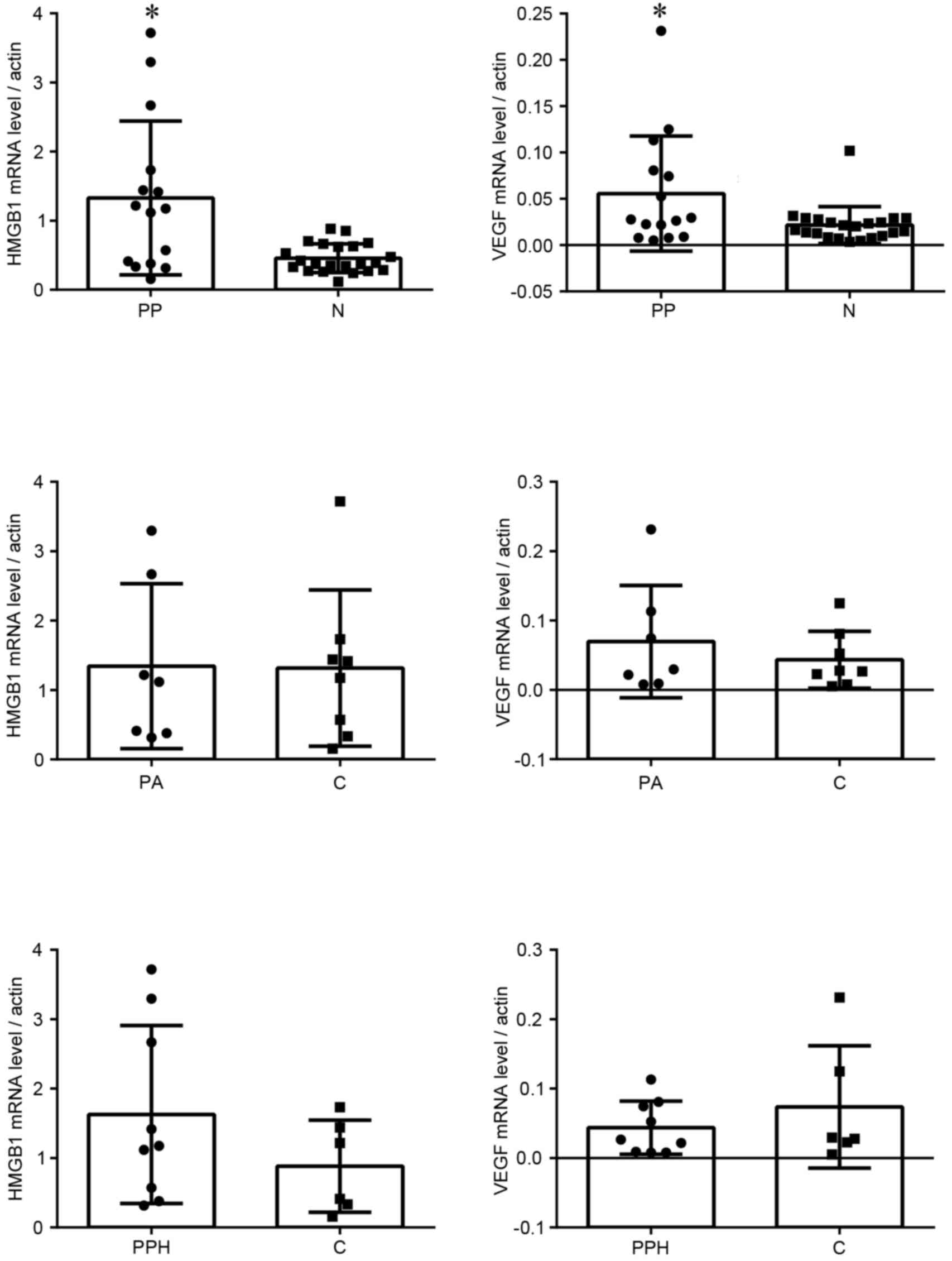
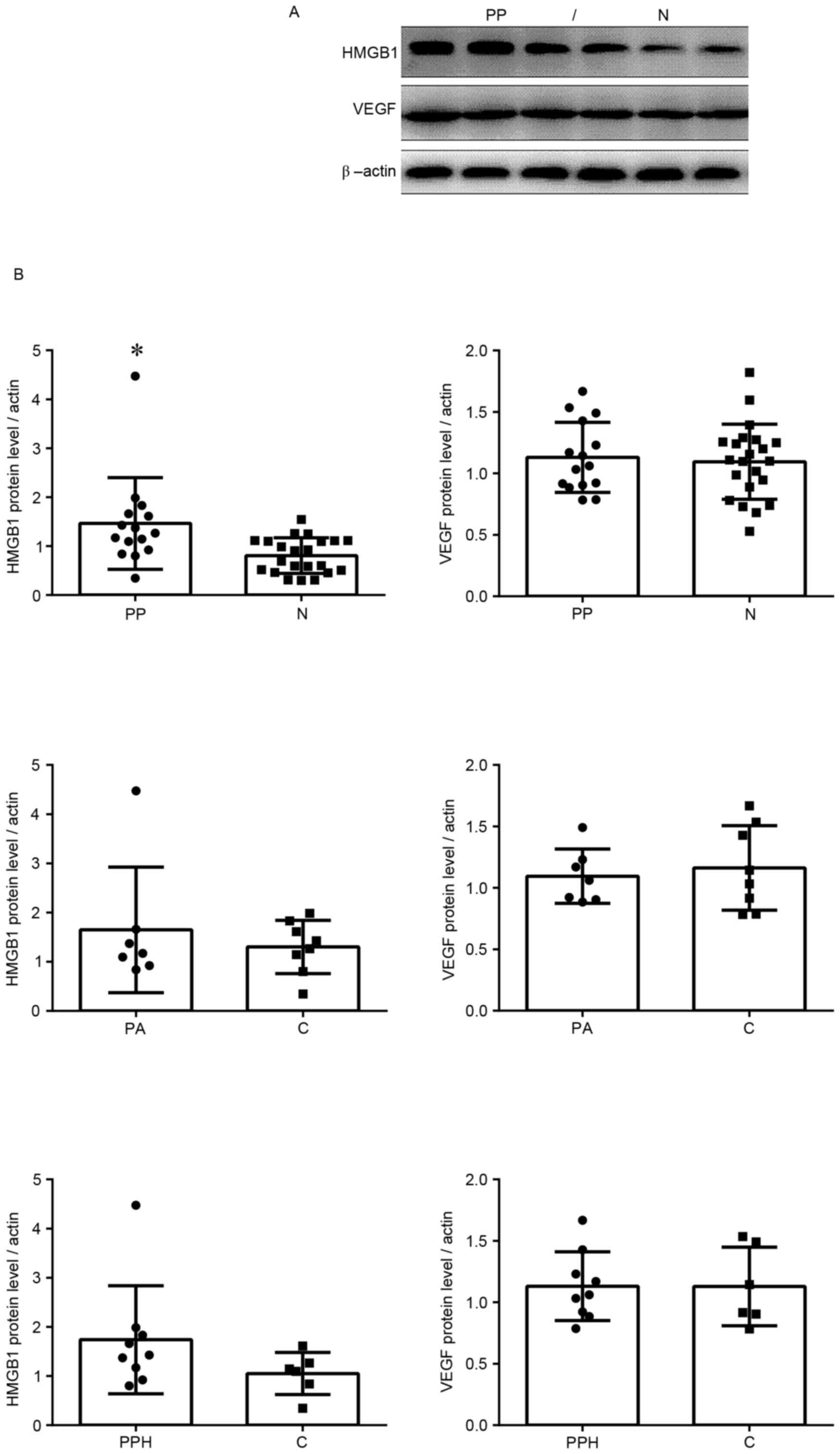
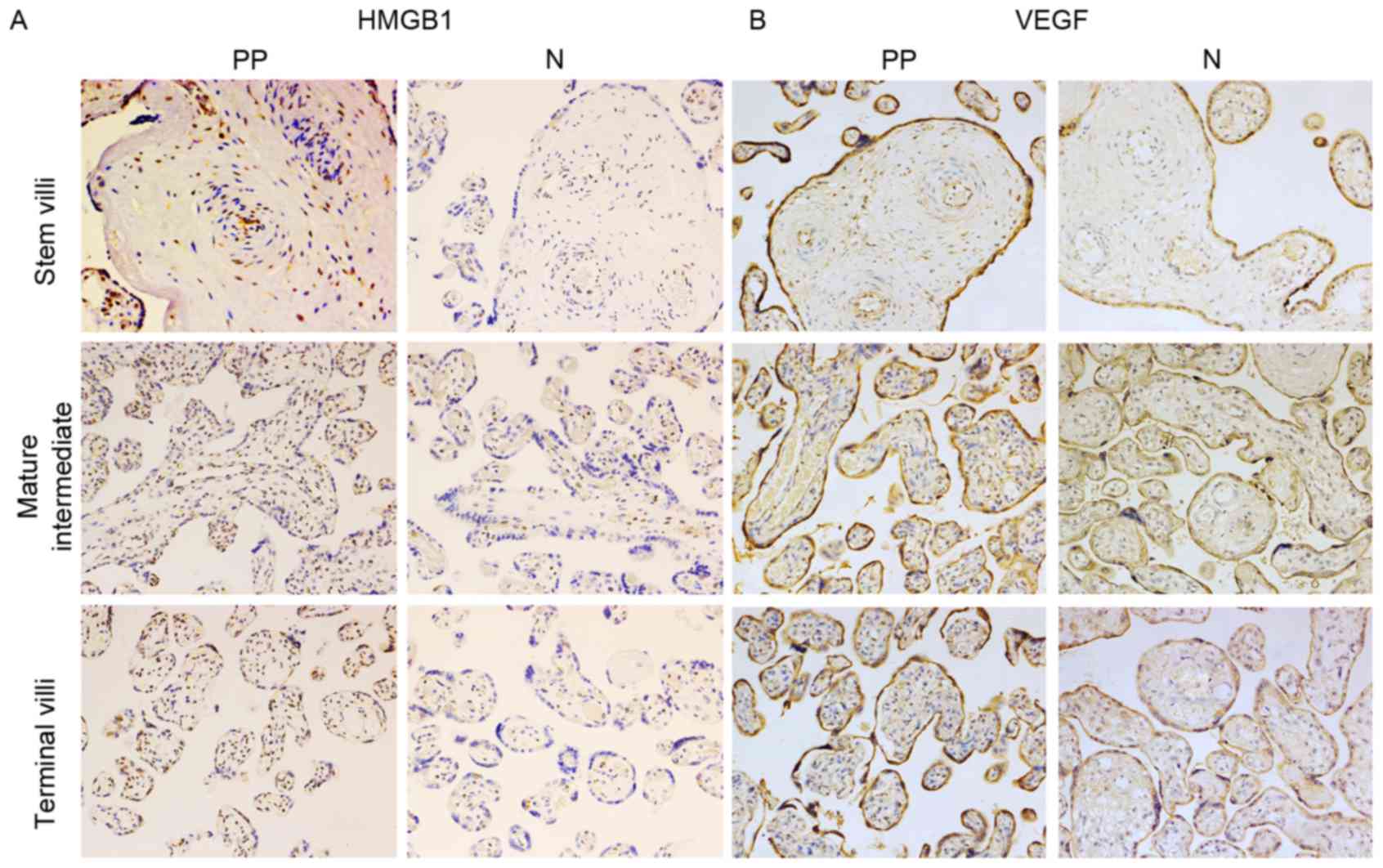
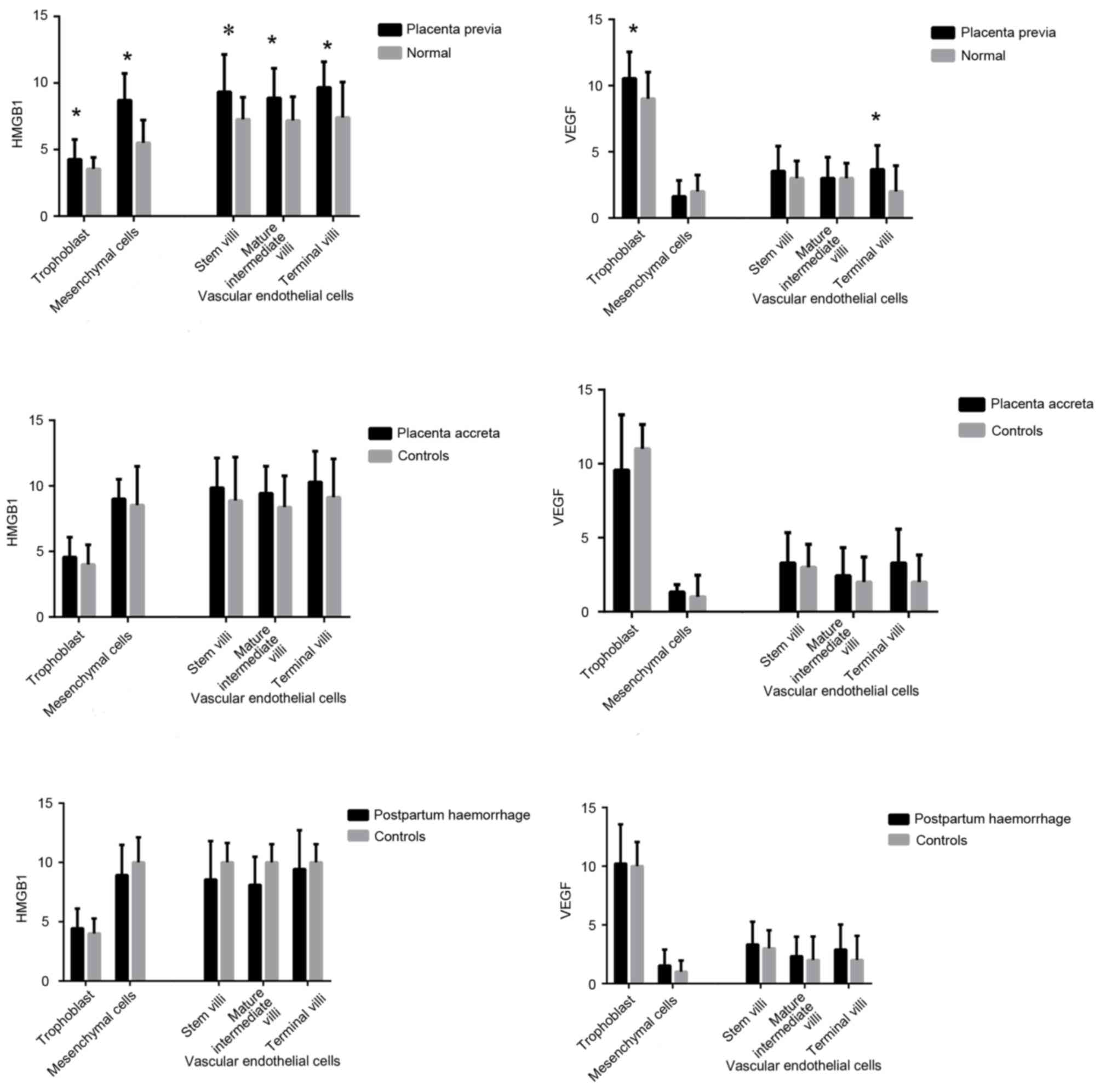
|
1
|
Royal College of Obstetricians and
Gynaecologists (RCOG), . Placenta Praevia, Placenta Praevia Accreta
and Vasa Praevia: Diagnosis and Management. RCOG Green-top
Guideline No. 27. https://www.rcog.org.uk/globalassets/documents/guidelines/gtg_27.pdfJanuary.
2011
|
|
2
|
Oya A, Nakai A, Miyake H, Kawabata I and
Takeshita T: Risk factors for peripartum blood transfusion in women
with placenta previa: A retrospective analysis. J Nippon Med Sch.
75:146–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Publications Committee, Society for
Maternal-Fetal Medicine and Belfort MA Placenta accreta. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 203:430–439. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Usta IM, Hobeika EM, Musa AA, Gabriel GE
