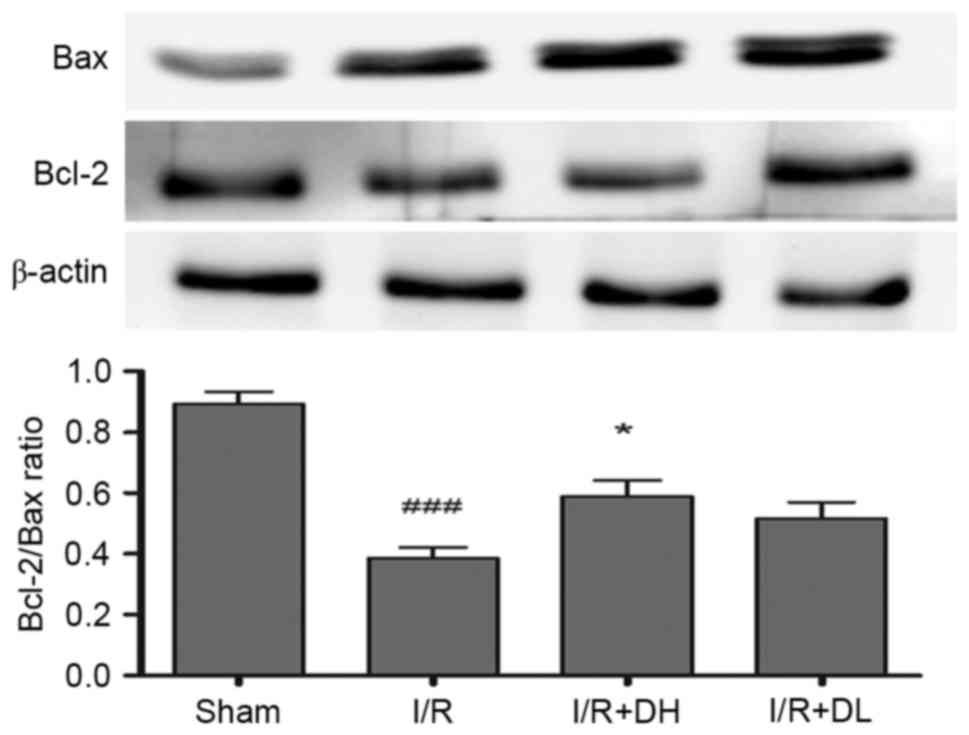
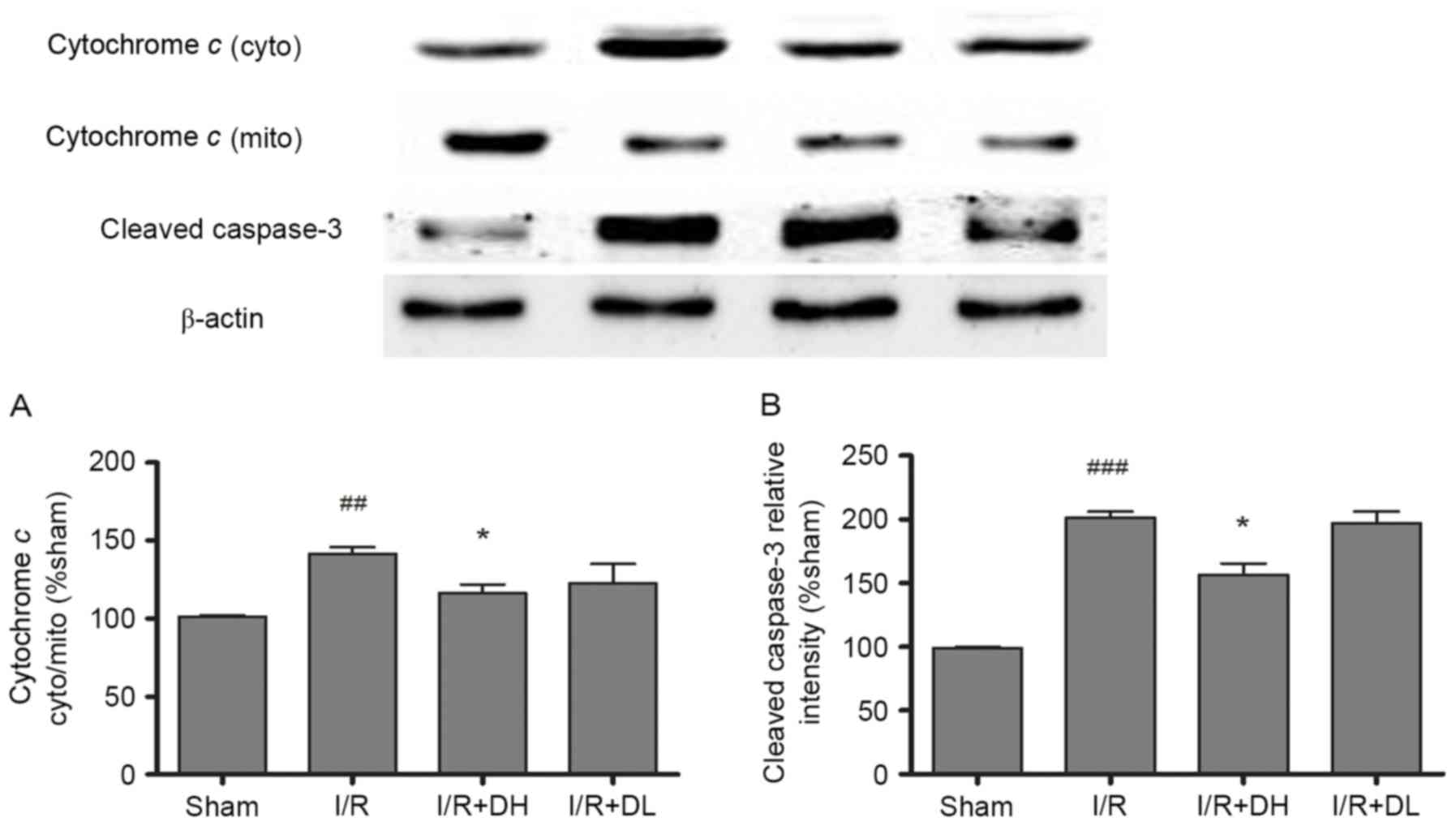
|
1
|
Abramov AY, Scorziello A and Duchen MR:
Three distinct mechanisms generate oxygen free radicals in neurons
and contribute to cell death during anoxia and reoxygenation. J
Neurosci. 27:1129–1138. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marlangue C Charriaut, Remolleau S,
Zouaoui D Aggoun and Ben-Ari Y: Apoptosis and programmed cell
death: A role in cerebral ischemia. Biomed Pharmacother.
52:264–269. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chan PH: Reactive oxygen radicals in
signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 21:2–14. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Allen CL and Bayraktutan U: Oxidative
stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int J
Stroke. 4:461–470. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Egleton RD and Davis TP: Bioavailability
and transport of peptides and peptide drugs into the brain.
Peptides. 18:1431–1439. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Navaratna D, Guo S, Arai K and Lo EH:
Mechanisms and targets for angiogenic therapy after stroke. Cell
Adh Migr. 3:216–223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dong QG, Zhang Y, Wang MS, Feng J, Zhang
HH, Wu YG, Gu TJ, Yu XH, Jiang CL, Chen Y, et al: Improvement of
enzymatic stability and intestinal permeability of
deuterohemin-peptide conjugates by specific multi-site
N-methylation. Amino Acids. 43:2431–2441. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang H, Sun Y, Guo W, Fang C, Fawcett JP,
Li W, Gao Y, Yang Y and Gu J: Determination of a
deuterohemin-peptide conjugate in rat plasma by liquid
chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and application to a
preclinical pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 98:401–406.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang L, Li P, Wang G, Guan S, Sun X and
Wang L: DhHP-6 extends lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by
enhancing nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity of
DAF-16. Free Radic Res. 47:316–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guan S, Li P, Luo J, Li Y, Huang L, Wang
G, Zhu L, Fan H, Li W and Wang L: A deuterohemin peptide extends
lifespan and increases stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Free Radic Res. 44:813–820. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xue H, Ji Y, Wei S, Yu Y, Yan X, Liu S,
Zhang M, Yao F, Lan X and Chen L: HGSD attenuates neuronal
apoptosis through enhancing neuronal autophagy in the brain of
diabetic mice: The role of AMP-activated protein kinase. Life Sci.
