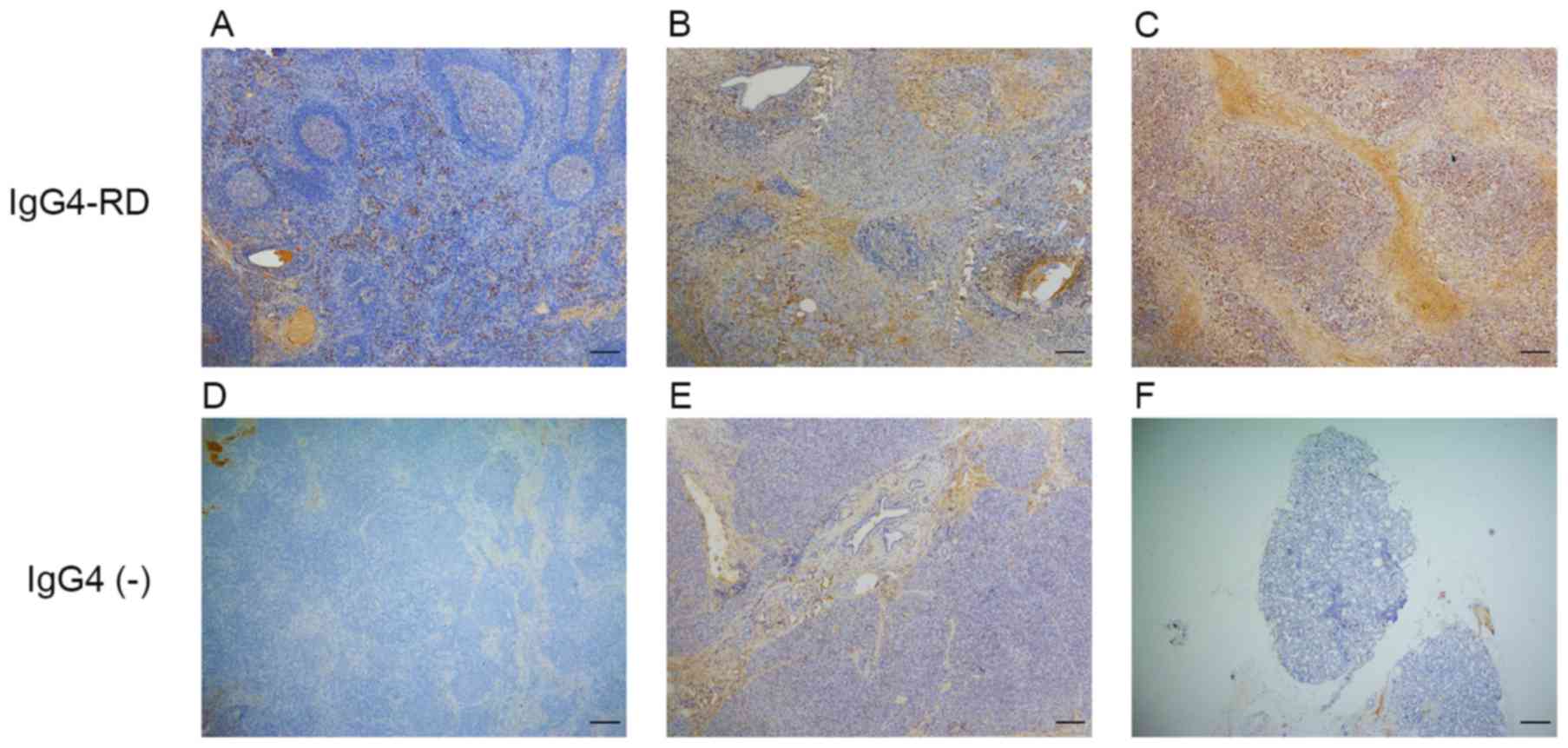
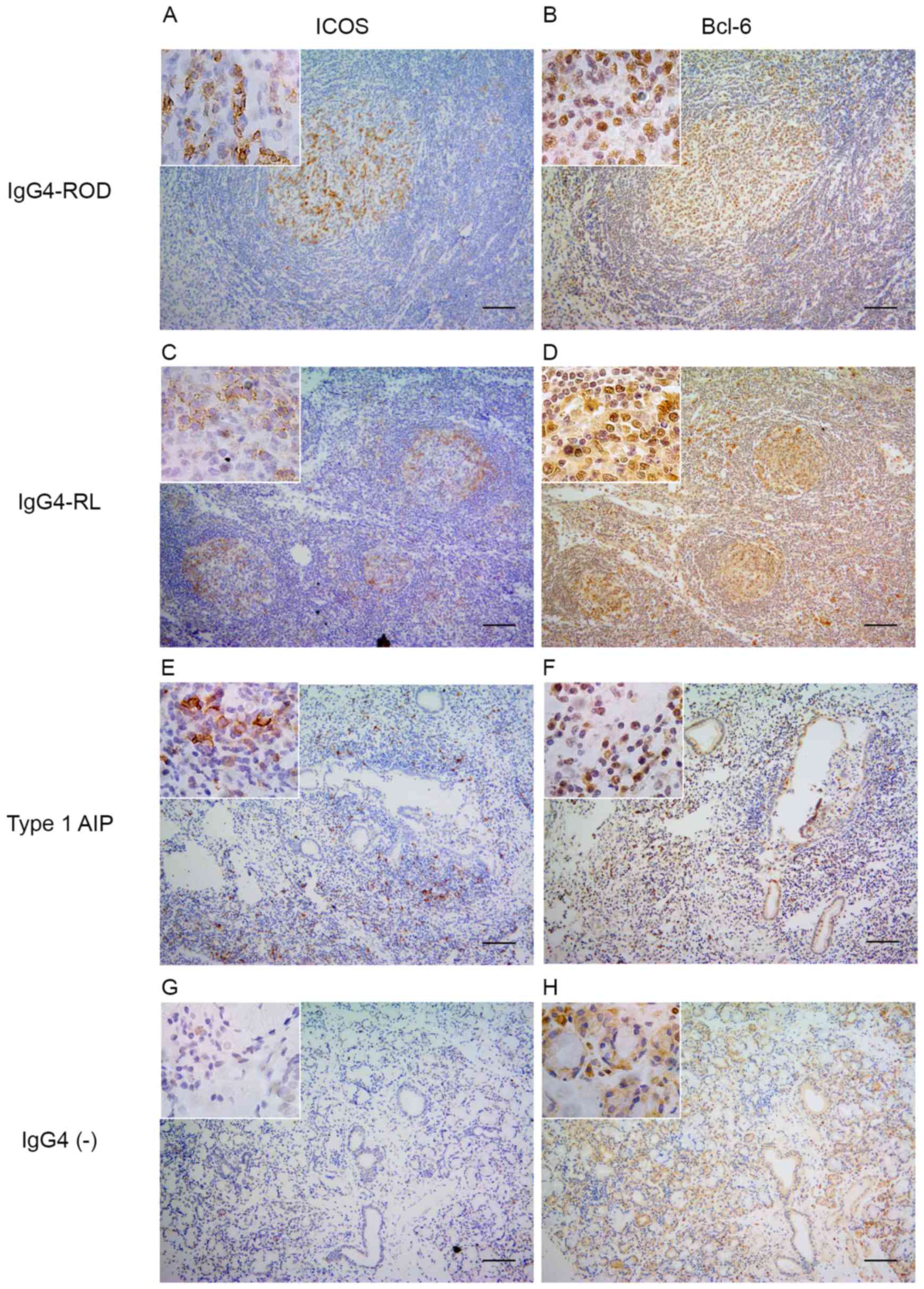
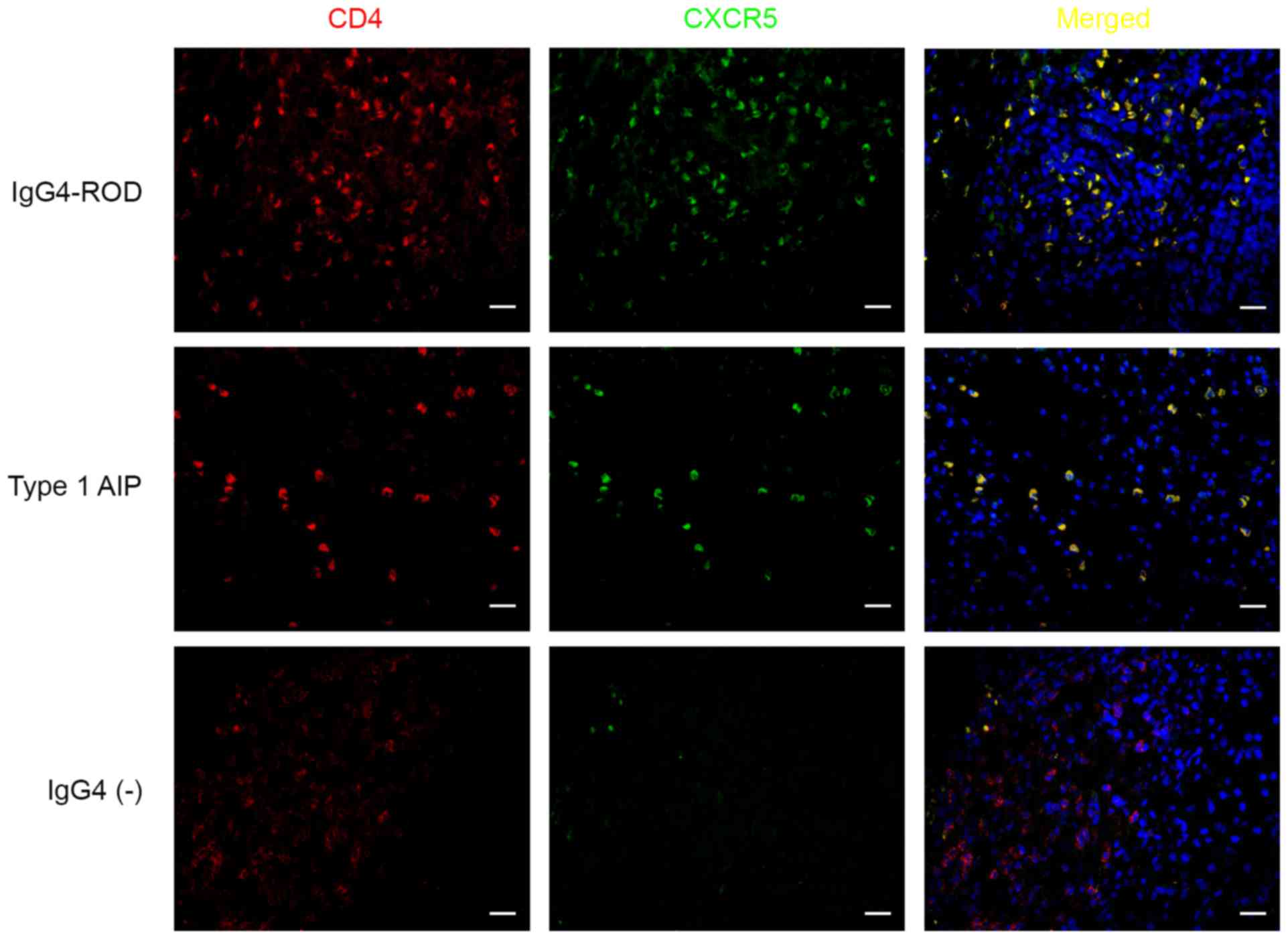
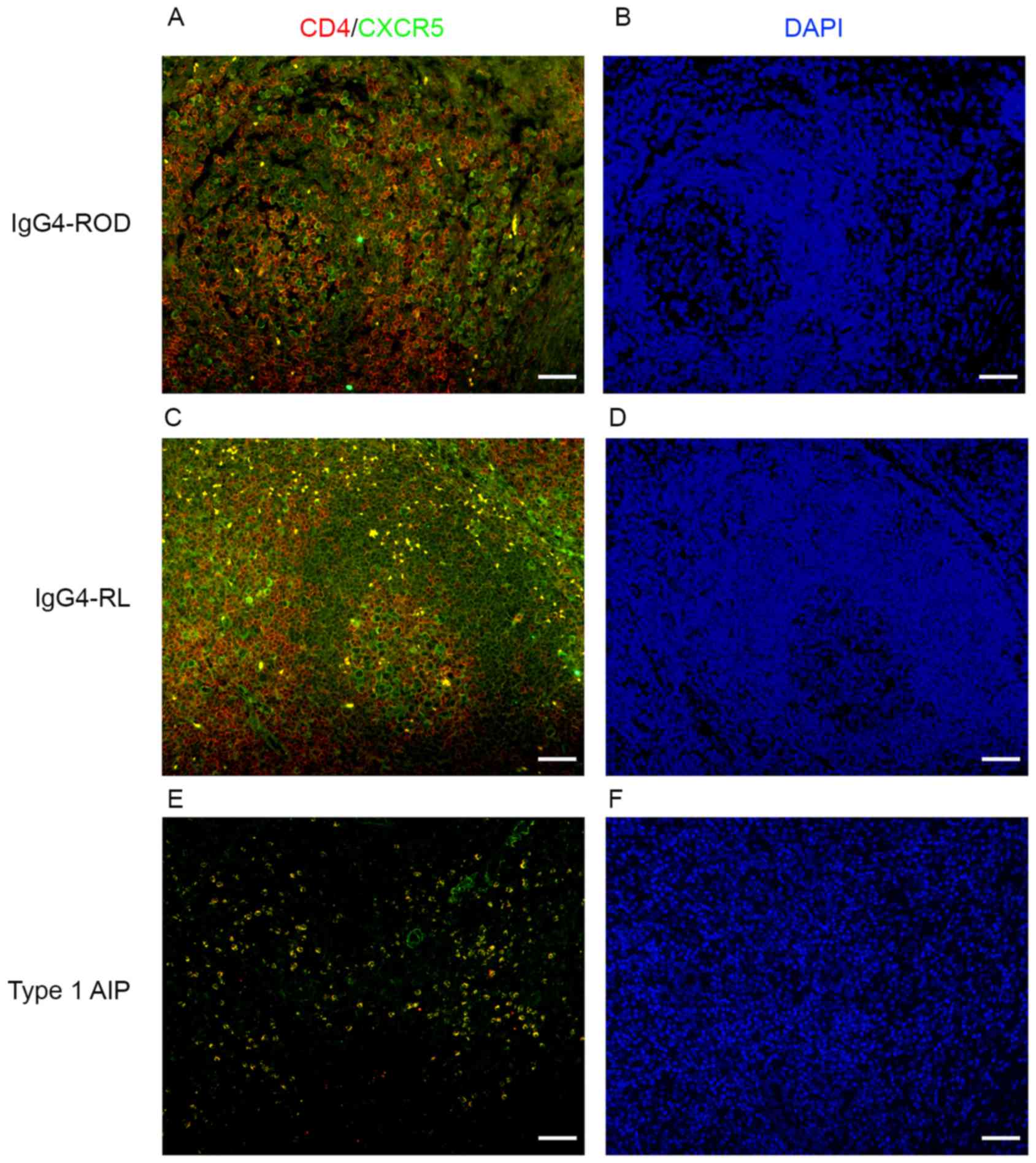
|
1
|
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H,
Furuya N, Akamatsu T, Fukushima M, Nikaido T, Nakayama K, Usuda N
and Kiyosawa K: High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with
sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 344:732–738. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hamanou H, Kawa S, Ochi Y, Unno H, Shiba
N, Wajiki M, Nakazawa K, Shimojo H and Kiyosawa K: Hydronephrosis
associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing
pancreatitis. Lancet. 359:1403–1404. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, Chan
JK, Heathcote JG, Aalberse R, Azumi A, Bloch DB, Brugge WR,
Carruthers MN, et al: Recommendations for the nomenclature of
IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system
manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 64:3061–3067. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M,
Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Matsui S, Sumida T, Mimori T, Tanaka Y, et al:
A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): General
concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 22:1–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato
Y, Yoshino T, Klöppel G, Heathcote JG, Khosroshahi A, Ferry JA, et
al: Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease.
