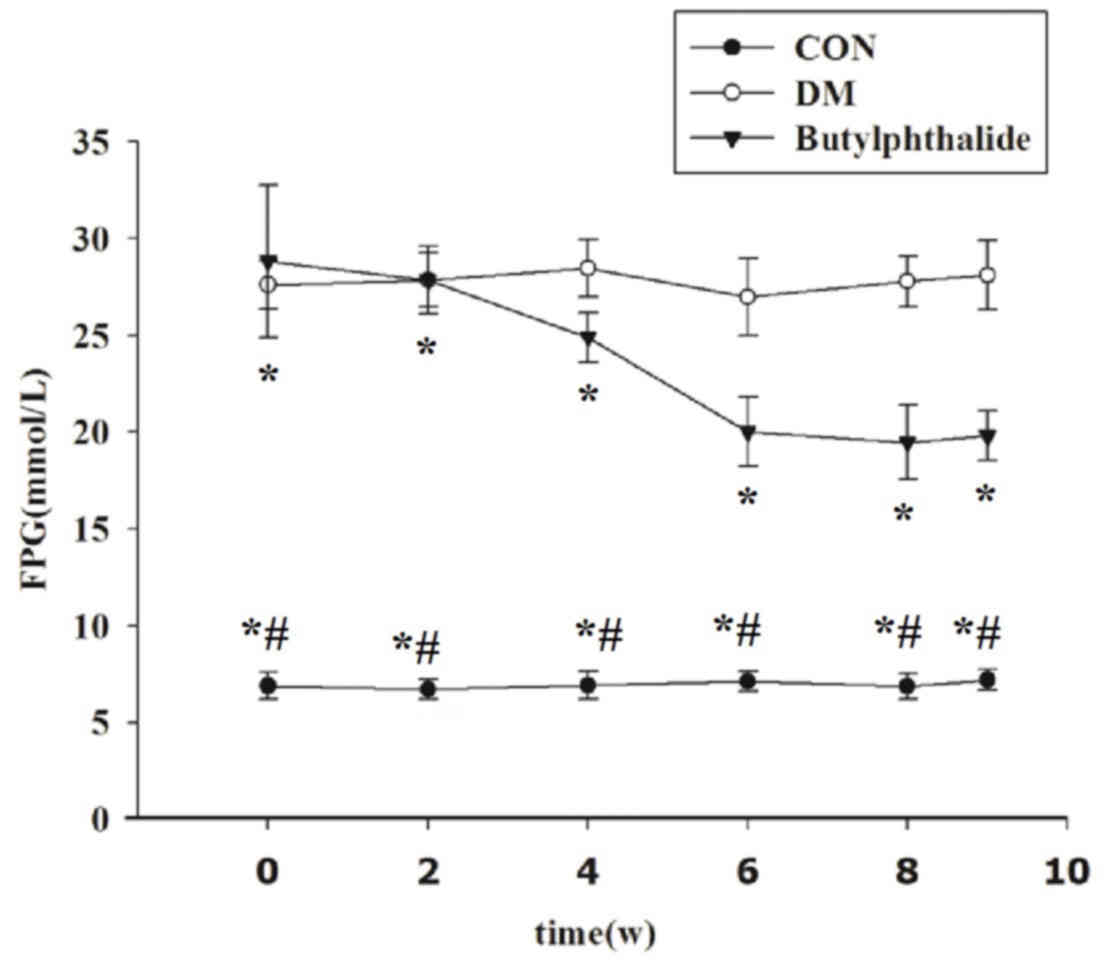
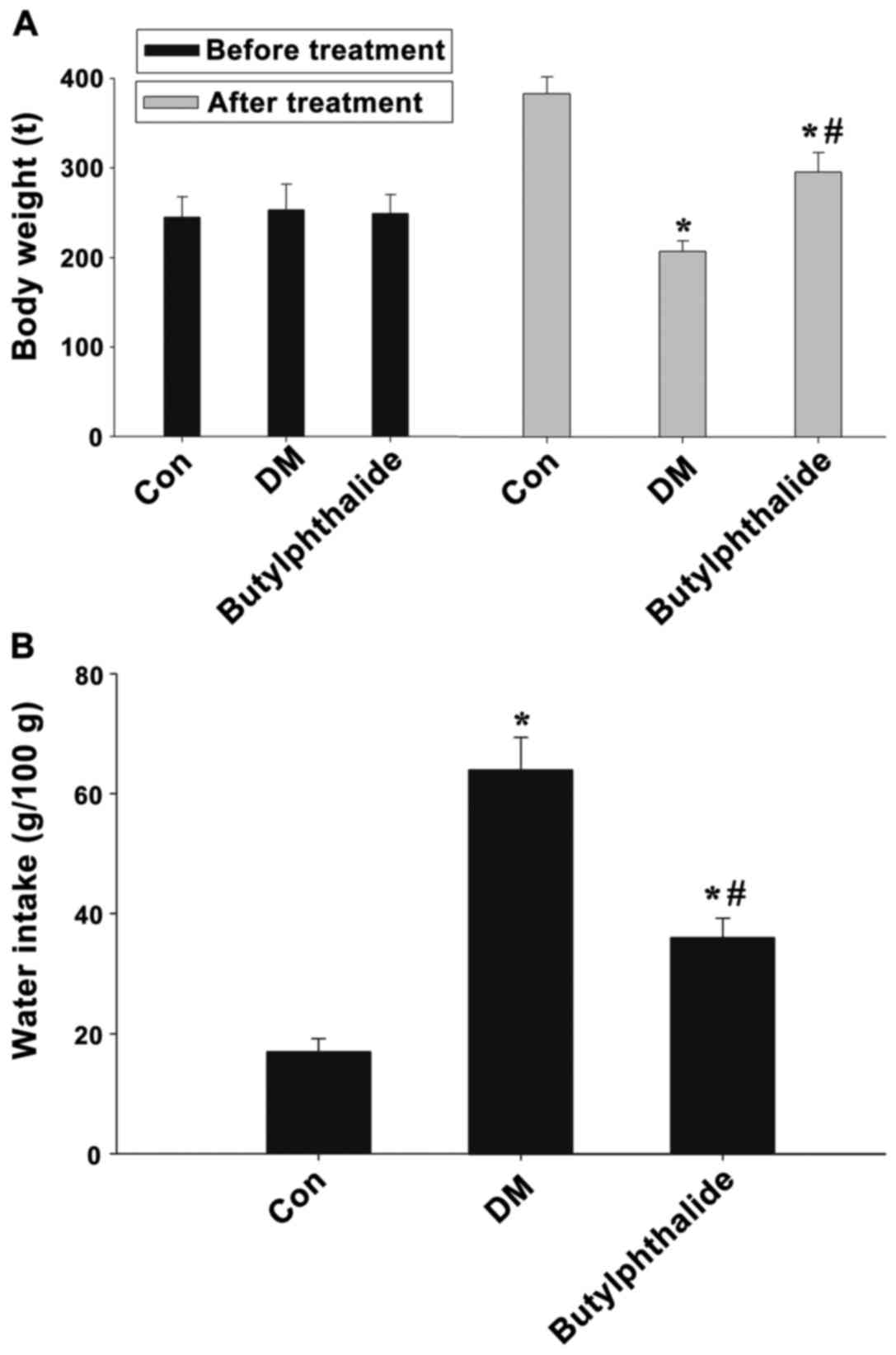
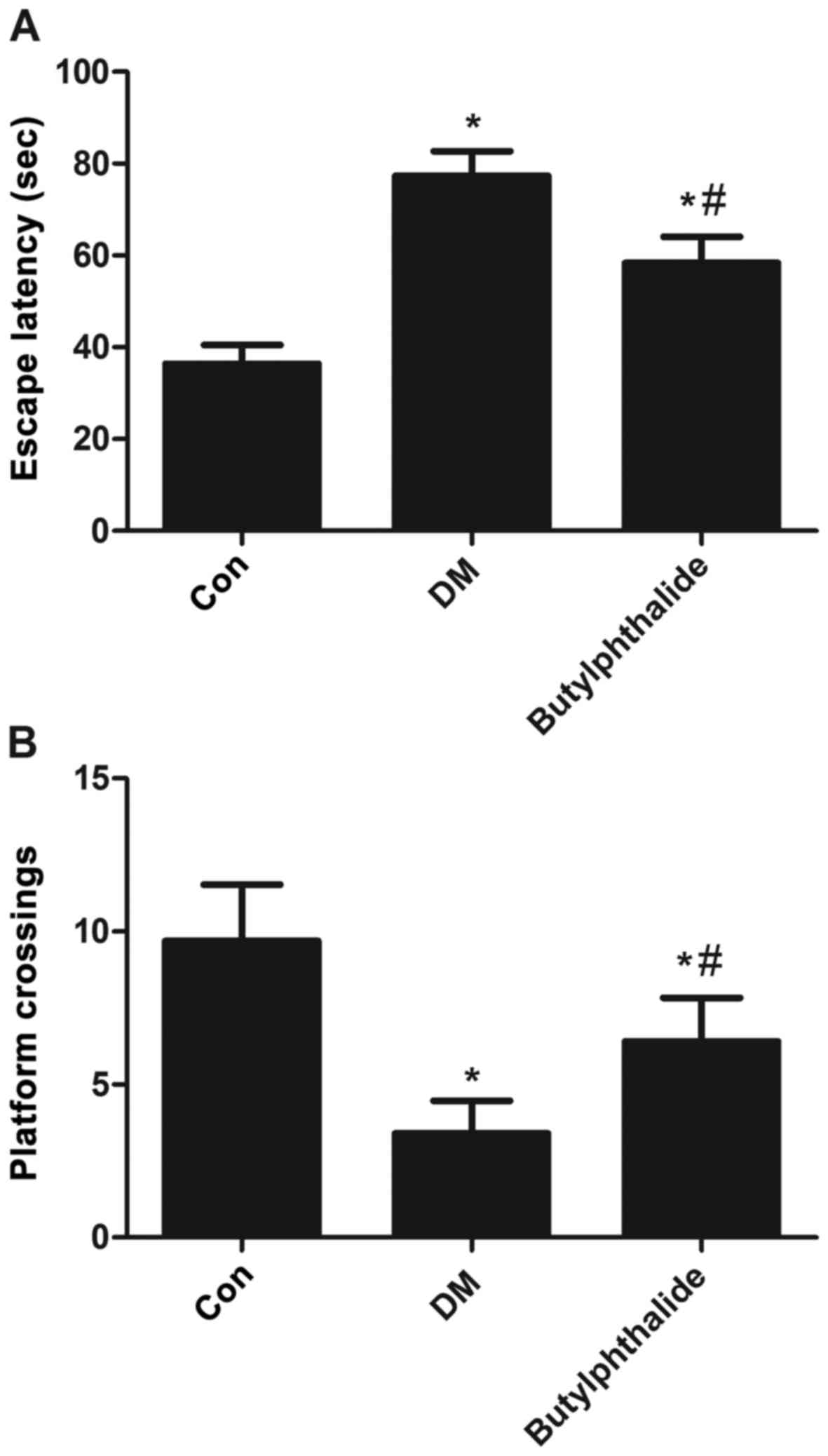
