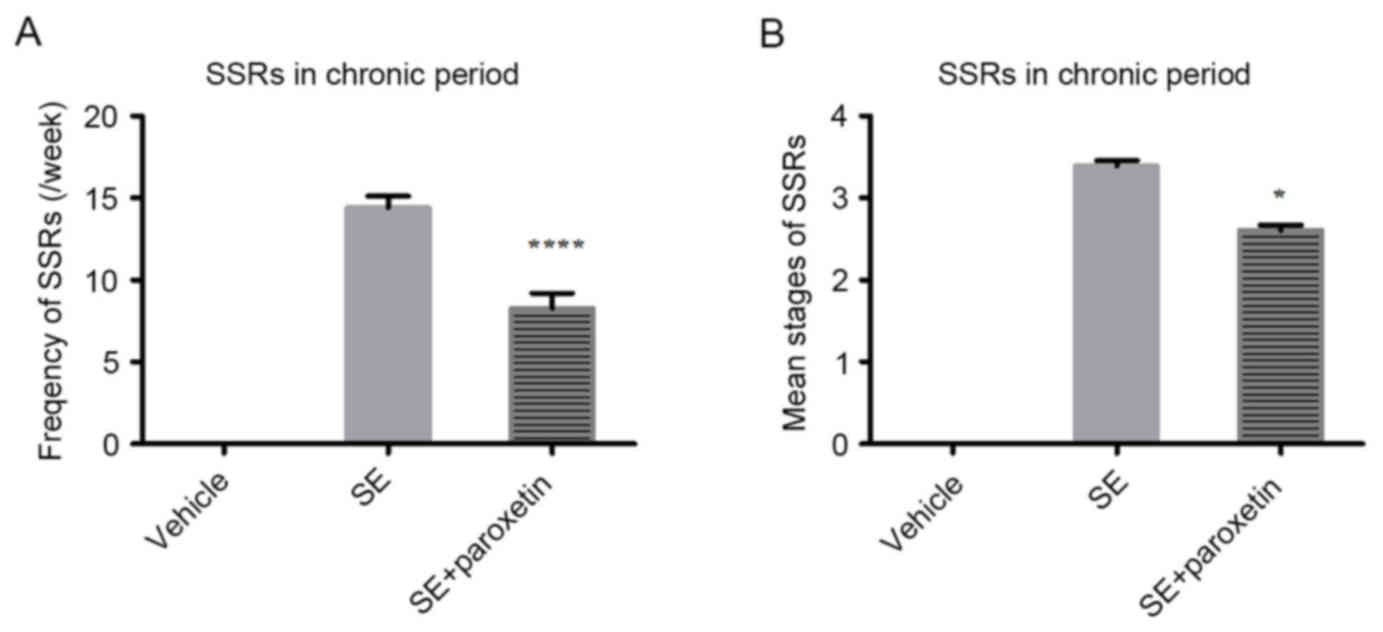
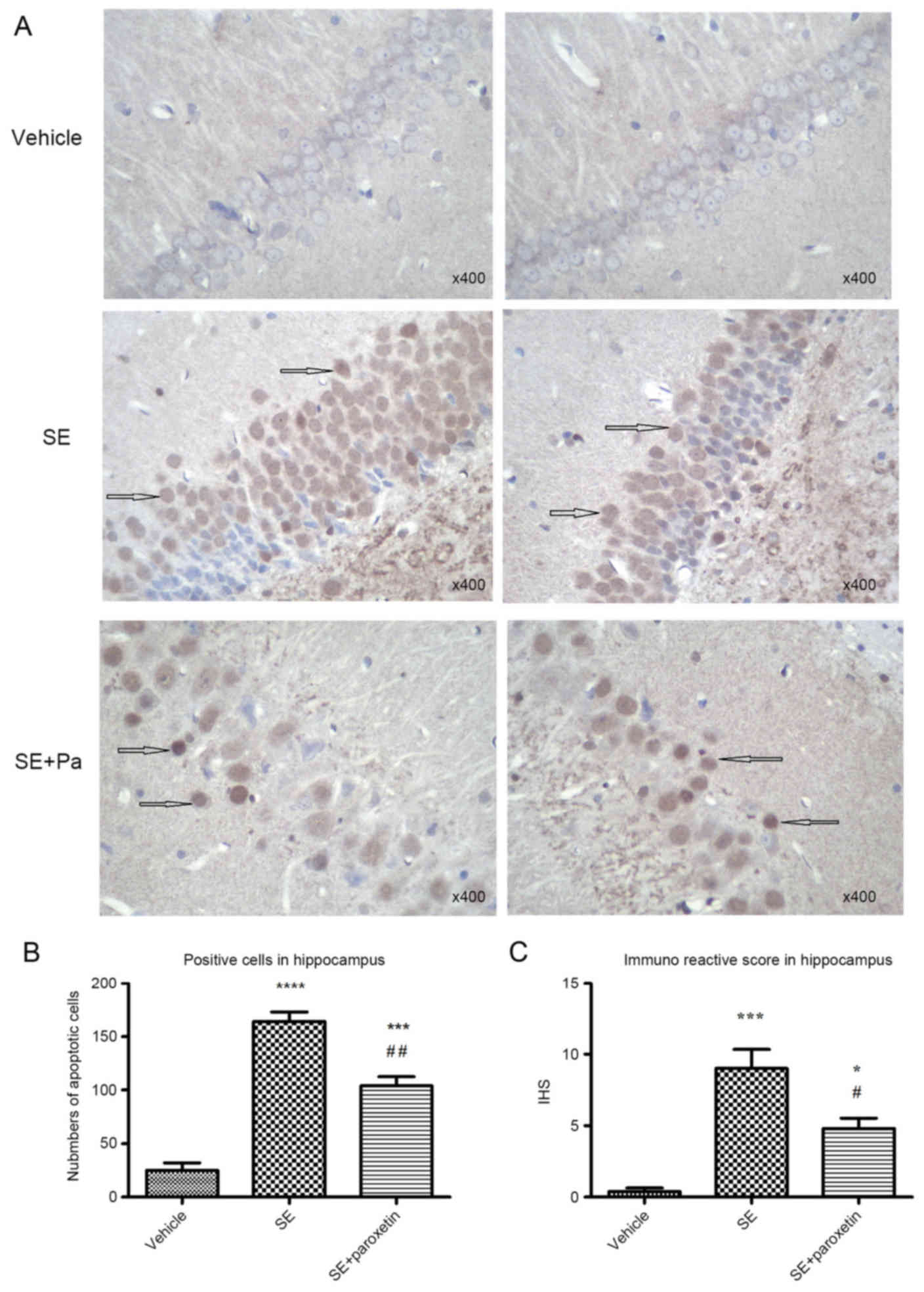
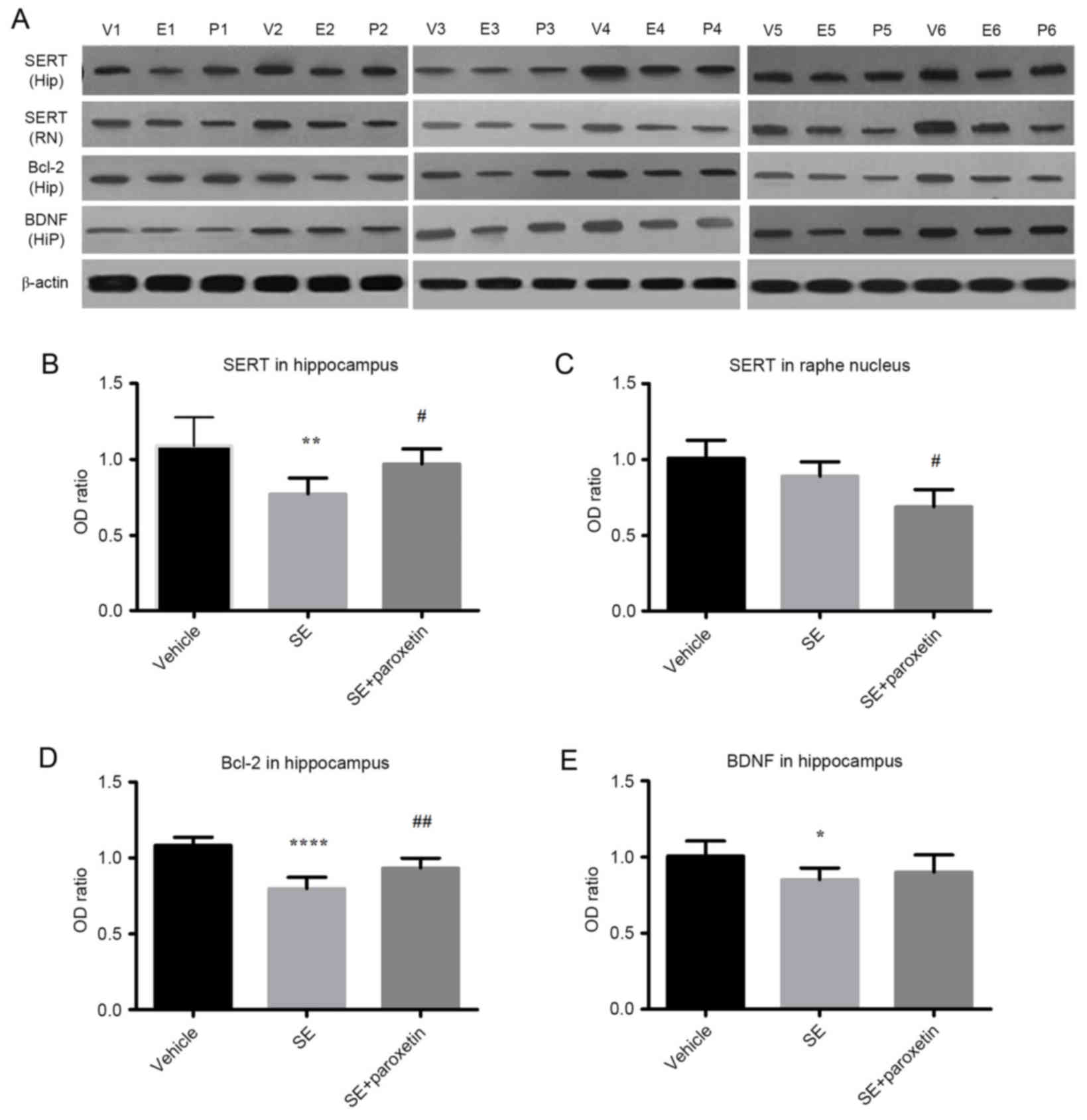
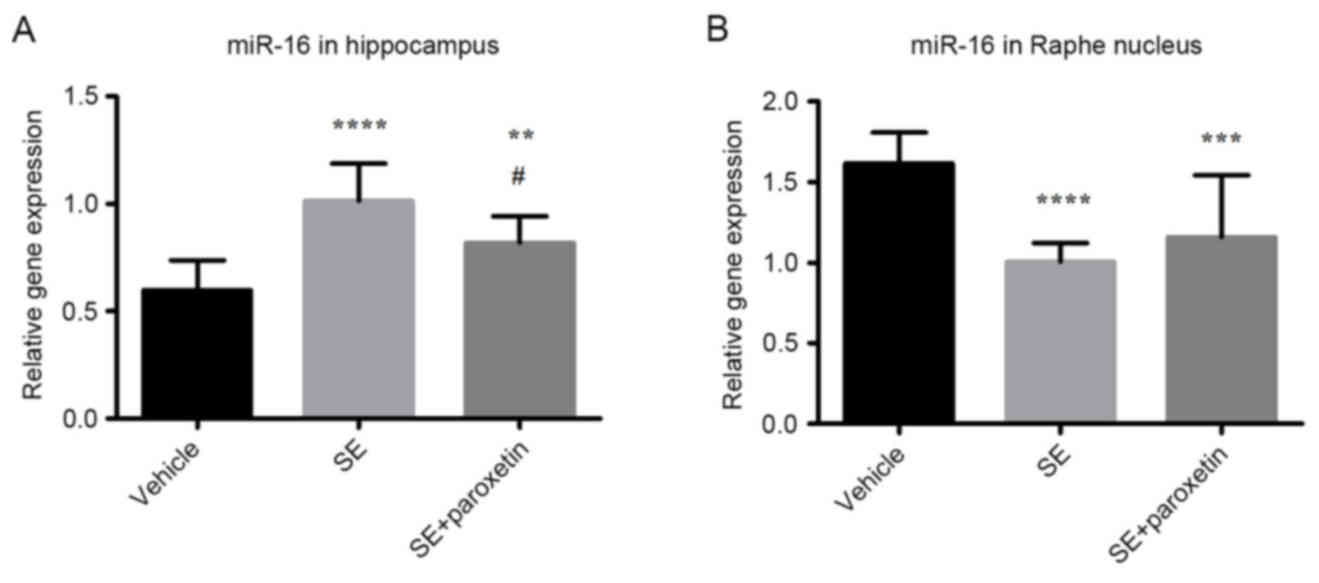
|
1
|
Curran S: Effect of paroxetine on seizure
length during electroconvulsive therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand.
92:239–240. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alper K, Schwartz KA, Kolts RL and Khan A:
Seizure incidence in psychopharmacological clinical trials: An
analysis of Food and Drug Administration (FDA) summary basis of
approval reports. Biol Psychiatry. 62:345–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Payandemehr B, Ghasemi M and Dehpour AR:
Citalopram as a good candidate for treatment of depression in
patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 44:96–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shiha AA, de Cristóbal J, Delgado M,
Fernández de la Rosa R, Bascuñana P, Pozo MA and García-García L:
Subacute administration of fluoxetine prevents short-term brain
hypometabolism and reduces brain damage markers induced by the
lithium-pilocarpine model of epilepsy in rats. Brain Res Bull.
111:36–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vermoesen K, Massie A, Smolders I and
Clinckers R: The antidepressants citalopram and reboxetine reduce
seizure frequency in rats with chronic epilepsy. Epilepsia.
53:870–878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin WH, Huang HP, Lin MX, Chen SG, Lv XC,
Che CH and Lin JL: Seizure-induced 5-HT release and chronic
impairment of serotonergic function in rats. Neurosci Lett.
534:1–6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Launay JM, Mouillet-Richard S, Baudry A,
Pietri M and Kellermann O: Raphe-mediated signals control the
hippocampal response to SRI antidepressants via miR-16. Transl
Psychiatry. 1:e562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Yu JT and Tan L, Tian Y, Ma J, Tan
CC, Wang HF, Liu Y, Tan MS, Jiang T and Tan L: Genome-wide
circulating microRNA expression profiling indicates biomarkers for
epilepsy. Sci Rep. 5:95222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li MM, Jiang T, Sun Z, Zhang Q, Tan CC, Yu
JT and Tan L: Genome-wide microRNA expression profiles in
hippocampus of rats with chronic temporal lobe epilepsy. Sci Rep.
4:47342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Henshall DC: MicroRNA and epilepsy:
Profiling, functions and potential clinical applications. Curr Opin
Neurol. 27:199–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu K, Xie YY, Zhang C, Ouyang DS, Long HY,
Sun DN, Long LL, Feng L, Li Y and Xiao B: MicroRNA expression
profile of the hippocampus in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy
and miR-34a-targeted neuroprotection against hippocampal neurone
cell apoptosis post-status epilepticus. BMC Neurosci. 13:1152012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Omran A, Peng J, Zhang C, Xiang QL, Xue J,
Gan N, Kong H and Yin F: Interleukin-1β and microRNA-146a in an
immature rat model and children with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy.
