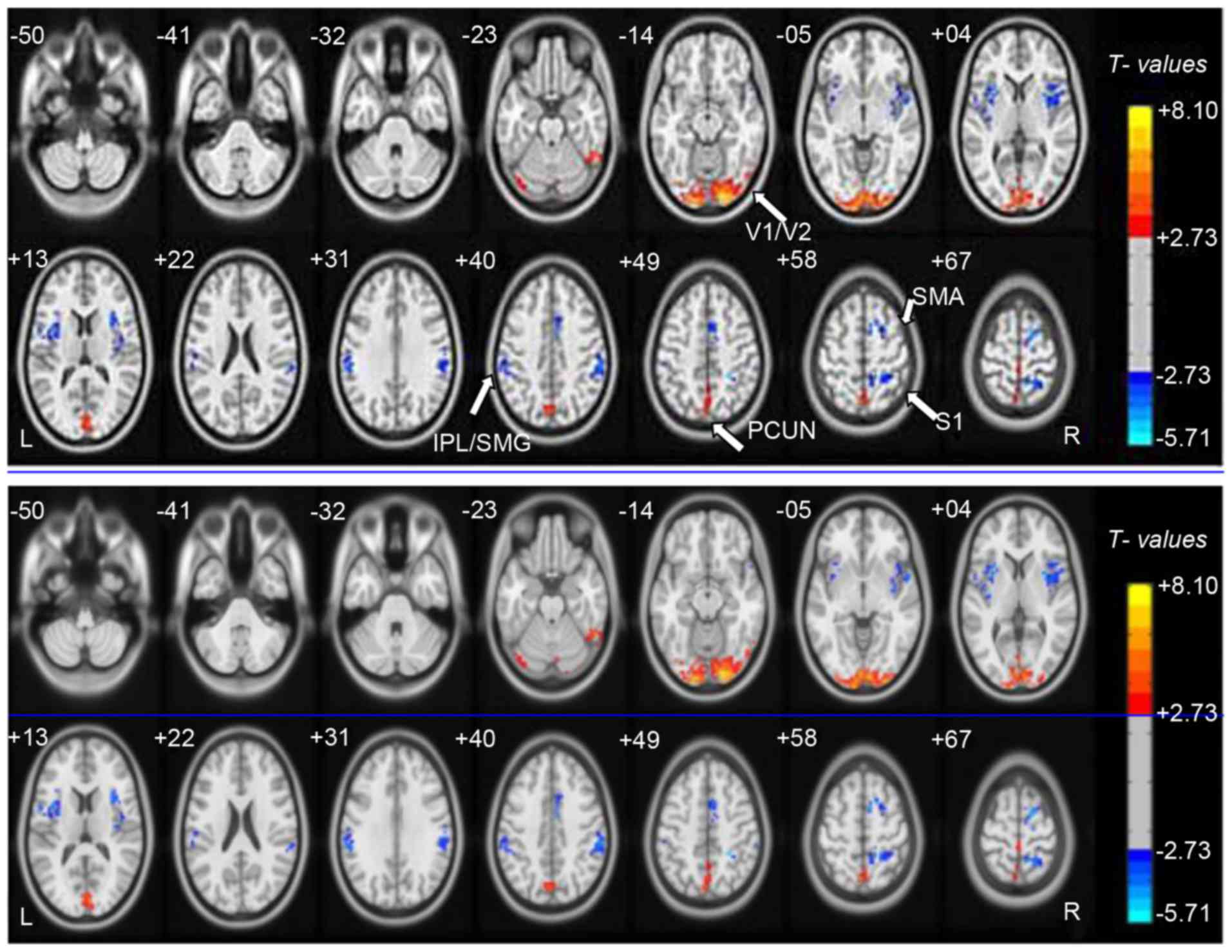
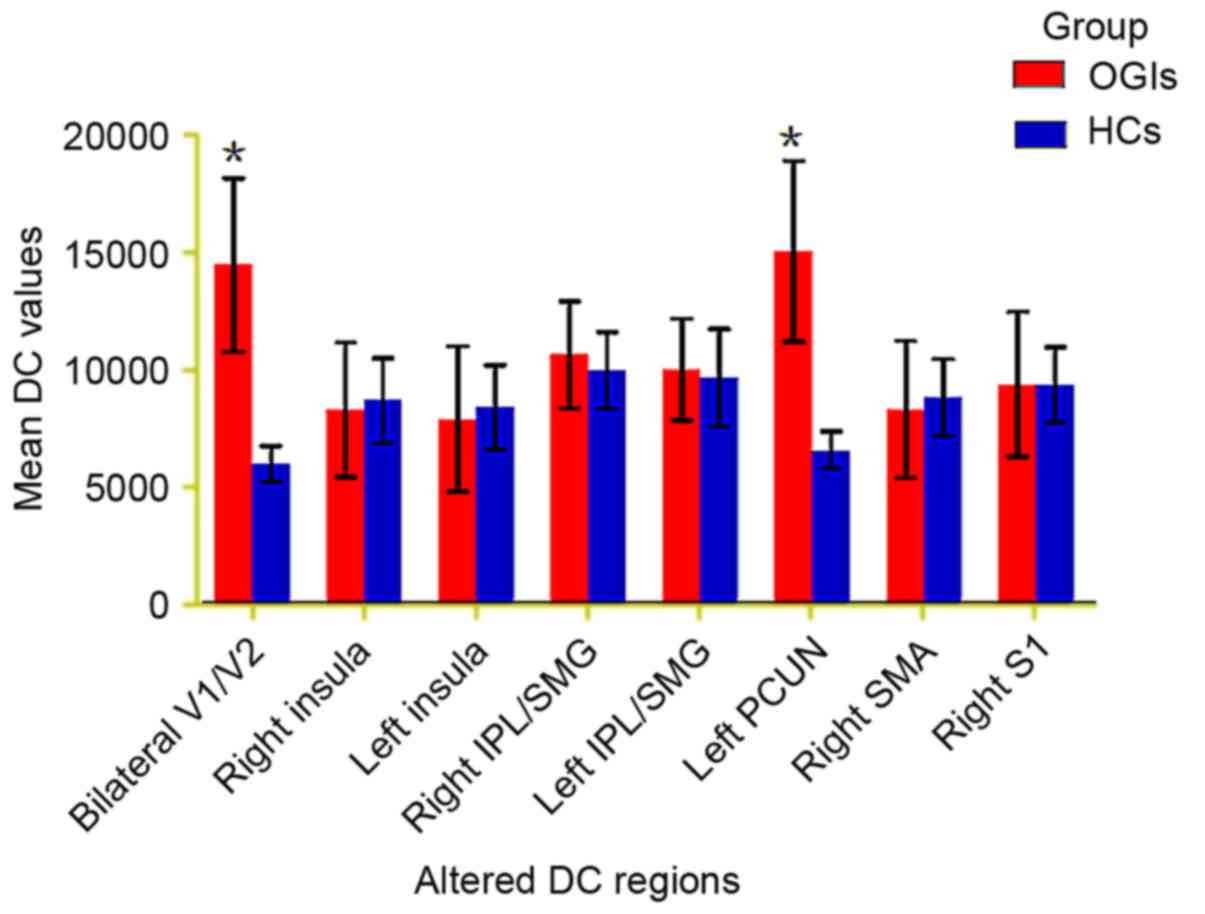
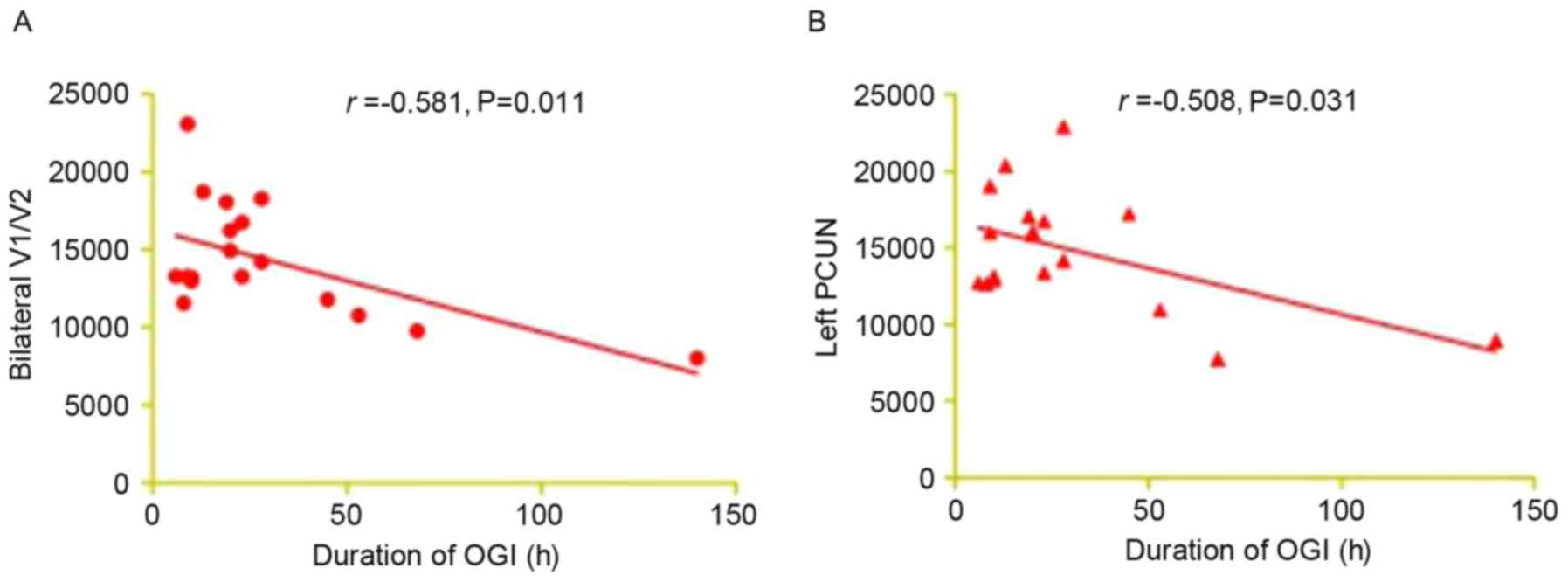
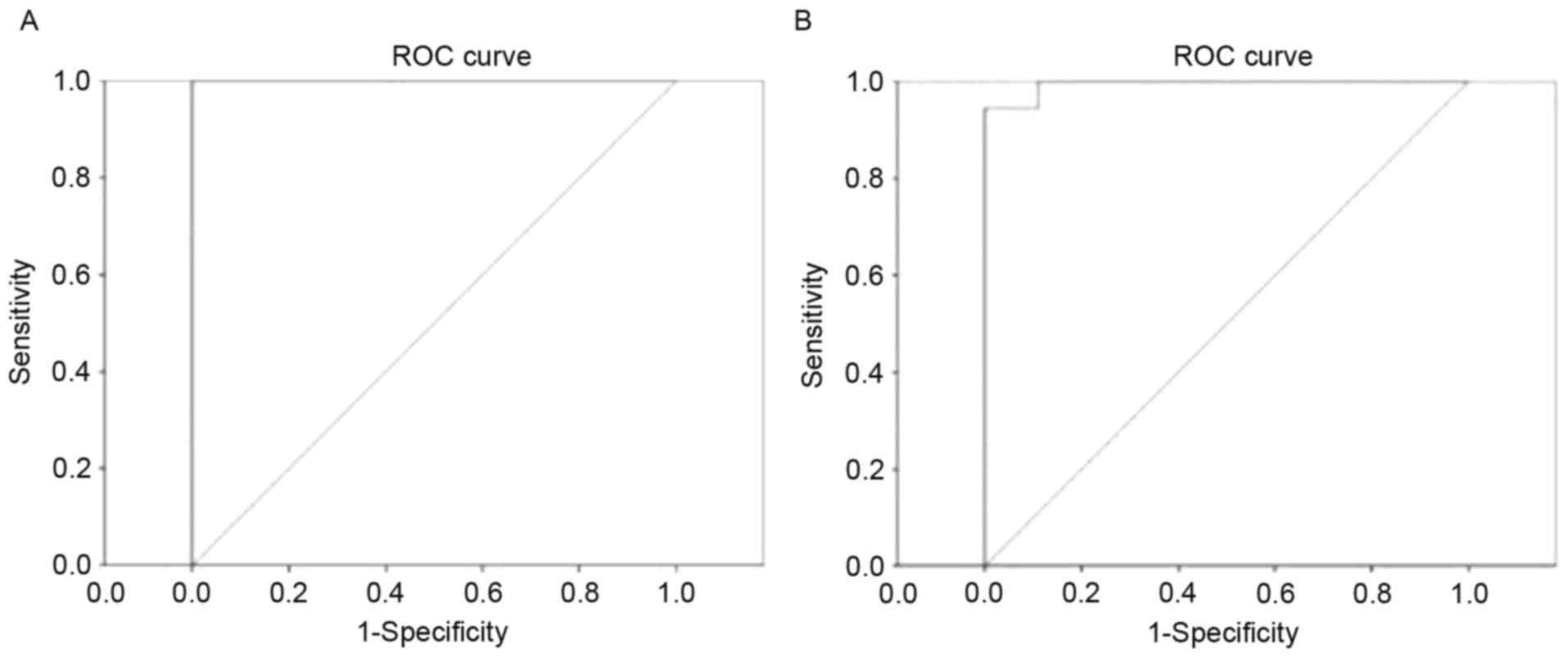
|
1
|
Chaikitmongkol V, Leeungurasatien T and
Sengupta S: Work-related eye injuries: Important occupational
health problem in northern Thailand. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila).
4:155–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vasu U, Vasnaik A, Battu RR, Kurian M and
George S: Occupational open globe injuries. Indian J Ophthalmol.
49:43–47. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cillino S, Casuccio A, Di Pace F,
Pillitteri F and Cillino G: A five-year retrospective study of the
epidemiological characteristics and visual outcomes of patients