Mod Pathol. 25:1181–1192. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stone JH, Zen Y and Deshpande V:
IgG4-Related Disease. N Engl J Med. 366:539–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goto H, Takahira M and Azumi A; Japanese
Study Group for IgG4-Related Ophthalmic Disease, : Diagnostic
criteria for IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. Jpn J Ophthalmol.
59:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
MacLennan IC: Germinal centers. Annu Rev
Immunol. 12:117–139. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Klein U and Dalla-Favera R: Germinal
centres: Role in B-cell physiology and malignancy. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:22–33. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Crotty S: Follicular helper CD4 T cells
(TFH). Annu Rev Immunol. 29:621–663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vinuesa CG, Linterman MA, Yu D and
MacLennan IC: Follicular Helper T Cells. Annu Rev Immunol.
34:335–368. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schaerli P, Willimann K, Lang AB, Lipp M,
Loetscher P and Moser B: Cxc chemokine receptor 5 expression
defines follicular homing T cells with B cell helper function. J
Exp Med. 192:1553–1562. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Breitfeld D, Ohl L, Kremmer EK, Ellwart J,
Sallusto F, Lipp M and Förster R: Follicular B helper T Cells
express Cxc chemokine receptor 5, Localize to B cell follicles and
support immunoglobulin production. J Exp Med. 192:1545–1552. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ansel KM, McHeyzer-Williams LJ, Ngo VN,
McHeyzer-Williams MG and Cyster JG: In vivo activated CD4 T cells
upregulate CXC chemokine receptor 5 and reprogram their response to
lymphoid chemokines. J Exp Med. 190:1123–1134. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zlotnik A and Yoshie O: Chemokines: A new
classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity.
12:121–127. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chtanova T, Tangye SG, Newton R, Frank N,
Hodge MR, Rolph MS and Mackay CR: T Follicular helper cells express
a distinctive transcriptional profile, reflecting their role as
Non-Th1/Th2 effector cells that provide help for B Cells. J
Immunol. 173:68–78. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johnston RJ, Poholek AC, DiToro D, Yusuf
I, Eto D, Barnett B, Dent AL, Craft J and Crotty S: Bcl6 and
Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular
helper cell differentiation. Science. 325:1006–1010. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Martinez GJ, Yang XO,
Tanaka S, Matskevitch TD, Wang YH and Dong C: Bcl6 mediates the
development of T follicular helper cells. Science. 325:1001–1005.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu D, Rao S, Tsai LM, Lee SK, He Y,
Sutcliffe EL, Srivastava M, Linterman M, Zheng L, Simpson N, et al:
The transcriptional repressor Bcl-6 directs T follicular helper
cell lineage commitment. Immunity. 31:457–468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
King C: New insights into the
differentiation and function of T follicular helper cells. Nat Rev
Immunol. 9:757–766. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi YS, Kageyama R, Eto D, Escobar TC,
Johnston RJ, Monticelli L, Lao C and Crotty S: ICOS receptor
instructs T follicular helper cell versus effector cell
differentiation via induction of the transcriptional repressor
Bcl6. Immunity. 34:932–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weber JP, Fuhrmann F, Feist RK, Lahmann A,
Al Baz MS, Gentz LJ, Vu Van D, Mages HW, Haftmann C, Riedel R, et
al: ICOS maintains the T follicular helper cell phenotype by
down-regulating Kruppel-like factor 2. J Exp Med. 212:217–233.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zen Y, Fujii M, Harada K, Kawano M, Yamada
K, Takahira M and Nakanuma Y: Th2 and regulatory immune reactions
are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis
