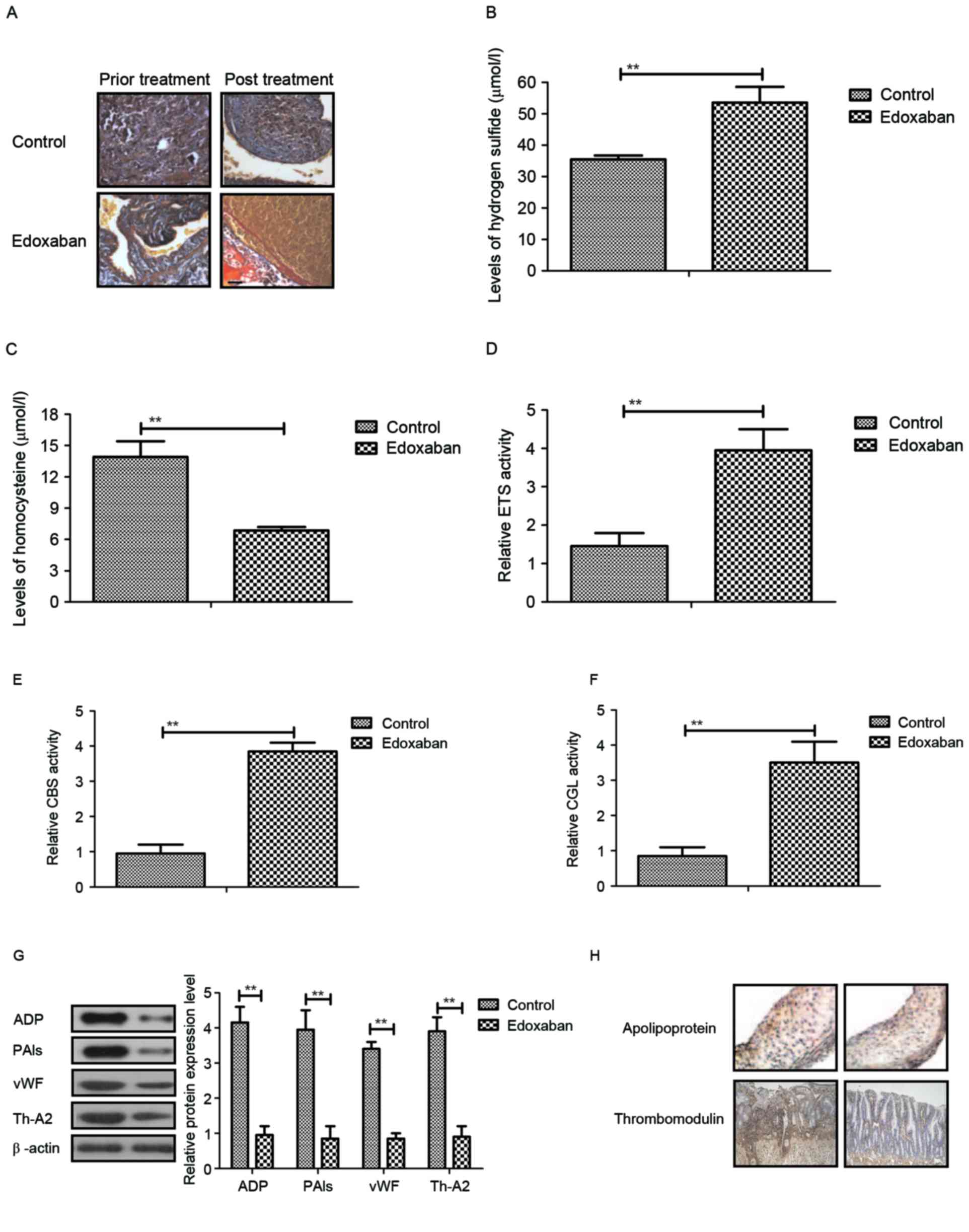
|
1
|
Shlebak A: Antiphospholipid syndrome
presenting as cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A case series and a
review. J Clin Pathol. 69:337–343. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Samos M, Bolek T, Ivanková J, Stančiaková
L, Kovář F, Galajda P, Kubisz P, Staško J and Mokáň M: Heparin
induced thrombocytopenia presenting with deep venous thrombosis and
pulmonary embolism successfully treated with rivaroxaban: Clinical
case report and review of current experiences. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 68:391–394. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jaqua NT, Stratton A, Yaccobe L, Tahir U,
Kenny P and Kerns T: A review of the literature on three
extraintestinal complications of ulcerative colitis: An ulcerative
colitis flare complicated by Budd-Chiari syndrome, cerebral venous
thrombosis and idiopathic thrombocytopenia. Acta Gastroenterol
Belg. 76:311–316. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barco S, Atema JJ, Coppens M, Serlie MJ
and Middeldorp S: Anticoagulants for the prevention and treatment
of catheter-related thrombosis in adults and children on parenteral
nutrition: A systematic review and critical appraisal. Blood
Transfus. 15:369–377. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hawbaker S: Venous thromboembolism in the
cancer population: Pathology, risk, and prevention. J Adv Pract
Oncol. 3:23–33. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vitale C, D'Amato M, Calabrò P, Stanziola
AA, Mormile M and Molino A: Venous thromboembolism and lung cancer:
A review. Multidiscip Respir Med. 10:282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ungprasert P, Tanratana P and Srivali N:
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia and venous thromboembolism: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Res. 136:1013–1017.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fernandez MM, Hogue S, Preblick R and
Kwong WJ: Review of the cost of venous thromboembolism. Clinicoecon
Outcomes Res. 7:451–462. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Corral J, Huntington JA, González-Conejero
R, Mushunje A, Navarro M, Marco P, Vicente V and Carrell RW:
Mutations in the shutter region of antithrombin result in formation
of disulfide-linked dimers and severe venous thrombosis. J Thromb
Haemost. 2:931–939. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vaya A, Gómez I, Mira Y, Ferrando F and
Corella D: Homocysteine levels in patients with deep vein
thrombosis lacking thrombophilic defects. Thromb Haemost.
