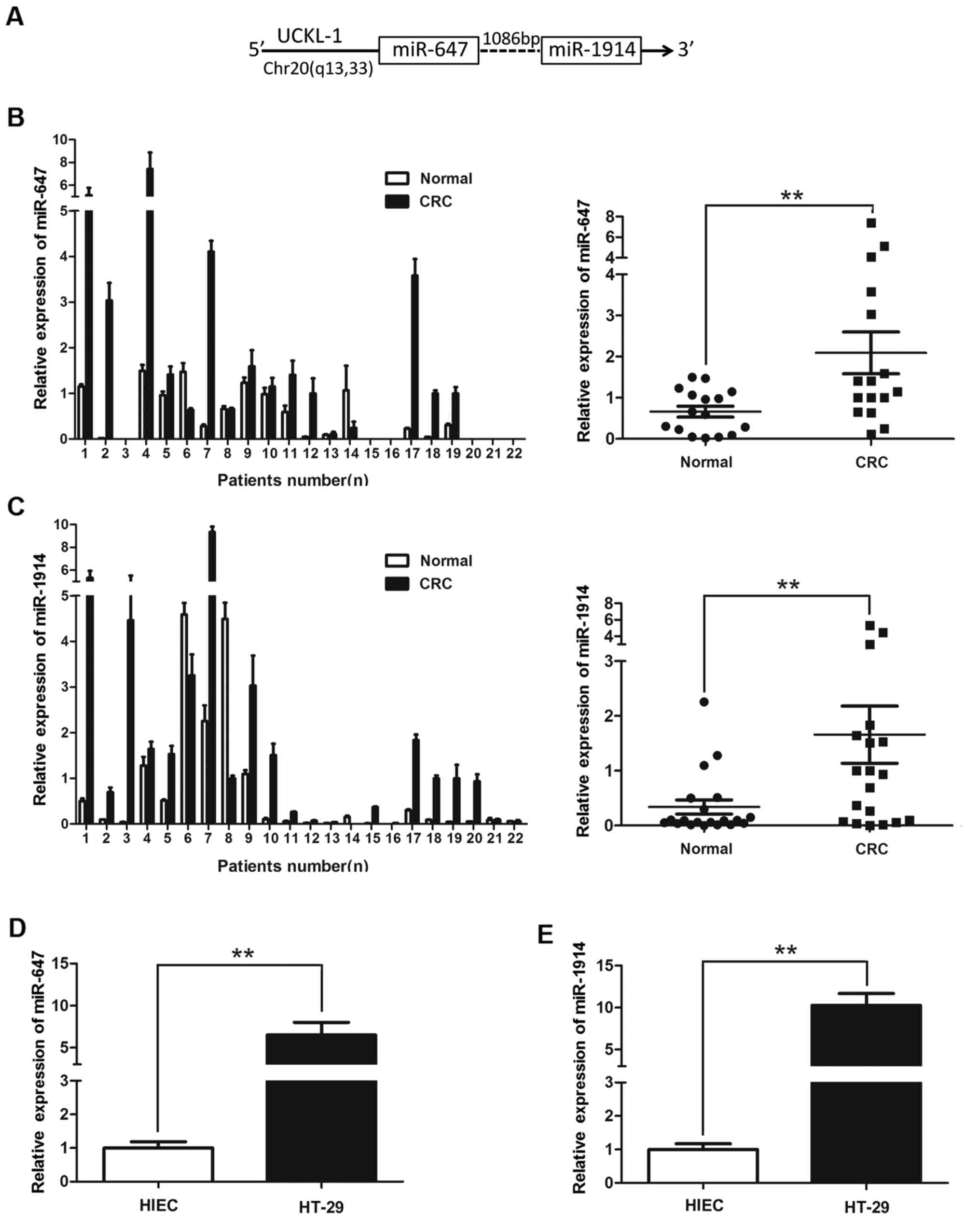
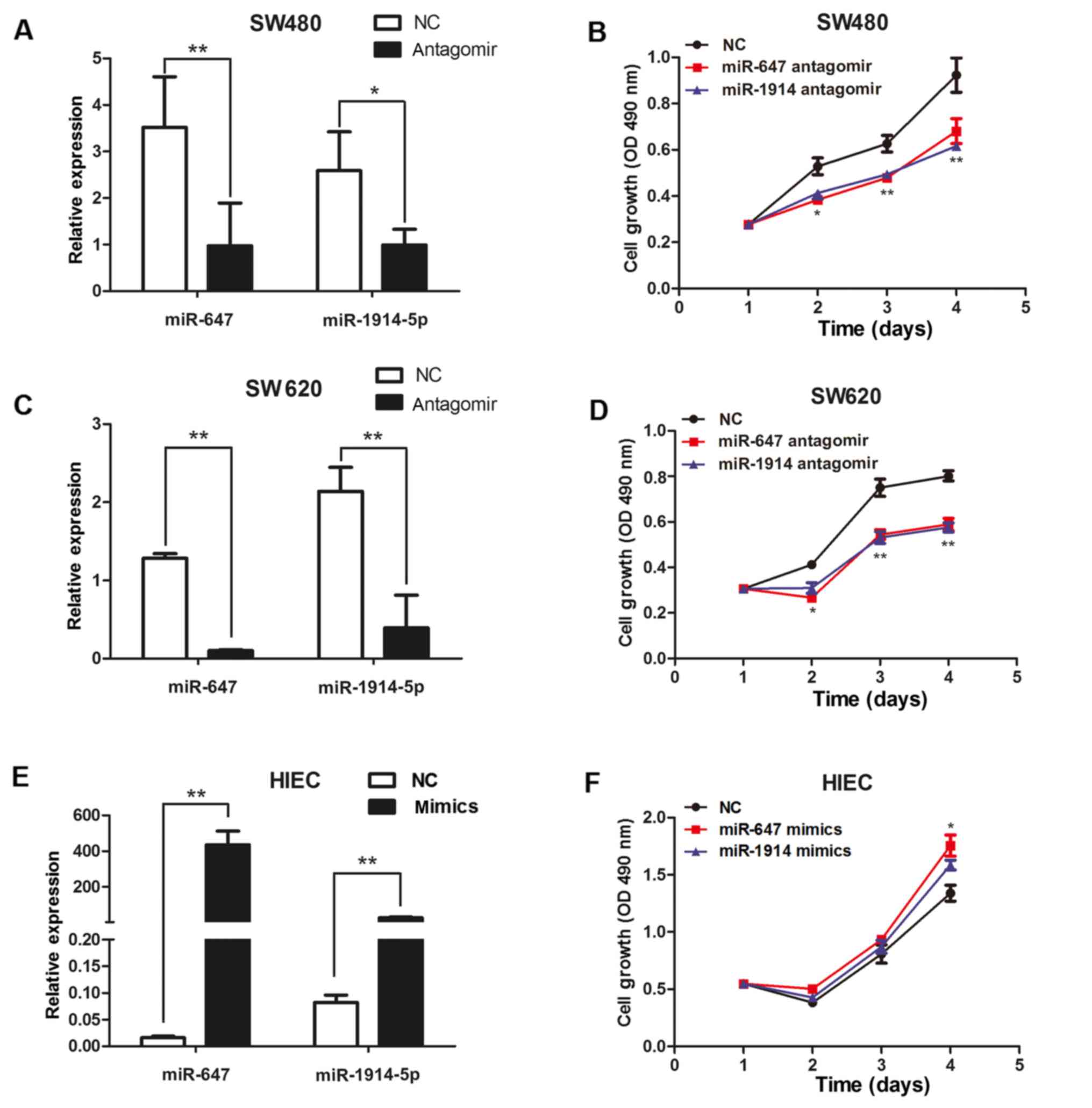
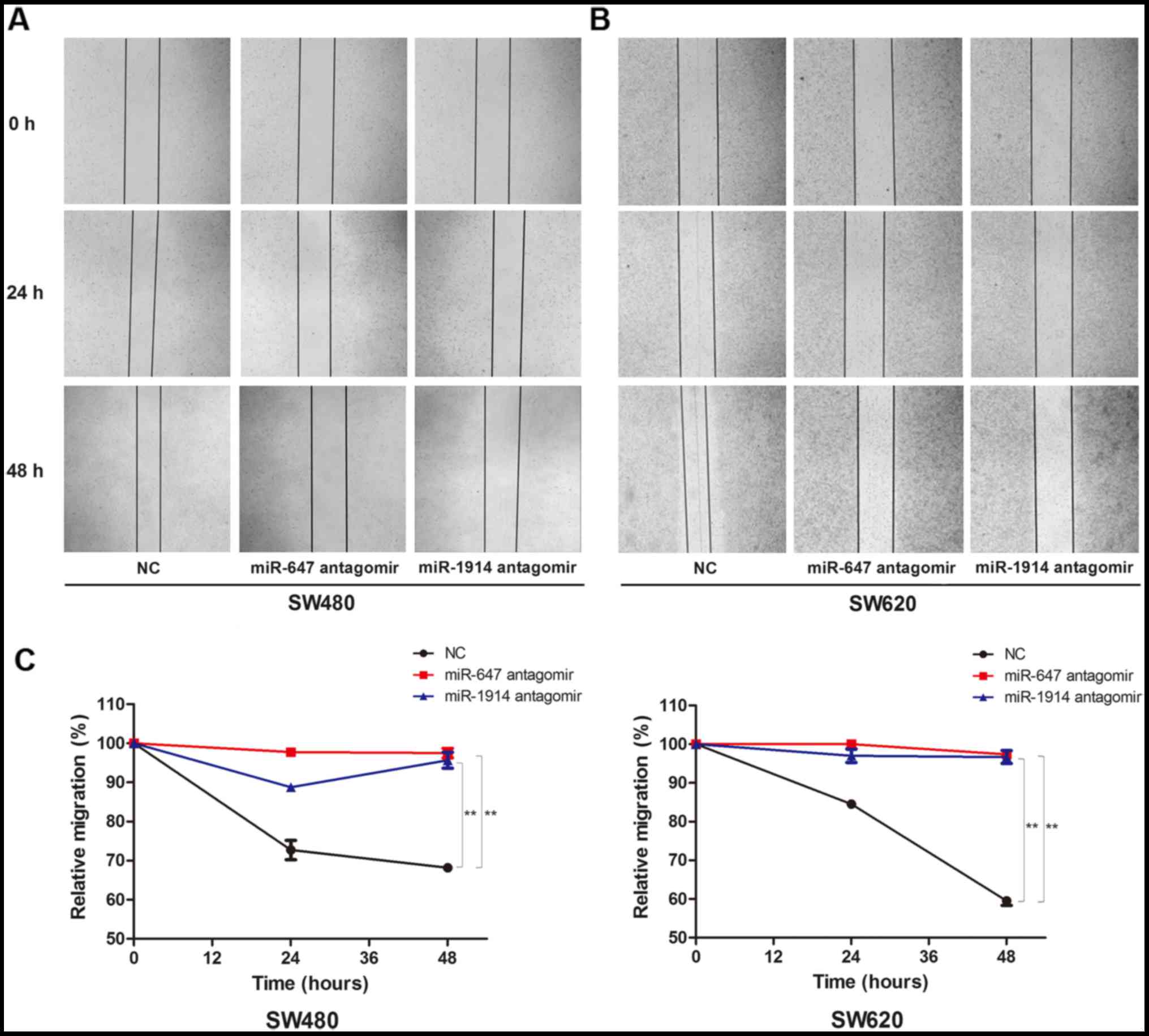
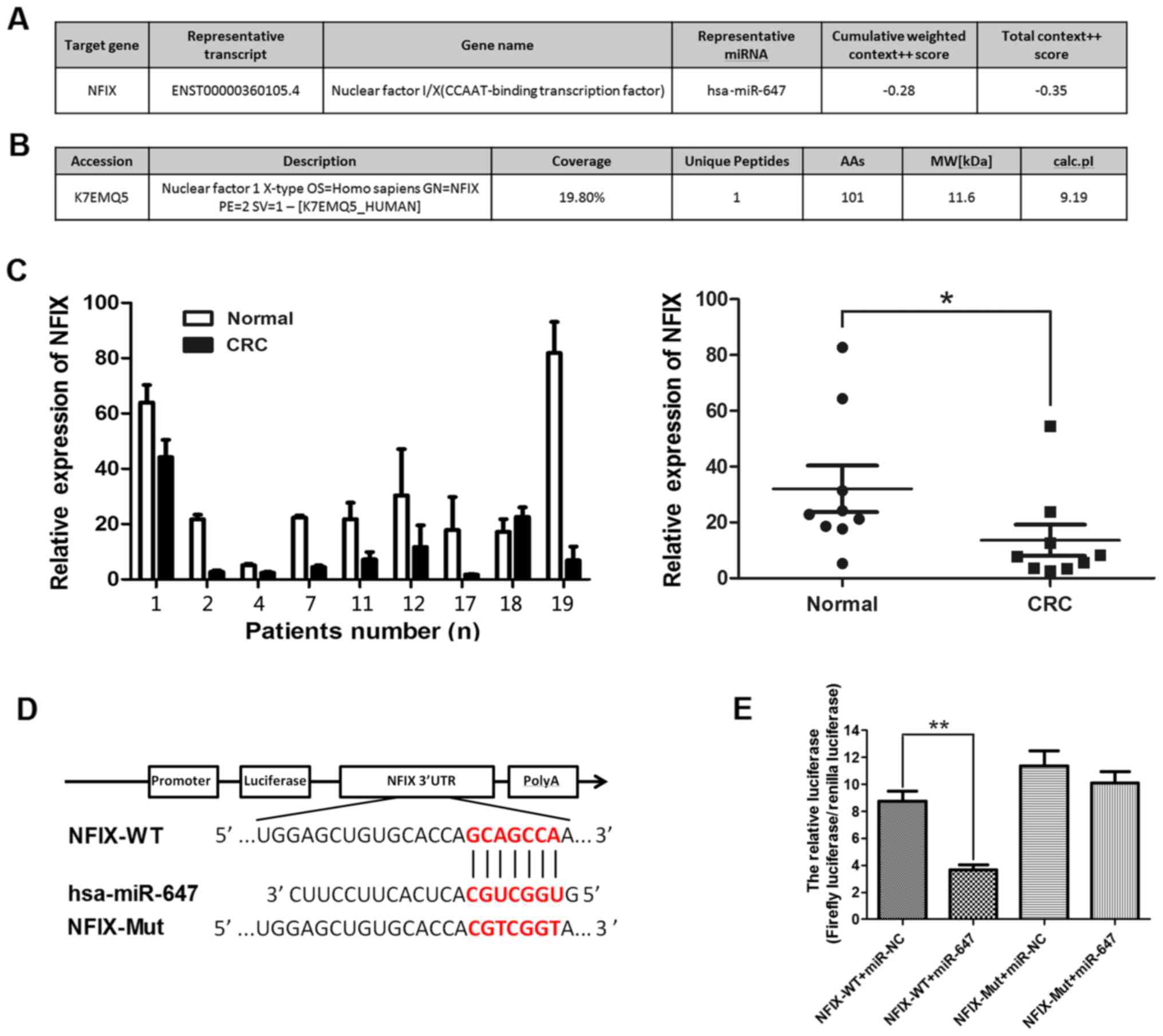
|
1
|
Chakradhar S: Colorectal cancer: 5 big
questions. Nature. 521:S162015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brody H: Colorectal cancer. Nature.
521:S12015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Van Cutsem E, Verheul HM, Flamen P,
Rougier P, Beets-Tan R, Glynne-Jones R and Seufferlein T: Imaging
in colorectal cancer: Progress and challenges for the clinicians.
Cancers (Basel). 8:E812016.doi: 10.3390/cancers8090081. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baratti D, Kusamura S, Pietrantonio F,
