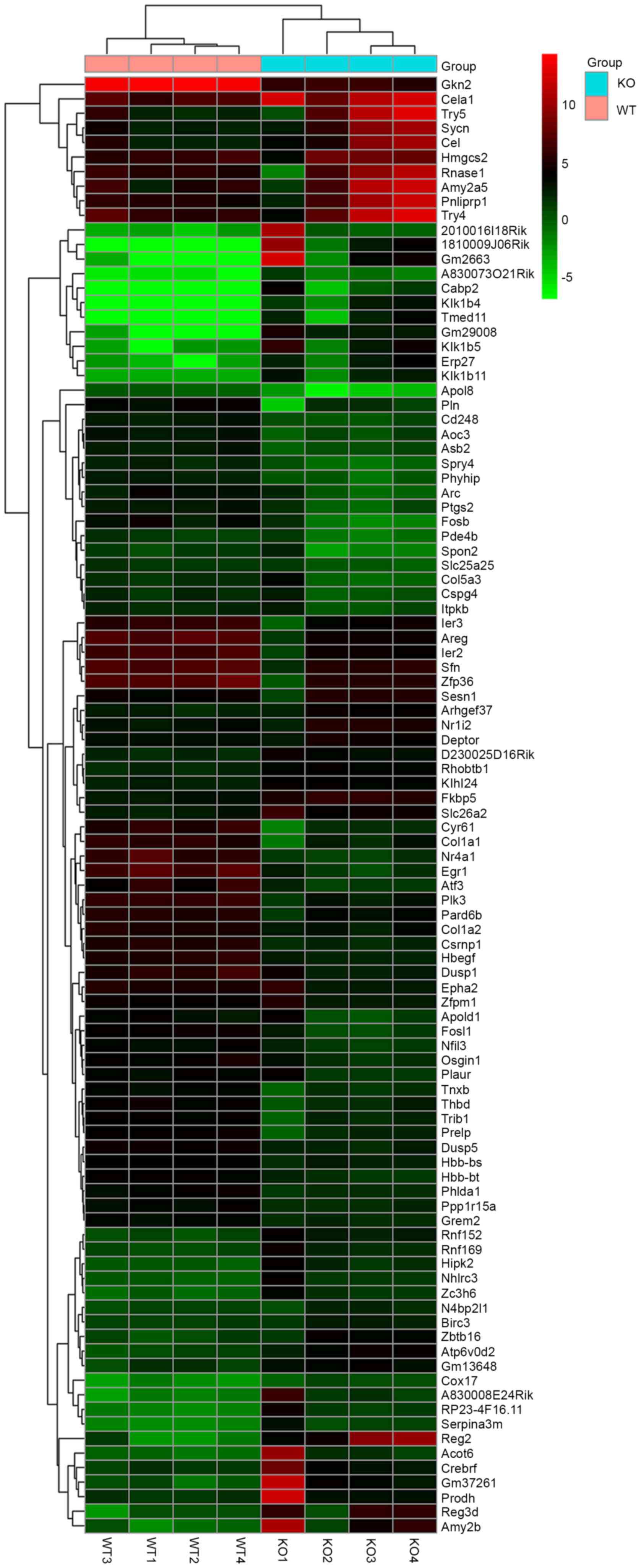
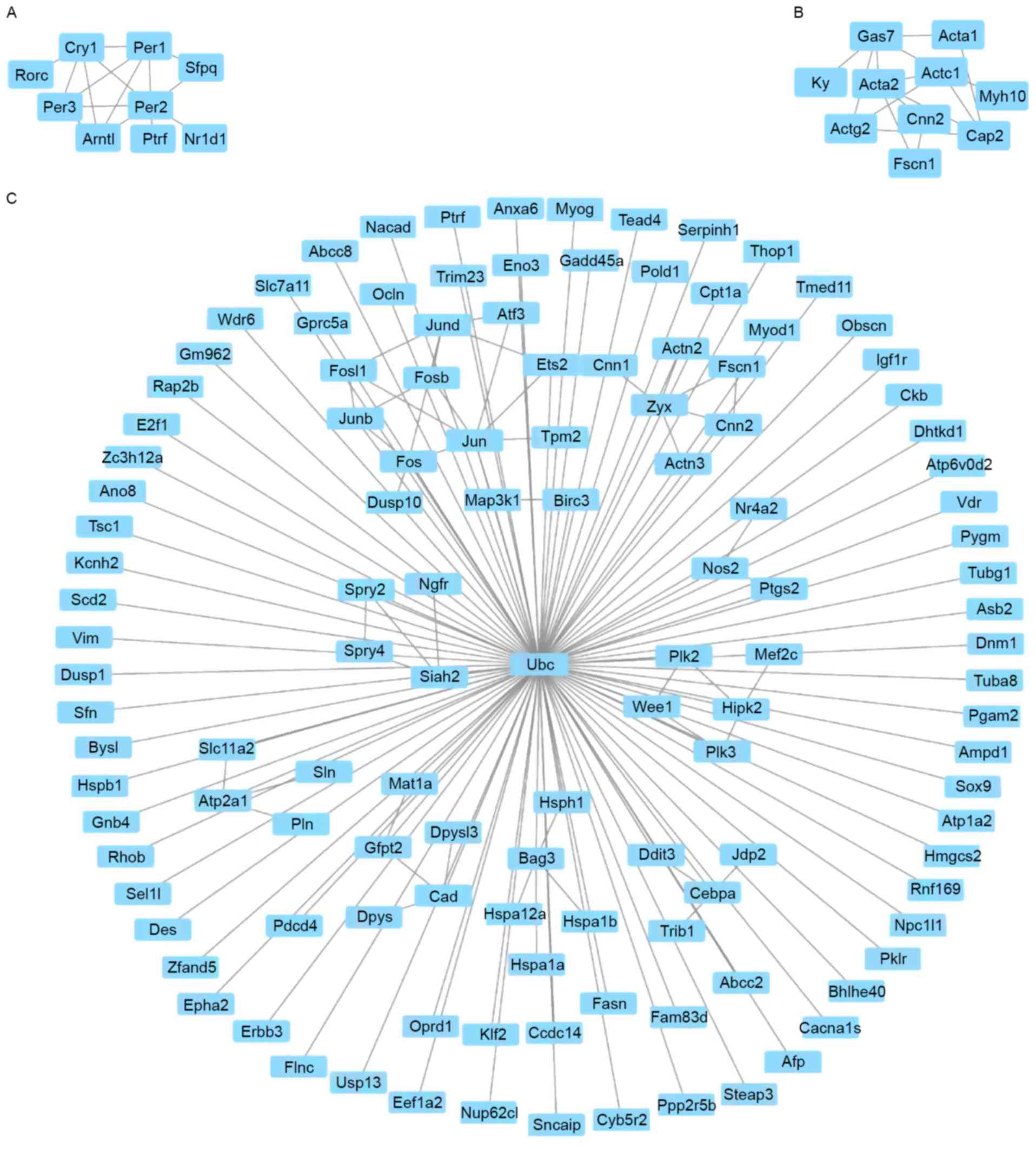
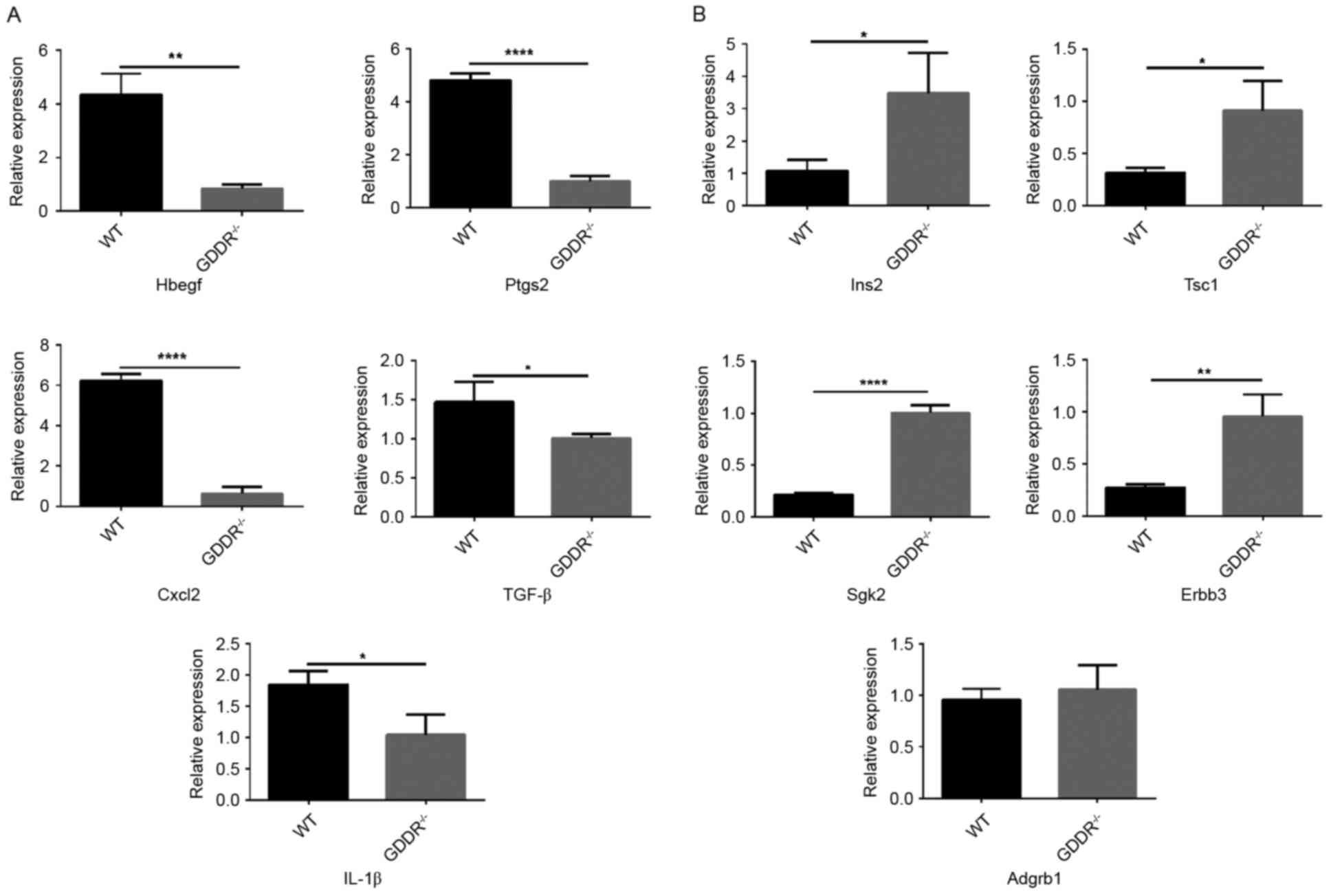
|
1
|
Brodie DA and Hooke KF: The effect of
vasoactive agents on stress-induced gastric hemorrhage in the rat.
Digestion. 4:193–204. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ernst H, Konturek PC, Brzozowski T, Lochs
H, Hahn EG and Konturek SJ: Adaptation of gastric mucosa to stress.
Effect of ranitidine. J Physiol Pharmacol. 49:405–419.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guo S, Gao Q, Jiao Q, Hao W, Gao X and Cao
JM: Gastric mucosal damage in water immersion stress: Mechanism and
prevention with GHRP-6. World J Gastroenterol. 18:3145–3155. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Robles TF and Carroll JE: Restorative
