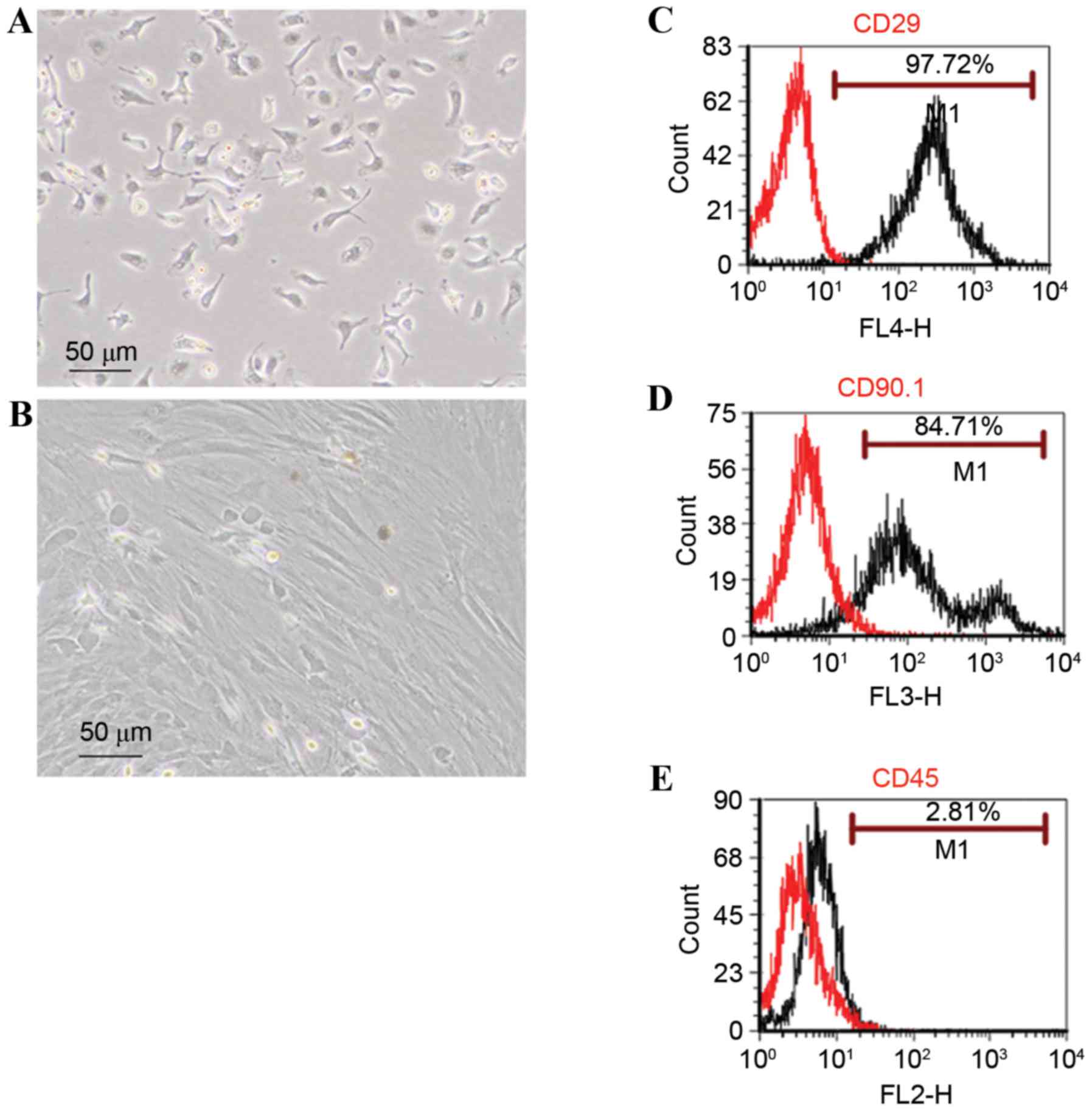
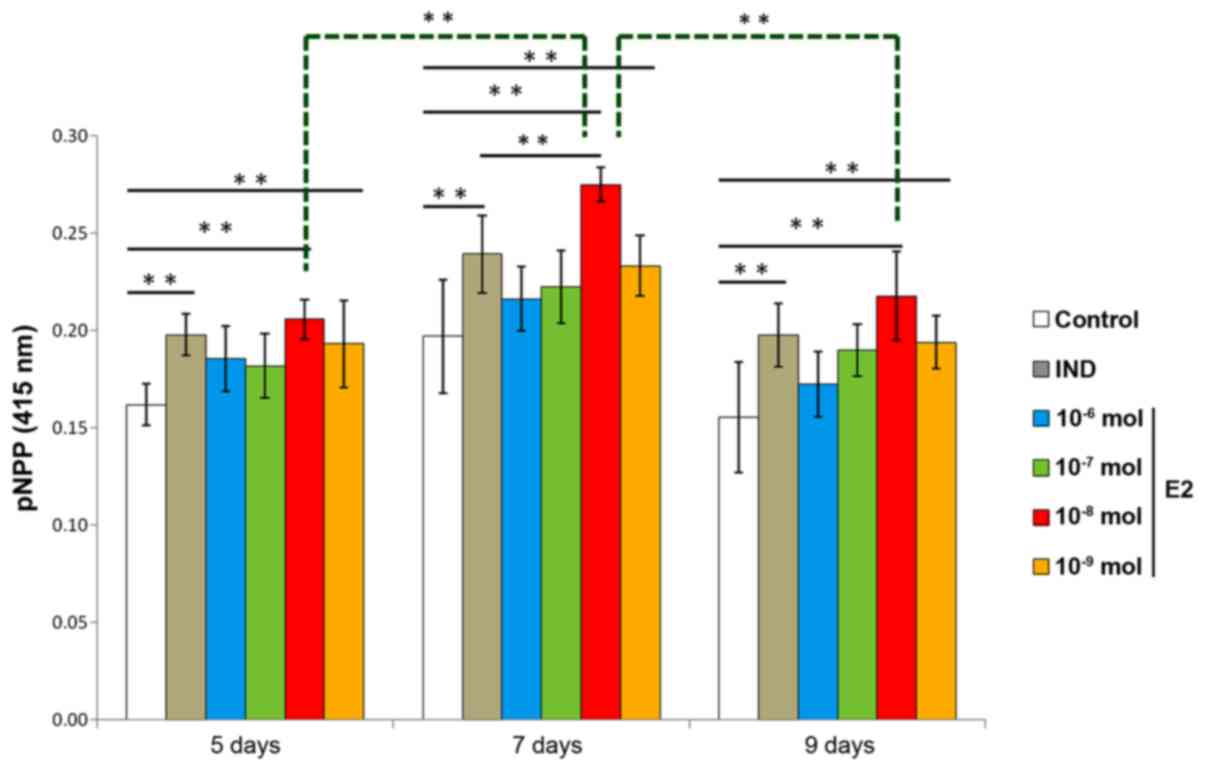
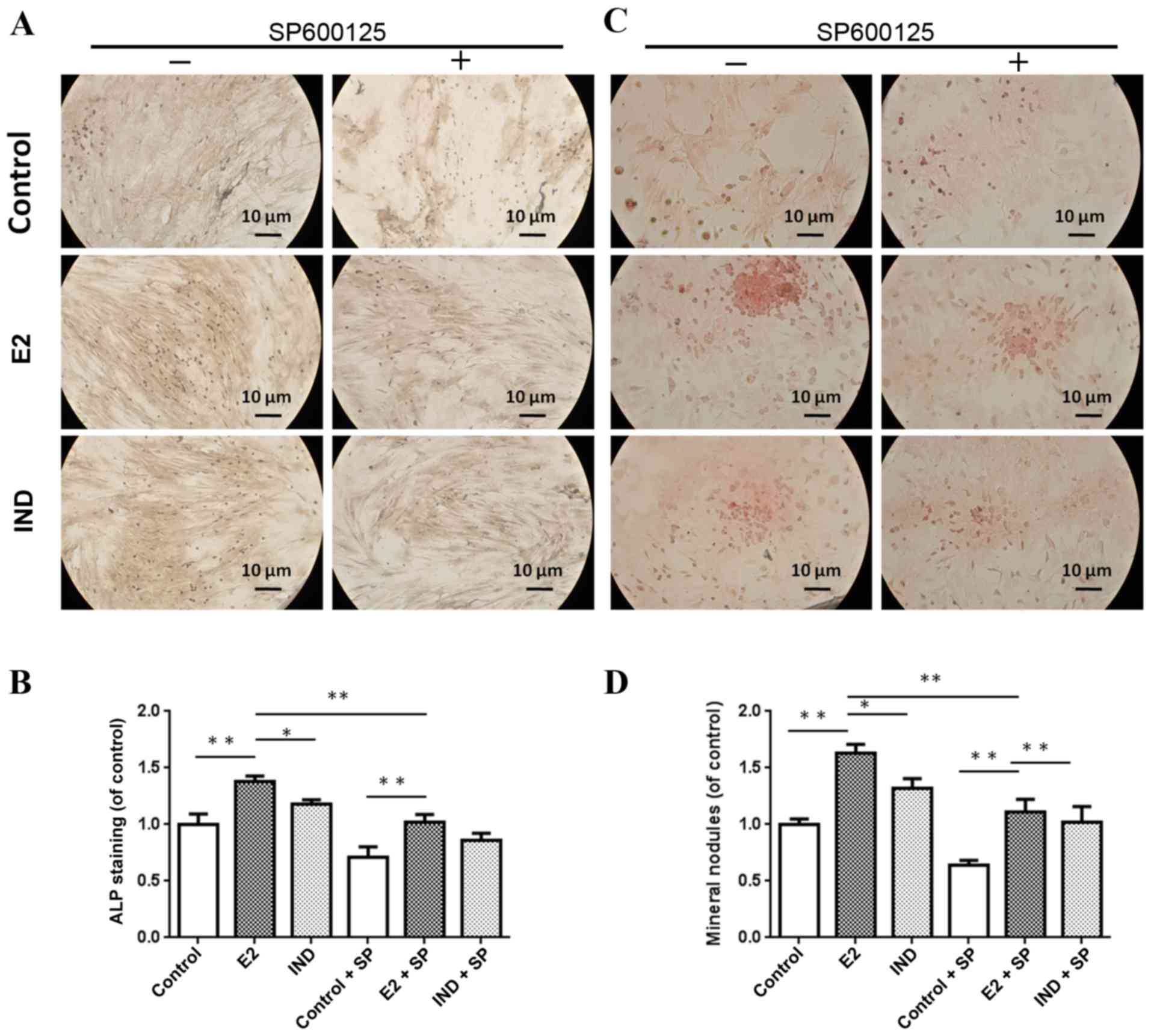
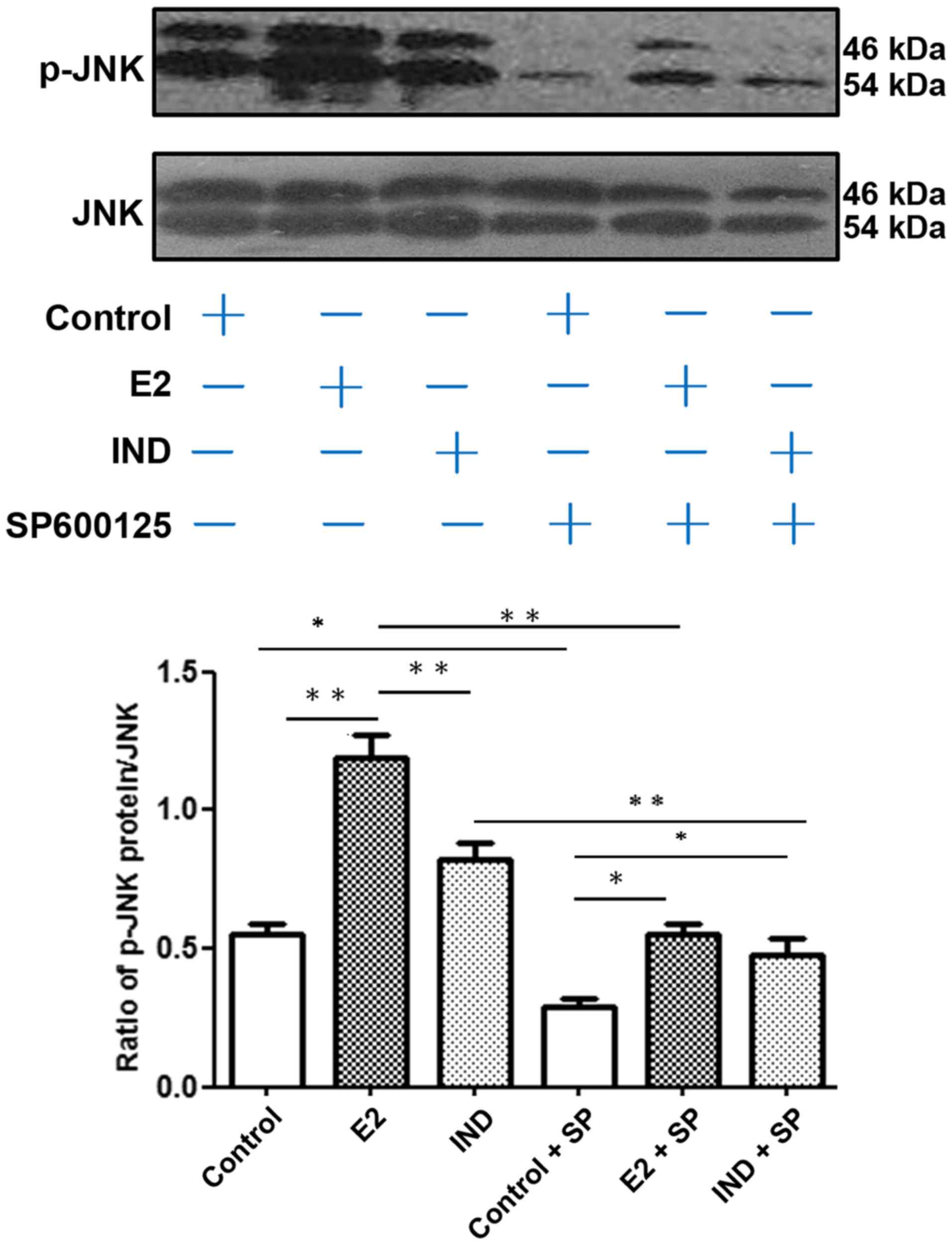
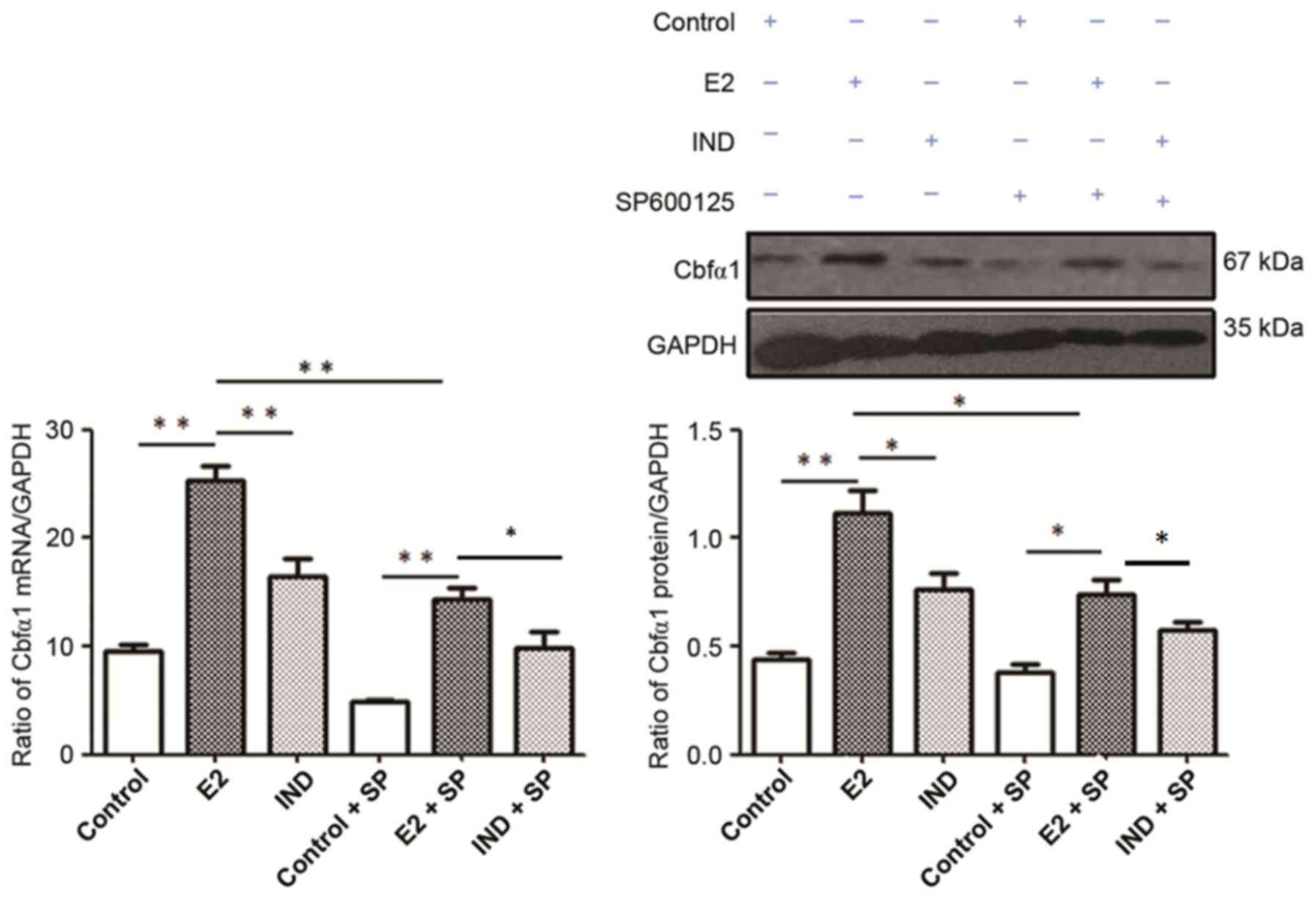