and cholangitis. Hepatology. 45:1538–1546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tanaka A, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, Miyake
K, Hayashida JN, Maehara T, Shinozaki S, Kubo Y and Nakamura S: Th2
and regulatory immune reactions contribute to IgG4 production and
the initiation of Mikulicz disease. Arthritis Rheum. 64:254–263.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Komori T, Kondo S, Wakisaka N, Nakanishi
Y, Nakanishi-Yagi S, Tsuji A, Endo K, Murono S and Yoshizaki T:
IL-18 is highly expressed in inflammatory infiltrates of
submandibular glands in patients with immunoglobulin G4-related
disease. Hum Pathol. 46:1850–1858. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Maehara T, Mattoo H, Ohta M, Mahajan VS,
Moriyama M, Yamauchi M, Drijvers J, Nakamura S, Stone JH and Pillai
SS: Lesional CD4+ IFN-γ+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in IgG4-related
dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:377–385. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Simpson N, Gatenby PA, Wilson A, Malik S,
Fulcher DA, Tangye SG, Manku H, Vyse TJ, Roncador G, Huttley GA, et
al: Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T
cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe
systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 62:234–244. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi JY, Ho JH, Pasoto SG, Bunin V, Kim
ST, Carrasco S, Borba EF, Goncalves CR, Costa PR, Kallas EG, et al:
Circulating follicular helper-like T cells in systemic lupus
erythematosus: Association with disease activity. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 67:988–999. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu C, Ma J, Liu Y, Tong J, Tian J, Chen
J, Tang X, Xu H, Lu L and Wang S: Increased frequency of follicular
helper T cells in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 97:943–950. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang M, Zhou Y, Guo J, Li H, Tian F, Gong
L, Wang X, Lan M, Li Z and Zhang W: Thymic TFH cells involved in
the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis with thymoma. Exp Neurol.
254:200–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang CJ, Gong Y, Zhu W, Qi Y, Yang CS, Fu
Y, Chang G, Li Y, Shi S, Wood K, et al: Augmentation of Circulating
Follicular Helper T Cells and Their Impact on Autoreactive B Cells
in Myasthenia Gravis. J Immunol. 197:2610–2617. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Akiyama M, Suzuki K, Yamaoka K, Yasuoka H,
Takeshita M, Kaneko Y, Kondo H, Kassai Y, Miyazaki T, Morita R, et
al: Number of circulating follicular helper 2 T cells correlates
with IgG4 and interleukin-4 levels and plasmablast numbers in
IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:2476–2481. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Akiyama M, Yasuoka H, Yamaoka K, Suzuki K,
Kaneko Y, Kondo H, Kassai Y, Koga K, Miyazaki T, Morita R, et al:
Enhanced IgG4 production by follicular helper 2 T cells and the
involvement of follicular helper 1 T cells in the pathogenesis of
IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 18:1672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M,
Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Matsui S, Yoshino T, Nakamura S, Kawa S, et
al: Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease
(IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 22:21–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Friedrichs K, Gluba S, Eidtrnann H and
Jonat W: Overexpression of p53 and Prognosis in Breast Cancer.
Cancer. 72:3641–3647. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu J, Yamane H and Paul WE:
Differentiation of effector CD4 T cell populations (*). Annu Rev
Immunol. 28:445–489. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sato Y, Ohshima K, Ichimura K, Sato M,
Yamadori I, Tanaka T, Takata K, Morito T, Kondo E and Yoshino T:
Ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease has uniform clinicopathology.
