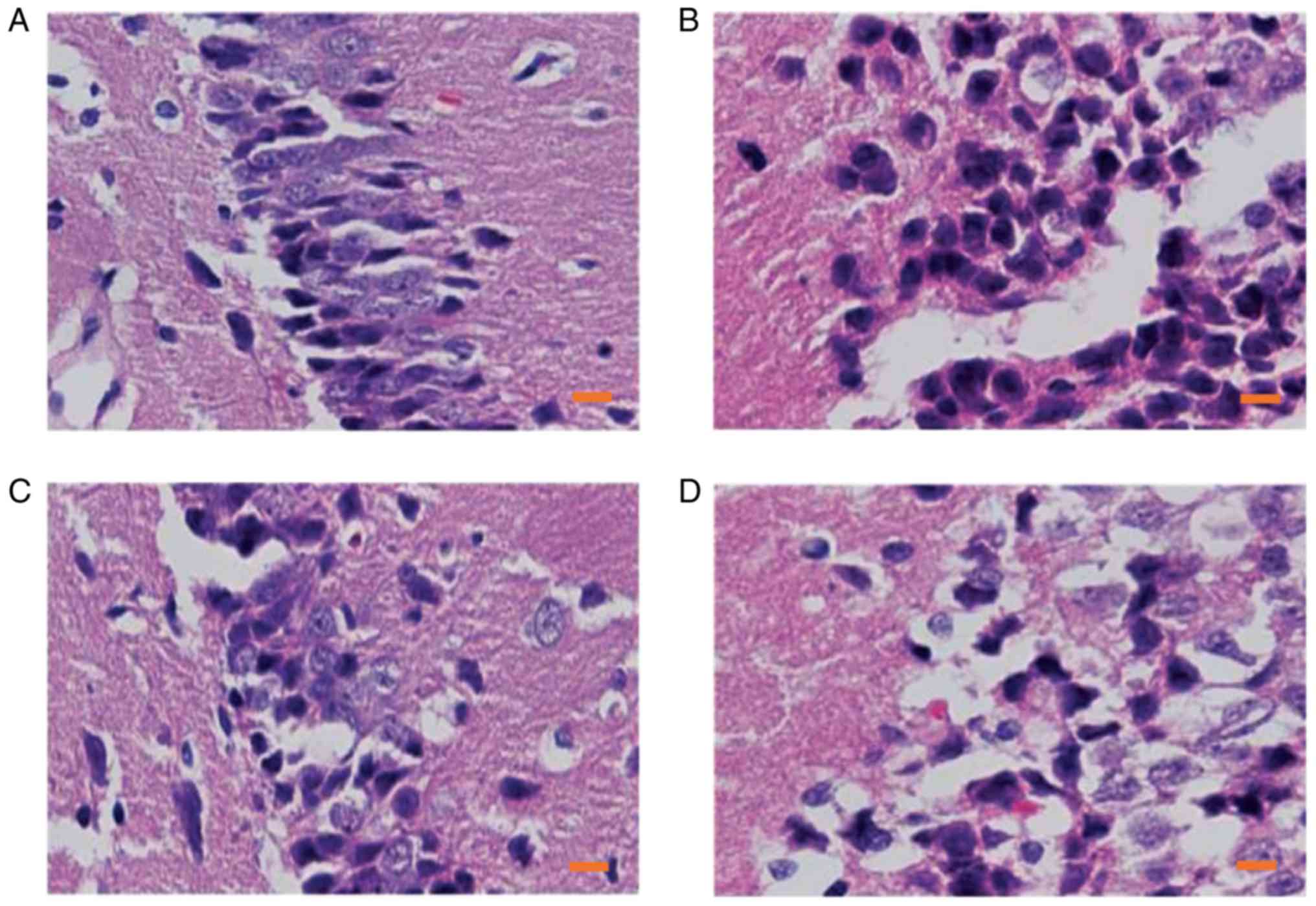
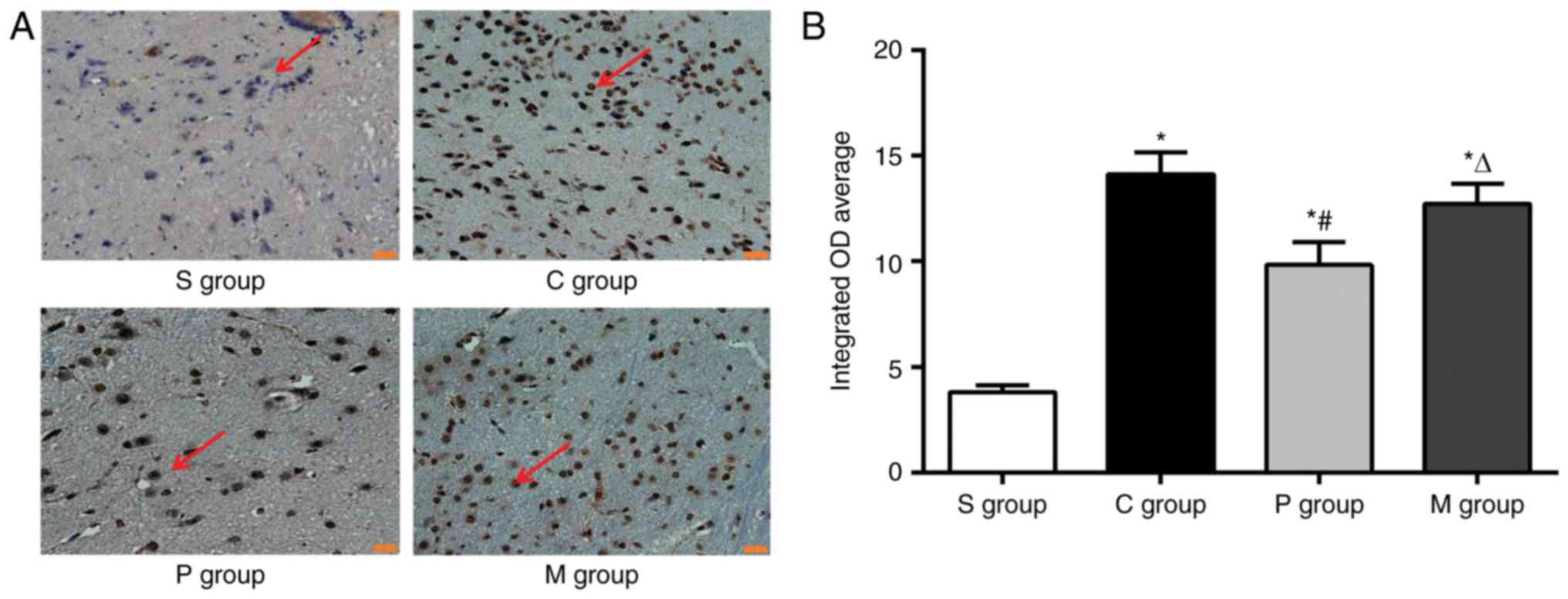
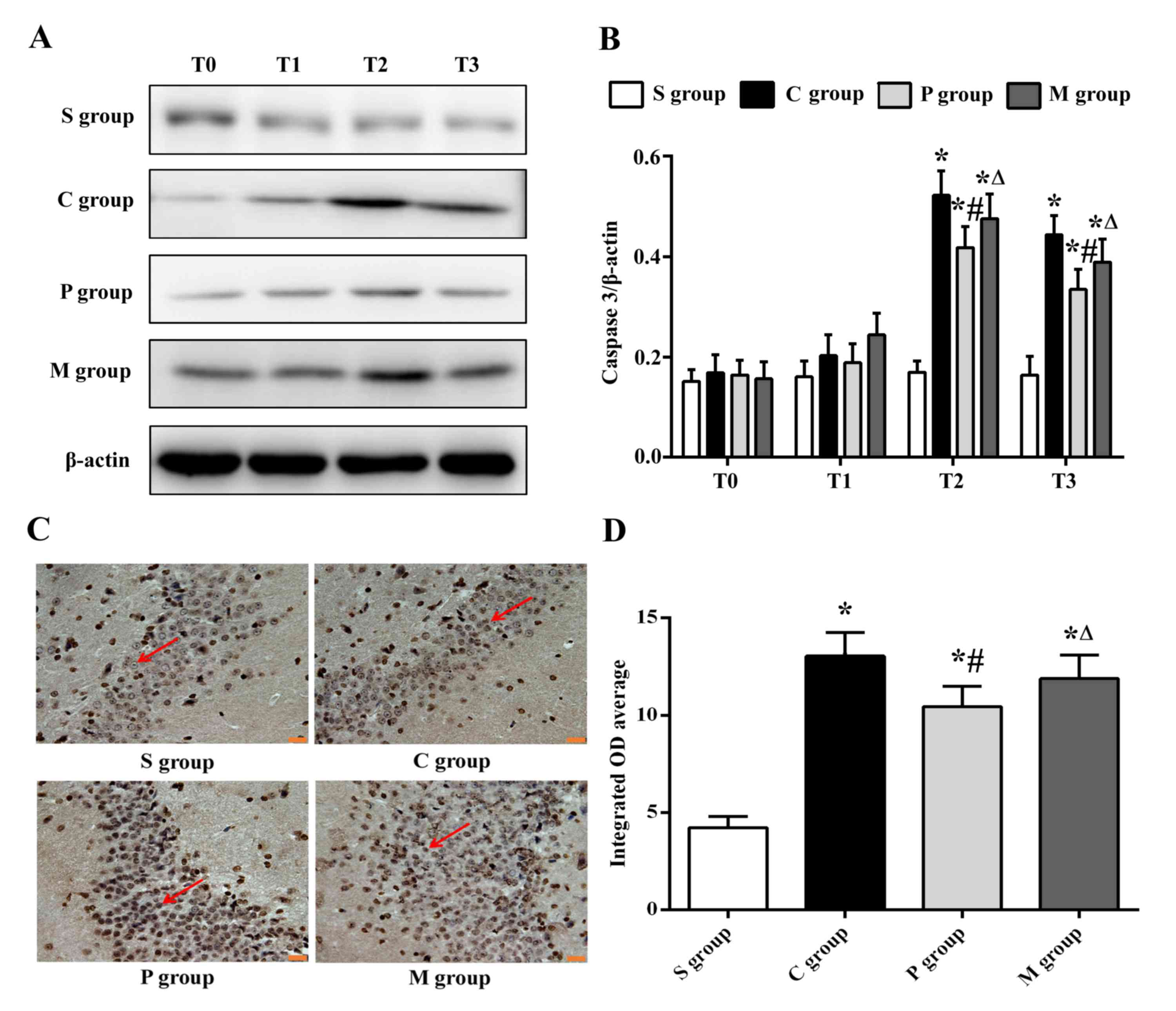
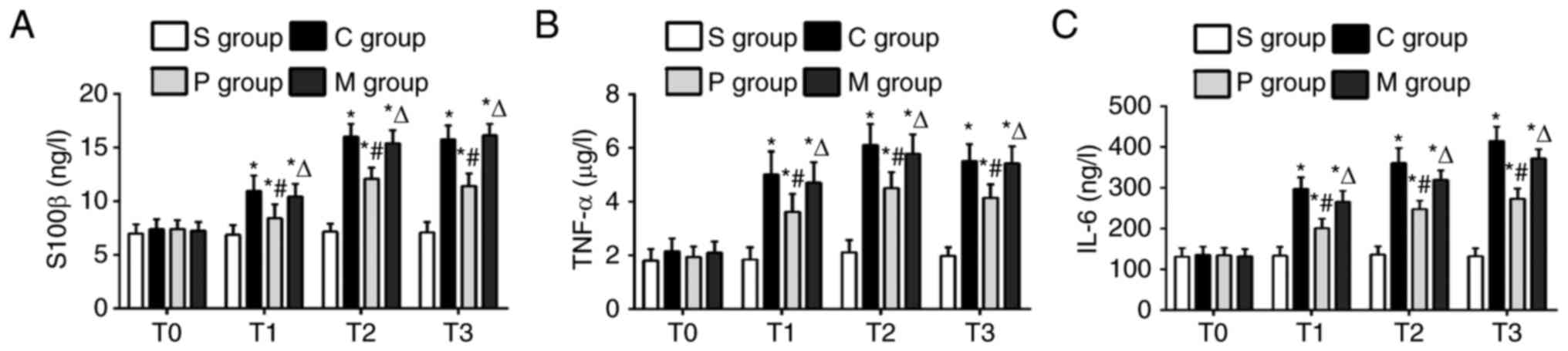
|
1
|
Salameh A and Dhein S: Strategies for
pharmacological organoprotection during extracorporeal circulation
targeting ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Pharmacol. 6:2962015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roach GW, Kanchuger M, Mangano CM, Newman
M, Nussmeier N, Wolman R, Aggarwal A, Marschall K, Graham SH and
Ley C: Adverse cerebral outcomes after coronary bypass surgery.
