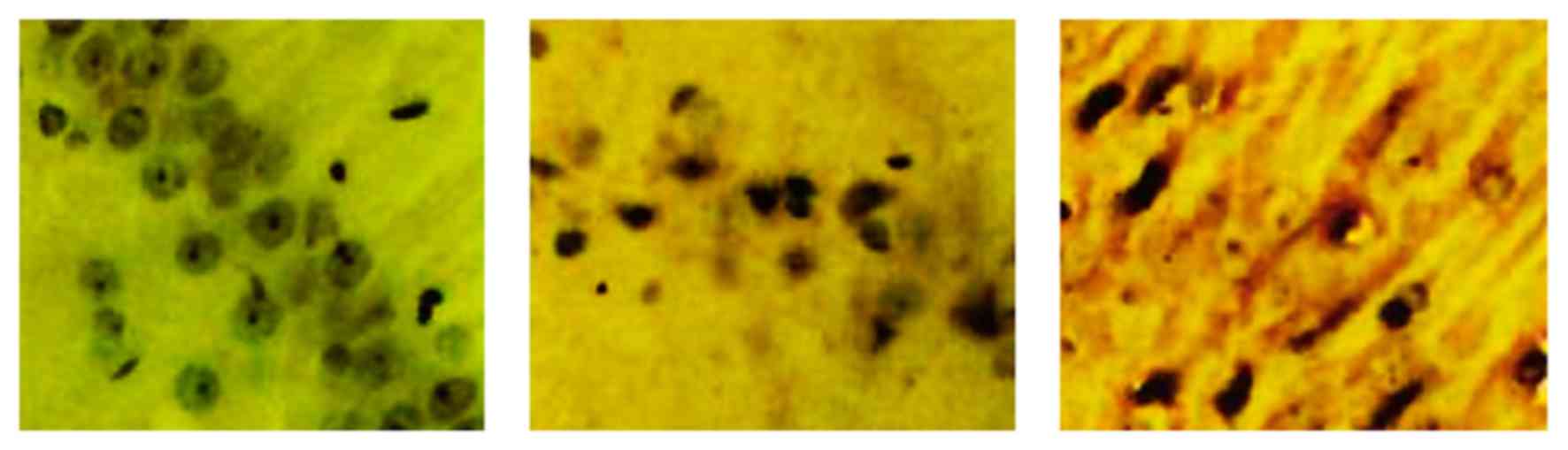
|
1
|
Lantz M, Sjöstrand C and Kostulas K:
Ischemic stroke and patent foramen ovale: Risk factors and genetic
profile. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 22:841–845. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
O'Brien JT and Thomas A: Vascular
dementia. Lancet. 386:1698–706. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yakushiji Y: Cerebral microbleeds:
Detection, associations and clinical implications. Front Neurol
Neurosci. 37:78–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ueno M, Chiba Y, Matsumoto K, Murakami R,
Fujihara R, Kawauchi M, Miyanaka H and Nakagawa T: Blood-brain
barrier damage in vascular dementia. Neuropathology. 36:115–124.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Hai S, Zhou Y and Dong BR:
Cholinesterase inhibitors for rarer dementias associated with
neurological conditions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD009444.
2015.
|
|
6
|
Kwon KJ, Kim MK, Lee EJ, Kim JN, Choi BR,
Kim SY, Cho KS, Han JS, Kim HY, Shin CY and Han SH: Effects of
donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, on neurogenesis in a
rat model of vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci. 347:66–77. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yin W, Lan L, Huang Z, Ji J, Fang J, Wang
X, Ji H, Peng S, Xu J and Zhang Y: Discovery of a ring-opened
derivative of 3-n-butylphthalide bearing NO/H2S-donating moieties
as a potential anti-ischemic stroke agent. Eur J Med Chem.
115:369–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wen XR, Tang M, Qi DS, Huang XJ, Liu HZ,
Zhang F, Wu J, Wang YW, Zhang XB, Guo JQ, et al: Butylphthalide
suppresses neuronal cells apoptosis and inhibits JNK-caspase3
signaling pathway after brain ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Cell
Mol Neurobiol. 36:1087–1095. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Niu H, Zhang Z, Wang H, Wang H, Zhang J,
Li C and Zhao L: The impact of butylphthalide on the
hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis of patients suffering from
cerebral infarction in the basal ganglia. Electron Physician.