Epilepsia. 53:1215–1224. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reschke CR and Henshall DC: microRNA and
epilepsy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 888:41–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ashhab MU, Omran A, Kong H, Gan N, He F,
Peng J and Yin F: Expressions of tumor necrosis factor alpha and
microRNA-155 in immature rat model of status epilepticus and
children with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci.
51:950–958. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kan AA, van Erp S, Derijck AA, de Wit M,
Hessel EV, O'Duibhir E, de Jager W, Van Rijen PC, Gosselaar PH, de
Graan PN and Pasterkamp RJ: Genome-wide microRNA profiling of human
temporal lobe epilepsy identifies modulators of the immune
response. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:3127–3145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin K, Farahani M, Yang Y, Johnson GG,
Oates M, Atherton M, Douglas A, Kalakonda N and Pettitt AR: Loss of
MIR15A and MIR16-1 at 13q14 is associated with increased TP53 mRNA,
de-repression of BCL2 and adverse outcome in chronic lymphocytic
leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 167:346–355. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Paxinos G and Watson C: The Rat Brain in
Stereotactic Coordinates. 5th edition. Elsevier Academic Press;
Boston, MA: pp. 1612005
|
|
18
|
Racine RJ: Modification of seizure
activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure.
Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 32:281–294. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Veliskova J: Behavioral characterization
of seizures in ratsModels of Seizures and Epilepsy. Elsevier
Academic Press; Burlington: pp. 601–611. 2006, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bagdy G, Kecskemeti V, Riba P and Jakus R:
Serotonin and epilepsy. J Neurochem. 100:857–873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Theodore WH: Does serotonin play a role in
epilepsy? Epilepsy Curr. 3:173–177. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gidal BE: Serotonin and epilepsy: The
story continues. Epilepsy Curr. 13:289–290. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Airaksinen EM: Uptake of taurine, GABA,
5-HT, and dopamine by blood platelets in progressive myoclonus
epilepsy. Epilepsia. 20:503–510. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bateman LM, Li CS, Lin TC and Seyal M:
Serotonin reuptake inhibitors are associated with reduced severity
of ictal hypoxemia in medically refractory partial epilepsy.
Epilepsia. 51:2211–2214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Trindade-Filho EM, de Castro-Neto EF, de A
Carvalho R, Lima E, Scorza FA, Amado D, Naffah-Mazzacoratti Mda G
and Cavalheiro EA: Serotonin depletion effects on the pilocarpine
model of epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 82:194–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
da Fonseca NC, Joaquim HP, Talib LL, de
Vincentiis S, Gattaz WF and Valente KD: Hippocampal serotonin
depletion is related to the presence of generalized tonic-clonic
seizures, but not to psychiatric disorders in patients with
temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 111:18–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cardamone L, Salzberg MR, Koe AS, Ozturk
E, O'Brien TJ and Jones NC: Chronic antidepressant treatment
accelerates kindling epileptogenesis in rats. Neurobiol Dis.
63:194–200. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Esmail EH, Labib DM and Rabie WA:
Association of serotonin transporter gene (5HTT) polymorphism and
juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: A case-control study. Acta Neurol
Belg. 115:247–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang K, Su J, Hu Z, Lang R, Sun X, Li X,
Wang D, Wei M and Yin J: Serotonin transporter (5-HTT) gene
polymorphisms and susceptibility to epilepsy: A meta-analysis and
meta-regression. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 17:890–897. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Martinez A, Finegersh A, Cannon DM, Dustin
I, Nugent A, Herscovitch P and Theodore WH: The 5-HT1A receptor and
5-HT transporter in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology.
