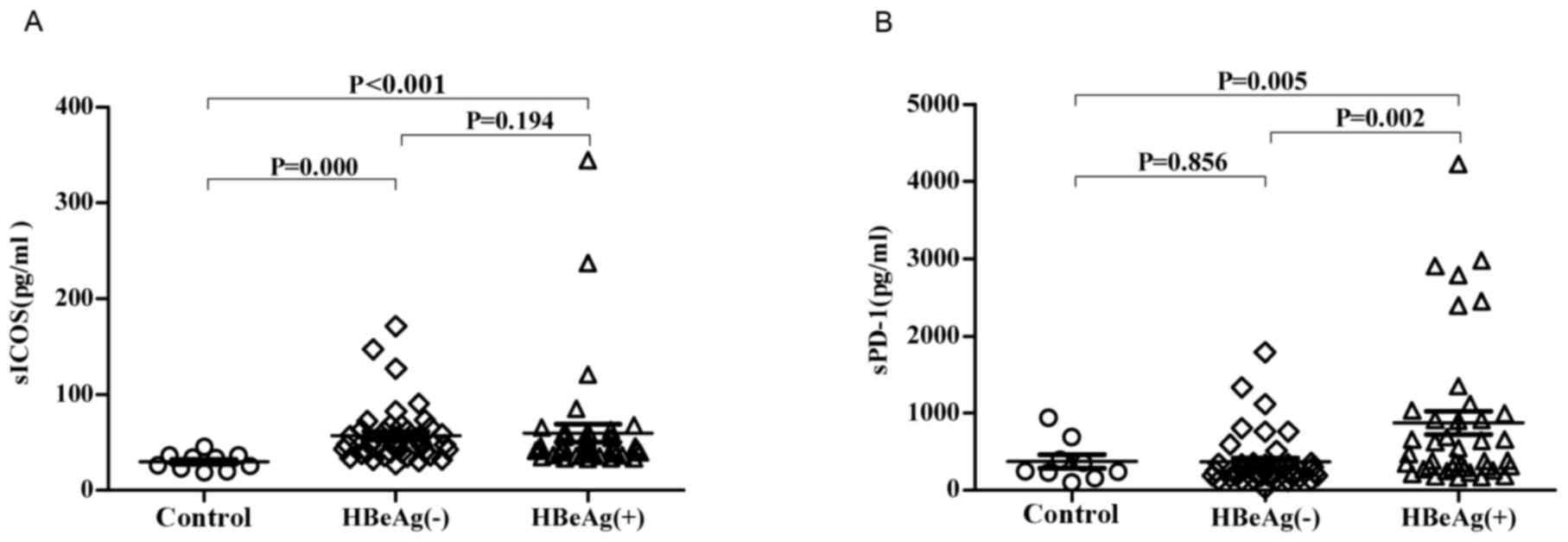
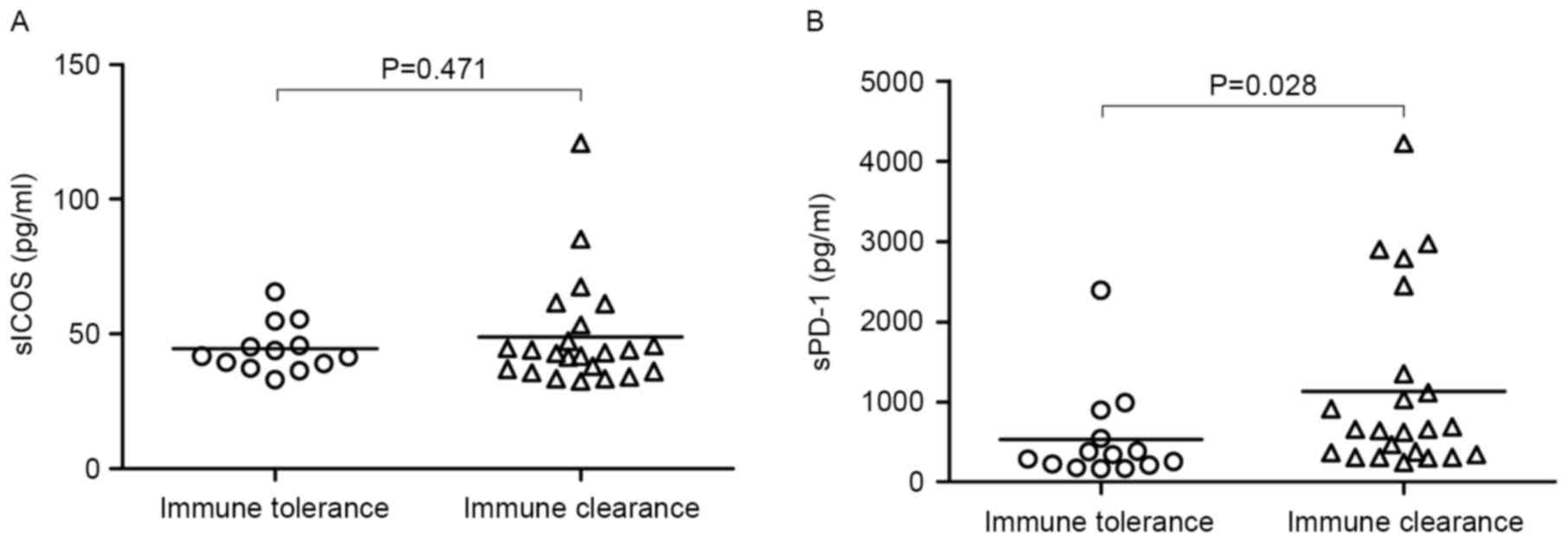
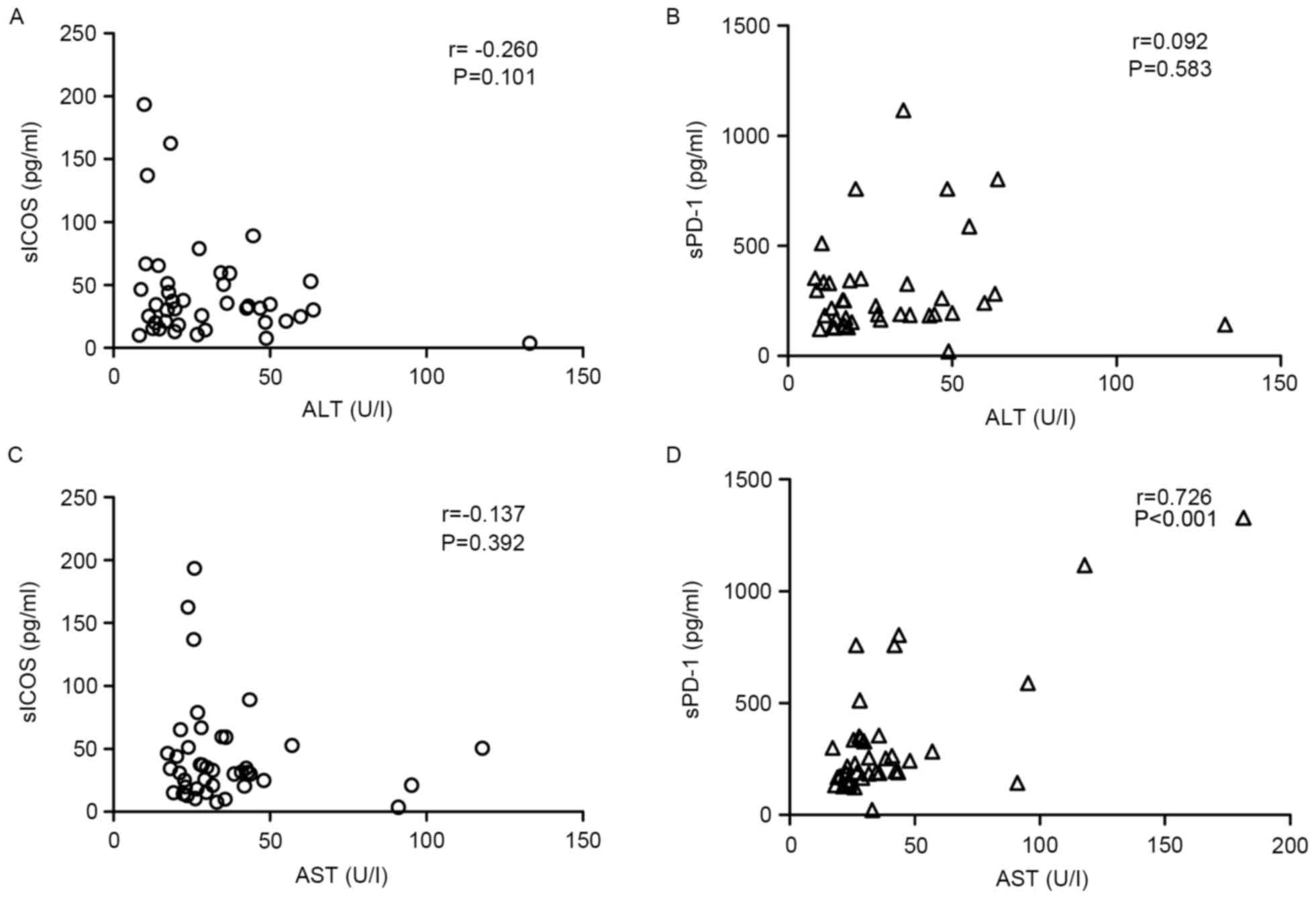