8:1759–1763. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang Y, Sun L, Xuan X and Wang J: Impacts
of N-Butylphthalide on expression of growth factors in rats with
focal cerebral ischemia. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 16:102–107.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee SH, Ko IG, Kim SE, Hwang L, Jin JJ,
Choi HH and Kim CJ: Aqueous extract of Cordyceps alleviates
cerebral ischemia-induced short-term memory impairment in gerbils.
J Exerc Rehabil. 12:69–78. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sawamoto A, Okuyama S, Yamamoto K, Amakura
Y, Yoshimura M, Nakajima M and Furukawa Y:
3,5,6,7,8,3′,4′-Heptamethoxyflavone, a citrus flavonoid,
ameliorates corticosterone-induced depression-like behavior and
restores brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression,
neurogenesis, and neuroplasticity in the Hippocampus. Molecules.
21:5412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fang M, Yuan Y, Lu J, Li HE, Zhao M, Ling
EA and Wu CY: Scutellarin promotes microglia-mediated astrogliosis
coupled with improved behavioral function in cerebral ischemia.
Neurochem Int. 97:154–171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xing M, Sun Q, Wang Y, Cheng Y and Zhang
N: Hydroxysafflor yellow A increases BDNF and NMDARs in the
hippocampus in a vascular dementia rat model. Brain Res.
1642:419–425. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kato M, Iwata H, Katayama T, Asai H,
Narita H and Endo T: Possible therapeutic effect of T-794, a novel
reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase-A, on post-stroke
emotional disturbances, assessed in animal models of depression.
Biol Pharm Bull. 20:349–353. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Du R, Teng JF, Wang Y, Zhao XY and Shi ZB:
Clinical study of Butylphthalide combined with Xue Shuan Tong on
serum inflammatory factors and prognosis effect of patients with
cerebral infarction. Pak J Pharm Sci. 28 5 Suppl:S1823–S1827.
2015.
|
|
17
|
Yang LC, Li J, Xu SF, Cai J, Lei H, Liu
DM, Zhang M, Rong XF, Cui DD, Wang L, et al: L-3-n-butylphthalide
promotes neurogenesis and neuroplasticity in cerebral ischemic
rats. CNS Neurosci Ther. 21:733–741. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao W, Luo C, Wang J, Gong J, Li B, Gong
Y, Wang J and Wang H: 3-N-butylphthalide improves neuronal
morphology after chronic cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res.
9:719–726. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao Y, Li J, Zhang P, Chen C and Li S:
Protective effects of dl-3n-butylphthalide against diffuse brain
injury. Neural Regen Res. 8:2615–2624. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu J, Wen Q, Wu Y, Li B and Gao P: The
effect of butylphthalide on the brain edema, blood-brain barrier of
rats after focal cerebral infarction and the expression of Rho A.
Cell Biochem Biophys. 69:363–368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Diao X, Pang X, Xie C, Guo Z, Zhong D and
Chen X: Bioactivation of 3-n-butylphthalide via sulfation of its
major metabolite 3-hydroxy-NBP: Mediated mainly by sulfotransferase
1A1. Drug Metab Dispos. 42:774–781. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ghadernezhad N, Khalaj L, Pazoki-Toroudi
H, Mirmasoumi M and Ashabi G: Metformin pretreatment enhanced
learning and memory in cerebral forebrain ischaemia: The role of
the AMPK/BDNF/P70SK signalling pathway. Pharm Biol. 54:2211–2219.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li J, Zhang S, Zhang L, Wang R and Wang M:
Effects of L-3-n-butylphthalide on cognitive dysfunction and NR2B
expression in hippocampus of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic
rats. Cell Biochem Biophys. 71:315–322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huai Y, Dong Y, Xu J, Meng N, Song C, Li W
and Lv P: L-3-n-butylphthalide protects against vascular dementia
via activation of the Akt kinase pathway. Neural Regen Res.
8:1733–1742. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|