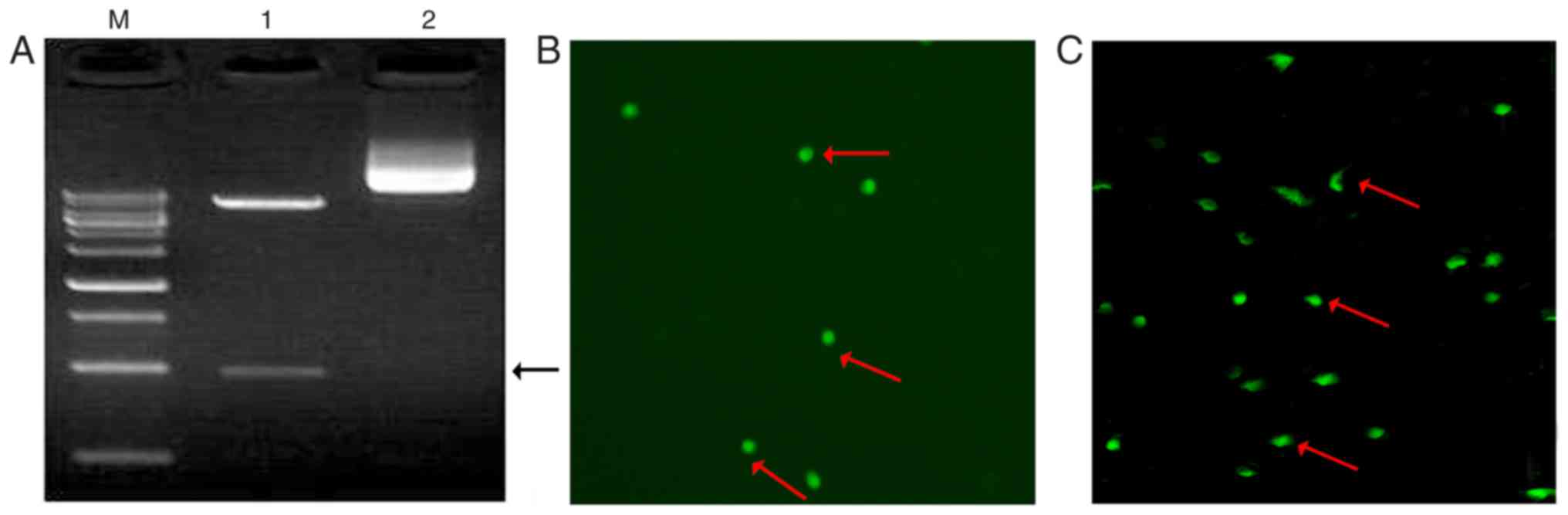
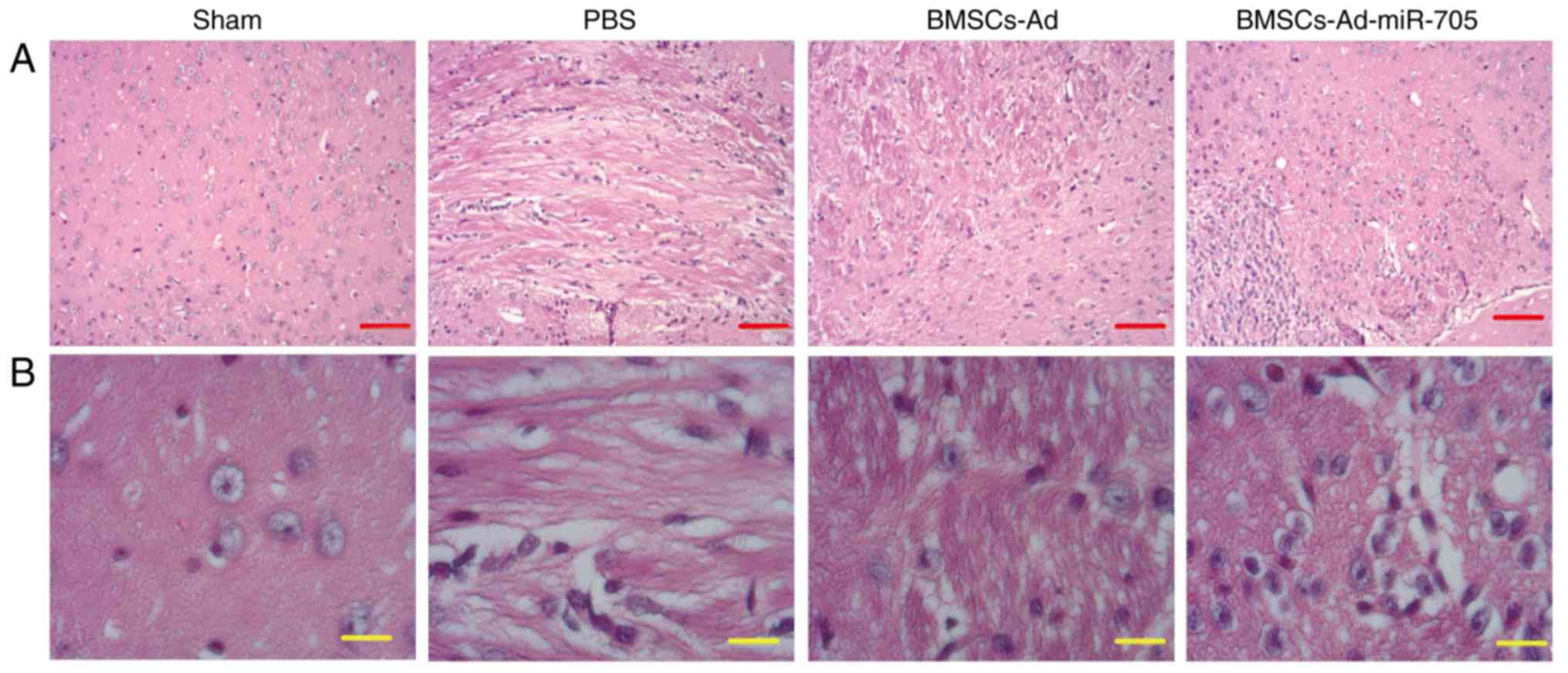
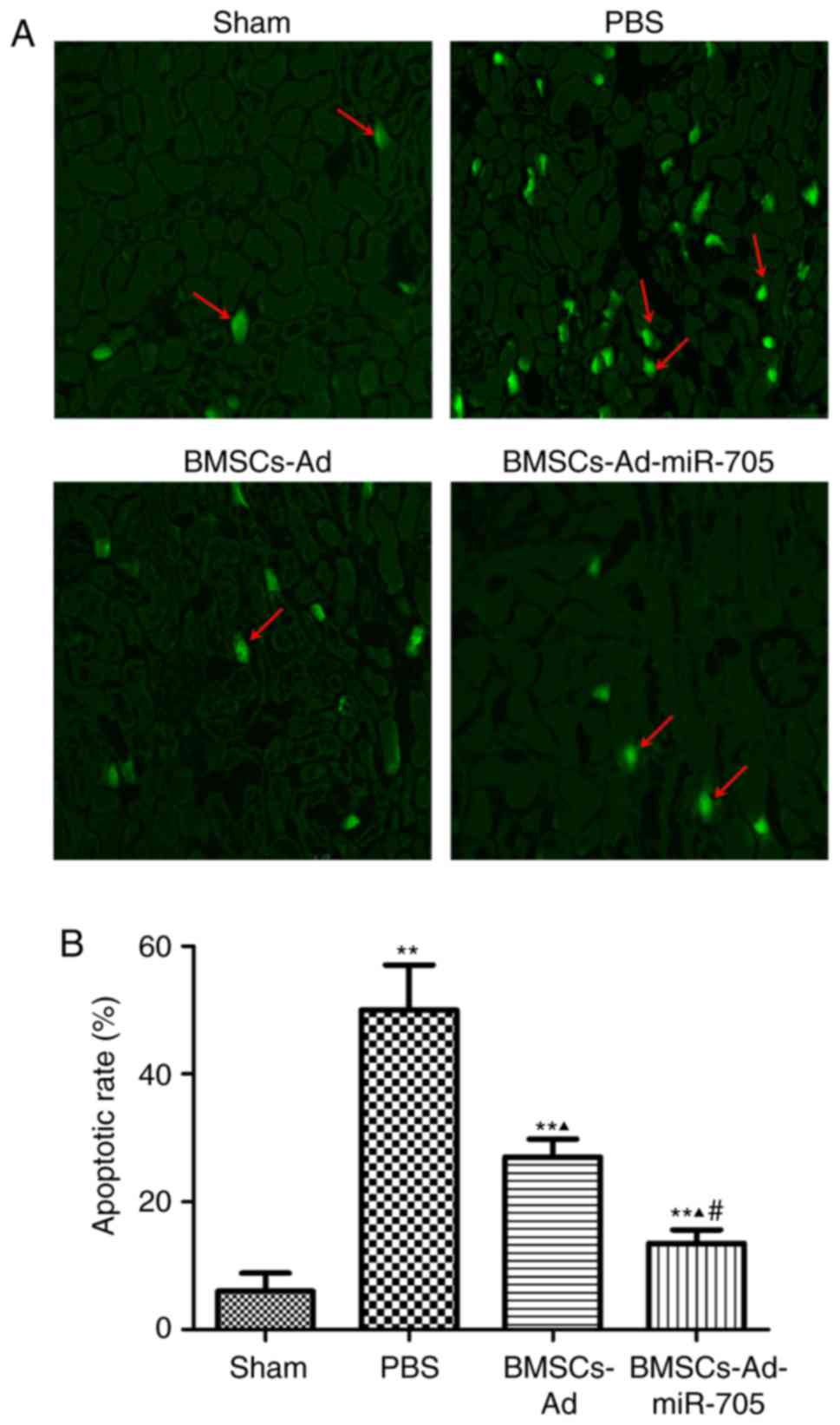
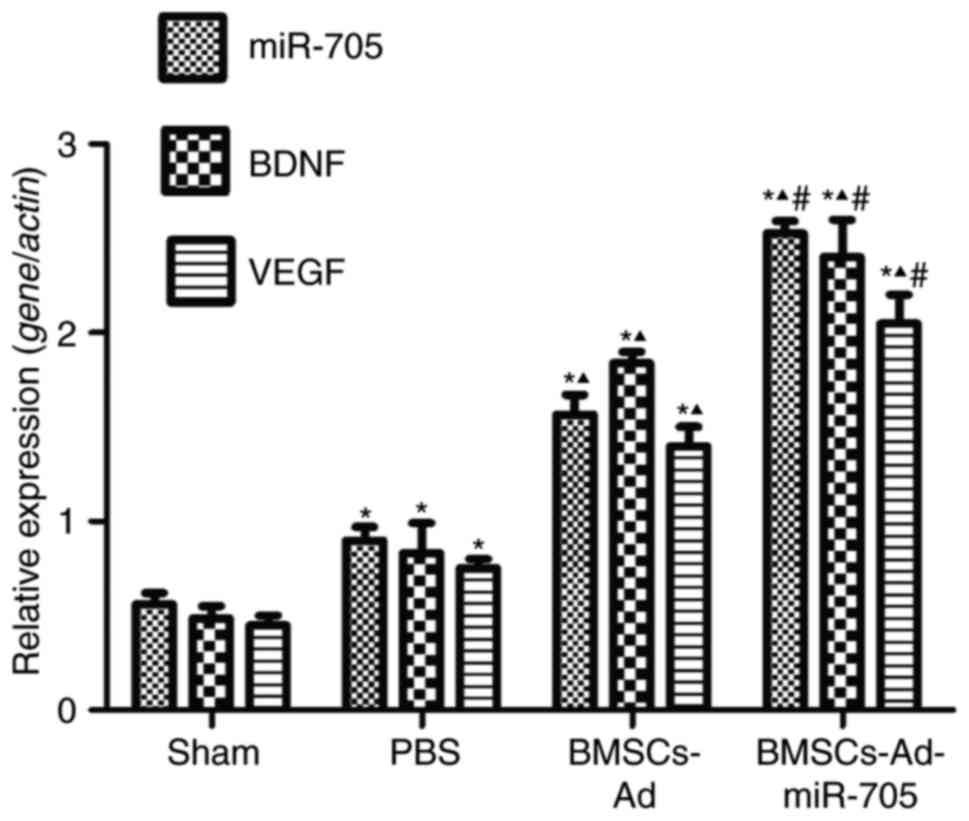
|
1
|
Wang Hy, Wang Gl, Yu Yh and Wang Y: The
role of phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt pathway in propofol-induced
postconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
in rats. Brain Res. 1297:177–184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schouten JW, Fulp CT, Royo NC, Saatman KE,
Watson DJ, Snyder EY, Trojanowski JQ, Prockop DJ, Maas AI and
McIntosh TK: A review and rationale for the use of cellular
transplantation as a therapeutic strategy for traumatic brain
injury. J Neurotrauma. 21:1501–1538. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang Z, Cai X, Xu A, Xu F and Liang Q:
Bone marrow stromal cell transplantation through tail vein
injection promotes angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth
factor expression in cerebral infarct area in rats. Cytotherapy.