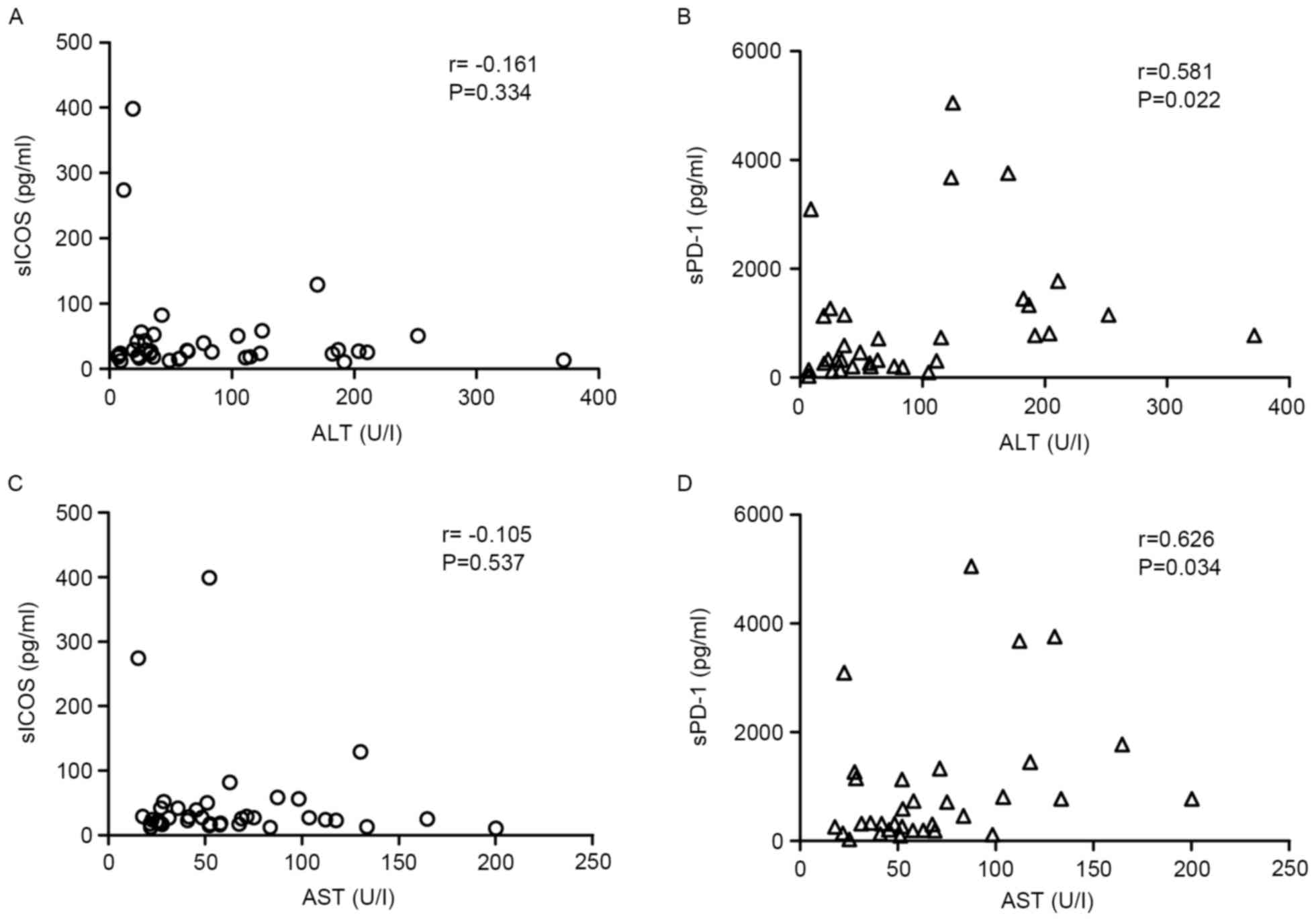
|
1
|
Lok AS: The maze of treatments for
hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 352:2743–2746. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferrari C: HBV and the immune response.
