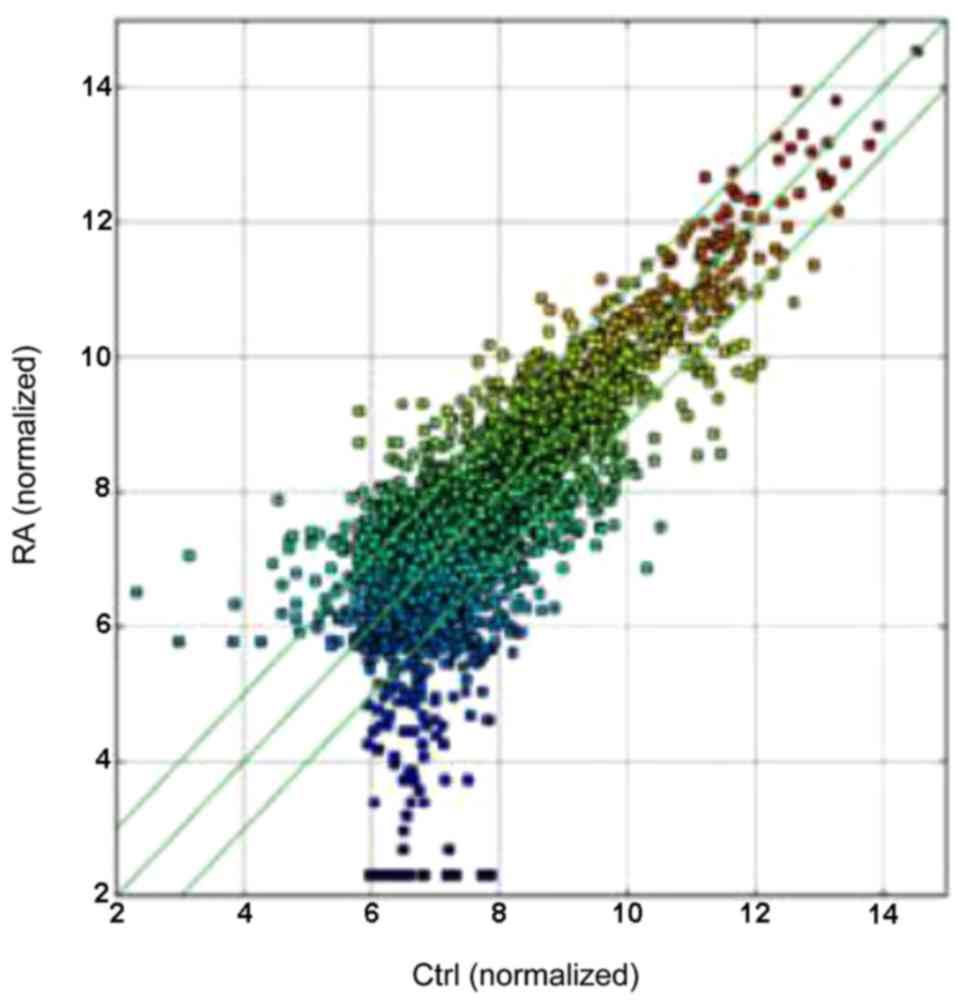
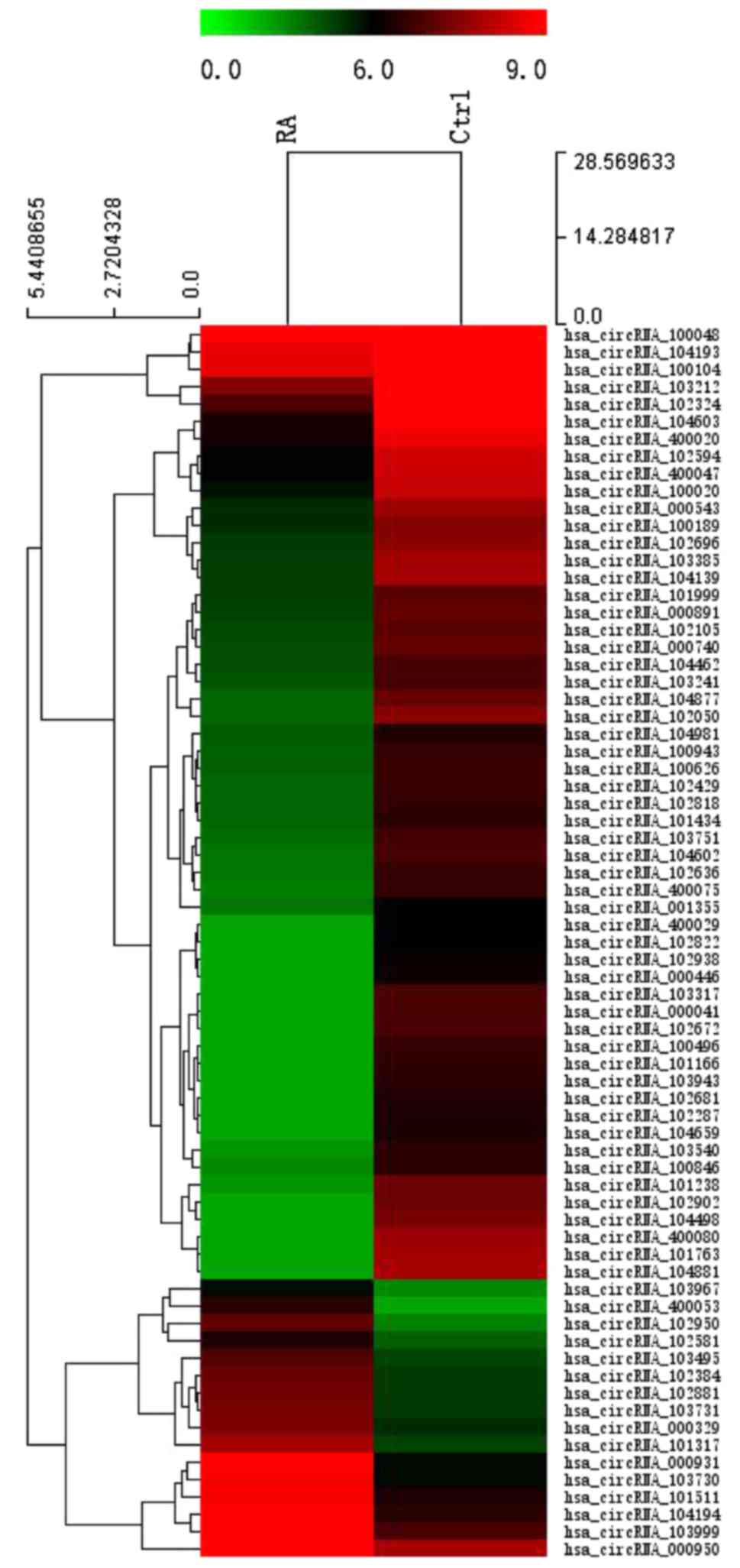
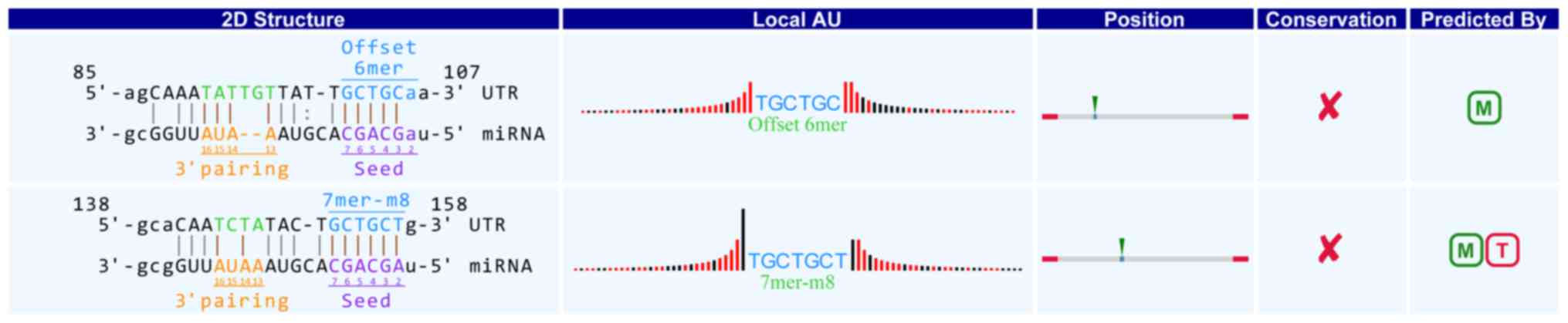
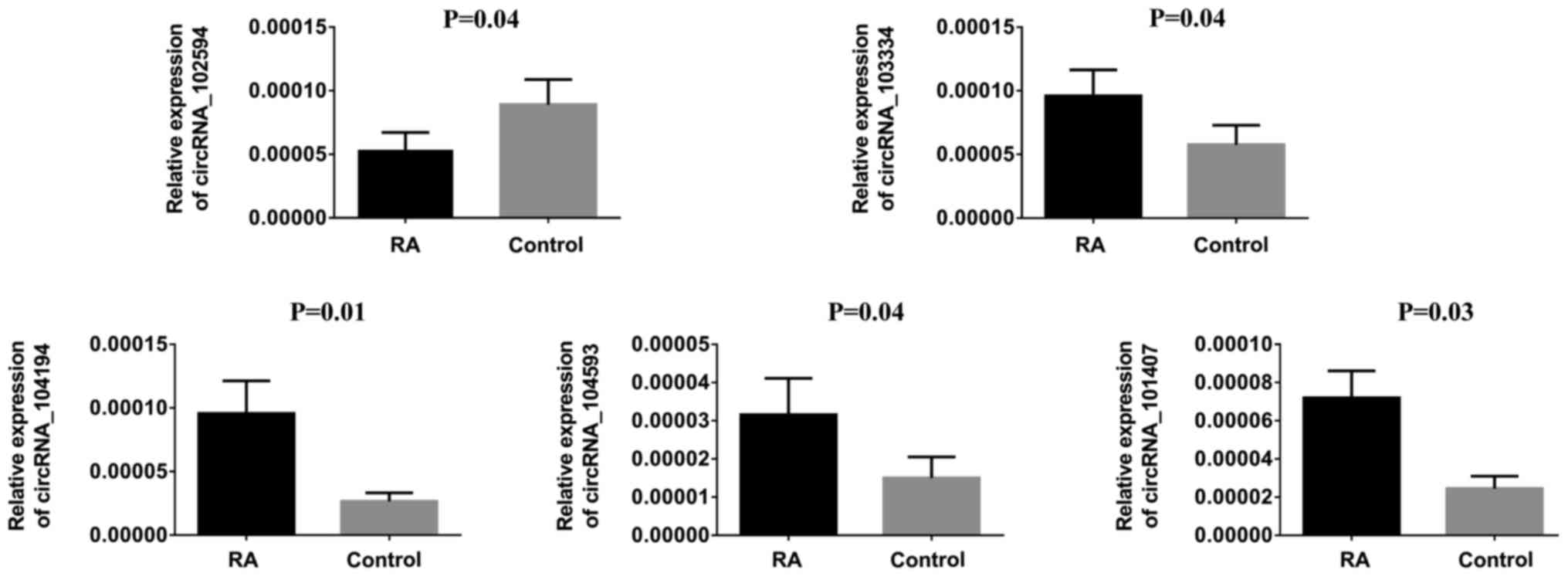
|
1
|
Firestein GS: Evolving concepts of
rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 423:356–361. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Salemi S, Biondo MI, Fiorentino C, Argento
G, Paolantonio M, Di Murro C, Malagnino VA, Canzoni M, Diamanti AP
and D'Amelio R: Could early rheumatoid arthritis resolve after
periodontitis treatment only?: Case report and review of the
literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 93:e1952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ursini F, Russo E, Hribal M Letizia, Mauro
D, Savarino F, Bruno C, Tripolino C, Rubino M, Naty S and Grembiale
RD: Abatacept improves whole-body insulin sensitivity in rheumatoid
arthritis: An observational study. Medicine (Baltimore).
94:e8882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J,
Felson DT, Bingham CO III, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP,
Cohen MD, et al: 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria:
An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against
Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 62:2569–2581.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra
JK, Allaart CF, van Zeben D, Kerstens PJ, Hazes JM, Zwinderman AH,
Ronday HK, Han KH, Westedt ML, et al: Clinical and radiographic
outcomes of four different treatment strategies in patients with
early rheumatoid arthritis (the BeSt study): A randomized,
controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 52:3381–3390. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen XM, Huang QC, Yang SL, Chu YL, Yan
YH, Han L, Huang Y and Huang RY: Role of Micro RNAs in the
pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: Novel perspectives based on
review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e13262015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang
R, Sun W, Dou K and Li H: Circular RNA: A new star of noncoding
RNAs. Cancer Lett. 365:141–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Conn VM,
Salmanidis M, Phillips CA, Roslan S, Schreiber AW, Gregory PA and
Goodall GJ: The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of
circRNAs. Cell. 160:1125–1134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qu S, Song W, Yang X, Wang J, Zhang R,
Zhang Z, Zhang H and Li H: Microarray expression profile of
circular RNAs in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genom
Data. 5:385–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ
and Kleinschmidt AK: Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed
circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like
structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 73:pp. 3852–3856. 1976;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hansen TB, Kjems J and Damgaard CK:
Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5609–5612. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kulcheski FR, Christoff AP and Margis R:
Circular RNAs are miRNA sponges and can be used as a new class of
biomarker. J Biotechnol. 238:42–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li F, Zhang L, Li W, Deng J, Zheng J, An
M, Lu J and Zhou Y: Circular RNA ITCH has inhibitory effect on ESCC
by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 6:6001–6013.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nagpal JK, Dasgupta S, Jadallah S, Chae
YK, Ratovitski EA, Toubaji A, Netto GJ, Eagle T, Nissan A,
Sidransky D and Trink B: Profiling the expression pattern of GPI
transamidase complex subunits in human cancer. Mod Pathol.