Guaglio M, Niger M and Deraco M: Progress in treatments for
colorectal cancer peritoneal metastases during the years 2010–2015.
A systematic review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 100:209–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hardingham JE, Grover P, Winter M, Hewett
PJ, Price TJ and Thierry B: Detection and clinical significance of
circulating tumor cells in colorectal cancer-20 years of progress.
Mol Med. 21 Suppl 1:S25–S31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cummins JM, He Y, Leary RJ, Pagliarini R,
Diaz LA Jr, Sjoblom T, Barad O, Bentwich Z, Szafranska AE,
Labourier E, et al: The colorectal microRNAome. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:pp. 3687–3692. 2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Landi D, Gemignani F, Pardini B, Naccarati
A, Garritano S, Vodicka P, Vodickova L, Canzian F, Novotny J,
Barale R and Landi S: Identification of candidate genes carrying
polymorphisms associated with the risk of colorectal cancer by
analyzing the colorectal mutome and microRNAome. Cancer.
118:4670–4680. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li L and Ma HQ: MicroRNA-216a inhibits the
growth and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4B. Mol Med Rep.
12:3156–3162. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mohammadi A, Mansoori B and Baradaran B:
The role of microRNAs in colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
84:705–713. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chatterjee V, Beard RS Jr, Reynolds JJ,
Haines R, Guo M, Rubin M, Guido J, Wu MH and Yuan SY: MicroRNA-147b
regulates vascular endothelial barrier function by targeting ADAM15
expression. PLoS One. 9:e1102862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wei Y, Li M, Yu S, Ye M,
Zhang H, Chen S, Liu W and Zhang J: miR-129-3p promotes docetaxel
resistance of breast cancer cells via CP110 inhibition. Sci Rep.