Liver Int. 35 Suppl 1:S121–S128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lee JA, Kim YM, Hyun PM, Jeon JW, Park JK,
Suh GH, Jung BG and Lee BJ: Honeybee (Apis mellifera) venom
reinforces viral clearance during the early stage of infection with
porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus through the
up-regulation of Th1-specific immune responses. Toxins (Basel).
7:1837–1853. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Klein J and Sato A: The HLA system. First
of two parts. N Engl J Med. 343:702–709. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang D, Zhou D, DU Q, Liang Q, Wang Q,
Fang L, Wang G, Fan Q, Liu B, Zhou J, et al: Aberrant production of
soluble inducible T-cell co-stimulator (sICOS) and soluble
programmed cell death protein 1 (sPD-1) in patients with chronic
hepatitis C. Mol Med Rep. 7:1197–1202. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cao J, Zhang L, Huang S, Chen P, Zou L,
Chen H, Xiang Y, Lai X and Ren G: Aberrant production of soluble
co-stimulatory molecules CTLA-4 and CD28 in patients with chronic
hepatitis B. Microb Pathog. 51:262–267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang L, Zhao C, Peng Q, Shi J and Gu G:
Expression levels of CD28, CTLA-4, PD-1 and Tim-3 as novel
indicators of T-cell immune function in patients with chronic
hepatitis B virus infection. Biomed Rep. 2:270–274. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nurieva RI, Mei XM, Forbush K, Bevan MJ
and Dong C: B7h is required for T cell activation, differentiation,
and effector function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:pp. 14163–14168.
2003; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yanaba K, Asano Y, Noda S, Akamata K,
Aozasa N, Taniguchi T, Takahashi T, Ichimura Y, Toyama T, Sumida H,
et al: Increased production of soluble inducible costimulator in
patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Arch Dermatol
Res. 305:17–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu X, Zhang H, Xing Q, Cui J, Li J, Li Y,
Tan Y and Wang S: PD-1(+) CD8(+) T Cells are exhausted in tumours
and functional in draining lymph nodes of colorectal cancer
patients. Br J Cancer. 111:1391–1399. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Her M, Kim D, Oh M, Jeong H and Choi I:
Increased expression of soluble inducible costimulator ligand
(ICOSL) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus.
18:501–507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wan B, Nie H, Liu A, Feng G, He D, Xu R,
Zhang Q, Dong C and Zhang JZ: Aberrant regulation of synovial T
cell activation by soluble costimulatory molecules in rheumatoid
arthritis. J Immunol. 177:8844–8850. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Method. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ye B, Liu X, Li X, Kong H, Tian L and Chen
Y: T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B infection: Current
knowledge and clinical significance. Cell Death Dis. 6:e16942015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bengsch B, Martin B and Thimme R:
Restoration of HBV-specific CD8+ T cell function by PD-1 blockade
in inactive carrier patients is linked to T cell differentiation. J
Hepatol. 61:1212–1219. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Magistrelli G, Jeannin P, Elson G, Gauchat
JF, Nguyen TN, Bonnefoy JY and Delneste Y: Identification of three
alternatively spliced variants of human CD28 mRNA. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 259:34–37. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hutloff A, Dittrich AM, Beier KC,
Eljaschewitsch B, Kraft R, Anagnostopoulos I and Kroczek RA: ICOS
is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally
related to CD28. Nature. 397:263–266. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K and Honjo
T: Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin
gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 11:3887–3895.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang W: Blockade of B7-H1 enhances
dendritic cell-mediated T cell response and antiviral immunity in
HBV transgenic mice. Vaccine. 30:758–766. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shankar EM, Che KF, Messmer D, Lifson JD
and Larsson M: Expression of a broad array of negative
costimulatory molecules and Blimp-1 in T cells following priming by
HIV-1 pulsed dendritic cells. Mol Med. 17:229–240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheng HY, Kang PJ, Chuang YH, Wang YH, Jan
MC, Wu CF, Lin CL, Liu CJ, Liaw YF, Lin SM, et al: Circulating
programmed death-1 as a marker for sustained high hepatitis B viral
load and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e958702014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thio CL, Mosbruger TL, Kaslow RA, Karp CL,
Strathdee SA, Vlahov D, O'Brien SJ, Astemborski J and Thomas DL:
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 gene and recovery from hepatitis B
virus infection. J Virol. 78:11258–11262. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|