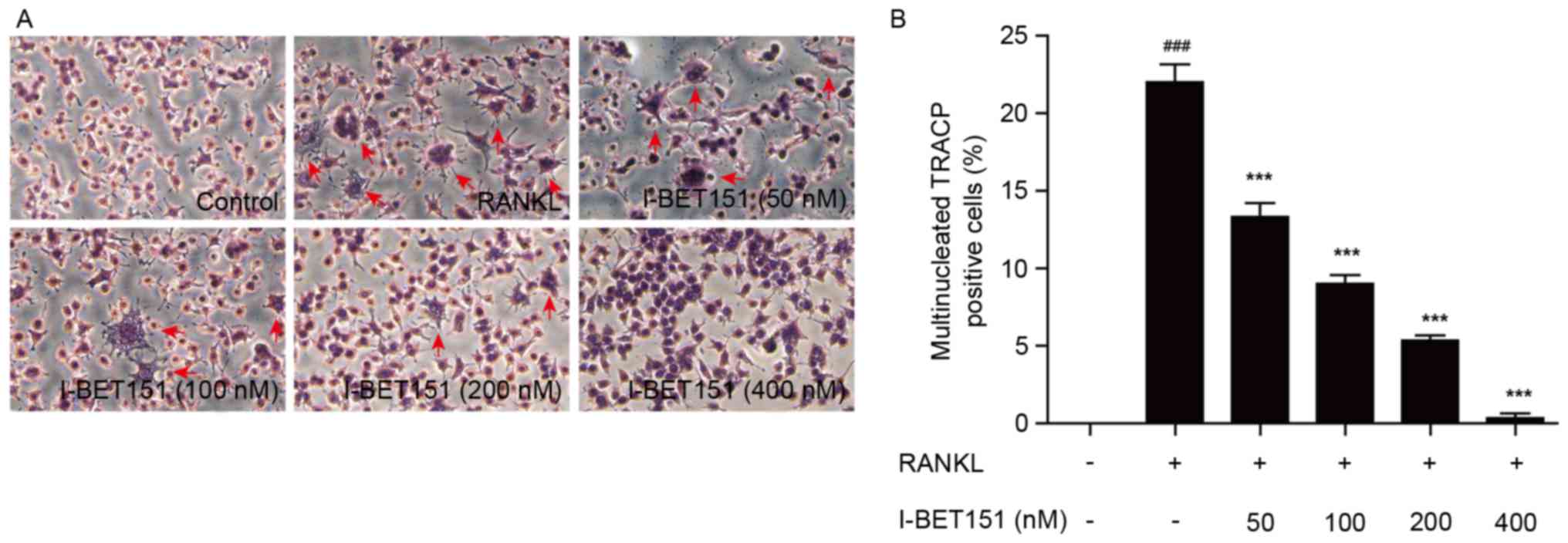
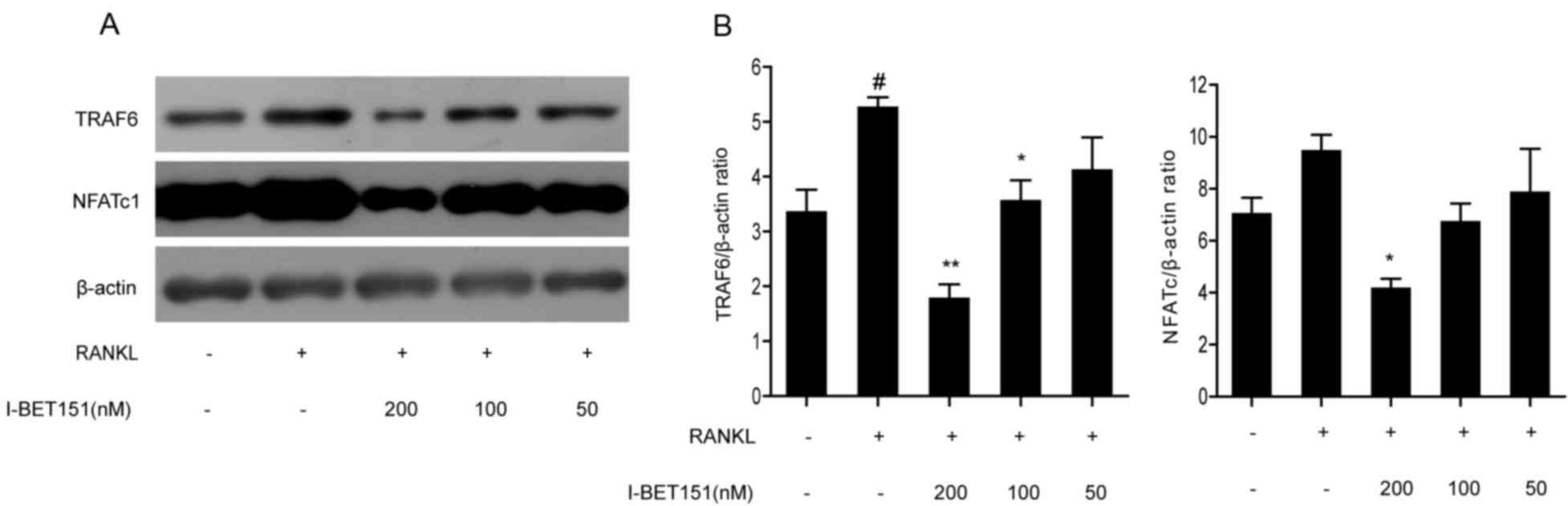
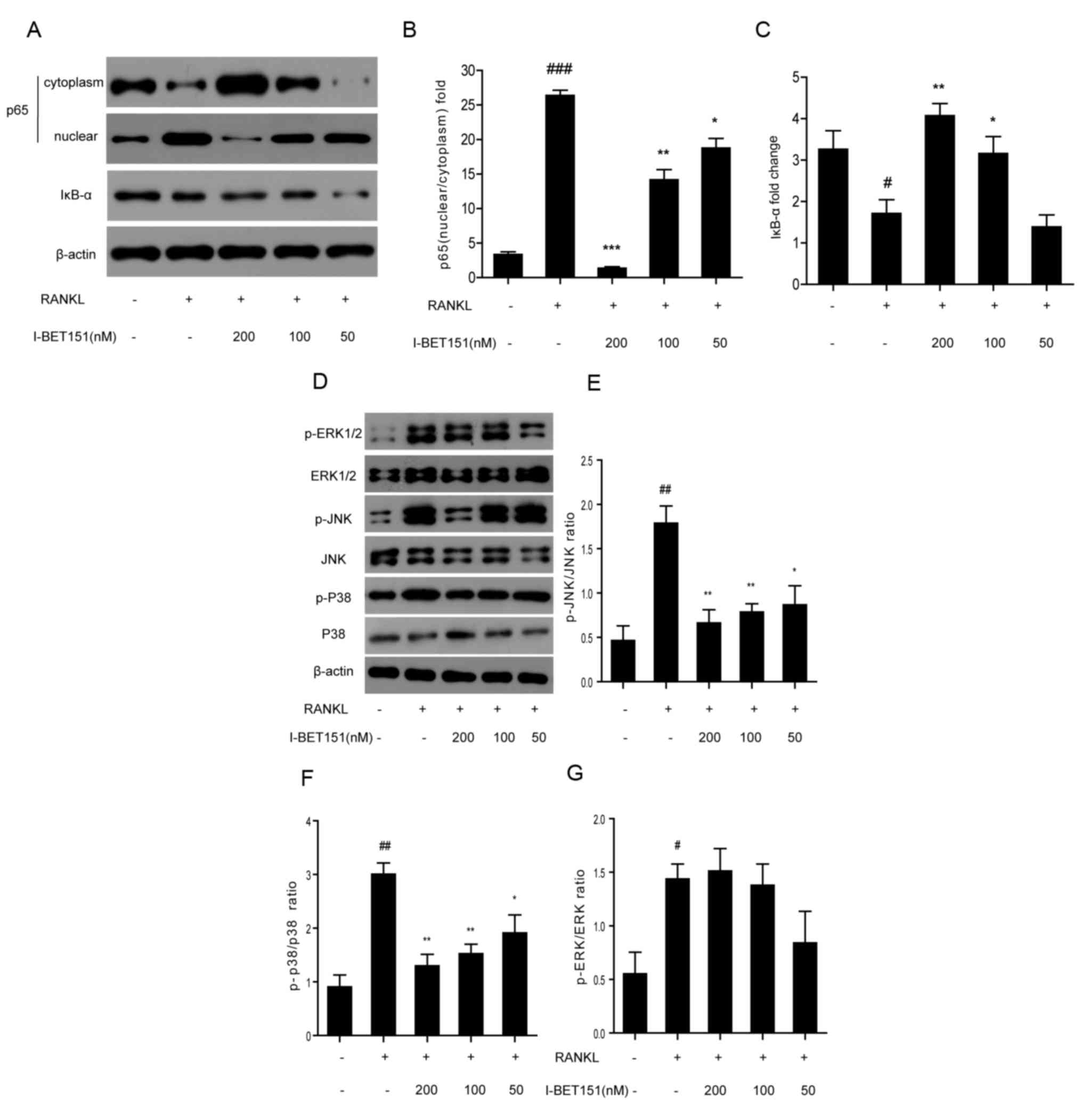
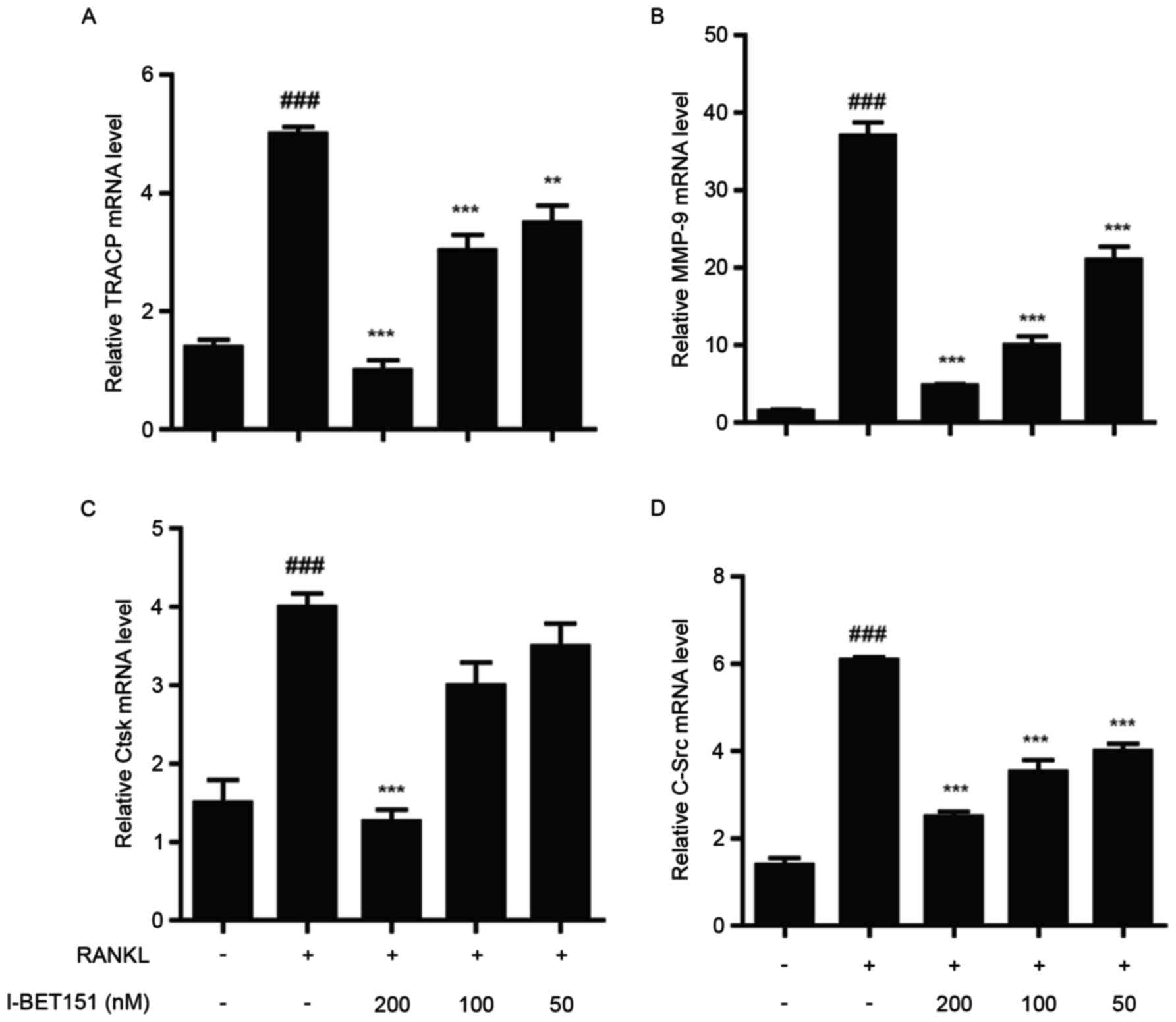
|
1
|
Weivoda MM, Ruan M, Hachfeld CM, Pederson
L, Howe A, Davey RA, Zajac JD, Kobayashi Y, Williams BO, Westendorf
JJ, et al: Wnt signaling inhibits osteoclast differentiation by
activating canonical and noncanonical cAMP/PKA pathways. J Bone
Miner Res. 31:65–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Longo V, Brunetti O, D'Oronzo S, Dammacco
F and Silvestris F: Therapeutic approaches to myeloma bone disease:
An evolving story. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:787–797. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Delaisse JM, B A, Ali NN, et al: The
effects of both cysteine proteinase and collagenase inhibitors on
dentine resorption by isolated osteoclasts-Bone. Bone. 44:45–46.
