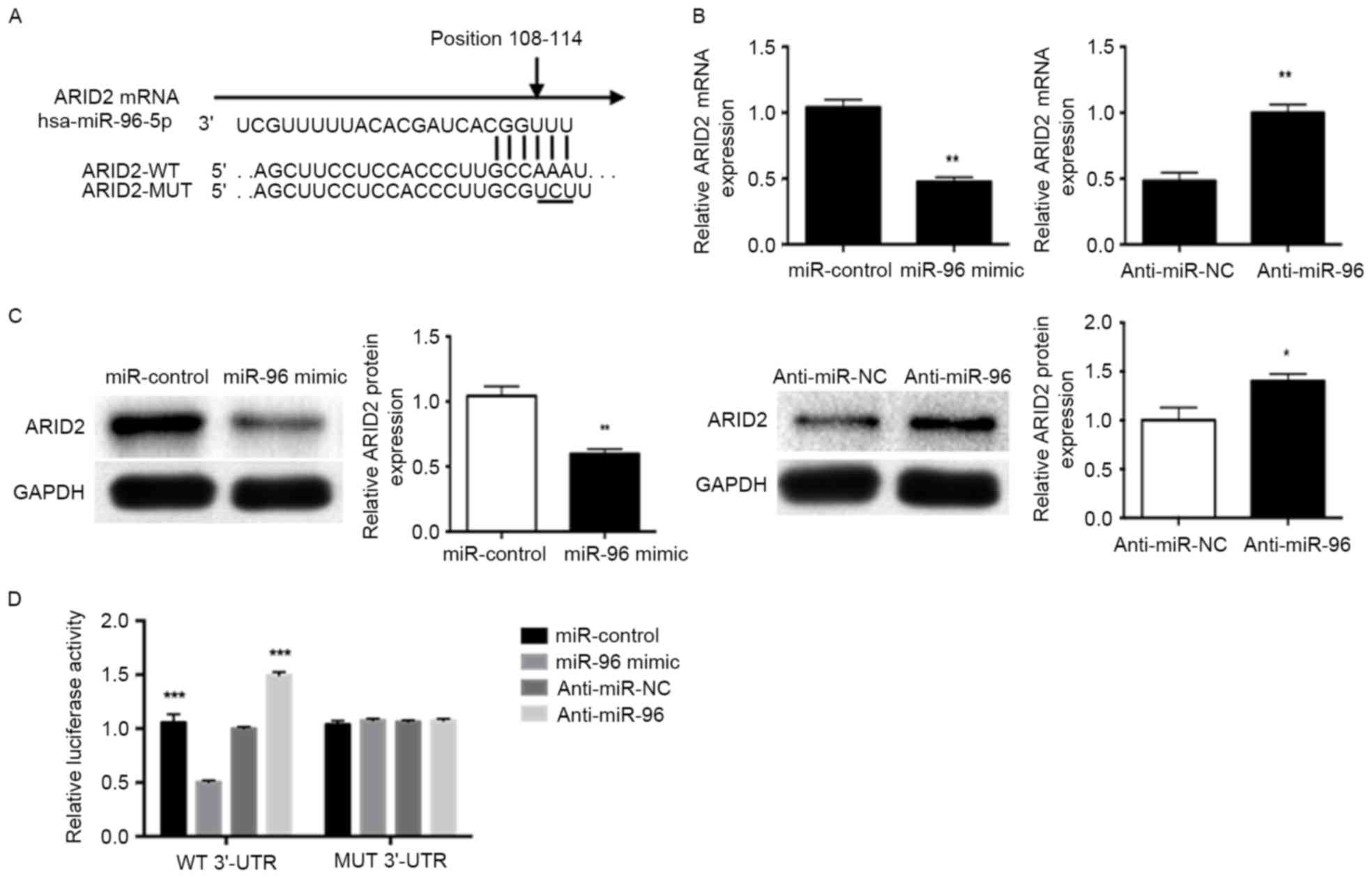
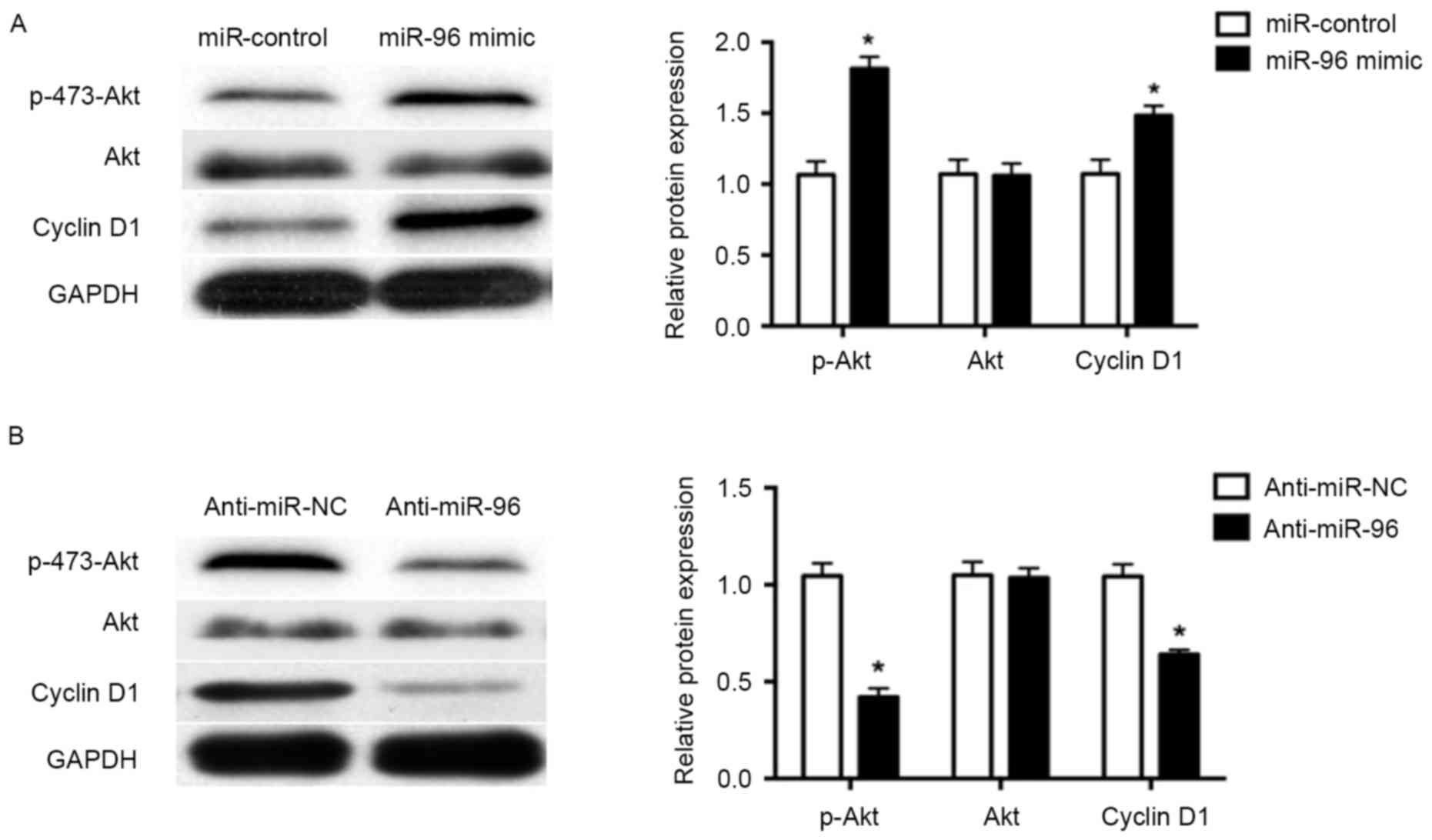
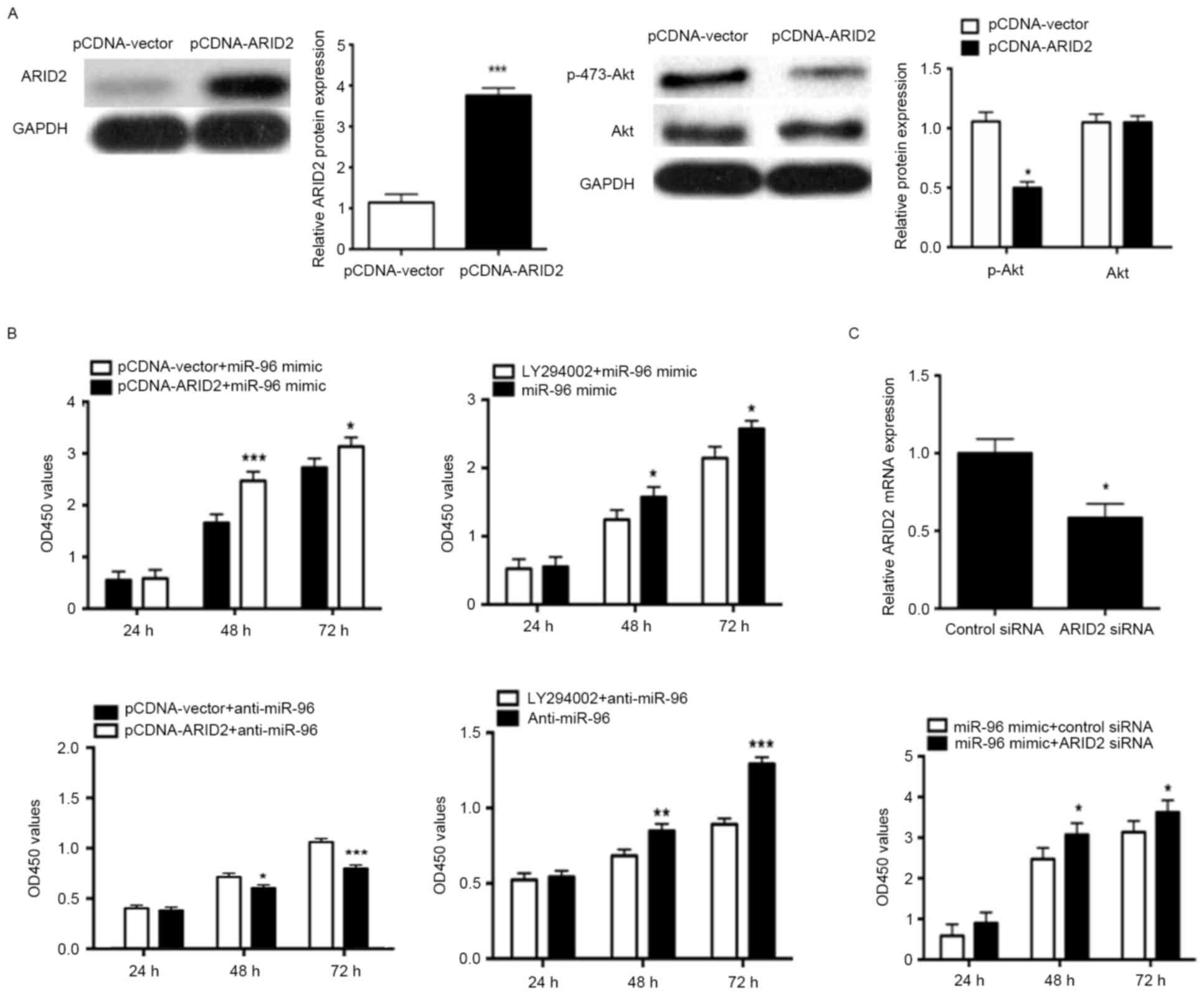
|
1
|
Feuerstein M, Marcus SC and Huang GD:
National trends in nonoperative care for nonspecific back pain.
Spine J. 4:56–63. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Katz JN: Lumbar disc disorders and
low-back pain: Socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint
Surg Am. 88 Suppl 2:S21–S24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lee HJ, Seo JC, Kwak MA, Park SH, Min BM,
Cho MS, Shin I, Jung JY and Roh WS: Acupuncture for low back pain
due to spondylolisthesis: Study protocol for a randomized
controlled pilot trial. Trials. 15:1052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Freemont TJ, LeMaitre C, Watkins A and
Hoyland JA: Degeneration of intervertebral discs: Current
understanding of cellular and molecular events, and implications
for novel therapies. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2001:1–10. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mooney V: The classification of low back
pain. Ann Med. 21:321–325. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Z, Liang J, Wu WK, Yu X, Yu J, Weng X