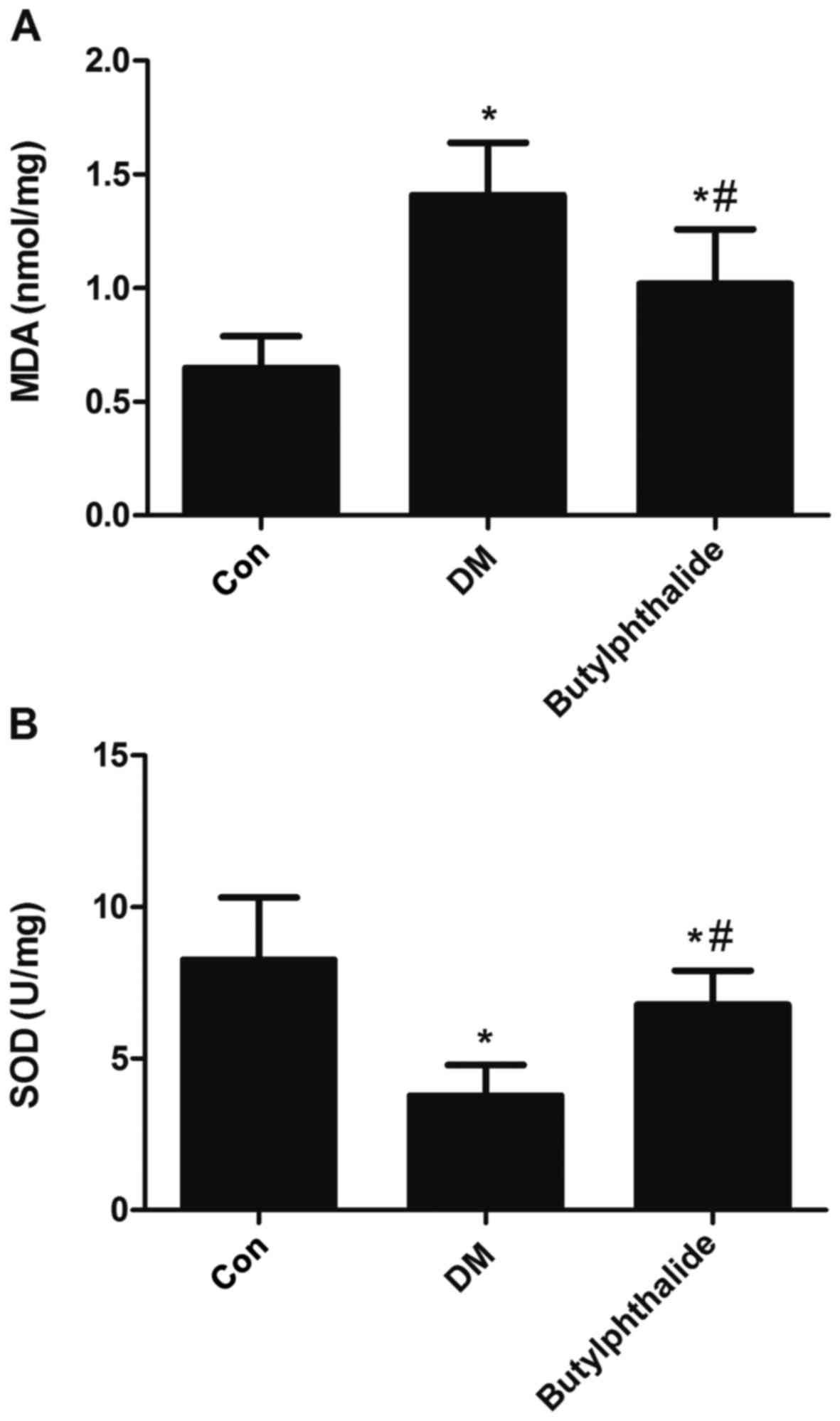
|
1
|
Seto SW, Yang GY, Kiat H, Bensoussan A,
Kwan YW and Chang D: Diabetes mellitus, cognitive impairment, and
traditional Chinese medicine. Int J Ednocrinol.
2015:8104392015.
|
|
2
|
Hölscher C: Diabetes as a risk factor for
Alzheimer's disease: Insulin signalling impairment in the brain as
an alternative model of Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Soc Trans.
