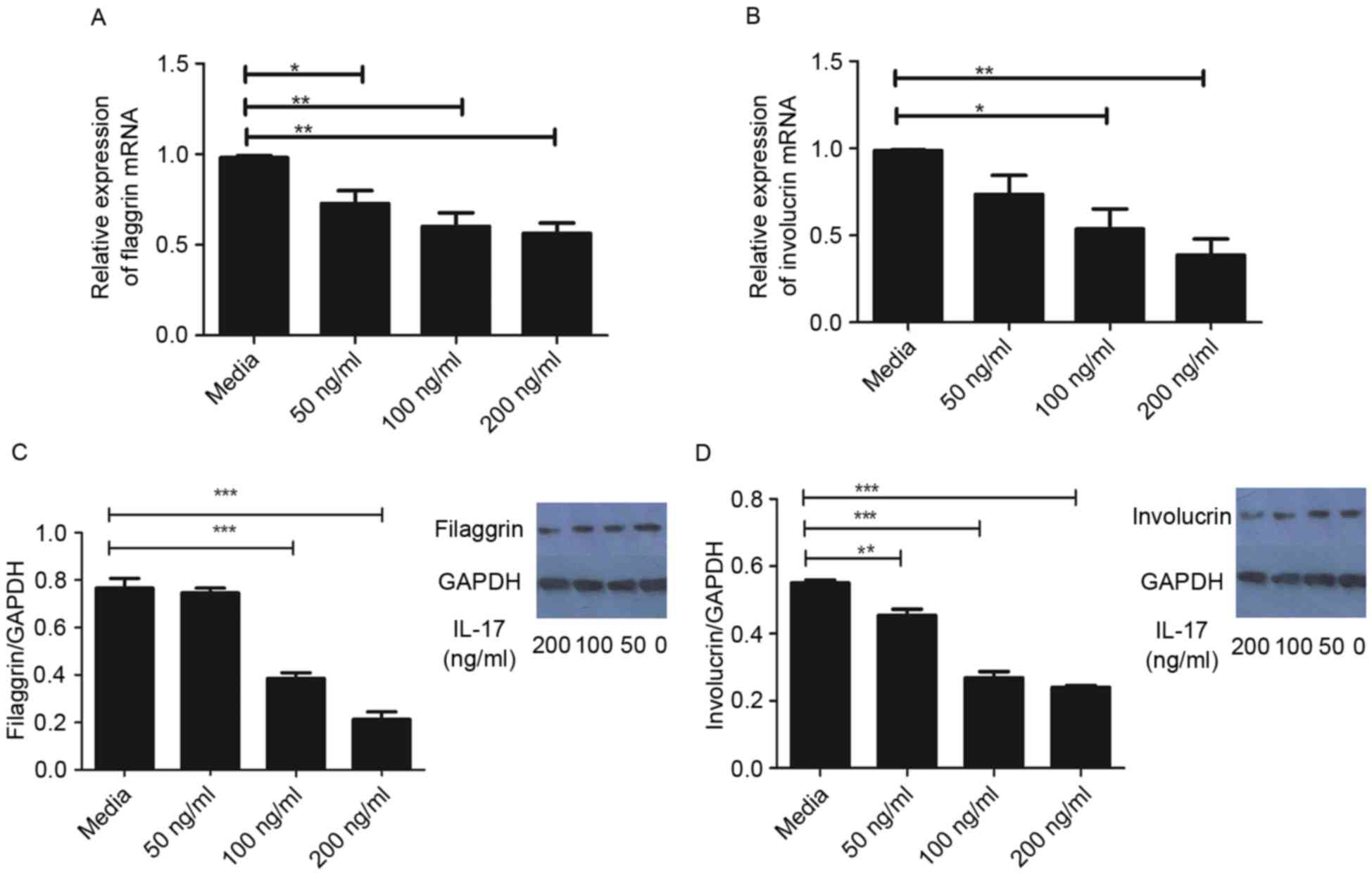
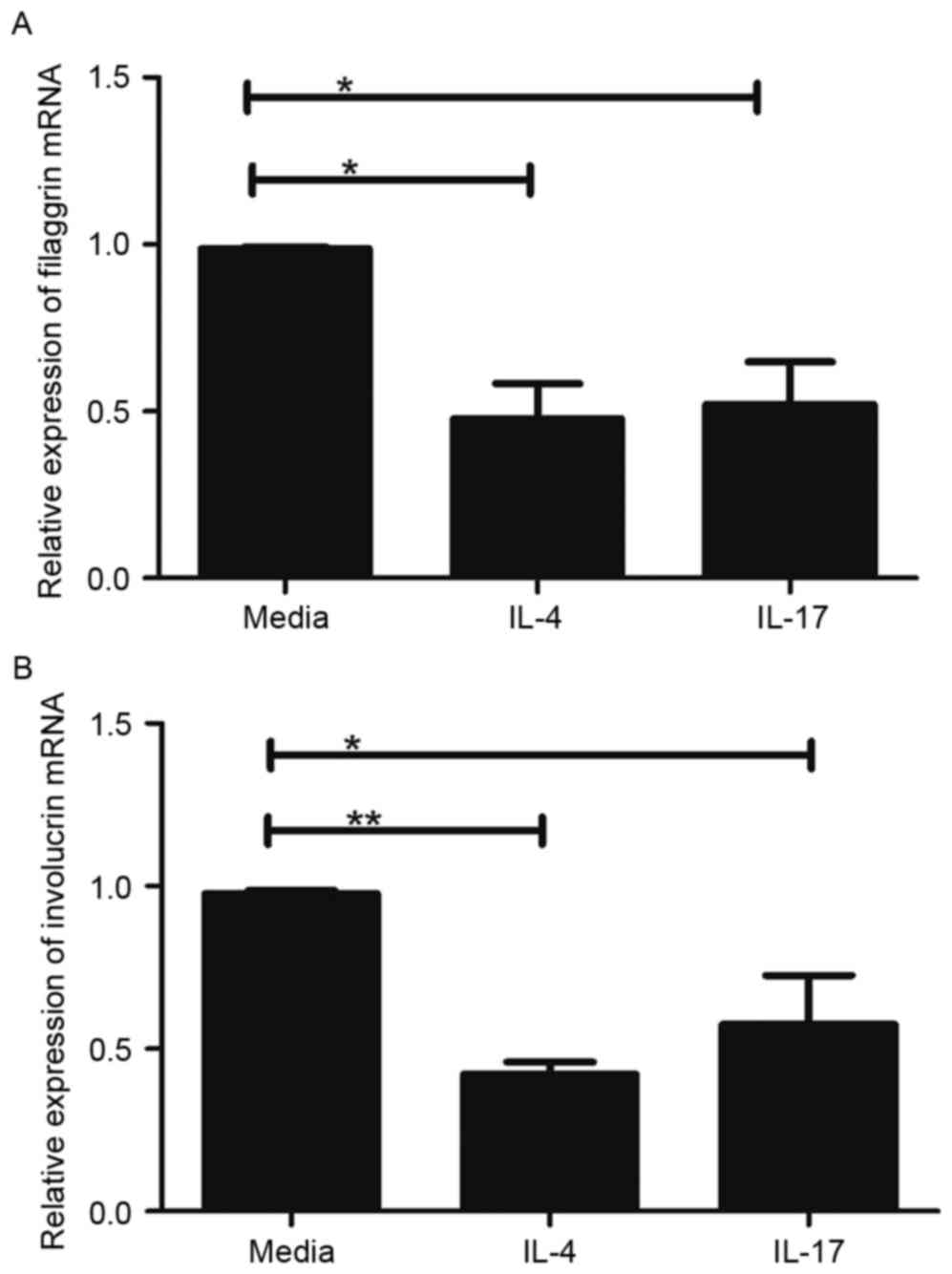
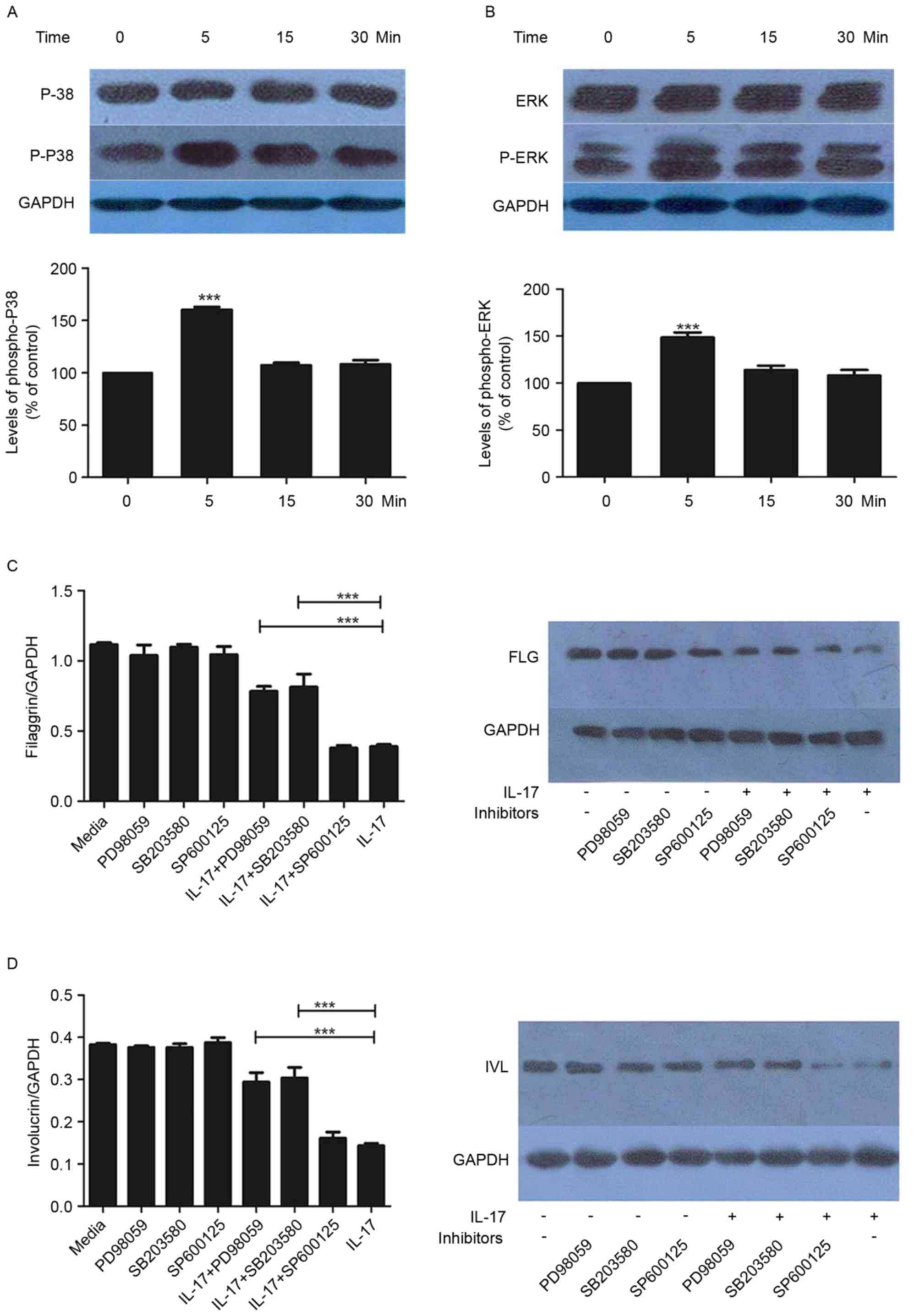
|
1
|
Williams H and Flohr C: How epidemiology
has challenged 3 prevailing concepts about atopic dermatitis. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 118:209–213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Flohr C, England K, Radulovic S, McLean
WH, Campbel LE, Barker J, Perkin M and Lack G: Filaggrin
loss-of-function mutations are associated with early-onset eczema,
eczema severity and transepidermal water loss at 3 months of age.
Br J Dermatol. 163:1333–1336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang H, Guo Y, Wang W, Shi M, Chen X and
Yao Z: Mutations in the filaggrin gene in Han Chinese patients with
atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 66:420–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lloyd CM and Hessel EM: Functions of T