hospitalized for ocular trauma in a Mediterranean area. BMC
Ophthalmol. 8:82008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu X, Liu Z, Liu Y, Zhao L, Xu S, Su G
and Zhao J: Determination of visual prognosis in children with open
globe injuries. Eye (Lond). 28:852–856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cao H, Li L and Zhang M: Epidemiology of
patients hospitalized for ocular trauma in the Chaoshan region of
China, 2001–2010. PLoS One. 7:e483772012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Négrel AD and Thylefors B: The global
impact of eye injuries. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 5:143–169. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nawani N, Vazirani J, Ojha H and Sangwan
VS: Conjunctival pedicle flap in management of open globe injury
with corneal tissue loss. BMJ Case Rep. 2016:pii:
bcr20152137032016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Stryjewski TP, Andreoli CM and Eliott D:
Retinal detachment after open globe injury. Ophthalmology.
121:327–333. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Osman EA: Glaucoma after open globe
injury. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 29:222–224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Zhang MN, Jiang CH, Yao Y and
Zhang K: Endophthalmitis following open globe injury. Br J
Ophthalmol. 94:111–114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feng K, Hu YT and Ma Z: Prognostic
indicators for no light perception after open-globe injury: Eye
injury vitrectomy study. Am J Ophthalmol. 152:654–662.e2. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Heidari E and Taheri N: Surgical treatment
of severely traumatized eyes with no light perception. Retina.
30:294–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Arey ML, Mootha VV, Whittemore AR, Chason
DP and Blomquist PH: Computed tomography in the diagnosis of occult
open-globe injuries. Ophthalmology. 114:1448–1452. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Allon G, Beiran I, Seider N and Blumenthal
EZ: The role of computed tomography in the immediate workup of open
globe injury. Eur J Ophthalmol. 26:503–504. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Andreoli MT, Yiu G, Hart L and Andreoli
CM: B-scan ultrasonography following open globe repair. Eye (Lond).