2014.
|
|
4
|
Bara JJ, Richards RG, Alini M and Stoddart
MJ: Concise review: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
change phenotype following in vitro culture: Implications for basic
research and the clinic. Stem Cells. 32:1713–1723. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Klein-Nulend J, Bakker AD, Bacabac RG,
Vatsa A and Weinbaum S: Mechanosensation and transduction in
osteocytes. Bone. 54:182–190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhai ZJ, Li HW, Liu GW, Qu XH, Tian B, Yan
W, Lin Z, Tang TT, Qin A and Dai KR: Andrographolide suppresses
RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in vitro and prevents inflammatory
bone loss in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 171:663–675. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cicek M, Vrabel A, Sturchio C, Pederson L,
Hawse JR, Subramaniam M, Spelsberg TC and Oursler MJ: TGF-β
inducible early gene 1 regulates osteoclast differentiation and
survival by mediating the NFATc1, AKT and MEK/ERK signaling
pathways. Plos One. 6:e175222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
D'Amelio P, Isaia G and Isaia GC: The
osteoprotegerin/RANK/RANKL system: A bone key to vascular disease.
J Endocrinol Invest. 32(4 Suppl): S6–S9. 2014.
|
|
9
|
Jules J, Wang SQ, Shi ZQ, Liu JZ, Wei S
and Feng X: The IVVY motif and tumor necrosis factor
receptor-associated factor (TRAF) sites in the cytoplasmic domain
of the receptor activator of nuclear factor κB (RANK)
cooperate to induce osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem.
290:23738–23750. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Galibert L, Tometsko ME, Anderson DM,
Cosman D and Dougall WC: The involvement of multiple tumor necrosis
factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factors in the signaling
mechanisms of receptor activator of NF-kappaB, a member of the TNFR
superfamily. J Biol Chem. 273:34120–34127. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wong BR, Josien R, Lee SY, Vologodskaia M,
Steinman RM and Choi Y: The TRAF family of signal transducers
mediates NF-kappaB activation by the trance receptor. J Biol Chem.
273:28355–28359. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu H, Tamashiro S, Baritaki S, Penichet
M, Yu Y, Chen H, Berenson J and Bonavida B: TRAF6 activation in
multiple myeloma: A potential therapeutic target. Clin Lymphoma
Myeloma Leuk. 12:155–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kobayashi N, Kadono Y, Naito A, Matsumoto
K, Yamamoto T, Tanaka S and Inoue J: Segregation of TRAF6-mediated
signaling pathways clarifies its role in osteoclastogenesis. Embo
Journal. 20:1271–1280. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guan H, Mi B, Li Y, Wu W, Tan P, Fang Z,
Li J, Zhang Y and Li F: Decitabine represses osteoclastogenesis
through inhibition of RANK and NF-κB. Cell Signal.