and Shen J: Leptin activates RhoA/ROCK pathway to induce
cytoskeleton remodeling in nucleus pulposus cells. Int J Mol Sci.
15:1176–1188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu G, Cao P, Chen H, Yuan W, Wang J and
Tang X: miR-27a regulates apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells by
targeting PI3K. PLoS One. 8:e752512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Z, Shen J, Wu WK, Yu X, Liang J, Qiu G
and Liu J: Leptin induces cyclin D1 expression and proliferation of
human nucleus pulposus cells via JAK/STAT, PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK
pathways. PLoS One. 7:e531762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Johnson WE, Eisenstein SM and Roberts S:
Cell cluster formation in degenerate lumbar intervertebral discs is
associated with increased disc cell proliferation. Connect Tissue
Res. 42:197–207. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu H, Huang X, Liu X, Xiao S, Zhang Y,
Xiang T, Shen X, Wang G and Sheng B: miR-21 promotes human nucleus
pulposus cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT signaling. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:4007–4018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brennecke J and Cohen SM: Towards a
complete description of the microRNA complement of animal genomes.
Genome Biol. 4:2282003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Soifer HS, Rossi JJ and Saetrom P:
microRNAs in disease and potential therapeutic applications. Mol
Ther. 15:2070–2079. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu X and Li Z: microRNAs regulate vascular
smooth muscle cell functions in atherosclerosis (review). Int J Mol
Med. 34:923–933. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: microRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li W, Wang P, Zhang Z, Wang W, Liu Y and
Qi Q: miR-184 regulates proliferation in nucleus pulposus cells by
targeting GAS1. World Neurosurg. 97:710–715.e1. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen B, Huang SG, Ju L, Li M, Nie FF,
Zhang Y, Zhang YH, Chen X and Gao F: Effect of microRNA-21 on the
proliferation of human degenerated nucleus pulposus by targeting
programmed cell death 4. Braz J Med Biol. 49:pii2016.
|
|
20
|
Jing W and Jiang W: microRNA-93 regulates
collagen loss by targeting MMP3 in human nucleus pulposus cells.
