|
1
|
Kansara M, Teng MW, Smyth MJ and Thomas
DM: Translational biology of osteosarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer.
14:722–735. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Pisani P and Ferlay J: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 49:33–64. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bielack S, Kempf-Bielack B, Von Kalle T,
Schwarz R, Wirth T, Kager L and Whelan J: Controversies in
childhood osteosarcoma. Minerva Pediatr. 65:125–48. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
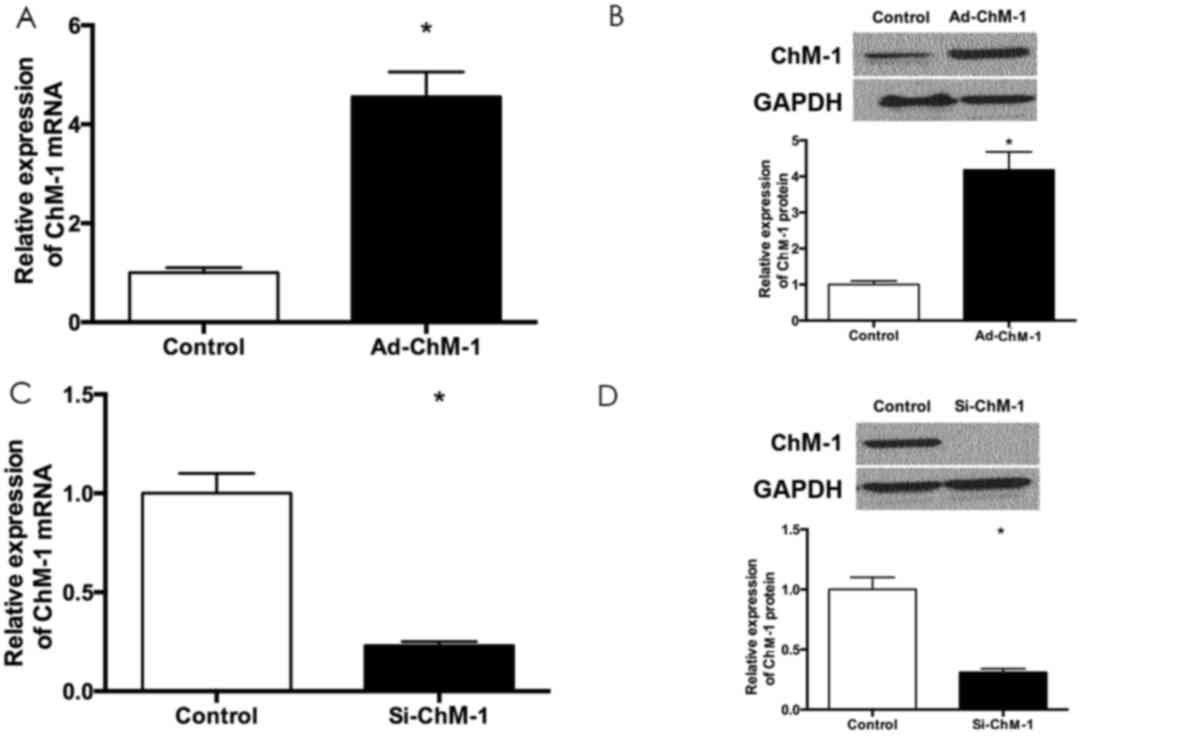
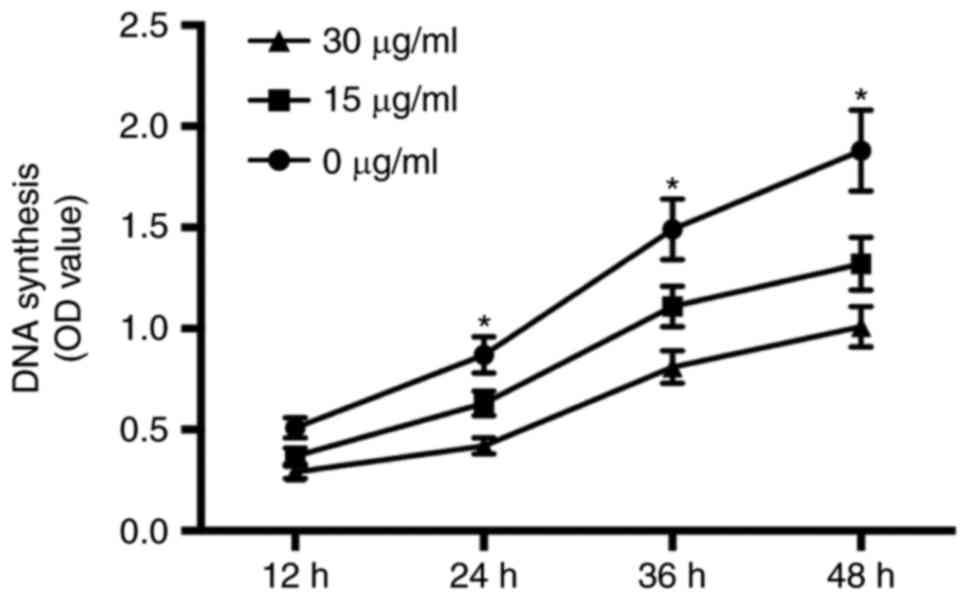
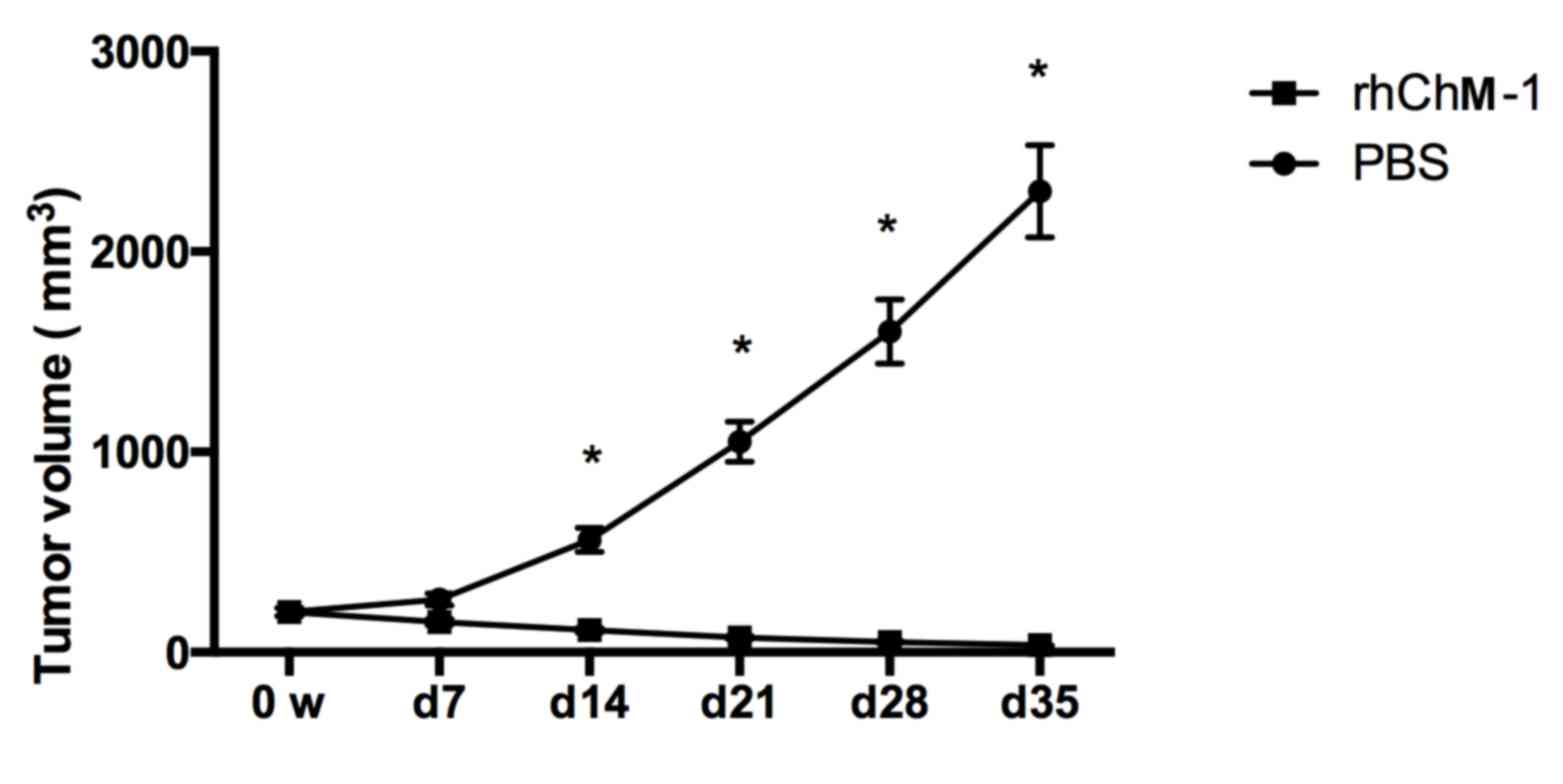
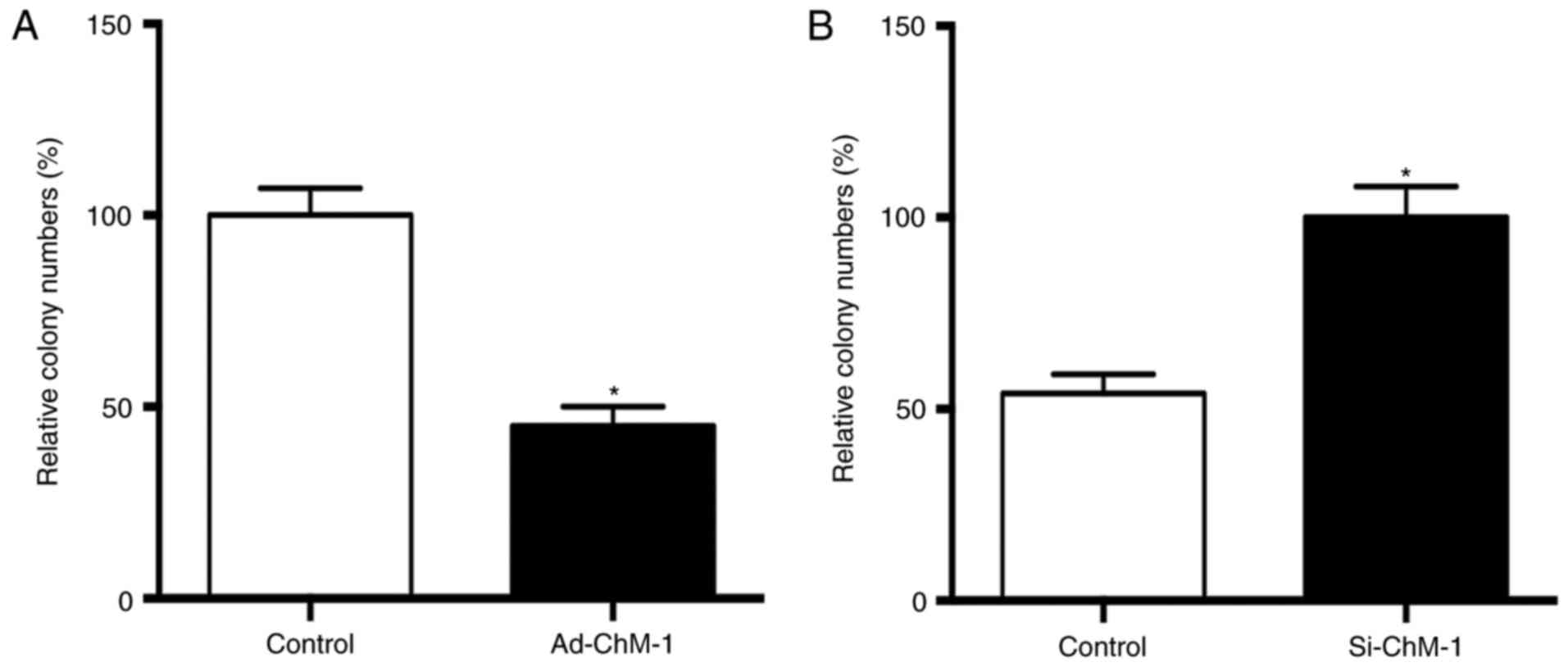
|
4
|
Moore DD and Luu HH: Osteosarcoma. Cancer
Treat Res. 162:65–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Isakoff MS, Bielack SS, Meltzer P and
Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: Current treatment and a collaborative
pathway to success. J Clin Oncol. 33:3029–3035. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fan Z, Patel S, Lewis VO, Guadagnolo BA
