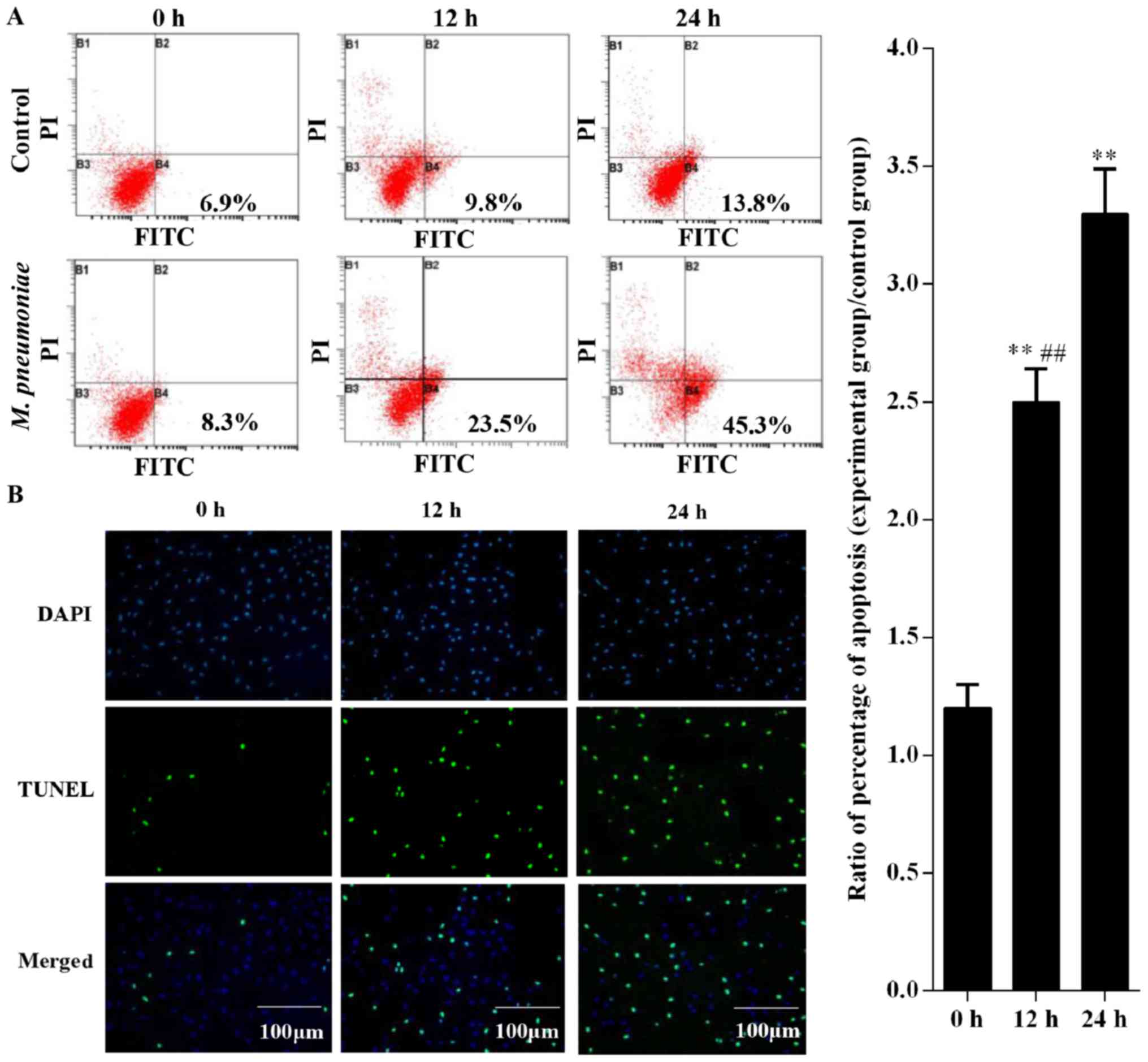