Multicenter study of perioperative ischemia research group and the
ischemia research and education foundation investigators. N Engl J
Med. 335:1857–1863. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van Harten AE, Scheeren TW and Absalom AR:
A review of postoperative cognitive dysfunction and
neuroinflammation associated with cardiac surgery and anaesthesia.
Anaesthesia. 67:280–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cao HJ, Sun YJ, Zhang TZ, Zhou J and Diao
YG: Penehyclidine hydrochloride attenuates the cerebral injury in a
rat model of cardiopulmonary bypass. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
91:521–527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Evora PR, Bottura C, Arcêncio L,
Albuquerque AA, Evora PM and Rodrigues AJ: Key Points for curbing
cardiopulmonary bypass inflammation. Acta Cir Bras. 31 Suppl
1:S45–S52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ouk T, Amr G, Azzaoui R, Delassus L,
Fossaert E, Tailleux A, Bordet R and Modine T: Lipid-lowering drugs
prevent neurovascular and cognitive consequences of cardiopulmonary
bypass. Vascul Pharmacol. 80:59–66. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou J, Zhou N, Wu XN, Cao HJ, Sun YJ,
Zhang TZ, Chen KY and Yu DM: Role of the Toll-like receptor 3
signaling pathway in the neuroprotective effect of sevoflurane
pre-conditioning during cardiopulmonary bypass in rats. Mol Med
Rep. 12:7859–7868. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang X, Xue Q, Yan F, Li L, Liu J, Li S
and Hu S: Ulinastatin as a neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory
agent in infant piglets model undergoing surgery on hypothermic
low-flow cardiopulmonary bypass. Paediatr Anaesth. 23:209–216.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H,
Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW and Tracey
KJ: Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory
response to endotoxin. Nature. 405:458–462. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ulloa L: The vagus nerve and the nicotinic
anti-inflammatory pathway. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:673–684. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu JS, Wei XD, Lu ZB, Xie P, Zhou HL,
Chen YY, Ma JM and Yu LZ: Liang-Ge-San, a classic traditional
Chinese medicine formula, protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through cholinergic
anti-inflammatory pathway. Oncotarget. 7:21222–21234. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng Z, Li-Sha G, Jing-Lin Z, Wen-Wu Z,
Xue-Si C, Xing-Xing C and Yue-Chun L: Protective role of the
cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in a mouse model of viral
myocarditis. PLoS One. 9:e1127192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Koopman FA, Vosters JL, Roescher N,
Broekstra N, Tak PP and Vervoordeldonk MJ: Cholinergic
anti-inflammatory pathway in the non-obese diabetic mouse model.
Oral Dis. 21:858–865. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang Y, Li L, Liu B, Zhang Y, Chen Q and
Li C: Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates cerebral ischemia and
reperfusion injury via endogenous cholinergic pathway in rat. PLoS
One. 9:e1023422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Terrando N, Yang T, Ryu JK, Newton PT,
Monaco C, Feldmann M, Ma D, Akassoglou K and Maze M: Stimulation of
the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor protects against
neuroinflammation after tibia fracture and endotoxemia in mice. Mol
Med. 20:667–675. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han Z, Shen F, He Y, Degos V, Camus M,
Maze M, Young WL and Su H: Activation of α-7 nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor reduces ischemic stroke injury through
reduction of pro-inflammatory macrophages and oxidative stress.
PLoS One. 9:e1057112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su X, Matthay MA and Malik AB: Requisite
role of the cholinergic alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
pathway in suppressing Gram-negative sepsis-induced acute lung
inflammatory injury. J Immunol. 184:401–410. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Terrando N, Eriksson LI, Ryu JK, Yang T,
Monaco C, Feldmann M, Fagerlund M Jonsson, Charo IF, Akassoglou K
and Maze M: Resolving postoperative neuroinflammation and cognitive
decline. Ann Neurol. 70:986–995. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Duris K, Manaenko A, Suzuki H, Rolland WB,
Krafft PR and Zhang JH: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist
PNU-282987 attenuates early brain injury in a perforation model of
subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke. 42:3530–3536. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McComb S, Mulligan R and Sad S: Caspase-3
is transiently activated without cell death during early antigen
driven expansion of CD8(+) T cells in vivo. PLoS One. 5:e153282010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang G, Fang H, Zhen Y, Xu G, Tian J,
Zhang Y, Zhang D, Zhang G, Xu J, Zhang Z, et al: Sulforaphane
prevents neuronal apoptosis and memory impairment in diabetic rats.