and Nassar AH: Placenta previa-accreta: Risk factors and
complications. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 193:1045–1049. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gielchinsky Y, Rojansky N, Fasouliotis SJ
and Ezra Y: Placenta accreta-summary of 10 years: A survey of 310
cases. Placenta. 23:210–214. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ananth CV, Smulian JC and Vintzileos AM:
The association of placenta previa with history of cesarean
delivery and abortion: A meta analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
177:1071–1078. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chantraine F, Blacher S, Berndt S,
Palacios-Jaraquemada J, Sarioglu N, Nisolle M, Braun T, Munaut C
and Foidart JM: Abnormal vascular architecture at the
placental-maternal interface in placenta increta. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 207:188.e1–189.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Knofler M: Critical growth factors and
signalling pathways controlling human trophoblast invasion. Int J
Dev Biol. 54:269–280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abe A, Kuwata T, Yamauchi C, Higuchi Y and
Ochiai A: High mobility group box1 (HMGB1) released from cancer
cells induces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in
peritoneal fibroblasts. Pathol Int. 64:267–275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang B, Koga K, Osuga Y, Hirata T, Saito
A, Yoshino O, Hirota Y, Harada M, Takemura Y, Fujii T, et al: High
mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) levels in the placenta and in serum in
preeclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol. 66:143–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Knofler M: Critical growth factors and
signalling pathways controlling human trophoblast invasion. Int J
Dev Biol. 54:269–280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Siu MK, Chan HY, Kong DS, Wong ES, Wong
OG, Ngan HY, Tam KF, Zhang H, Li Z, Chan QK, et al: p21-activated
kinase 4 regulates ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration,
and invasion and contributes to poor prognosis in patients. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp. 18622–18627. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu W, Xia YH, Qu JJ, He YY, Li BL, Lu C,
Luo X and Wan XP: p21-activated kinase 4 regulation of endometrial
cancer cell migration and invasion involves the ERK1/2 pathway
mediated MMP-2 secretion. Neoplasma. 60:493–503. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vitali R, Stronati L, Negroni A, Di Nardo
G, Pierdomenico M, del Giudice E, Rossi P and Cucchiara S: Fecal
HMGB1 is a novel marker of intestinal mucosal inflammation in
pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol.