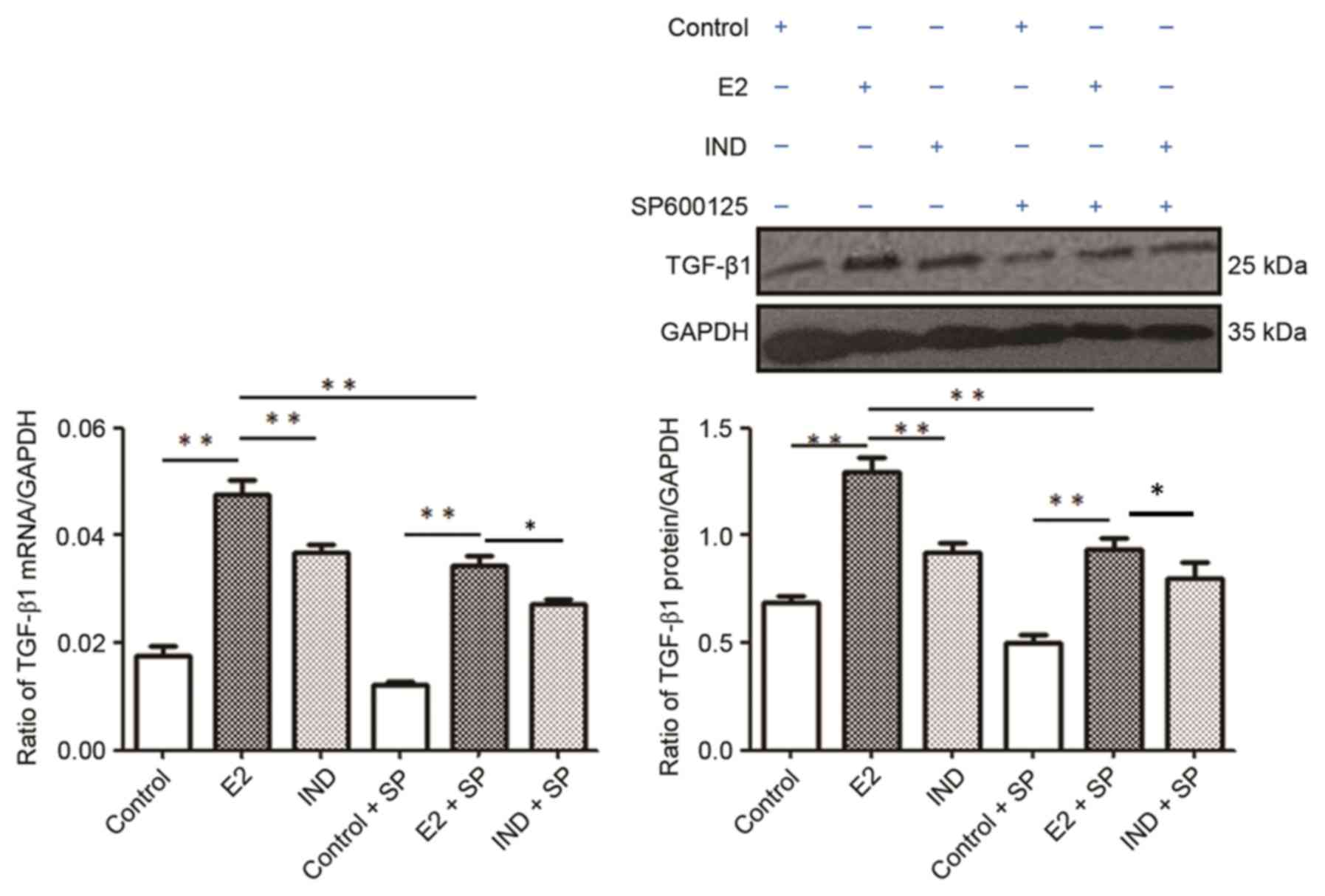
|
1
|
Siris ES, Miller PD, Barrett-Connor E,
Faulkner KG, Wehren LE, Abbott TA, Berger ML, Santora AC and
Sherwood LM: Identification and fracture outcomes of undiagnosed
low bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: Results from the
National Osteoporosis Risk Assessment. JAMA. 286:2815–2822. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rachner TD, Khosla S and Hofbauer LC:
Osteoporosis: Now and the future. Lancet. 377:1276–1287. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Al-Rahbi B, Zakaria R, Othman Z, Hassan A
and Ahmad AH: Enhancement of BDNF concentration and restoration of
the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis accompany reduced
depressive-like behaviour in stressed ovariectomised rats treated
with either Tualang honey or estrogen. ScientificWorldJournal.