biological processes and health. Soc Personal Psychol Compass.
5:518–537. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin HP, Lin HY, Lin WL and Huang AC:
Effects of stress, depression, and their interaction on heart rate,
skin conductance, finger temperature, and respiratory rate:
Sympathetic-parasympathetic hypothesis of stress and depression. J
Clin Psychol. 67:1080–1091. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Du JJ, Dou KF, Peng SY, Wang WZ, Wang ZH,
Xiao HS, Guan WX, Liu YB and Gao ZQ: Down-regulated full-length
novel gene GDDR and its effect on gastric cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue
Za Zhi. 83:1166–1168. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Du JJ, Dou KF, Peng SY, Li JT, Wang WZ,
Guan WX and Gao ZQ: Study on novel gene GDDR related to gastric
cancer. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 43:10–13. 2005.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
May FE, Griffin SM and Westley BR: The
trefoil factor interacting protein TFIZ1 binds the trefoil protein
TFF1 preferentially in normal gastric mucosal cells but the
co-expression of these proteins is deregulated in gastric cancer.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:632–640. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baus-Loncar M, Lubka M, Pusch CM, Otto WR,
Poulsom R and Blin N: Cytokine regulation of the trefoil factor
family binding protein GKN2 (GDDR/TFIZ1/blottin) in human
gastrointestinal epithelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem.