106:2029–2040. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nehil M, Paquette J, Tokuyasu T and
McCormick F: High mobility group box 1 promotes tumor cell
migration through epigenetic silencing of semaphorin 3A. Oncogene.
33:5151–5162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fang P, Pan HC, Lin SL, Zhang WQ, Rauvala
H, Schachner M and Shen YQ: HMGB1 contributes to regeneration after
spinal cord injury in adult zebrafish. Mol Neurobiol. 49:472–483.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Palone F, Vitali R, Cucchiara S,
Pierdomenico M, Negroni A, Aloi M, Nuti F, Felice C, Armuzzi A and
Stronati L: Role of HMGB1 as a suitable biomarker of subclinical
intestinal inflammation and mucosal healing in patients with
inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 20:1448–1457. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang PS, Kim DH, Lee YJ, Lee SE, Kang WJ,
Chang HJ and Shin JS: Glycyrrhizin, inhibitor of high mobility
group box-1, attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary
hypertension and vascular remodeling in rats. Respir Res.
15:1482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Campana L, Santarella F, Esposito A,
Maugeri N, Rigamonti E, Monno A, Canu T, Del Maschio A, Bianchi ME,
Manfredi AA, et al: Leukocyte HMGB1 is required for vessel
remodeling in regenerating muscles. J Immunol. 192:5257–5264. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bhutada S, Basak T, Savardekar L, Katkam
RR, Jadhav G, Metkari SM, Chaudhari UK, Kumari D, Kholkute SD,
Sengupta S, et al: High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein in
human uterine fluid and its relevance in implantation. Hum Reprod.
29:763–780. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Girard S, Heazell AE, Derricott H, Allan
SM, Sibley CP, Abrahams VM and Jones RL: Circulating cytokines and
alarmins associated with placental inflammation in high-risk
pregnancies. Am J Reprod Immunol. 72:422–434. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mitola S, Belleri M, Urbinati C, Coltrini
D, Sparatore B, Pedrazzi M, Melloni E and Presta M: Cutting edge:
Extracellular high mobility group box-1 protein is a proangiogenic
cytokine. J Immunol. 176:12–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee SA, Kwak MS, Kim S and Shin JS: The
role of high mobility group box 1 in innate immunity. Yonsei Med J.
55:1165–1176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Degryse B, Bonaldi T, Scaffidi P, Muller
S, Resnati M, Sanvito F, Arrigoni G and Bianchi ME: The high
mobility group (HMG) boxes of the nuclear protein HMG1 induce
chemotaxis and cytoskeleton reorganization in rat smooth muscle
cells. J Cell Biol. 152:1197–1206. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Frantz S, Vincent KA, Feron O and Kelly
RA: Innate immunity and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 96:15–26. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schlueter C, Weber H, Meyer B, Rogalla P,
Roser K, Hauke S and Bullerdiek J: Angiogenetic signaling through
hypoxia: HMGB1: An angiogenetic switch molecule. Am J Pathol.
166:1259–1263. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Biscetti F, Straface G, De Cristofaro R,
Lancellotti S, Rizzo P, Arena V, Stigliano E, Pecorini G, Egashira
K, De Angelis G, et al: High-mobility group box-1 protein promotes
angiogenesis after peripheral ischemia in diabetic mice through a
VEGF-dependent mechanism. Diabetes. 59:1496–1505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Naumnik W, Nilklinska W, Ossolinska M and
Chyczewska E: Serum levels of HMGB1, survivin, and VEGF in patients
with advanced non-small cell lung cancer during chemotherapy. Folia
Histochem Cytobiol. 47:703–709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chuangui C, Peng T and Zhentao Y: The
expression of high mobility group box 1 is associated with lymph
node metastasis and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 18:1021–1027. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Holmlund U, Wahamaa H, Bachmayer N, Bremme
K, Sverremark-Ekstrom E and Palmblad K: The novel inflammatory
cytokine high mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) is expressed by
human term placenta. Immunology. 122:430–437. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tseng JJ, Chou MM, Hsieh YT, Wen MC, Ho ES
and Hsu SL: Differential expression of vascular endothelial growth
factor, placenta growth factor and their receptors in placentae
from pregnancies complicated by placentaaccreta. Placenta.
27:70–78. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|