2014:3108212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen FP, Hu CH and Wang KC: Estrogen
modulates osteogenic activity and estrogen receptor mRNA in
mesenchymal stem cells of women. Climacteric. 16:154–160. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Prockop DJ: Marrow stromal cells as stem
cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 276:71–74. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tan SL, Ahmad TS, Selvaratnam L and
Kamarul T: Isolation, characterization and the multi-lineage
differentiation potential of rabbit bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stem cells. J Anat. 222:437–450. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen M, Feng W, Cao H, Zou L, Chen C,
Baatrup A, Nielsen AB, Li H, Kassem M, Zou X and Bünger C: A
traditional Chinese medicine formula extracts stimulate
proliferation and inhibit mineralization of human mesenchymal stem
cells in vitro. J Ethnopharmacol. 125:75–82. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou DA, Zheng HX, Wang CW, Shi D and Li
JJ: Influence of glucocorticoids on the osteogenic differentiation
of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 15:2392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cargnello M and Roux PP: Activation and
function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated
protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 75:50–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim HK, Kim MG and Leem KH: Osteogenic
activity of collagen peptide via ERK/MAPK pathway mediated boosting
of collagen synthesis and its therapeutic efficacy in osteoporotic
bone by back-scattered electron imaging and microarchitecture
analysis. Molecules. 18:15474–15489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sonowal H, Kumar A, Bhattacharyya J, Gogoi
PK and Jaganathan BG: Inhibition of actin polymerization decreases
osteogeneic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through p38
MAPK pathway. J Biomed Sci. 20:712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kwon HS, Johnson TV and Tomarev SI:
Myocilin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem
cells through mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J Biol
Chem. 288:16882–16894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Marom R, Shur I, Solomon R and Benayahu D:
Characterization of adhesion and differentiation markers of
osteogenic marrow stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 202:41–48. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li XD, Wang JS, Chang B, Chen B, Guo C,
Hou GQ, Huang DY and Du SX: Panax notoginseng saponins promotes
proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow
stromal cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 134:268–274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Komori T: Animal models for osteoporosis.
Eur J Pharmacol. 759:287–294. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guicheux J, Lemonnier J, Ghayor C, Suzuki
A, Palmer G and Caverzasio J: Activation of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase and c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase by BMP-2 and their
implication in the stimulation of osteoblastic cell
differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 18:2060–2068. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Byers BA, Pavlath GK, Murphy TJ, Karsenty
G and Garcia AJ: Cell-type-dependent up-regulation of in vitro
mineralization after overexpression of the osteoblast-specific
transcription factor Runx2/Cbfal. J Bone Miner Res. 17:1931–1944.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Teplyuk NM, Haupt LM, Ling L, Dombrowski
C, Mun FK, Nathan SS, Lian JB, Stein JL, Stein GS, Cool SM and van
Wijnen AJ: The osteogenic transcription factor Runx2 regulates
components of the fibroblast growth factor/proteoglycan signaling
axis in osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 107:144–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ngueguim FT, Khan MP, Donfack JH, Siddiqui
JA, Tewari D, Nagar GK, Tiwari SC, Theophile D, Maurya R and
Chattopadhyay N: Evaluation of cameroonian plants towards
experimental bone regeneration. J Ethnopharmacol. 141:331–337.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|