21:979–991. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mendell JT, ap Rhys CM and Dietz HC:
Separable roles for rent1/hUpf1 in altered splicing and decay of
nonsense transcripts. Science. 298:419–422. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peng L, Yuan XQ and Li GC: The emerging
landscape of circular RNA ciRS-7 in cancer (Review). Oncol Rep.
33:2669–2674. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thomas LF and Saetrom P: Circular RNAs are
depleted of polymorphisms at microRNA binding sites.
Bioinformatics. 30:2243–2246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Y and Wang Z: Efficient backsplicing
produces translatable circular mRNAs. RNA. 21:172–179. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gilbert WV: Alternative ways to think
about cellular internal ribosome entry. J Biol Chem.
285:29033–29038. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H and Bartel DP:
Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular
RNAs. Genome Biol. 15:4092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK,
Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF and Sharpless NE: Circular RNAs are
abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA.
19:141–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang G, Zhu H, Shi Y, Wu W, Cai H and
Chen X: cir-ITCH plays an inhibitory role in colorectal cancer by
regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01312252015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao ZJ and Shen J: Circular RNA
participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of
cancer. RNA Biol. 14:514–521. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qin M, Liu G, Huo X, Tao X, Sun X, Ge Z,
Yang J, Fan J, Liu L and Qin W: Hsa_circ_0001649: A circular RNA
and potential novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Biomark. 16:161–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R,
Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, et al:
Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human
microRNAs. Nat Genet. 37:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cheng DL, Xiang YY, Ji LJ and Lu XJ:
Competing endogenous RNA interplay in cancer: Mechanism,
methodology, and perspectives. Tumour Biol. 36:479–488. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Weinfeld M, Mani RS, Abdou I, Aceytuno RD
and Glover JN: Tidying up loose ends: The role of polynucleotide
kinase/phosphatase in DNA strand break repair. Trends Biochem Sci.
36:262–271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hitchon CA and El-Gabalawy HS: Oxidation
in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 6:265–278. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Phaniendra A, Jestadi DB and Periyasamy L:
Free radicals: Properties, sources, targets, and their implication
in various diseases. Indian J Clin Biochem. 30:11–26. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Das A, Wiederhold L, Leppard JB, Kedar P,
Prasad R, Wang H, Boldogh I, Karimi-Busheri F, Weinfeld M,
Tomkinson AE, et al: NEIL2-initiated, APE-independent repair of
oxidized bases in DNA: Evidence for a repair complex in human
cells. DNA Repair (Amst). 5:1439–1448. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ralph SJ, Rodriguez-Enriquez S, Neuzil J,
Saavedra E and Moreno-Sánchez R: The causes of cancer revisited:
‘Mitochondrial malignancy’ and ROS-induced oncogenic
transformation-why mitochondria are targets for cancer therapy. Mol
Aspects Med. 31:145–170. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rasouli-Nia A, Karimi-Busheri F and
Weinfeld M: Stable down-regulation of human polynucleotide kinase
enhances spontaneous mutation frequency and sensitizes cells to
genotoxic agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:pp. 6905–6910. 2004;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tahbaz N, Subedi S and Weinfeld M: Role of
polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase in mitochondrial DNA repair.
Nucleic Acids Res. 40:3484–3495. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nie Z, Stanley KT, Stauffer S, Jacques KM,
Hirsch DS, Takei J and Randazzo PA: AGAP1, an endosome-associated,
phosphoinositide-dependent ADP-ribosylation factor
GTPase-activating protein that affects actin cytoskeleton. J Biol
Chem. 277:48965–48975. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bartok B, Hammaker D and Firestein GS:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ regulates migration and invasion of
synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 192:2063–2070.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel
RA, Ginsberg MH, Borisy G, Parsons JT and Horwitz AR: Cell
migration: Integrating signals from front to back. Science.