39:891–897. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Katon W, Lyles CR, Parker MM, Karter AJ,
Huang ES and Whitmer RA: Association of depression with increased
risk of dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes: The diabetes and
aging study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 69:410–417. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Strachan MW, Reynolds RM, Frier BM,
Mitchell RJ and Price JF: The relationship between type 2 diabetes
and dementia. Br Med Bull. 88:131–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Messier C, Awad N and Gagnon M: The
relationships between atherosclerosis, heart disease, type 2
diabetes and dementia. Neurol Res. 26:567–572. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scott AR: Diabetes and Cerebrovascular
DiseaseVascular Complications of Diabetes: Current Issues in
Pathogenesis and Treatment. Second Edition. Donnelly R and Horton
E: Blackwell Publishing. Inc; Malden, MA: pp. 45–50. 2007
|
|
7
|
Lan Z, Xu X, Xu W, Li J, Liang Z, Zhang X,
Lei M and Zhao C: Discovery of
3-n-butyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-one as a potential
anti-ischemic stroke agent. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:3377–3391.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng Y, Xing C, Xu S, Lemere CA, Chen G,
Liu B, Wang L, Feng Y and Wang X: L-3-n-butylphthalide improves
cognitive impairment induced by intracerebroventricular infusion of
amyloid-beta peptide in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 621:38–45. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huai Y, Dong Y, Xu J, Meng N, Song C, Li W
and Lv P: L-3-n-butylphthalide protects against vascular dementia
via activation of the Akt kinase pathway. Neural Regen Res.
8:1733–1742. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao S, Kai H, Yang C, Wang X, Ji H, Xu J,
Huang Z and Zhang Y: Novel hybrids of 3-n-butylphthalide and
edaravone: Design, synthesis and evaluations as potential
anti-ischemic stroke agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 25:3535–3540.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peng Y, Xu S, Chen G, Wang L, Feng Y and
Wang X: l-3-n-Butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment induced
by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
321:902–910. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang F, Chen H, Sun XJ and Ke ZJ:
Improvement of cognitive deficits in SAMP8 mice by
3-n-butylphthalide. Neurol Res. 36:224–233. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang F, Ma J, Han F, Guo X, Meng L, Sun Y,
Jin C, Duan H, Li H and Peng Y: DL-3-n-butylphthalide delays the
onset and progression of diabetic cataract by inhibiting oxidative
stress in rat diabetic model. Sci Rep. 6:193962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang T, Jia W and Sun X:
3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) reduces apoptosis and enhances vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) up-regulation in diabetic rats.
Neurol Res. 32:390–396. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barcia JM, Floresbellver M, Muriach M,
Sancho-Pelluz J, Lopez-Malo D, Urdaneta AC, Martinez-Gil N,
Atienzar-Aroca S and Romero FJ: Matching diabetes and alcoholism:
Oxidative stress, inflammation, and neurogenesis are commonly
involved. Mediators Inflamm. 2015:6242872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Gong B, Zhao W, Tang C, Varghese
M, Nguyen T, Bi W, Bilski A, Begum S, Vempati P, et al: Epigenetic
mechanisms linking diabetes and synaptic impairments. Diabetes.
63:645–654. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang S, Wang Y, Gan X, Fang D, Zhong C,
Wu L, Hu G, Sosunov AA, McKhann GM, Yu H and Yan SS: Drp1-mediated
mitochondrial abnormalities link to synaptic injury in diabetes
model. Diabetes. 64:1728–1742. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huber JD: Diabetes, cognitive function,
and the blood-brain barrier. Curr Pharm Des. 14:1594–1600. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
González-Reyes RE, Aliev G,
Ávila-Rodrigues M and Barreto GE: Alterations in glucose metabolism
on cognition: A possible link between diabetes and dementia. Curr
Pharm Des. 22:812–818. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Perantie DC, Lim A, Wu J, Weaver P, Warren
SL, Sadler M, White NH and Hershey T: Effects of prior hypoglycemia
and hyperglycemia on cognition in children with type 1 diabetes
mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes. 9:87–95. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Krentz AJ, Clough G and Byrne CD:
Interactions between microvascular and macrovascular disease in
diabetes: Pathophysiology and therapeutic implications. Diabetes
Obes Metab. 9:781–791. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Caballero AE, Arora S, Saouaf R, Lim SC,
Smakowski P, Park JY, King GL, LoGerfo FW, Horton ES and Veves A:
Microvascular and macrovascular reactivity is reduced in subjects
at risk for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 48:1856–1862. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sebastião I, Candeias E, Santos MS, de
Oliveira CR, Moreira PI and Duarte AI: Insulin as a bridge between
type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease-how anti-diabetics could be a
solution for dementia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
5:1102014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS and
Spiegelman BM: Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha:
Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science.