cells in asthma: More than just T (H)2 cells. Nat Rev Immunol.
10:838–848. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsai HC, Velichko S, Hung LY and Wu R:
IL-17A and Th17 cells in lung inflammation: An update on the role
of Th17 cell differentiation and IL-17R signaling in host defense
against infection. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:2679712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koga C, Kabashima K, Shiraishi N,
Kobayashi M and Tokura Y: Possible pathogenic role of Th17 cells
for atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 128:2625–2630. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nograles KE, Zaba LC, Guttman-Yassky E,
Fuentes-Duculan J, Suárez-Fariñas M, Cardinale I, Khatcherian A,
Gonzalez J, Pierson KC, White TR, et al: Th17 cytokines interleukin
(IL)-17 and IL-22 modulate distinct inflammatory and
keratinocyte-response pathways. Br J Dermatol. 159:1092–1102.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boguniewicz M and Leung DY: Atopic
dermatitis: A disease of altered skin barrier and immune
dysregulation. Immunol Rev. 242:233–246. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leung DY: New insights into atopic
dermatitis: Role of skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Allergol
Int. 62:151–161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Candi E, Schmidt R and Melino G: The
cornified envelope: A model of cell death in the skin. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 6:328–340. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Noh M, Yeo H, Ko J, Kim HK and Lee CH:
MAP17 is associated with the T-helper cell cytokine-induced
down-regulation of filaggrin transcription in human keratinocytes.