99:1132–1134. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xue M, Yin H, Zhang L, Guo C, Jiang Y, Wu
C, Li X and Chen K: Dynamic expression of the main related
indicators of thrombosis, inflammatory reaction and tissue damage
in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Mol Med Rep. 4:693–696.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cao H, Zhang L, Sun ZB, Cheng XH, Zhang Y
and Zou HB: Salvia miltiorrhiza prevents deep vein thrombosis via
antioxidative effects in endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep.
11:3593–3600. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li G, Han ZL, Dong HG, Zhang X, Kong XQ
and Jin X: Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 gene
125C/G polymorphism is associated with deep vein thrombosis. Mol
Med Rep. 12:2203–2210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ye S, Mao B, Yang L, Fu W and Hou J:
Thrombosis recanalization by paeoniflorin through the upregulation
of urokinase-type plasminogen activator via the MAPK signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 13:4593–4598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Emerson M: Hydrogen sulfide and platelets:
A possible role in thrombosis. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 230:153–162.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ghaznavi H, Soheili Z, Samiei S and
Soltanpour MS: Plasma homocysteine levels, methylene
tetrahydrofolate reductase A1298C gene polymorphism and risk of
retinal vein thrombosis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 27:679–683.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qin YR, You SJ, Zhang Y, Li Q, Wang XH,
Wang F, Hu LF and Liu CF: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates ferric
chloride-induced arterial thrombosis in rats. Free Radic Res.
50:654–665. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ekim M, Ekim H, Yilmaz YK, Kulah B, Polat
MF and Gocmen AY: Study on relationships among deep vein
thrombosis, homocysteine and related B group vitamins. Pak J Med
Sci. 31:398–402. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fay WP: Homocysteine and thrombosis: Guilt
by association? Blood. 119:2977–2978. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Di Minno MN, Tremoli E, Coppola A, Lupoli
R and Di Minno G: Homocysteine and arterial thrombosis: Challenge
and opportunity. Thromb Haemost. 103:942–961. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mahadeo KM, Dhall G, Panigrahy A, Lastra C
and Ettinger LJ: Subacute methotrexate neurotoxicity and cerebral
venous sinus thrombosis in a 12-year-old with acute lymphoblastic
leukemia and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T
polymorphism: Homocysteine-mediated methotrexate neurotoxicity via
direct endothelial injury. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 27:46–52. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ravari H, Zafarghandi MR, Alvandfar D and
Saadat S: Serum homocysteine in deep venous thrombosis, peripheral
atherosclerosis and healthy Iranians: A case-control study. Pak J
Biol Sci. 12:1019–1024. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Loscalzo J: Homocysteine-mediated
thrombosis and angiostasis in vascular pathobiology. J Clin Invest.
119:3203–3205. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Srivastava AK, Kalita J, Haris M, Gupta RK
and Misra UK: Radiological and histological changes following
cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in a rat model. Neurosci Res.
65:343–346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weeks CL, Singh S, Madzelan P, Banerjee R
and Spiro TG: Heme regulation of human cystathionine beta-synthase
activity: Insights from fluorescence and Raman spectroscopy. J Am
Chem Soc. 131:12809–12816. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cai J, Shi X, Wang H, Fan J, Feng Y, Lin
X, Yang J, Cui Q, Tang C, Xu G and Geng B: Cystathionine γ
lyase-hydrogen sulfide increases peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor γ activity by sulfhydration at C139 site thereby promoting
glucose uptake and lipid storage in adipocytes. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1861:419–429. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pan EY and Sobieraj DM: Considerations for
prescribing target-specific oral anticoagulants in the setting of
renal dysfunction or drug interactions. Conn Med. 80:105–111.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Senger S, Keiner D, Hendrix P and Oertel
J: New target-specific oral anticoagulants and intracranial
bleeding: Management and outcome in a Single-Center case series.
