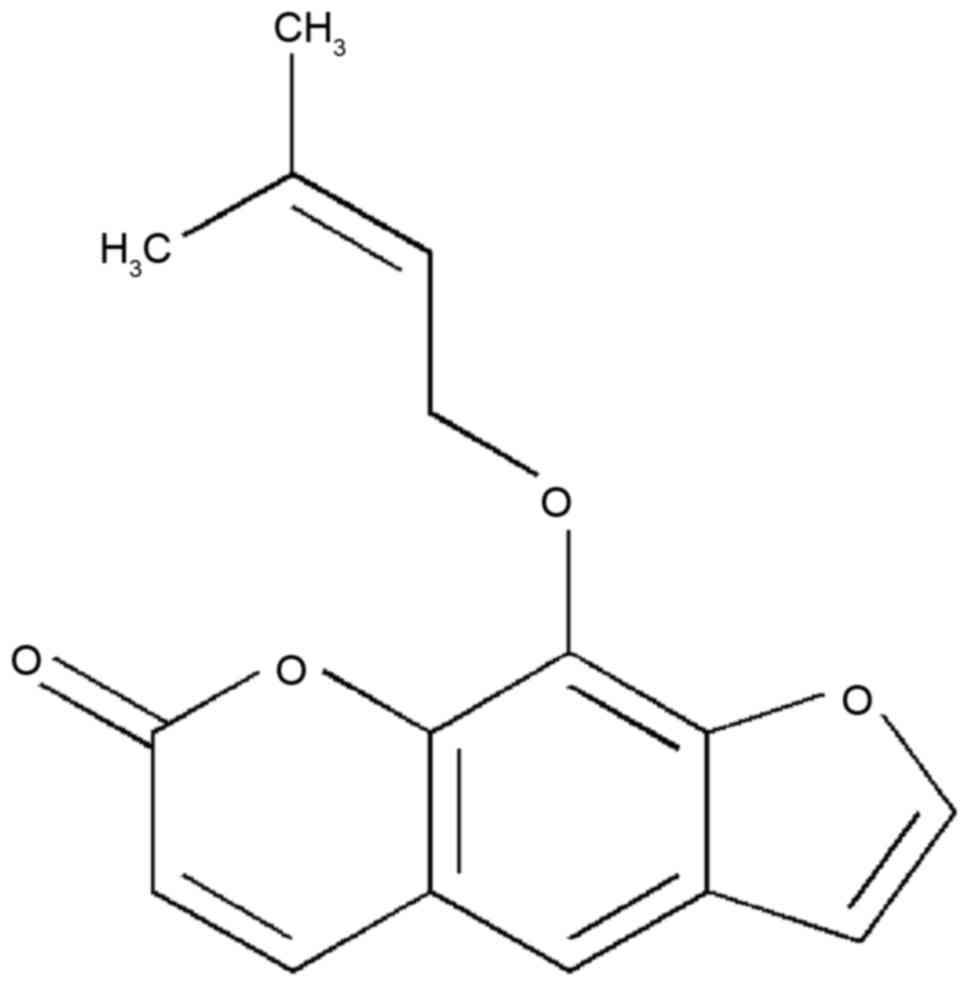
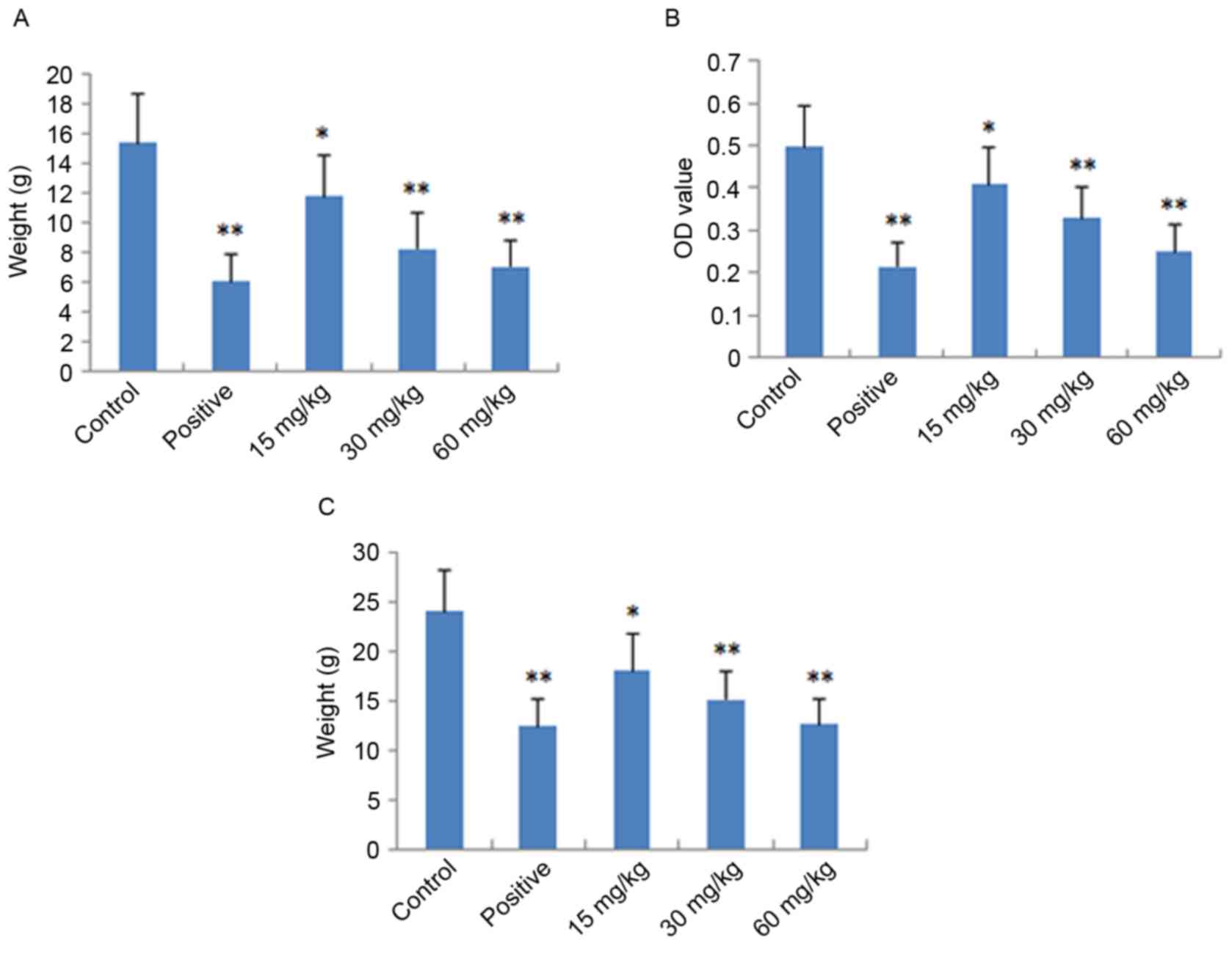
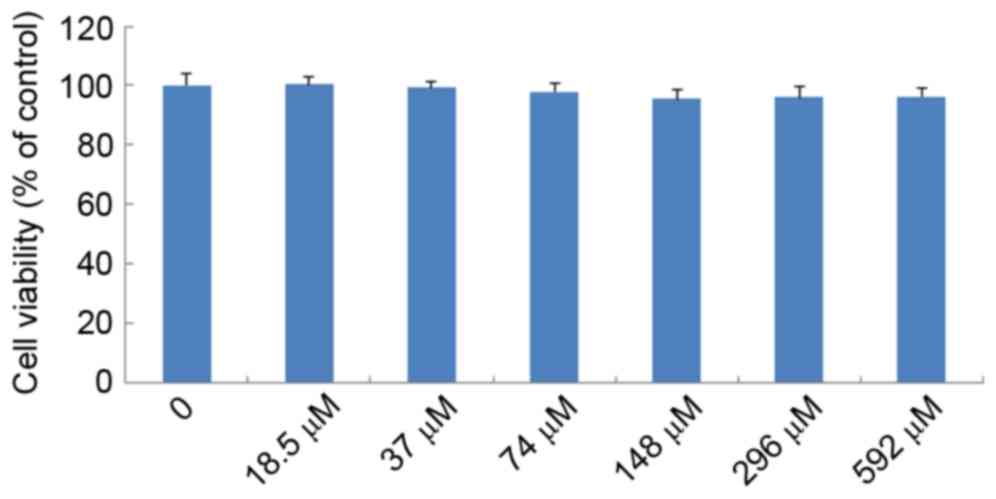
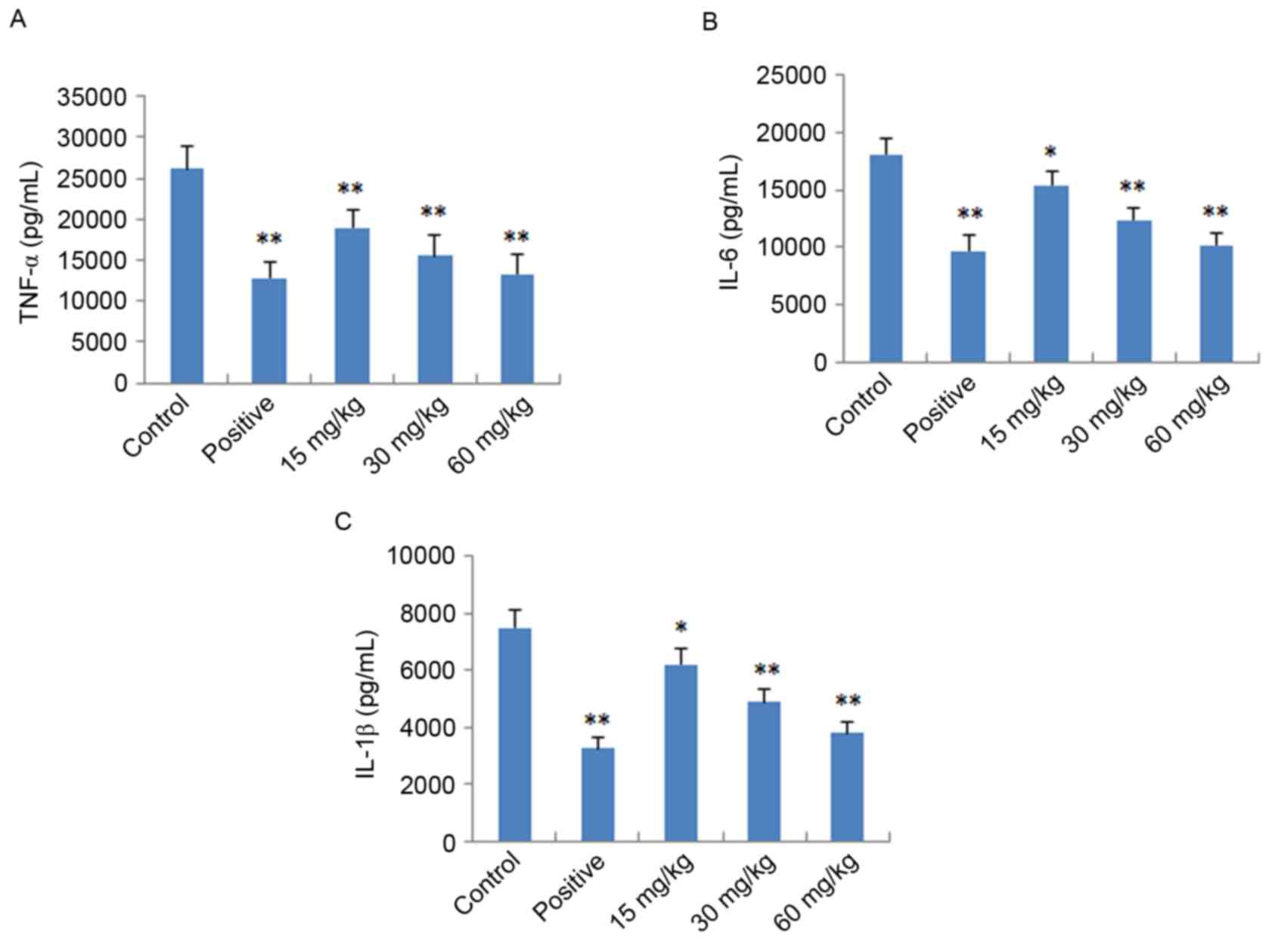
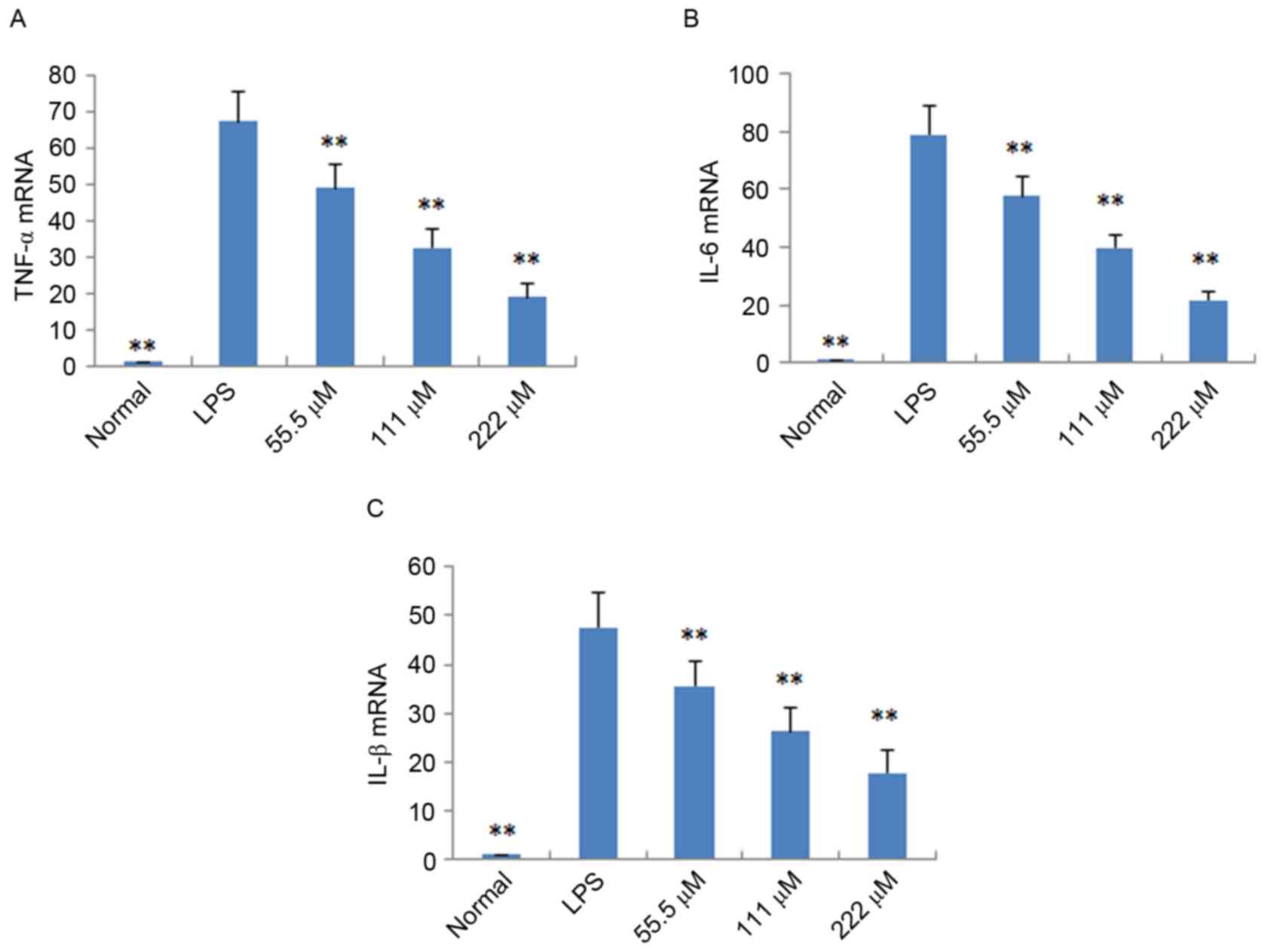