Exp Dermatol. 19:355–362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Elias PM, Hatano Y and Williams ML: Basis
for the barrier abnormality in atopic dermatitis:
Outside-inside-outside pathogenic mechanisms. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 121:1337–1343. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Steven AC, Bisher ME, Roop DR and Steinert
PM: Biosynthetic pathways of filaggrin and loricrin-two major
proteins expressed by terminally differentiated epidermal
keratinocytes. J Struct Biol. 104:150–162. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kalinin A, Marekov LN and Steinert PM:
Assembly of the epidermal cornified cell envelope. J Cell Sci.
114:3069–3070. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Howell MD, Kim BE, Gao P, Grant AV,
Boguniewicz M, DeBenedetto A, Schneider L, Beck LA, Barnes KC and
Leung DY: Cytokine modulation of atopic dermatitis filaggrin skin
expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 124(3 Suppl 2): R7–R12. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma L, Xue HB, Guan XH, Shu CM, Wang F,
Zhang JH and An RZ: The Imbalance of Th17 cells and CD4 (+) CD25
(high) Foxp3 (+) Treg cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. J
Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 28:1079–1086. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johansen C, Kragballe K, Westergaard M,
Henningsen J, Kristiansen K and Iversen L: The mitogen-activated
protein kinases p38 and ERK1/2 are increased in lesional psoriatic
skin. Br J Dermatol. 152:37–42. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maintz L and Novak N: Getting more and
more complex: The pathophysiology of atopic eczema. Eur J Dermatol.
17:267–283. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
de Guzman Strong C, Conlan S, Deming CB,
Cheng J, Sears KE and Segre JA: A milieu of regulatory elements in
the epidermal differentiation complex syntenic block: Implications
for atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Hum Mol Genet. 19:1453–1460.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim BE, Leung DY, Boguniewicz M and Howell
MD: Loricrin and involucrin expression is down-regulated by Th2
cytokines through STAT-6. Clin Immunol. 126:332–337. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aggarwal S and Gurney AL: IL-17: Prototype
member of an emerging cytokine family. J Leukoc Biol. 71:1–8.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Iwakura Y, Ishigame H, Saijo S and Nakae
S: Functional specialization of interleukin-17 family members.
Immunity. 34:149–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kirkham BW, Kavanaugh A and Reich K:
Interleukin-17A: A unique pathway in immune-mediated diseases:
Psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Immunology. 141:133–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feingold KR and Elias PM: Role of lipids
in the formation and maintenance of the cutaneous permeability
barrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:280–294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gutowska-Owsiak D, Schaupp AL, Salimi M,
Selvakumar TA, McPherson T, Taylor S and Ogg GS: IL-17
downregulates filaggrin and affects keratinocyte expression of
genes associated with cellular adhesion. Exp Dermatol. 21:104–110.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Spergel JM, Mizoguchi E, Brewer JP, Martin
TR, Bhan AK and Geha RS: Epicutaneous sensitization with protein
antigen induces localized allergic dermatitis and
hyperresponsiveness to methacholine after single exposure to
aerosolized antigen in mice. J Clin Invest. 101:1614–1622. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
De Benedetto A, Rafaels NM, McGirt LY,
Ivanov AI, Georas SN, Cheadle C, Berger AE, Zhang K, Vidyasagar S,
Yoshida T, et al: Tight junction defects in patients with atopic
dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 127:773–786. e1-e7. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen JQ, Man XY, Li W, Zhou J, Landeck L,
Cai SQ and Zheng M: Regulation of involucrin in psoriatic epidermal
keratinocytes: The roles of ERK1/2 and GSK-3β. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 66:523–528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miossec P and Kolls JK: Targeting IL-17
and TH17 cells in chronic inflammation. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
11:763–776. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Simon D and Lang K Kernland: Atopic
dermatitis: From new pathogenic insights toward a barrier-restoring
and anti-inflammatory therapy. Curr Opin Pediatr. 23:647–652. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Noh G and Lee J: Atopic dermatitis and
cytokines: The immunoregulatory and therapeutic implications of
cytokines in atopic dermatitis-part II: Negative regulation and
cytokine therapy in atopic dermatitis. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy
Drug Discov. 6:248–261. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Roesner LM, Werfel T and Heratizadeh A:
The adaptive immune system in atopic dermatitis and implications on
therapy. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 12:787–796. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|