20:193–204. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Menheniott TR, O'Connor L, Chionh YT,
Däbritz J, Scurr M, Rollo BN, Ng GZ, Jacobs S, Catubig A, Kurklu B,
et al: Loss of gastrokine-2 drives premalignant gastric
inflammation and tumor progression. J Clin Invest. 126:1383–1400.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moss SF, Lee JW, Sabo E, Rubin AK, Rommel
J, Westley BR, May FE, Gao J, Meitner PA, Tavares R and Resnick MB:
Decreased expression of gastrokine 1 and the trefoil factor
interacting protein TFIZ1/GKN2 in gastric cancer: Influence of
tumor histology and relationship to prognosis. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4161–4167. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chu G, Qi S, Yang G, Dou K, Du J and Lu Z:
Gastrointestinal tract specific gene GDDR inhibits the progression
of gastric cancer in a TFF1 dependent manner. Mol Cell Biochem.
359:369–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi LS, Wang H, Wang F, Feng M, Wang M and
Guan WX: Effects of gastrokine2 expression on gastric cancer cell
apoptosis by activation of extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Mol Med
Rep. 10:2898–2904. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim O, Yoon JH, Choi WS, Ashktorab H,
Smoot DT, Nam SW, Lee JY and Park WS: GKN2 contributes to the
homeostasis of gastric mucosa by inhibiting GKN1 activity. J Cell
Physiol. 229:762–771. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Menheniott TR, Kurklu B and Giraud AS:
Gastrokines: Stomach-specific proteins with putative homeostatic
and tumor suppressor roles. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 304:G109–G121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gang W, Chen F, Xiangui L, et al: The role
of new gene GDDR in the acute and chronic gastric mucosal injury in
mice. Progress in Modern Biomedicine. 10:1836–1839. 2015.
|
|
17
|
Shimozawa N, Okajima K, Harada N, Arai M,
Ishida Y, Shimada S, Kurihara H and Nakagata N: Contribution of
sensory neurons to sex difference in the development of
stress-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice. Gastroenterology.
131:1826–1834. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Menheniott TR, Peterson AJ, O'Connor L,
Lee KS, Kalantzis A, Kondova I, Bontrop RE, Bell KM and Giraud AS:
A novel gastrokine, Gkn3, marks gastric atrophy and shows evidence
of adaptive gene loss in humans. Gastroenterology. 138:1823–1835.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Santucci L, Fiorucci S, Giansanti M,
Brunori PM, Di Matteo FM and Morelli A: Pentoxifylline prevents
indomethacin induced acute gastric mucosal damage in rats: Role of
tumour necrosis factor alpha. Gut. 35:909–915. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Trapnell C, Pachter L and Salzberg SL:
TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics.
25:1105–1111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gene Ontology C: The Gene Ontology (GO)
project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Research. 34:D322–326. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barabási AL and Oltvai ZN: Network
biology: Understanding the cell's functional organization. Nat Rev
Genet. 5:101–113. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Prieto C, Risueño A, Fontanillo C and De
las Rivas J: Human gene coexpression landscape: Confident network
derived from tissue transcriptomic profiles. PLoS One. 3:e39112008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang L, Wang S and Li W: RSeQC: Quality
control of RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics. 28:2184–2185. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nishida K, Ohta Y and Ishiguro I: Changes
in nitric oxide production with lesion development in the gastric
mucosa of rats with water immersion restraint stress. Res Commun
Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 100:201–212. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
S Kwiecien S, Pawlik MW, Brzozowski T,
Konturek PC, Sliwowski Z, Pawlik WW and Konturek SJ: Nitric oxide
(NO)-releasing aspirin and (NO) donors in protection of gastric
mucosa against stress. J Physiol Pharmacol. 59 Suppl 2:S103–S115.
