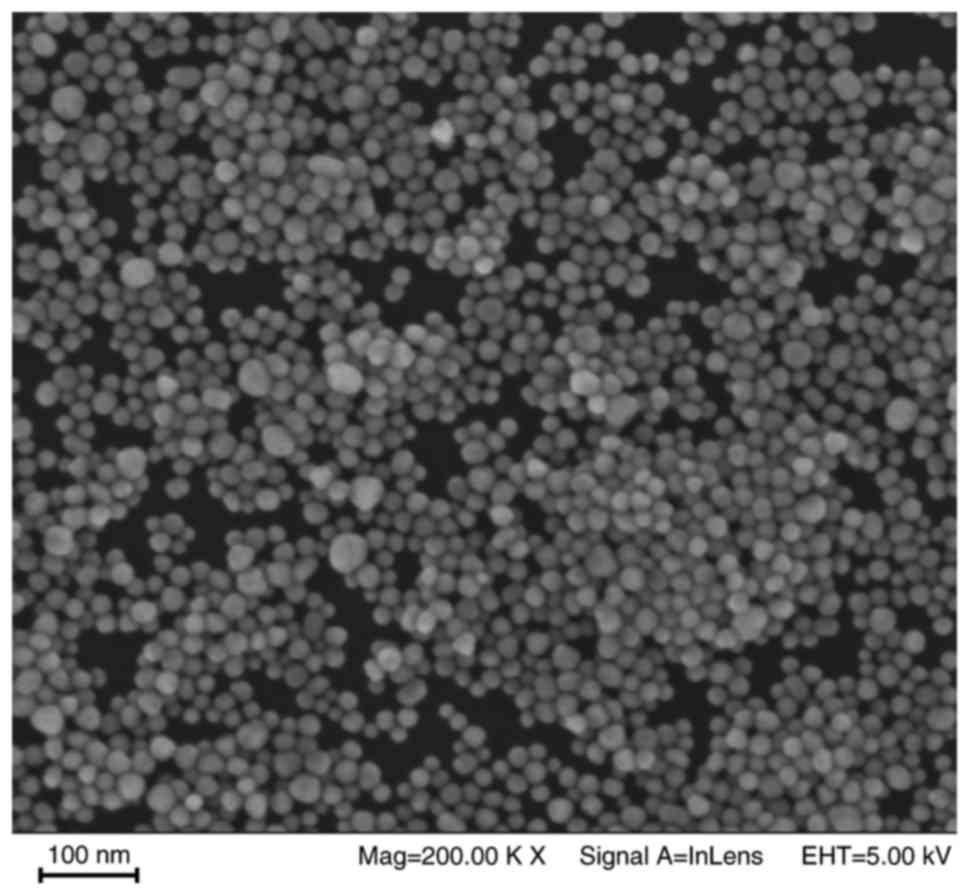
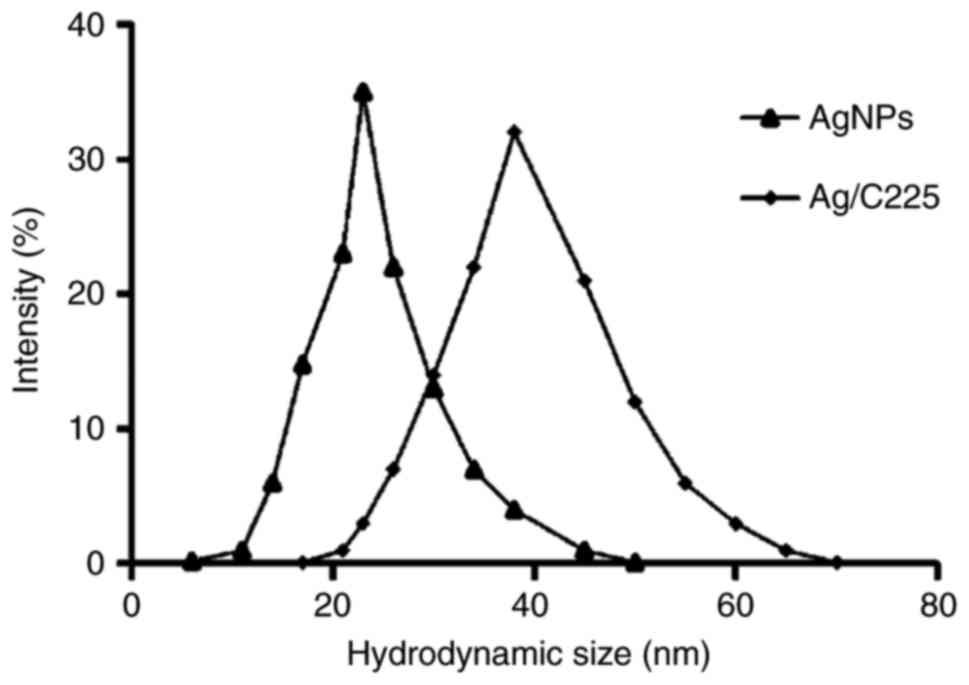
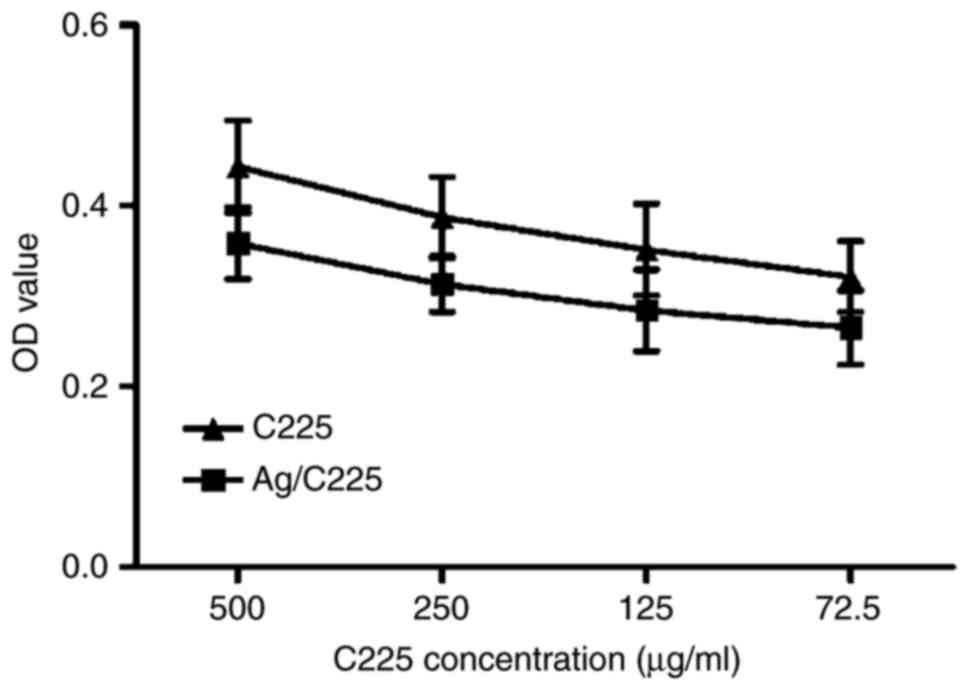
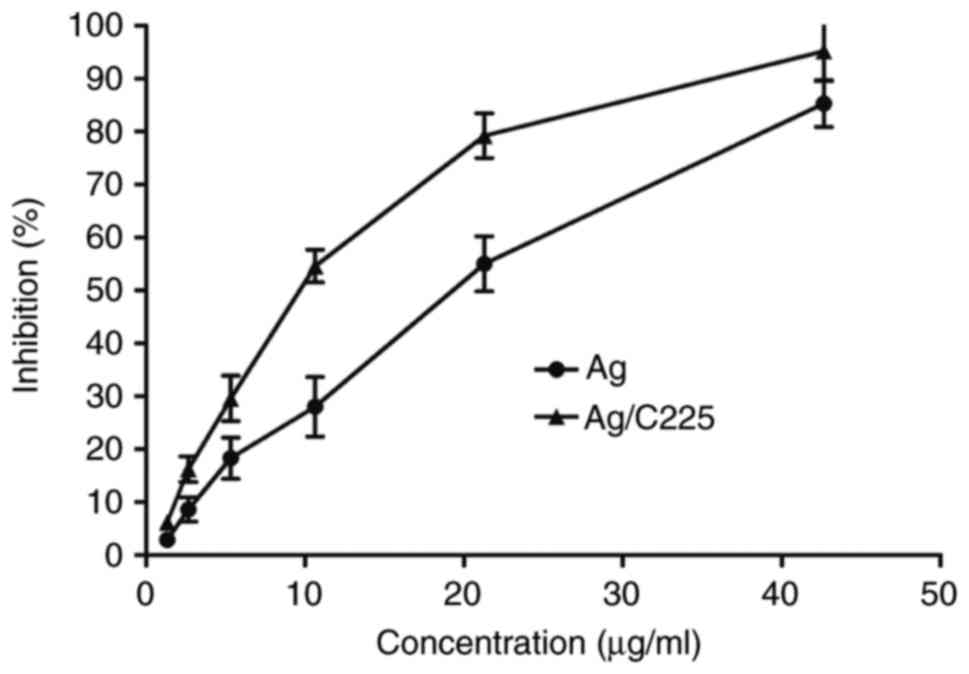
|
1
|
Elnaggar YS: Multifaceted applications of
bile salts in pharmacy: An emphasis on nanomedicine. Int J
Nanomedicine. 10:3955–3971. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim SS, Harford JB, Pirollo KF and Chang
EH: Effective treatment of glioblastoma requires crossing the
blood-brain barrier and targeting tumors including cancer stem
cells: The promise of nanomedicine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
468:485–489. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ishihara M, Nguyen VQ, Mori Y, Nakamura S
and Hattori H: Adsorption of silver nanoparticles onto different
surface structures of chitin/chitosan and correlations with
antimicrobial activities. Int J Mol Sci. 16:13973–13988. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saravanakumar G, Kim K, Park JH, Rhee K
and Kwon IC: Current status of nanoparticle-based imaging agents
for early diagnosis of cancer and atherosclerosis. J Biomed
Nanotechnol. 5:20–35. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Verma A, Uzun O, Hu Y, Hu Y, Han HS,
Watson N, Chen S, Irvine DJ and Stellacci F:
Surface-structure-regulated cell-membrane penetration by
monolayer-protected nanoparticles. Nat Mater. 7:588–595. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cedervall T, Lynch I, Lindman S, Berggård
T, Thulin E, Nilsson H, Dawson KA and Linse S: Understanding the
nanoparticle-protein corona using methods to quantify exchange
rates and affinities of proteins for nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 104:pp. 2050–2055. 2007; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chithrani BD, Ghazani AA and Chan WC:
Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle
uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 6:662–668. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Buckle T, Chin PT and van Leeuwen FW:
(Non-targeted) radioactive/fluorescent nanoparticles and their
potential in combined pre- and intraoperative imaging during
sentinel lymph node resection. Nanotechnology. 21:4820012010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bailet JW, Mark RJ, Abemayor E, Lee SP,
Tran LM, Juillard G and Ward PH: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
Treatment results with primary radiation therapy. Laryngoscope.
102:965–972. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fandi A and Cvitkovic E: Biology and
treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 7:255–263.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mendelsohn J: Targeting the epidermal
growth factor receptor for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 20(18
Suppl): 1S–13S. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gril B, Palmieri D, Bronder JL, Herring
JM, Vega-Valle E, Feigenbaum L, Liewehr DJ, Steinberg SM, Merino
MJ, Rubin SD and Steeg PS: Effect of lapatinib on the outgrowth of
metastatic breast cancer cells to the brain. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:1092–1103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Unruh A, Ressel A, Mohamed HG, Johnson RS,
Nadrowitz R, Richter E, Katschinski DM and Wenger RH: The
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha is a negative factor for tumor
therapy. Oncogene. 22:3213–3220. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Le QT, Denko NC and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxic
gene expression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 23:293–310.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N,
Shin DM, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur R, Raben D, Jassem J, et al:
Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head