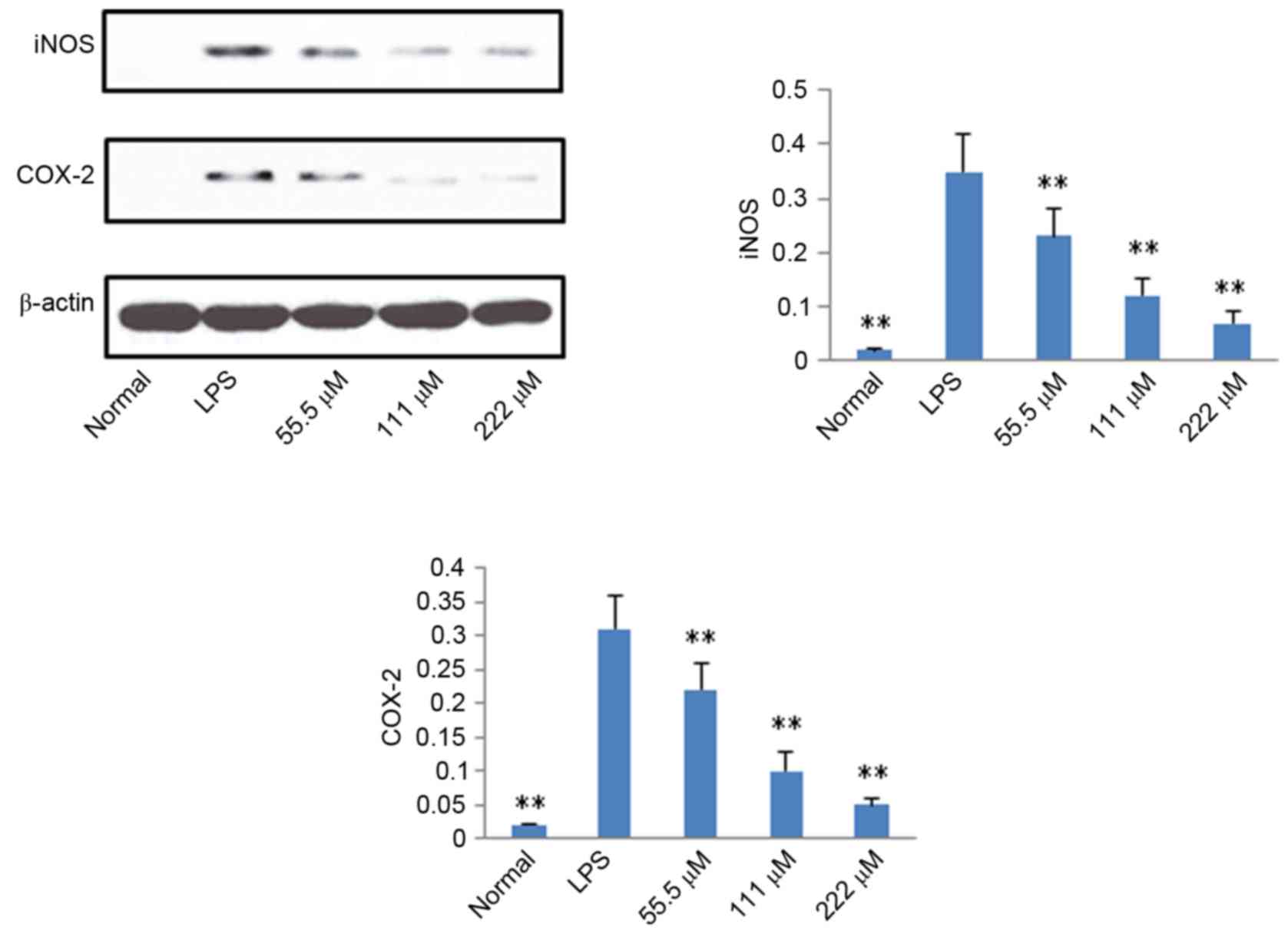
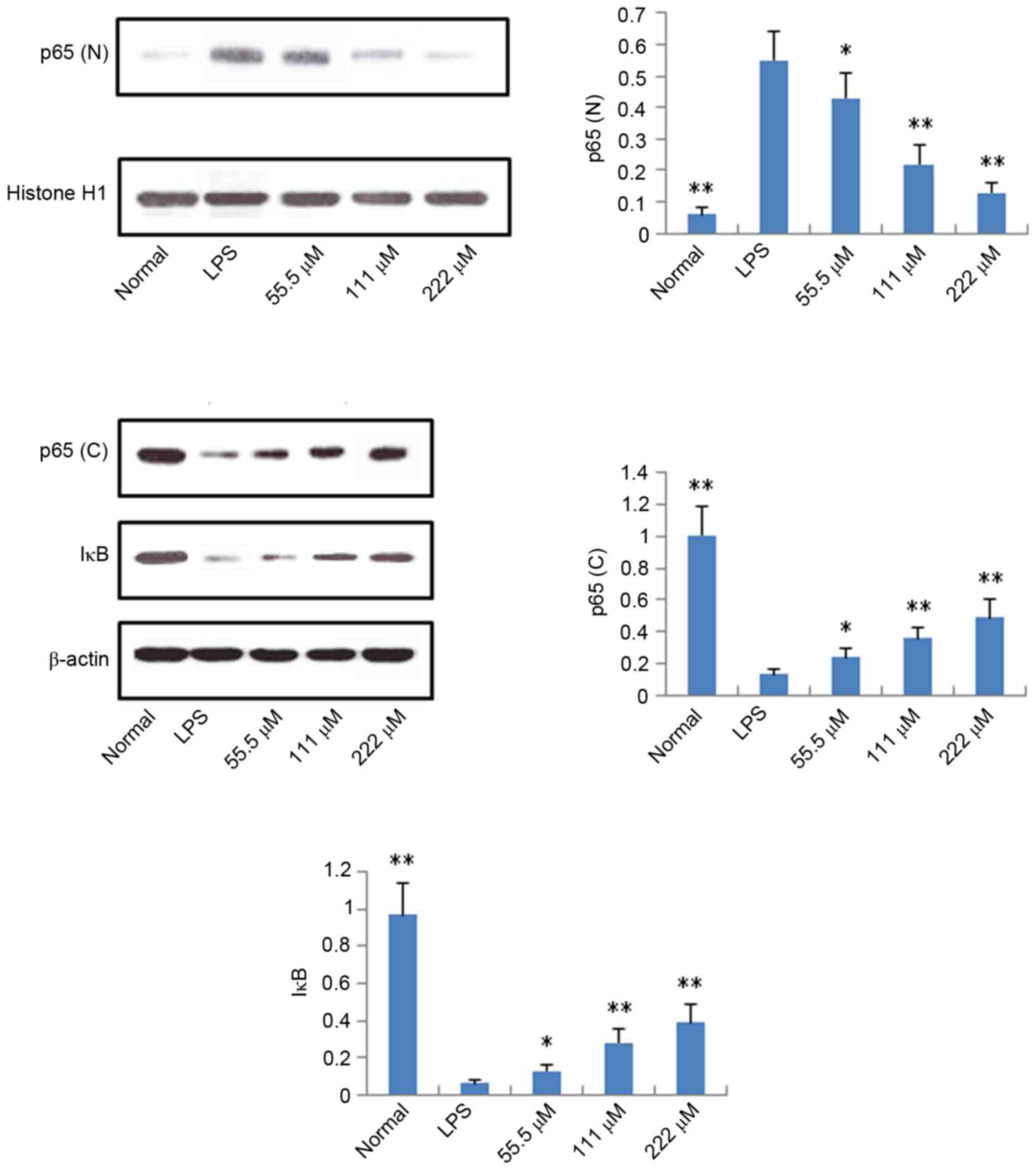
|
1
|
Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS
and Girardin SE: Chronic inflammation: Importance of NOD2 and NALP3
in interleukin-1beta generation. Clin Exp Immunol. 147:227–235.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ryan GB and Majno G: Acute inflammation. A
review. Am J Pathol. 86:183–276. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ward PA: Acute and Chronic
InflammationFundamentals of Inflammation. Cambridge University
Press; Cambridge: pp. 1–16. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shacter E and Weitzman SA: Chronic
inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 16:217–226.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV and Sung B:
Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of
cancer: Short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin Cancer Res.