27:969–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Vries TJ, Schoenmaker T, Aerts D,
Grevers LC, Souza PP, Nazmi K, van de Wiel M, Ylstra B, Lent PL,
Leenen PJ and Everts V: M-CSF priming of osteoclast precursors can
cause osteoclastogenesis-insensitivity, which can be prevented and
overcome on bone. J Cell Physiol. 230:210–225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wikto-rjedrzejczak W, Bartocci A, Ferrante
AW Jr, Ahmed-Ansari A, Sell KW, Pollard JW and Stanley ER: Total
absence of colony-stimulating factor 1 in the macrophage-deficient
osteopetrotic (op/op) mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:pp.
4828–4832. 1990; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim HJ, Yoon HJ, Yoon KA, Gwon MR, Jin
Seong S, Suk K, Kim SY and Yoon YR: Lipocalin-2 inhibits osteoclast
formation by suppressing the proliferation and differentiation of
osteoclast lineage cells. Exp Cell Res. 334:301–309. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goettsch C, Babelova A, Trummer O, Erben
RG, Rauner M, Rammelt S, Weissmann N, Weinberger V, Benkhoff S,
Kampschulte M, et al: NADPH oxidase 4 limits bone mass by promoting
osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest. 123:4731–4738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ross FP and Teitelbaum SL: Alphavbeta3 and
macrophage colony-stimulating factor: Partners in osteoclast
biology. Immunol Rev. 208:88–105. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lamoureux F, Baud'huin M, Calleja LR,
Jacques C, Berreur M, Rédini F, Lecanda F, Bradner JE, Heymann D
and Ory B: Selective inhibition of BET bromodomain epigenetic
signalling interferes with the bone-associated tumour vicious
cycle. Nature Communications. 5:2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park-Min KH, Lim E, Lee MJ, Park SH,
Giannopoulou E, Yarilina A, Van der Meulen M, Zhao B, Smithers N,
Witherington J, et al: Inhibition of osteoclastogenesis and
inflammatory bone resorption by targeting BET proteins and
epigenetic regulation. Nat Commun. 5:54182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chaidos A, Caputo V, Gouvedenou K, Liu B,
Marigo I, Chaudhry MS, Rotolo A, Tough DF, Smithers NN, Bassil AK,
et al: Potent antimyeloma activity of the novel bromodomain
inhibitors I-BET151 and I-BET762. Blood. 123:697–705. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gallagher SJ, Mijatov B, Gunatilake D,
Tiffen JC, Gowrishankar K, Jin L, Pupo GM, Cullinane C, Prinjha RK,
Smithers N, et al: The epigenetic regulator I-BET151 induces
BIM-dependent apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human melanoma
cells. J Invest Dermatol. 134:2795–2805. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Klein K, Kabala PA, Grabiec AM, Gay RE,
Kolling C, Lin LL, Gay S, Tak PP, Prinjha RK, Ospelt C and
Reedquist KA: The bromodomain protein inhibitor I-BET151 suppresses
expression of inflammatory genes and matrix degrading enzymes in
rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Ann Rheum Dis.
75:422–429. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meng S, Zhang L, Tang Y, Tu Q, Zheng L, Yu
L, Murray D, Cheng J, Kim SH, Zhou X and Chen J: BET inhibitor JQ1
blocks inflammation and bone destruction. J Dent Res. 93:657–662.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu X, Li Z, Yang Z, Zheng C, Jing J, Chen
Y, Ye X, Lian X, Qiu W, Yang F, et al: Caffeic acid
3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester suppresses receptor activator of
NF-κB ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents
ovariectomy-induced bone loss through inhibition of
mitogen-activated protein kinase/activator protein 1 and
Ca2+-nuclear factfactor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic
1 signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Res. 27:1298–1308. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He LG, Duan H, Li XL, Wang S, Zhang Y, Lei
L, Xu J, Liu S and Li X: Sinomenine down-regulates TLR4/TRAF6
expression and attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis. Eur J Pharmacol. 779:66–79.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li X, He L, Hu Y, Duan H, Li X, Tan S, Zou
M, Gu C, Zeng X, Yu L, et al: Sinomenine suppresses osteoclast
formation and mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra-induced bone loss by
modulating RANKL signaling pathways. Plos One. 8:2013.
|
|
30
|
Kular J, Tickner J, Chim SM and Xu JK: An
overview of the regulation of bone remodelling at the cellular
level. Clin Biochem. 45:863–873. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Deal C: Bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis:
Systemic, periarticular and focal. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 14:231–237.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|