Pathol Int. 58:465–470. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Poholek AC, Hansen K, Hernandez SG, Eto D,
Chandele A, Weinstein JS, Dong X, Odegard JM, Kaech SM, Dent AL, et
al: In vivo regulation of Bcl6 and T follicular helper cell
development. J Immunol. 185:313–326. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hatzi K, Nance JP, Kroenke MA, Bothwell M,
Haddad EK, Melnick A and Crotty S: BCL6 orchestrates Tfh cell
differentiation via multiple distinct mechanisms. J Exp Med.
212:539–553. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fazilleau N, Mark L, McHeyzer-Williams LJ
and McHeyzer-Williams MG: Follicular helper T cells: Lineage and
location. Immunity. 30:324–335. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
King C, Tangye SG and Mackay CR: T
follicular helper (TFH) cells in normal and dysregulated immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 26:741–766. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zen Y: The Pathology of IgG4-Related
Disease in the Bile Duct and Pancreas. Semin Liver Dis. 36:242–256.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Spolski R and Leonard WJ: IL-21 and T
follicular helper cells. Int Immunol. 22:7–12. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Good KL, Bryant VL and Tangye SG: Kinetics
of Human B cell behavior and amplification of proliferative
responses following stimulation with IL-21. J Immunol.
177:5236–5247. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bryant VL, Ma CS, Avery DT, Li Y, Good KL,
Corcoran LM, de Waal Malefyt R and Tangye SG: Cytokine-mediated
regulation of human B cell differentiation into ig-secreting cells:
Predominant Role of IL-21 produced by CXCR5+ T follicular helper
cells. J Immunol. 179:8180–8190. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zotos D, Coquet JM, Zhang Y, Light A,
D'Costa K, Kallies A, Corcoran LM, Godfrey DI, Toellner KM, Smyth
MJ, et al: IL-21 regulates germinal center B cell differentiation
and proliferation through a B cell-intrinsic mechanism. J Exp Med.
207:365–378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Linterman MA, Beaton L, Yu D, Ramiscal RR,
Srivastava M, Hogan JJ, Verma NK, Smyth MJ, Rigby RJ and Vinuesa
CG: IL-21 acts directly on B cells to regulate Bcl-6 expression and
germinal center responses. J Exp Med. 207:353–363. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Maehara T, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, Miyake
K, Hayashida JN, Tanaka A, Shinozaki S, Kubo Y and Nakamura S:
Interleukin-21 contributes to germinal centre formation and
immunoglobulin G4 production in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and
sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz's disease. Ann Rheum Dis.
71:2011–2019. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Martinez-Valle F, Fernandez-Codina A,
Pinal-Fernandez I, Orozco-Galvez O and Vilardell-Tarres M:
IgG4-related disease: Evidence from six recent cohorts. Autoimmun
Rev. 16:168–172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yamamoto M, Awakawa T and Takahashi H: Is
rituximab effective for IgG4-related disease in the long term?
Experience of cases treated with rituximab for 4 years. Ann Rheum
Dis. 74:e462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Takano K, Shimizu
Y, Sakurai N, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yajima H, Awakawa T, Himi T and
Nakase H: Efficacy of abatacept for IgG4-related disease over 8
months. Ann Rheum Dis. 75:1576–1578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bai F, Tian H, Niu Z, Liu M, Ren G, Yu Y,
Sun T, Li S and Li D: Chimeric anti-IL-17 full-length monoclonal
antibody is a novel potential candidate for the treatment of
rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Med. 33:711–721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yoshiga Y, Goto D, Segawa S, Ohnishi Y,
Matsumoto I, Ito S, Tsutsumi A, Taniguchi M and Sumida T: Invariant
NKT cells produce IL-17 through IL-23-dependent and -independent
pathways with potential modulation of Th17 response in
collagen-induced arthritis. Int J Mol Med. 22:369–374.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|