and Lin PP: Should High-grade extraosseous osteosarcoma Be treated
with multimodality therapy like other soft tissue sarcomas? Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 473:3604–3611. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jones KB, Ferguson PC, Lam B, Biau DJ,
Hopyan S, Deheshi B, Griffin AM, White LM and Wunder JS: Effects of
neoadjuvant chemotherapy on image-directed planning of surgical
resection for distal femoral osteosarcoma. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
94:1399–1405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peng N, Gao S, Guo X, Wang G, Cheng C, Li
M and Liu K: Silencing of VEGF inhibits human osteosarcoma
angiogenesis and promotes cell apoptosis via VEGF/PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 8:1005–1015. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dossi R, Frapolli R, Di Giandomenico S,
Paracchini L, Bozzi F, Brich S, Castiglioni V, Borsotti P, Belotti
D, Uboldi S, et al: Antiangiogenic activity of trabectedin in
myxoid liposarcoma: Involvement of host TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 and tumor
thrombospondin-1. Int J Cancer. 136:721–729. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miura S, Kondo J, Takimoto A, Sano-Takai
H, Guo L, Shukunami C, Tanaka H and Hiraki Y: The N-terminal
cleavage of chondromodulin-I in growth-plate cartilage at the
hypertrophic and calcified zones during bone development. PLoS One.
9:e942392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aoyama T, Okamoto T, Fukiage K, Otsuka S,
Furu M, Ito K, Jin Y, Ueda M, Nagayama S, Nakayama T, et al:
Histone modifiers, YY1 and p300, regulate the expression of
cartilage-specific gene, chondromodulin-I, in mesenchymal stem
cells. J Biol Chem. 285:29842–29850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hiraki Y and Shukunami C: Chondromodulin-I
as a novel cartilage-specific growth-modulating factor. Pediatr
Nephrol. 14:602–605. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hiraki Y, Inoue H, Iyama K, Kamizono A,
Ochiai M, Shukunami C, Iijima S, Suzuki F and Kondo J:
Identification of chondromodulin I as a novel endothelial cell
growth inhibitor. Purification and its localization in the
avascular zone of epiphyseal cartilage. J Biol Chem.
272:32419–32426. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yukata K, Matsui Y, Shukunami C, Takimoto
A, Hirohashi N, Ohtani O, Kimura T, Hiraki Y and Yasui N:
Differential expression of Tenomodulin and Chondromodulin-1 at the
insertion site of the tendon reflects a phenotypic transition of
the resident cells. Tissue Cell. 42:116–120. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oshima Y, Sato K, Tashiro F, Miyazaki J,
Nishida K, Hiraki Y, Tano Y and Shukunami C: Anti-angiogenic action
of the C-terminal domain of tenomodulin that shares homology with
chondromodulin-I. J Cell Sci. 117:2731–2744. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsai AC, Pan SL, Sun HL, Wang CY, Peng CY,
Wang SW, Chang YL, Kuo SC, Lee KH and Teng CM: CHM-1, a new
vascular targeting agent, induces apoptosis of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells via p53-mediated death receptor 5 up-regulation.