Cell Prolif. 48:284–292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamada Y, Enokida H, Kojima S, Kawakami K,
Chiyomaru T, Tatarano S, Yoshino H, Kawahara K, Nishiyama K, Seki N
and Nakagawa M: miR-96 and miR-183 detection in urine serve as
potential tumor markers of urothelial carcinoma: Correlation with
stage and grade, and comparison with urinary cytology. Cancer Sci.
102:522–529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu XM, Qian JC, Deng ZL, Cai Z, Tang T,
Wang P, Zhang KH and Cai JP: Expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-96
and miR-135b is correlated with the clinical parameters of
colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 4:339–345. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Y, Han Y, Zhang H, Nie L, Jiang Z, Fa
P, Gui Y and Cai Z: Synthetic miRNA-mowers targeting miR-183-96-182
cluster or miR-210 inhibit growth and migration and induce
apoptosis in bladder cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e522802012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M,
Hodler J and Boos N: Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
26:1873–1878. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Z, Shen J, Wu WK, Yu X, Liang J, Qiu G
and Liu J: The role of leptin on the organization and expression of
cytoskeleton elements in nucleus pulposus cells. J Orthop Res.
31:847–857. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–528. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu X, Liao W, Yuan Q, Ou Y and Huang J:
TTK activates Akt and promotes proliferation and migration of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 6:34309–34320.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang ZQ, Cai Q, Hu L, He CY, Li JF, Quan
ZW, Liu BY, Li C and Zhu ZG: Long noncoding RNA UCA1 induced by SP1
promotes cell proliferation via recruiting EZH2 and activating AKT
pathway in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 8:e28392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li J, Li P, Chen T, Gao G, Chen X, Du Y,
Zhang R, Yang R, Zhao W, Dun S, et al: Expression of microRNA-96
and its potential functions by targeting FOXO3 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:685–692. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Kong X, Li J, Luo Q, Li X, Shen
L, Chen L and Fang L: miR-96 promotes tumor proliferation and
invasion by targeting RECK in breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
31:1357–1363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu L, Pu X, Wang Q, Cao J, Xu F, Xu LI and
Li K: miR-96 induces cisplatin chemoresistance in non-small cell
lung cancer cells by downregulating SAMD9. Oncol Lett. 11:945–952.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xia H, Chen S, Chen K, Huang H and Ma H:
miR-96 promotes proliferation and chemo-or radioresistance by
down-regulating RECK in esophageal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
68:951–958. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu D, He X, Chang Y, Xu C, Jiang X, Sun S
and Lin J: Inhibition of miR-96 expression reduces cell
proliferation and clonogenicity of HepG2 hepatoma cells. Oncol Rep.
29:653–661. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cai P, Yang T, Jiang X, Zheng M, Xu G and
Xia J: Role of miR-15a in intervertebral disc degeneration through
targeting MAP3K9. Biomed Pharmacother. 87:568–574. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Lv G, Li J, Wang B, Zheng Q and Lu
C: LncRNA-RP11-296A18.3/miR-138/HIF1A pathway regulates the
proliferation ECM synthesis of human nucleus pulposus cells
(HNPCs). J Cell Biochem. May 24–2017.doi: 10.1002/jcb.26166. (Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
36
|
Li Z, Yu X, Shen J, Chan MT and Wu WK:
microRNA in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif.
48:278–283. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Madden HP, Breslin RJ, Wasserkrug HL,
Efron G and Barbul A: Stimulation of T cell immunity by arginine
enhances survival in peritonitis. J Surg Res. 44:658–663. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu P, Wu D, You Y, Sun J, Lu L, Tan J and
Bie P: miR-208-3p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell
proliferation and invasion through regulating ARID2 expression. Exp
Cell Res. 336:232–241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang L, Wang W, Li X, He S, Yao J, Wang
X, Zhang D and Sun X: microRNA-155 promotes tumor growth of human
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting ARID2. Int J Oncol.
48:2425–2434. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Aso T, Uozaki H, Morita S, Kumagai A and
Watanabe M: Loss of ARID1A, ARID1B, and ARID2 expression during
progression of gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 35:6819–6827.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Duan Y, Tian L, Gao Q, Liang L, Zhang W,
Yang Y, Zheng Y, Pan E, Li S and Tang N: Chromatin remodeling gene
ARID2 targets cyclin D1 and cyclin E1 to suppress hepatoma cell
progression. Oncotarget. 7:45863–45875. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|