259:87–91. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tateya S, Kim F and Tamori Y: Recent
advances in obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 4:932013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu W, Wang X, Xiang Q, Meng X, Peng Y, Du
N, Liu Z, Sun Q, Wang C and Liu X: Astaxanthin alleviates brain
aging in rats by attenuating oxidative stress and increasing BDNF
levels. Food Funct. 5:158–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Singh R, Kaur N, Kishore L and Gupta GK:
Management of diabetic complications: A chemical constituents based
approach. J Ethnopharmacol. 150:51–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhong SZ, Ge QH, Qu R, Li Q and Ma SP:
Paeonol attenuates neurotoxicity and ameliorates cognitive
impairment induced by d-galactose in ICR mice. J Neurol Sci.
277:58–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao CH, Liu HQ, Cao R, Ji AL, Zhang L,
Wang F and Yang RH: Effects of dietary fish oil on learning
function and apoptosis of hippocampal pyramidal neurons in
streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Brain Res. 1457:33–43. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang X, Wang L, Li T, Huang Z, Lai Y, Ji
H, Wan X, Xu J, Tian J and Zhang Y: Novel hybrids of optically
active ring-opened 3-n-butylphthalide derivative and isosorbide as
potential anti-ischemic stroke agents. J Med Chem. 56:3078–3089.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang JZ, Chen YZ, Su M, Zheng HF, Yang
YP, Chen J and Liu CF: dl-3-n-Butylphthalide prevents oxidative
damage and reduces mitochondrial dysfunction in an MPP(+)-induced
cellular model of Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 475:89–94.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen M, Qi L, Min T, Wen S, Pi R and Lin
D: Synthesis and biological evaluation of n-butylphthalide
derivatives as anti-platelet aggregation agents. Nat Prod Res. 1–4.
2016.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
33
|
Wang HM, Zhang T, Huang JK and Sun XJ:
3-N-butylphthalide (NBP) attenuates the amyloid-β-induced
inflammatory responses in cultured astrocytes via the nuclear
factor-κB signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:235–242.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang YG, Li Y, Wang CY, Ai JW, Dong XY,
Huang HY, Feng ZY, Pan YM, Lin Y, Wang BX and Yao LL:
L-3-n-butylphthalide protects rats' cardiomyocytes from
ischaemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis by affecting the
mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 210:524–533.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yin W, Lan L, Huang Z, Ji J, Fang J, Wang
X, Ji H, Peng S, Xu J and Zhang Y: Discovery of a ring-opened
derivative of 3-n-butylphthalide bearing NO/H2S-donating moieties
as a potential anti-ischemic stroke agent. Eur J Med Chem.
115:369–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li J, Yin L, Ogle M, Xin Zhou, Minke Song,
Ping Yu Shan and Ling Wei: dl-3-n-Butylphthalide prevents neuronal
cell death after focal cerebral ischemia in mice via the JNK
pathway. Brain Res. 1359:216–226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tiwari BK, Pandey KB, Abidi AB and Rizvi
SI: Markers of oxidative stress during diabetes mellitus. J
Biomark. 2013:1–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Bandeira SM, Gda S Guedes, da Fonseca LJ,
Pires AS, Gelain DP, Moreira JC, Rabelo LA, Vasconcelos SM and
Goulart MO: Characterization of blood oxidative stress in type 2
diabetes mellitus patients: Increase in lipid peroxidation and SOD
activity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012:8193102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pencea V, Bingaman KD, Wiegand SJ and
Luskin MB: Infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor into the
lateral ventricle of the adult rat leads to new neurons in the
parenchyma of the striatum, septum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. J
Neurosci. 21:6706–6717. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mizuno M, Yamada K, Olariu A, Nawa H and
Nabeshima T: Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in
spatial memory formation and maintenance in a radial arm maze test
in rats. J Neurosci. 20:7116–7121. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|