28:381–385. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Biswal BB: Resting state fMRI: A personal
history. Neuroimage. 62:938–944. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Y, Yu C, Liang M, Li J, Tian L, Zhou
Y, Qin W, Li K and Jiang T: Whole brain functional connectivity in
the early blind. Brain. 130:2085–2096. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fujii T, Tanabe HC, Kochiyama T and Sadato
N: An investigation of cross-modal plasticity of effective
connectivity in the blind by dynamic causal modeling of functional
MRI data. Neurosci Res. 65:175–186. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan WJ, Wu G, Li CX, Lin F, Sun J and Lei
H: Progressive atrophy in the optic pathway and visual cortex of
early blind Chinese adults: A voxel-based morphometry magnetic
resonance imaging study. Neuroimage. 37:212–220. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zuo XN, Ehmke R, Mennes M, Imperati D,
Castellanos FX, Sporns O and Milham MP: Network centrality in the
human functional connectome. Cereb Cortex. 22:1862–1875. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang X, Cai FQ, Hu PH, Zhong YL, Zhang Y,
Wei R, Pei CG, Zhou FQ and Shao Y: Disturbed spontaneous
brain-activity pattern in patients with optic neuritis using
amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation: A functional magnetic
resonance imaging study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 11:3075–3083.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shao Y, Cai FQ, Zhong YL, Huang X, Zhang
Y, Hu PH, Pei CG, Zhou FQ and Zeng XJ: Altered intrinsic regional
spontaneous brain activity in patients with optic neuritis: A
resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study.
Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 11:3065–3073. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Di Martino A, Zuo XN, Kelly C, Grzadzinski
R, Mennes M, Schvarcz A, Rodman J, Lord C, Castellanos FX and
Milham MP: Shared and distinct intrinsic functional network
centrality in autism and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
Biol Psychiatry. 74:623–632. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garcia-Garcia I, Jurado MÁ, Garolera M,
Marqués-Iturria I, Horstmann A, Segura B, Pueyo R, Sender-Palacios
MJ, Vernet-Vernet M, Villringer A, et al: Functional network
centrality in obesity: A resting-state and task fMRI study.
Psychiatry Res. 233:331–338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lou Y, Huang P, Li D, Cen Z, Wang B, Gao
J, Xuan M, Yu H, Zhang M and Luo W: Altered brain network
centrality in depressed Parkinson's disease patients. Mov Disord.
30:1777–1784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai H, Yin D, Hu C, Morelli JN, Hu S, Yan
X and Xu D: Whole-brain voxel-based analysis of diffusion tensor
MRI parameters in patients with primary open angle glaucoma and
correlation with clinical glaucoma stage. Neuroradiology.
55:233–243. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang X, Li HJ, Zhang Y, Peng DC, Hu PH,
Zhong YL, Zhou FQ and Shao Y: Microstructural changes of the whole
brain in patients with comitant strabismus: Evidence from a
diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat.
12:2007–2014. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang X, Li HJ, Ye L, Zhang Y, Wei R,
Zhong YL, Peng DC and Shao Y: Altered regional homogeneity in
patients with unilateral acute open-globe injury: A resting-state
functional MRI study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 12:1901–1906. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tan G, Huang X, Ye L, Wu AH, He LX, Zhong
YL, Jiang N, Zhou FQ and Shao Y: Altered spontaneous brain activity
patterns in patients with unilateral acute open globe injury using
amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation: A functional magnetic
resonance imaging study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 12:2015–2020.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cai F, Gao L, Gong H, Jiang F, Pei C,
Zhang X, Zeng X and Huang R: Network centrality of resting-state
fMRI in primary angle-closure glaucoma before and after surgery.