17:1200–1212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shichinohe H, Ishihara T, Takahashi K,
Tanaka Y, Miyamoto M, Yamauchi T, Saito H, Takemoto H, Houkin K and
Kuroda S: Bone marrow stromal cells rescue ischemic brain by
trophic effects and phenotypic change toward neural cells.
Neurorehab Neural Repair. 29:80–89. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen A, Xiong LJ, Tong Y and Mao M: The
neuroprotective roles of BDNF in hypoxic ischemic brain injury
(Review). Biomed Rep. 1:167–176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO,
Logvinova A and Greenberg DA: VEGF-induced neuroprotection,
neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J
Clin Invest. 111:1843–1851. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoshino H, Seki N, Itesako T, Chiyomaru T,
Nakagawa M and Enokida H: Aberrant expression of microRNAs in
bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 10:396–404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lian JB, Stein GS, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein
JL, Hassan MQ, Gaur T and Zhang Y: MicroRNA control of bone
formation and homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 8:212–227. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dolganiuc A, Petrasek J, Kodys K, Catalano
D, Mandrekar P, Velayudham A and Szabo G: MicroRNA expression
profile in Lieber-DeCarli diet-induced alcoholic and methionine
choline deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis models
in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 33:1704–1710. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liao L, Yang X, Su X, Hu C, Zhu X, Yang N,
Chen X, Shi S, Shi S and Jin Y: Redundant miR-3077-5p and miR-705
mediate the shift of mesenchymal stem cell lineage commitment to
adipocyte in osteoporosis bone marrow. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6002013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liao L, Su X, Yang X, Hu C, Li B, Lv Y,
Shuai Y, Jing H, Deng Z and Jin Y: TNF-α Inhibits FoxO1 by
Upregulating miR-705 to aggravate oxidative damage in bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells during osteoporosis. Stem
Cells. 34:1054–1067. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schallert T, Kozlowski DA, Humm JL and
Cocke RR: Use-dependent structural events in recovery of function.
Adv Neurol. 73:229–238. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jahromi G Pirzad, Seidi S, Sadr SS,
Shabanzadeh AP, Keshavarz M, Kaka GR, Hosseini SK, Sohanaki H and
Charish J: Therapeutic effects of a combinatorial treatment of
simvastatin and bone marrow stromal cells on experimental embolic
stroke. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 110:487–493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen B, Zhang F, Li QY, Gong A and Lan Q:
Protective effect of Ad-VEGF-bone mesenchymal stem cells on
cerebral infarction. Turk Neurosurg. 26:8–15. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gutiérrez-Fernández M, Rodríguez-Frutos B,
Ramos-Cejudo J, Vallejo-Cremades M Teresa, Fuentes B, Cerdán S and
Díez-Tejedor E: Effects of intravenous administration of allogenic
bone marrow-and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells on
functional recovery and brain repair markers in experimental
ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Lin Z, Shao B, Zhuge Q and Jin K:
Therapeutic applications of bone marrow-derived stem cells in
ischemic stroke. Neurol Res. 35:470–478. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu J, Sun Z, Sun HS, Wu J, Weisel RD,
Keating A, Li ZH, Feng ZP and Li RK: Intravenously administered
bone marrow cells migrate to damaged brain tissue and improve
neural function in ischemic rats. Cell Transplant. 16:993–1005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Q, Chen ZW, Zhao YH, Liu BW, Liu NW,
Ke CC and Tan HM: Bone marrow stromal cells combined with sodium
ferulate and n-butylidenephthalide promote the effect of
therapeutic angiogenesis via advancing astrocyte-derived trophic
factors after ischemic stroke. Cell Transplant. 26:229–242. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wan H, Li F, Zhu L, Wang J, Yang Z and Pan
Y: Update on therapeutic mechanism for bone marrow stromal cells in
ischemic stroke. J Mol Neurosci. 52:177–185. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yao RQ, Qi DS, Yu HL, Liu J, Yang LH and
Wu XX: Quercetin attenuates cell apoptosis in focal cerebral
ischemia rat brain via activation of BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Neurochem Res. 37:2777–2786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li N, Wang P, Ma XL, Wang J, Zhao LJ, Du
L, Wang LY, Wang XR and Liu KD: Effect of bone marrow stromal cell
transplantation on neurologic function and expression of VEGF in
rats with focal cerebral ischemia. Mol Med Rep. 10:2299–2305. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deindl E: Mechanistic insights into the
functional role of vascular endothelial growth factor and its
signalling partner brain-derived neurotrophic factor in angiogenic
tube formation. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 211:268–270. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|