302:1704–1709. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Parsons JT, Horwitz AR and Schwartz MA:
Cell adhesion: Integrating cytoskeletal dynamics and cellular
tension. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:633–643. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dai J, Xie Y, Wu Q, Wang L, Yin G, Ye X,
Zeng L, Xu J, Ji C, Gu S, et al: Molecular cloning and
characterization of a novel human hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-like
2 (HSDL2) cDNA from fetal brain. Biochem Genet. 41:165–174. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Skogsberg J, Lundström J, Kovacs A,
Nilsson R, Noori P, Maleki S, Köhler M, Hamsten A, Tegnér J and
Björkegren J: Transcriptional profiling uncovers a network of
cholesterol-responsive atherosclerosis target genes. PLoS Genet.
4:e10000362008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Peters MJ, Vis M, van Halm VP, Wolbink GJ,
Voskuyl AE, Lems WF, Dijkmans BA, Twisk JW, de Koning MH, van de
Stadt RJ and Nurmohamed MT: Changes in lipid profile during
infliximab and corticosteroid treatment in rheumatoid arthritis.
Ann Rheum Dis. 66:958–961. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pincus T, Sokka T and Wolfe F: Premature
mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Evolving concepts.
Arthritis Rheum. 44:1234–1236. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Boden G: Obesity and free fatty acids.
Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 37:635–646, viii-ix. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Siwek M, Slawinska A, Rydzanicz M, Wesoly
J, Fraszczak M, Suchocki T, Skiba J, Skiba K and Szyda J:
Identification of candidate genes and mutations in QTL regions for
immune responses in chicken. Anim Genet. 46:247–254. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gierut A, Perlman H and Pope RM: Innate
immunity and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am.
36:271–296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Roelofs MF, Wenink MH, Brentano F,
Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Oppers-Walgreen B, Barrera P, van Riel PL,
Joosten LA, Kyburz D, van den Berg WB and Radstake TR: Type I
interferons might form the link between Toll-like receptor (TLR)
3/7 and TLR4-mediated synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis
(RA). Ann Rheum Dis. 68:1486–1493. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sheng YJ, Gao JP, Li J, Han JW, Xu Q, Hu
WL, Pan TM, Cheng YL, Yu ZY, Ni C, et al: Follow-up study
identifies two novel susceptibility loci PRKCB and 8p11.21 for
systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 50:682–688.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nagata Y, Nakasa T, Mochizuki Y, Ishikawa
M, Miyaki S, Shibuya H, Yamasaki K, Adachi N, Asahara H and Ochi M:
Induction of apoptosis in the synovium of mice with
autoantibody-mediated arthritis by the intraarticular injection of
double-stranded MicroRNA-15a. Arthritis Rheum. 60:2677–2683. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nakasa T, Nagata Y, Yamasaki K and Ochi M:
A mini-review: microRNA in arthritis. Physiol Genomics. 43:566–570.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Baxter D, McInnes IB and
Kurowska-Stolarska M: Novel regulatory mechanisms in inflammatory
arthritis: A role for microRNA. Immunol Cell Biol. 90:288–292.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pauley KM, Satoh M, Chan AL, Bubb MR,
Reeves WH and Chan EK: Upregulated miR-146a expression in
peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis
patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:R1012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu Y, Dong J, Mu R, Gao Y, Tan X, Li Y,
Li Z and Yang G: MicroRNA-30a promotes B cell hyperactivity in
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus by direct interaction
with Lyn. Arthritis Rheum. 65:1603–1611. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang W, Zhang Y, Zhu B, Duan T, Xu Q, Wang
R, Lu L and Jiao Z: Plasma microRNA expression profiles in Chinese
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Oncotarget. 6:42557–42568.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Murata K, Yoshitomi H, Tanida S, Ishikawa
M, Nishitani K, Ito H and Nakamura T: Plasma and synovial fluid
microRNAs as potential biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis and
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 12:R862010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xu K, Xu P, Yao JF, Zhang YG, Hou WK and
Lu SM: Reduced apoptosis correlates with enhanced autophagy in
synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res. 62:229–237.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zafari S, Backes C, Meese E and Keller A:
Circulating biomarker panels in Alzheimer's disease. Gerontology.
61:497–503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Egloff C, Hugle T and Valderrabano V:
Biomechanics and pathomechanisms of osteoarthritis. Swiss Med Wkly.
142:w135832012.PubMed/NCBI
|