PLoS One. 10:e01413892015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tootell RB, Hadjikhani NK, Vanduffel W,
Liu AK, Mendola JD, Sereno MI and Dale AM: Functional analysis of
primary visual cortex (V1) in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:pp. 811–817. 1998; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Orban GA: Higher order visual processing
in macaque extrastriate cortex. Physiol Rev. 88:59–89. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Laramée ME, Bronchti G and Boire D:
Primary visual cortex projections to extrastriate cortices in
enucleated and anophthalmic mice. Brain Struct Funct.
219:2051–2070. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cunningham SI, Weiland JD, Bao P,
Lopez-Jaime GR and Tjan BS: Correlation of vision loss with
tactile-evoked V1 responses in retinitis pigmentosa. Vision Res.
111:197–207. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Burge WK, Griffis C, Nenert R, Elkhetali
A, Decarlo K, Ver Hoef W, Ross A and Visscher M: Cortical thickness
in human V1 associated with central vision loss. Sci Rep.
6:232682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu C, Liu Y, Li W, Wang D, Jiang T, Zhang
Y and Yu C: Increased regional homogeneity of blood oxygen
level-dependent signals in occipital cortex of early blind
individuals. Neuroreport. 22:190–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mahayana IT, Tcheang L, Chen CY, Juan CH
and Muggleton NG: The precuneus and visuospatial attention in near
and far space: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Brain
Stimul. 7:673–679. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bonni S, Veniero D, Mastropasqua C, Ponzo
V, Caltagirone C, Bozzali M and Koch G: TMS evidence for a
selective role of the precuneus in source memory retrieval. Behav
Brain Res. 282:70–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oshio R, Tanaka S, Sadato N, Sokabe M,
Hanakawa T and Honda M: Differential effect of double-pulse TMS
applied to dorsal premotor cortex and precuneus during internal
operation of visuospatial information. NeuroImage. 49:1108–1115.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Naidich TP, Kang E, Fatterpekar GM, Delman
BN, Gultekin SH, Wolfe D, Ortiz O, Yousry I, Weismann M and Yousry
TA: The insula: Anatomic study and MR imaging display at 1.5 T.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 25:222–232. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gu X, Hof PR, Friston KJ and Fan J:
Anterior insular cortex and emotional awareness. J Comp Neurol.
521:3371–3388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Seth AK, Suzuki K and Critchley HD: An
interoceptive predictive coding model of conscious presence. Front
Psychol. 2:3952012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gasquoine PG: Contributions of the insula
to cognition and emotion. Neuropsychol Rev. 24:77–87. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Grecucci A, Giorgetta C, Bonini N and
Sanfey AG: Reappraising social emotions: The role of inferior
frontal gyrus, temporo-parietal junction and insula in
interpersonal emotion regulation. Front Hum Neurosci. 7:5232013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Steward T, Picó-Pérez M, Mata F,
Martinez-Zalacain I, Cano M, Contreras-Rodriguez O,
Fernandez-Aranda F, Yucel M, Soriano-Mas C and Verdejo-Garcia A:
Emotion regulation and excess weight: Impaired affective processing
characterized by dysfunctional insula activation and connectivity.
PLoS One. 11:e01521502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Stein MB, Simmons AN, Feinstein JS and
Paulus MP: Increased amygdala and insula activation during emotion
processing in anxiety-prone subjects. Am J Psychiatry. 164:318–327.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Halsband U, Ito N, Tanji J and Freund HJ:
The role of premotor cortex and the supplementary motor area in the
temporal control of movement in man. Brain. 116:243–266. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Eccles JC: The initiation of voluntary
movements by the supplementary motor area. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr
(1970). 231:423–441. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Salardini A, Narayanan NS, Arora J,
Constable T and Jabbari B: Ipsilateral synkinesia involves the
supplementary motor area. Neurosci Lett. 523:135–138. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Florman JE, Duffau H and Rughani AI: Lower
motor neuron findings after upper motor neuron injury: Insights
from postoperative supplementary motor area syndrome. Front Hum
Neurosci. 7:852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|