2008.
|
|
30
|
Brzozowska I, Ptak-Belowska A, Pawlik M,
Pajdo R, Drozdowicz D, Konturek SJ, Pawlik WW and Brzozowski T:
Mucosal strengthening activity of central and peripheral melatonin
in the mechanism of gastric defense. J Physiol Pharmacol. 60 Suppl
7:47–56. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nur Azlina MF, Kamisah Y, Chua KH and
Qodriyah HM: Tocotrienol attenuates stress-induced gastric lesions
via activation of prostaglandin and upregulation of COX-1 mRNA.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:8047962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li YM, Lu GM, Zou XP, Li ZS, Peng GY and
Fang DC: Dynamic functional and ultrastructural changes of gastric
parietal cells induced by water immersion-restraint stress in rats.
World J Gastroenterol. 12:3368–3372. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brzozowski T: Role of renin-angiotensin
system and metabolites of angiotensin in the mechanism of gastric
mucosal protection. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 19:90–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rohani MG and Parks WC: Matrix remodeling
by MMPs during wound repair. Matrix Biol 44–46. 1–121. 2015.
|
|
35
|
Wilgus TA: Growth factor-extracellular
matrix interactions regulate wound repair. Adv Wound Care (New
Rochelle). 1:249–254. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun Z, Liu H, Yang Z, Shao D, Zhang W, Ren
Y, Sun B, Lin J, Xu M and Nie S: Intestinal trefoil factor
activates the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway to protect gastric mucosal
epithelium from damage. Int J Oncol. 45:1123–1132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Seibert K, Zhang Y, Leahy K, Hauser S,
Masferrer J, Perkins W, Lee L and Isakson P: Pharmacological and
biochemical demonstration of the role of cyclooxygenase 2 in
inflammation and pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:pp. 12013–12017.
1994; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wallace JL, McKnight W, Reuter BK and
Vergnolle N: NSAID-induced gastric damage in rats: Requirement for
inhibition of both cyclooxygenase 1 and 2. Gastroenterology.
119:706–714. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Baek YH, Lee KN, Jun DW, Yoon BC, Kim JM,
Oh TY and Lee OY: Augmenting effect of DA-9601 on ghrelin in an
acute gastric injury model. Gut Liver. 5:52–56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Adami M, Pozzoli C, Leurs R, Stark H and
Coruzzi G: Histamine H(3) receptors are involved in the protective
effect of ghrelin against HCl-induced gastric damage in rats.
Pharmacology. 86:259–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Okajima K, Murakami K, Liu W and Uchiba M:
Inhibition of neutrophil activation by ranitidine contributes to
prevent stress-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. Crit Care
Med. 28:2858–2865. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mifsud KR and Reul JM: Acute stress
enhances heterodimerization and binding of corticosteroid receptors
at glucocorticoid target genes in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 113:pp. 11336–11341. 2016; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Filaretova LP, Filaretov AA and Makara GB:
Corticosterone increase inhibits stress-induced gastric erosions in
rats. Am J Physiol. 274:G1024–G1030. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee Y, Jang AR, Francey LJ, Sehgal A and
Hogenesch JB: KPNB1 mediates PER/CRY nuclear translocation and
circadian clock function. ELife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang F, Wu W, Deng Z, Zheng X, Zhang J,
Deng S, Chen J, Ma Q, Wang Y, Yu X, et al: High altitude increases
the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and inducible
nitric oxide synthase with intest-inal mucosal barrier failure in
rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:5189–5195. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bogdan C: Nitric oxide synthase in innate
and adaptive immunity: An update. Trends Immunol. 36:161–178. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang T, Leng YF and Zhang Y, Xue X, Kang
YQ and Zhang Y: Oxidative stress and hypoxia-induced factor 1α
expression in gastric ischemia. World J Gastroenterol.
17:1915–1922. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Filaretova L: Glucocorticoids are
gastroprotective under physiologic conditions. Ther Adv Chronic
Dis. 2:333–342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Filaretova LP, Podvigina TT, Bagaeva TR,
Tanaka A and Takeuchi K: Mechanisms underlying the gastroprotective
action of glucocorticoids released in response to ulcerogenic
stress factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1018:288–292. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|