J Biol Chem. 285:5497–5506. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hsu SC, Yang JS, Kuo CL, Lo C, Lin JP,
Hsia TC, Lin JJ, Lai KC, Kuo HM, Huang LJ, et al: Novel quinolone
CHM-1 induces apoptosis and inhibits metastasis in a human
osterogenic sarcoma cell line. J Orthop Res. 27:1637–1644. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang P, Wang Y, Xu P, Song S, Zhu X, Shi
Z, Gao S and Feng X: Chondromodulin-1 functions as a tumor
suppressor in gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol. 47:941–950.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shao J, Gan L and Wang J: Transfection of
chondromodulin I into human breast cancer cells and its effect on
the inhibition of cancer cell growth. Mol Med Rep. 13:4303–4308.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Roloff F, Ziege S, Baumgärtner W, Wewetzer
K and Bicker G: Schwann cell-free adult canine olfactory
ensheathing cell preparations from olfactory bulb and mucosa
display differential migratory and neurite growth-promoting
properties in vitro. BMC Neurosci. 14:1412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman
J and van Bree C: Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc.
1:2315–2319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li P, Chen X, Su L, Li C, Zhi Q, Yu B,
Sheng H, Wang J, Feng R, Cai Q, et al: Epigenetic silencing of
miR-338-3p contributes to tumorigenicity in gastric cancer by
targeting SSX2IP. PLoS One. 8:e667822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shingu T, Holmes L, Henry V, Wang Q, Latha
K, Gururaj AE, Gibson LA, Doucette T, Lang FF, Rao G, et al:
Suppression of RAF/MEK or PI3K synergizes cytotoxicity of receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibitors in glioma tumor-initiating cells. J
Transl Med. 14:462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang Z, Li X, Yang Y, He Z, Qu X and Zhang
Y: Long noncoding RNAs in the progression, metastasis, and
prognosis of osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis. 7:e23892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board, .
Osteosarcoma and Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma of Bone Treatment
(PDQ®)PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet].
Health Professional Version. National Cancer Institute (US);
Bethesda: 2002
|
|
28
|
Abarrategi A, Tornin J, Martinez-Cruzado
L, Hamilton A, Martinez-Campos E, Rodrigo JP, González MV, Baldini
N, Garcia-Castro J and Rodriguez R: Osteosarcoma: Cells-of-Origin,
cancer stem cells, and targeted therapies. Stem Cells Int.
2016:36317642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li CJ, Liu XZ, Zhang L, Chen LB, Shi X, Wu
SJ and Zhao JN: Advances in Bone-targeted drug delivery systems for
neoadjuvant chemotherapy for osteosarcoma. Orthop Surg. 8:105–110.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Friebele JC, Peck J, Pan X, Abdel-Rasoul M
and Mayerson JL: Osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis and review of the
literature. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 44:547–553.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li S, Sun W, Wang H, Zuo D, Hua Y and Cai
Z: Research progress on the multidrug resistance mechanisms of
osteosarcoma chemotherapy and reversal. Tumour Biol. 36:1329–1338.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dass CR and Choong PF: Gene therapy for
osteosarcoma: Steps towards clinical studies. J Pharm Pharmacol.
60:405–413. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Clark JC, Dass CR and Choong PF: A review
of clinical and molecular prognostic factors in osteosarcoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 134:281–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis: Past,
present and the near future. Carcinogenesis. 21:505–515. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maione F and Giraudo E: Tumor
angiogenesis: Methods to analyze tumor vasculature and vessel
normalization in mouse models of cancer. Methods Mol Biol.
1267:349–365. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kubota Y: Tumor angiogenesis and
anti-angiogenic therapy. Keio J Med. 61:47–56. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Klinger P, Surmann-Schmitt C, Brem M,
Swoboda B, Distler JH, Carl HD, von der Mark K, Hennig FF and Gelse
K: Chondromodulin 1 stabilizes the chondrocyte phenotype and
inhibits endochondral ossification of porcine cartilage repair
tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 63:2721–2731. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Miura S, Kondo J, Kawakami T, Shukunami C,
Aimoto S, Tanaka H and Hiraki Y: Synthetic disulfide-bridged cyclic
peptides mimic the anti-angiogenic actions of chondromodulin-I.
Cancer Sci. 103:1311–1318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liang CC, Park AY and Guan JL: In vitro
scratch assay: A convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of
cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2:329–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|