Cell Physiol Bioche. 39:901–907. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Salazar JD, Wityk RJ, Grega MA, Borowicz
LM, Doty JR, Petrofski JA and Baumgartner WA: Stroke after cardiac
surgery: Short- and long-term outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg.
72:1195–1202. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vedel AG, Holmgaard F, Rasmussen LS,
Paulson OB, Thomsen C, Danielsen ER, Langkilde A, Goetze JP, Lange
T, Ravn HB and Nilsson JC: Perfusion Pressure Cerebral Infarct
(PPCI) trial-the importance of mean arterial pressure during
cardiopulmonary bypass to prevent cerebral complications after
cardiac surgery: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.
Trials. 17:2472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han Z, Li L, Wang L, Degos V, Maze M and
Su H: Alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist treatment
reduces neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and brain injury in
mice with ischemic stroke and bone fracture. J Neurochem.
131:498–508. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li YP, Huang J, Huang SG, Xu YG, Xu YY,
Liao JY, Feng X, Zhang XG, Wang JH and Wang J: The compromised
inflammatory response to bacterial components after pediatric
cardiac surgery is associated with cardiopulmonary
bypass-suppressed Toll-like receptor signal transduction pathways.
J Crit Care. 29:312.e7–e13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yuan SM: S100 and S100β: Biomarkers of
cerebral damage in cardiac surgery with or without the use of
cardiopulmonary bypass. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 29:630–641.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Einav S, Shoshan Y, Ovadia H, Matot I,
Hersch M and Itshayek E: Early postoperative serum S100 beta levels
predict ongoing brain damage after meningioma surgery: A
prospective observational study. Crit Care. 10:R1412006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Zhang B, Yu JY, Liu LQ, Peng L, Chi F, Wu
CH, Jong A, Wang SF, Cao H and Huang SH: Alpha7 nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor is required for blood-brain barrier
injury-related CNS disorders caused by Cryptococcus neoformans and
HIV-1 associated comorbidity factors. Bmc Infect Dis. 15:3522015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chugani HT: Biological basis of emotions:
Brain systems and brain development. Pediatrics. 102(5 Suppl E):
S1225–S1229. 1998.
|
|
30
|
Zhu YM, Wang CC, Chen L, Qian LB, Ma LL,
Yu J, Zhu MH, Wen CY, Yu LN and Yan M: Both PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2
pathways participate in the protection by dexmedetomidine against
transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain
Res. 1494:1–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang HY, Zhang X, Wang ZG, Shi HX, Wu FZ,
Lin BB, Xu XL, Wang XJ, Fu XB, Li ZY, et al: Exogenous basic
fibroblast growth factor inhibits ER stress-induced apoptosis and
improves recovery from spinal cord injury. CNS Neurosci Ther.
19:20–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Krafft PR, Altay O, Rolland WB, Duris K,
Lekic T, Tang J and Zhang JH: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
agonism confers neuroprotection through GSK-3β inhibition in a
mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 43:844–850. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dong M, Hu N, Hua Y, Xu X, Kandadi MR, Guo
R, Jiang S, Nair S, Hu D and Ren J: Chronic Akt activation
attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction via
Akt/GSK3β-dependent inhibition of apoptosis and ER stress. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1832:848–863. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pan JJ, Chang QS, Wang X, Son YO, Liu J,
Zhang Z, Bi YY and Shi X: Activation of Akt/GSK3β and Akt/Bcl-2
signaling pathways in nickel-transformed BEAS-2B cells. Int J
Oncol. 39:1285–1294. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hong Y, Shao A, Wang J, Chen S, Wu H,
McBride DW, Wu Q, Sun X and Zhang J: Neuroprotective effect of
hydrogen-rich saline against neurologic damage and apoptosis in
early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage: Possible role
of the Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway. PLoS One. 9:e962122014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|