15:425–430. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baek NI, Ahn EM, Kim HY and Park YD:
Furanocoumarins from the root of Angelica dahurica. Arch Pharm Res.
23:467–470. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang XH and Hu X: Advance in pharmacology
of imperatorin and isoimperatorin pharmacology. J Nanchang Uni Med
Sic. 52:95–97. 2012.
|
|
8
|
García-Argáez AN, Ramírez Apan TO, Delgado
H Parra, Velázquez G and Martínez-Vázquez M: Anti-inflammatory
activity of coumarins from Decatropis bicolor on TPA ear mice
model. Plant Med. 66:279–281. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kawaii S, Tomono Y, Ogawa K, Sugiura M,
Yano M, Yoshizawa Y, Ito C and Furukawa H: Antiproliferative effect
of isopentenylated coumarins on several cancer cell lines.
Anticancer Res. 21:1905–1911. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Luszczki JJ, Wojda E, Andres-Mach M,
Cisowski W, Glensk M, Glowniak K and Czuczwar SJ: Anticonvulsant
and acute neurotoxic effects of imperatorin, osthole and valproate
in the maximal electroshock seizure and chimney tests in mice: A
comparative study. Epilepsy Res. 85:293–299. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang MY, Ma YY and Li XB: Pharmcological
effect of four linear furocomarins in Radix Angelicae dahuricae.
Nat Prod Res Dev. 22:485–489. 2010.
|
|
12
|
Abad MJ, de las Heras B, Silván AM,
Pascual R, Bermejo P, Rodriguez B and Villar AM: Effects of
furocoumarins from Cachrys trifida on some macrophage functions. J
Pharm Pharmacol. 53:1163–1168. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ban HS, Lim SS, Suzuki K, Jung SH, Lee S,
Lee YS, Shin KH and Ohuchi K: Inhibitory effects of furanocoumarins
isolated from the roots of Angelica dahurica on prostaglandin E2
production. Planta Med. 69:408–412. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang GJ, Deng JS, Liao JC, Hou WC, Wang
SY, Sung PJ and Kuo YH: Inducible nitric oxide synthase and
cyclooxygenase-2 participate in anti-inflammatory activity of
imperatorin from Glehnia littoralis. J Agric Food Chem.
60:1673–1681. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Q, Yang S, Yang S, Xin F and Wang M:
Anti-inflammatory activity of phlomisoside F isolated from Phlomis
younghusbandii Mukerjee. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:724–730. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Santos F and Rao VS: Antiinflammatory and
antinociceptive effects of 1,8-cineole a terpenoid oxide present in
many plant essential oils. Phytother Res. 14:240–244. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Winter CA and Porter CC: Effect of
alterations in side chain upon anti-inflammatory and liver glycogen
activities of hydrocortisone esters. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm
Assoc. 46:515–519. 1957. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang QS, Yang L, Cui WY, Chen L and Jiang
YH: Anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities of methanol
extract from aerial part of Phlomis younghusbandii Mukerjee. PLoS
One. 9:e891492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Watkins LR, Maier SF and Goehler LE:
Immune activation: The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in
inflammation, illness responses and pathological pain states. Pain.
63:289–302. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feghali CA and Wright TM: Cytokines in
acute and chronic inflammation. Front Biosci. 2:d12–d26. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Murakami A and Ohigashi H: Targeting NOX,
INOS and COX-2 in inflammatory cells: Chemoprevention using food
phytochemicals. Int J Cancer. 121:2357–2363. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vane JR and Botting RM: Mechanism of
Action of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs. Am J Med.
104:2S–8S; 21S-22S. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baeuerle PA and Baichwal VR: NF-kappaB as
a frequent target for immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory
molecules. Adv Immunol. 65:111–137. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee KM, Kang BS, Lee HL, Son SJ, Hwang SH,
Kim DS, Park JS and Cho HJ: Spinal NF-kB activation induces COX-2
upregulation and contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity.
Eur J Neurosci. 19:3375–3381. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brown KD, Claudio E and Siebenlist U: The
roles of the classical and alternative nuclear factor-kappaB
pathways: Potential implications for autoimmunity and rheumatoid
arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:2122008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|