and neck. N Engl J Med. 354:567–578. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu R, Ma J, Sun X, Chen Z, Jiang X, Guo Z,
Huang L, Li Y, Wang M, Wang C, et al: Ag nanoparticles sensitize
IR-induced killing of cancer cells. Cell Res. 19:1031–1034. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang Y, Shi J, Tanaka T and Nogami M:
Self-assembled silver nanochains for surface-enhanced Raman
scattering. Langmuir. 23:12042–12047. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Neklasova NY, Zharinov GM and Grebenyuk
AN: Modification of radiosensitivity in maignant and normal tissues
during radiotherapy of malignant neoplasms. Radiats Biol Radioecol.
54:597–605. 2014.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pelevina II, Aleshchenko AV, Antoshchina
MM, Birjukov VA, Reva EV and Minaeva NG: The radiosensitivity
change after low-dose irradiation, possible mechanisms and
regularities. Radiats Biol Radioecol. 55:57–62. 2015.(In Russian).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao D, Sun X, Tong J, Ma J, Bu X, Xu R
and Fan R: A novel multifunctional nanocomposite C225-conjugated
Fe3O4/Ag enhances the sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
to radiotherapy. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 44:678–684.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Evans-Axelsson S, Timmermand O
Vilhelmsson, Welinder C, Borrebaeck CA, Strand SE, Tran TA and
Jansson B: Preclinical evaluation of (111)In-DTPA-INCA-X
anti-Ku70/Ku80 monoclonal antibody in prostate cancer. Am J Nucl
Med Mol Imaging. 4:311–323. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
O'Sullivan D, Henry M, Joyce H, Walsh N,
Mc Auley E, Dowling P, Swan N, Moriarty M, Barnham P, Clynes M and
Larkin A: 7B7: A novel antibody directed against the Ku70/Ku80
heterodimer blocks invasion in pancreatic and lung cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 35:6983–6997. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|