5:154242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marí-Alexandre J, Sánchez-Izquierdo D,
Gilabert-Estellés J, Barceló-Molina M, Braza-Boïls A and Sandoval
J: miRNAs regulation and its role as biomarkers in endometriosis.
Int J Mol Sci. 17:E932016.doi: 10.3390/ijms17010093. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang LL, Wang L, Wang XY, Shang D, Yin SJ,
Sun LL and Ji HB: MicroRNA-218 inhibits the proliferation,
migration and invasion and promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer
cells by targeting LASP1. Tumour Biol. 37:15241–15252. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan S, Li R, Ding K, Lobie PE and Zhu T:
miR-198 inhibits migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells by targeting the HGF/c-MET pathway. FEBS Lett. 585:2229–2234.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu M, Zhang Y, Tang A and Tian L: miR-506
inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting TET family in
colorectal cancer. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 19:316–322.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun XF, Sun JP, Hou HT, Li K, Liu X and Ge
QX: MicroRNA-27b exerts an oncogenic function by targeting Fbxw7 in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:15325–15332. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Y, Uzair-Ur-Rehman, Guo Y, Liang H,
Cheng R, Yang F, Hong Y, Zhao C, Liu M, Yu M, et al: miR-181b
functions as an oncomiR in colorectal cancer by targeting PDCD4.
Protein Cell. 7:722–734. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rawlings-Goss RA, Campbell MC and Tishkoff
SA: Global population-specific variation in miRNA associated with
cancer risk and clinical biomarkers. BMC Med Genomics. 7:532014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rossi G, Antonini S, Bonfanti C,
Monteverde S, Vezzali C, Tajbakhsh S, Cossu G and Messina G: Nfix
regulates temporal progression of muscle regeneration through
modulation of myostatin expression. Cell Rep. 14:2238–2249. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Heng YH, Zhou B, Harris L, Harvey T, Smith
A, Horne E, Martynoga B, Andersen J, Achimastou A, Cato K, et al:
NFIX regulates proliferation and migration within the murine SVZ
neurogenic niche. Cereb Cortex. 25:3758–3778. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mao Y, Liu J, Zhang D and Li B: miR-1290
promotes cancer progression by targeting nuclear factor I/X(NFIX)
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Biomed Pharmacother.
76:82–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu J, Cai G, Xu Y and Cai S: The plasma
microRNA miR-1914* and −1915 suppresses chemoresistant in
colorectal cancer patients by down-regulating NFIX. Curr Mol Med.
16:70–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bertero T, Grosso S, Robbe-Sermesant K,
Lebrigand K, Hénaoui IS, Puisségur MP, Fourre S, Zaragosi LE,
Mazure NM, Ponzio G, et al: ‘Seed-Milarity’ confers to hsa-miR-210
and hsa-miR-147b similar functional activity. PLoS One.
7:e449192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng L, Xie Y, Zhang H and Wu Y:
Down-regulation of NDRG2 gene expression in human colorectal cancer
involves promoter methylation and microRNA-650. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 406:534–538. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Omrane I and Benammar-Elgaaied A: The
immune microenvironment of the colorectal tumor: Involvement of
immunity genes and microRNAs belonging to the TH17 pathway. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1856:28–38. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao XD, Lu YY, Guo H, Xie HH, He LJ, Shen
GF, Zhou JF, Li T, Hu SJ, Zhou L, et al: MicroRNA-7/NF-kB signaling
regulatory feedback circuit regulates gastric carcinogenesis. J
Cell Biol. 210:613–627. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Krützfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev
KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M and Stoffel M: Silencing of microRNAs in
vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature. 438:685–689. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sokilde R, Newie I, Persson H, Borg Å and
Rovira C: Passenger strand loading in overexpression experiments
using microRNA mimics. RNA Biol. 12:787–791. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang B, Jing C, Wang J, Guo X, Chen Y, Xu
R, Peng L, Liu J and Li L: Identification of microRNAs associated
with lymphangiogenesis in human gastric cancer. Clin Transl Oncol.
16:374–379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cao W, Wei W, Zhan Z, Xie D, Xie Y and
Xiao Q: Role of miR-647 in human gastric cancer suppression. Oncol
Rep. 37:1401–1411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|