World Neurosurg. 88:132–139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kundu A, Sen P, Sardar P, Chatterjee S,
Kapoor A and McManus DD: Intracranial hemorrhage with target
specific oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation:
An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J
Cardiol. 203:1000–1002. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hurst KV, O'Callaghan JM and Handa A: Risk
impact of edoxaban in the management of stroke and venous
thromboembolism. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 12:329–335. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Partida RA and Giugliano RP: Edoxaban:
Pharmacological principles, preclinical and early-phase clinical
testing. Future Cardiol. 7:459–470. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu XQ, Liu XQ, Jiang P, Huang H and Yan
Y: Plasma levels of endogenous hydrogen sulfide and homocysteine in
patients with Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia and the
significance thereof. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 88:2246–2249.
2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Obeid OA, Johnston K and Emery PW: Plasma
taurine and cysteine levels following an oral methionine load:
Relationship with coronary heart disease. Eur J Clin Nutr.
58:105–109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Klerk M, Lievers KJ, Kluijtmans LA, Blom
HJ, den Heijer M, Schouten EG, Kok FJ and Verhoef P: The 2756A>G
variant in the gene encoding methionine synthase: Its relation with
plasma homocysteine levels and risk of coronary heart disease in a
Dutch case-control study. Thromb Res. 110:87–91. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tohti I, Tursun M, Umar A, Turdi S, Imin H
and Moore N: Aqueous extracts of Ocimum basilicum L. (sweet basil)
decrease platelet aggregation induced by ADP and thrombin in vitro
and rats Arterio-venous shunt thrombosis in vivo. Thromb Res.
118:733–739. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang L, Du JR, Wang J, Yu DK, Chen YS, He
Y and Wang CY: Z-ligustilide extracted from Radix Angelica sinensis
decreased platelet aggregation induced by ADP ex vivo and
Arterio-venous shunt thrombosis in vivo in rats. Yakugaku Zasshi.
129:855–859. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bernat A, Vallee E, Maffrand JP and Gordon
JL: The role of platelets and ADP in experimental thrombosis
induced by venous stasis in the rat. Thromb Res. 52:65–70. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Krleza J Lenicek, Jakovljevic G, Bronic A,
Herak D Coen, Bonevski A, Stepan-Giljevic J and Roic G:
Contraception-related deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
in a 17-year-old girl heterozygous for factor V leiden, prothrombin
G20210A mutation, MTHFR C677T and homozygous for PAI-1 mutation:
Report of a family with multiple genetic risk factors and review of
the literature. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 37:24–29. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kazanci S Yaroglu, Yesilbas O, Ersoy M,
Kihtir HS, Yildirim HM and Sevketoglu E: Cerebral infarction and
femoral venous thrombosis detected in a patient with diabetic
ketoacidosis and heterozygous factor V Leiden G1691A and PAI-1
4G/5G mutations. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 28:1183–1186.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bittar LF, de Paula EV, Mello TB, Siqueira
LH, Orsi FL and Annichino-Bizzacchi JM: Polymorphisms and mutations
in vWF and ADAMTS13 genes and their correlation with plasma levels
of FVIII and vWF in patients with deep venous thrombosis. Clin Appl
Thromb Hemost. 17:514–518. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tarantino E, Amadio P, Squellerio I, Porro
B, Sandrini L, Turnu L, Cavalca V, Tremoli E and Barbieri SS: Role
of thromboxane-dependent platelet activation in venous thrombosis:
Aspirin effects in mouse model. Pharmacol Res. 107:415–425. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang XP, Ding H, Lu JD, Tang YH, Deng BX
and Deng CQ: Autophagy in cerebral ischemia and the effects of
traditional Chinese medicine. J Integr Med. 13:289–296. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Guidetti GF, Canobbio I and Torti M:
PI3K/Akt in platelet integrin signaling and implications in
thrombosis. Adv Biol Regul. 59:36–52. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Su W, Chen Y, Wang C, Ding X, Rwibasira G
and Kong Y: Human cathelicidin LL-37 inhibits platelet aggregation
and thrombosis via Src/PI3K/Akt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 473:283–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
McFadyen J and Peter K: Forget about
thrombosis: Platelets and Alzheimer's disease, yet another sticky
situation. Sci Signal. 9:fs92016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|