80:1465–1471. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schenkel LC, Bragatti JA, Torres CM,
Martin KC, Gus-Manfro G, Leistner-Segal S and Bianchin MM:
Serotonin transporter gene (5HTT) polymorphisms and temporal lobe
epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 95:152–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kobow K and Blümcke I: The methylation
hypothesis: Do epigenetic chromatin modifications play a role in
epileptogenesis? Epilepsia. 52(Suppl 4): S15–S19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Serikawa T, Mashimo T, Kuramoro T, Voigt
B, Ohno Y and Sasa M: Advances on genetic rat models of epilepsy.
Exp Anim. 64:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ran X, Li J, Shao Q, Chen H, Lin Z, Sun ZS
and Wu J: EpilepsyGene: A genetic resource for genes and mutations
related to epilepsy. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(Database issue):
D893–D899. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Weber YG, Nies AT, Schwab M and Lerche H:
Genetic biomarkers in epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics. 11:324–333.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Moon J, Lee ST, Choi J, Jung KH, Yang H,
Khalid A, Kim JM, Park KI, Shin JW, Ban JJ, et al: Unique
behavioral characteristics and microRNA signatures in a drug
resistant epilepsy model. PloS one. 9:e856172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jimenez-Mateos EM and Henshall DC:
Epilepsy and microRNA. Neuroscience. 238:218–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang S, Zou X, Zhu JN, Fu YH, Lin QX,
Liang YY, Deng CY, Kuang SJ, Zhang MZ, Liao YL, et al: Attenuation
of microRNA-16 derepresses the cyclins D1, D2 and E1 to provoke
cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Cell Mol Med. 19:608–619. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li W, Qi Z, Wei Z, Liu S, Wang P, Chen Y
and Zhao Y: Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and induces
apoptosis of human glioma cells via microRNA-16 upregulation and
matrix metalloproteinase-9 downregulation. Mol Med Rep.
12:2735–2740. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mobarra N, Shafiee A, Rad SM, Tasharrofi
N, Soufi-Zomorod M, Hafizi M, Movahed M, Kouhkan F and Soleimani M:
Overexpression of microRNA-16 declines cellular growth,
proliferation and induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells.
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 51:604–611. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bai M, Zhu X, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Zhang L,
Xue L, Yi J, Yao S and Zhang X: Abnormal hippocampal BDNF and
miR-16 expression is associated with depression-like behaviors
induced by stress during early life. PLoS One. 7:e469212012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun YX, Yang J, Wang PY, Li YJ, Xie SY and
Sun RP: Cisplatin regulates SH-SY5Y cell growth through
downregulation of BDNF via miR-16. Oncol Rep. 30:2343–2349. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kilany A, Raouf ER, Gaber AA, Aloush TK,
Aref HA, Anwar M, Henshall DC and Abdulghani MO: Elevated serum
Bcl-2 in children with temporal lobe epilepsy. Seizure. 21:250–253.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Henshall DC, Clark RS, Adelson PD, Chen M,
Watkins SC and Simon RP: Alterations in bcl-2 and caspase gene
family protein expression in human temporal lobe epilepsy.
Neurology. 55:250–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Scharfman H: Does BDNF contribute to
temporal lobe epilepsy? Epilepsy Curr. 2:92–94. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kuramoto S, Yasuhara T, Agari T, Kondo A,
Jing M, Kikuchi Y, Shinko A, Wakamori T, Kameda M, Wang F, et al:
BDNF-secreting capsule exerts neuroprotective effects on epilepsy
model of rats. Brain Res. 1368:281–289. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Song MF, Dong JZ, Wang YW, He J, Ju X,
Zhang L, Zhang YH, Shi JF and Lv YY: CSF miR-16 is decreased in
major depression patients and its neutralization in rats induces
depression-like behaviors via a serotonin transmitter system. J
Affect Disord. 178:25–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zurawek D, Kusmider M, Faron-Gorecka A,
Gruca P, Pabian P, Solich J, Kolasa M, Papp M and
Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M: Reciprocal microrna expression in
mesocortical circuit and its interplay with serotonin transporter
define resilient rats in the chronic mild stress. Mol Neurobiol.
Sep 22–2016.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|