153:23–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yenari MA, Xu L, Tang XN, Qiao Y and
Giffard RG: Microglia potentiate damage to blood-brain barrier
constituents: Improvement by minocycline in vivo and in vitro.
Stroke. 37:1087–1093. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang N, Zhang Y, Wu L, Wang Y, Cao Y, He
L, Li X and Zhao J: Puerarin protected the brain from cerebral
ischemia injury via astrocyte apoptosis inhibition.
Neuropharmacology. 79:282–289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang D, Yuan X, Liu T, Liu L, Hu Y, Wang Z
and Zheng Q: Neuroprotective activity of lavender oil on transient
focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Molecules. 17:9803–9817. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kwon SH, Hong SI, Kim JA, Jung YH, Kim SY,
Kim HC, Lee SY and Jang CG: The neuroprotective effects of Lonicera
japonica THUNB. against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis via
phosphorylation of MAPKs and PI3K/Akt in SH-SY5Y cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 49:1011–1019. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu SM and Kim SJ: Thymoquinone-induced
reactive oxygen species causes apoptosis of chondrocytes via
PI3K/Akt and p38kinase pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
238:811–820. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim DW, Jeong HJ, Kang HW, Shin MJ, Sohn
EJ, Kim MJ, Ahn EH, An JJ, Jang SH, Yoo KY, et al: Transduced human
PEP-1-catalase fusion protein attenuates ischemic neuronal damage.
Free Radic Biol Med. 47:941–952. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan R, Rong Z, She Y, Cao Y, Chang LW and
Lee WH: Sodium pyruvate reduced hypoxic-ischemic injury to neonatal
rat brain. Pediatr Res. 72:479–489. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang F, Wang S, Signore AP and Chen J:
Neuroprotective effects of leptin against ischemic injury induced
by oxygen-glucose deprivation and transient cerebral ischemia.
Stroke. 38:2329–2336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chan PH: Role of oxidants in ischemic
brain damage. Stroke. 27:1124–1129. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Keller JN, Kindy MS, Holtsberg FW, St
Clair DK, Yen HC, Germeyer A, Steiner SM, Bruce-Keller AJ, Hutchins
JB and Mattson MP: Mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase
prevents neural apoptosis and reduces ischemic brain injury:
Suppression of peroxynitrite production, lipid peroxidation, and
mitochondrial dysfunction. J Neurosci. 18:687–697. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ryter SW, Kim HP, Hoetzel A, Park JW,
Nakahira K, Wang X and Choi AM: Mechanisms of cell death
inoxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:49–89. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Namura S, Zhu J, Fink K, Endres M,
Srinivasan A, Tomaselli KJ, Yuan J and Moskowitz MA: Activation and
cleavage of caspase-3 in apoptosis induced by experimental cerebral
ischemia. J NeuroSci. 18:3659–3668. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen
GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S and Reed JC: Regulation of
cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science.
282:1318–1321. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xing Y, Zhang X, Zhao K, Cui L, Wang L,
Dong L, Li Y, Liu Z, Wang C, Zhang X, et al: Beneficial effects of
sulindac in focal cerebral ischemia: A positive role in
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Brain Res. 1482:71–80. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoshida H, Kong YY, Yoshida R, Elia AJ,
Hakem A, Hakem R, Penninger JM and Mak TW: Apaf1 is required for
mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and brain development. Cell.
94:739–750. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
González-Sarrías A, Núñez-Sánchez MÁ,
Tomás-Barberán FA and Espín JC: Neuroprotective effects of
bioavailable polyphenol-derived metabolites against oxidative
stress-induced cytotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. J
Agric Food Chem. 65:752–758. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li F, Omori N, Jin G, Wang SJ, Sato K,
Nagano I, Shoji M and Abe K: Cooperative expression of survival
p-ERK and p-Akt signals in rat brain neurons after transient MCAO.
Brain Res. 962:21–26. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Friguls B, Justicia C, Pallàs M and Planas
AM: Focal cerebischemia causes two temporal waves of Akt
activation. Neuroreport. 12:3381–3384. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun B, Feng M, Tian X, Lu X, Zhang Y, Ke
X, Huang S, Cao J and Ding X: DL-3-n-Butylphthalide protects rat
bone marrow stem cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death
through antioxidation and activation of PI3K-Akt pathway. Neurosci
Lett. 516:247–252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|