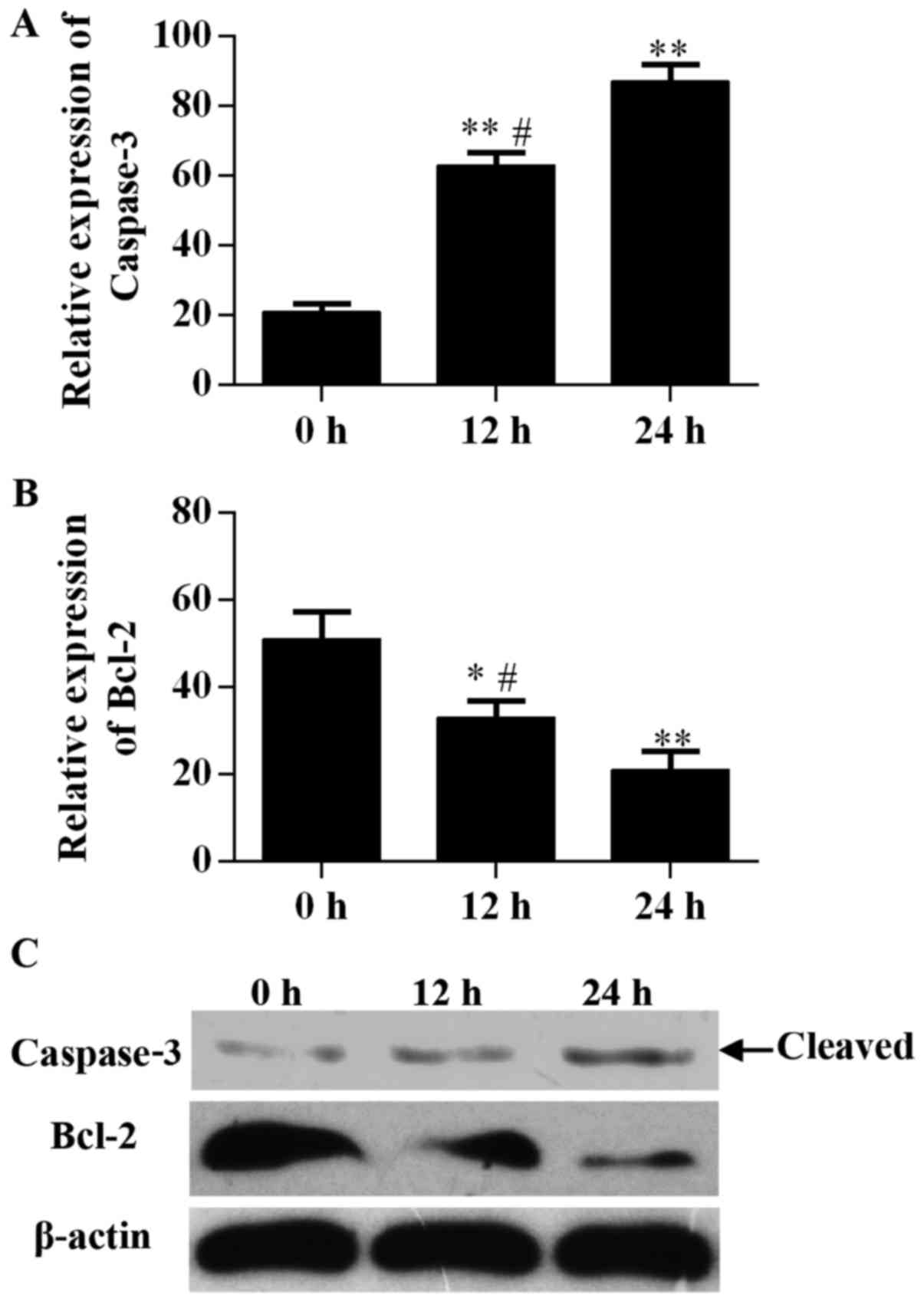
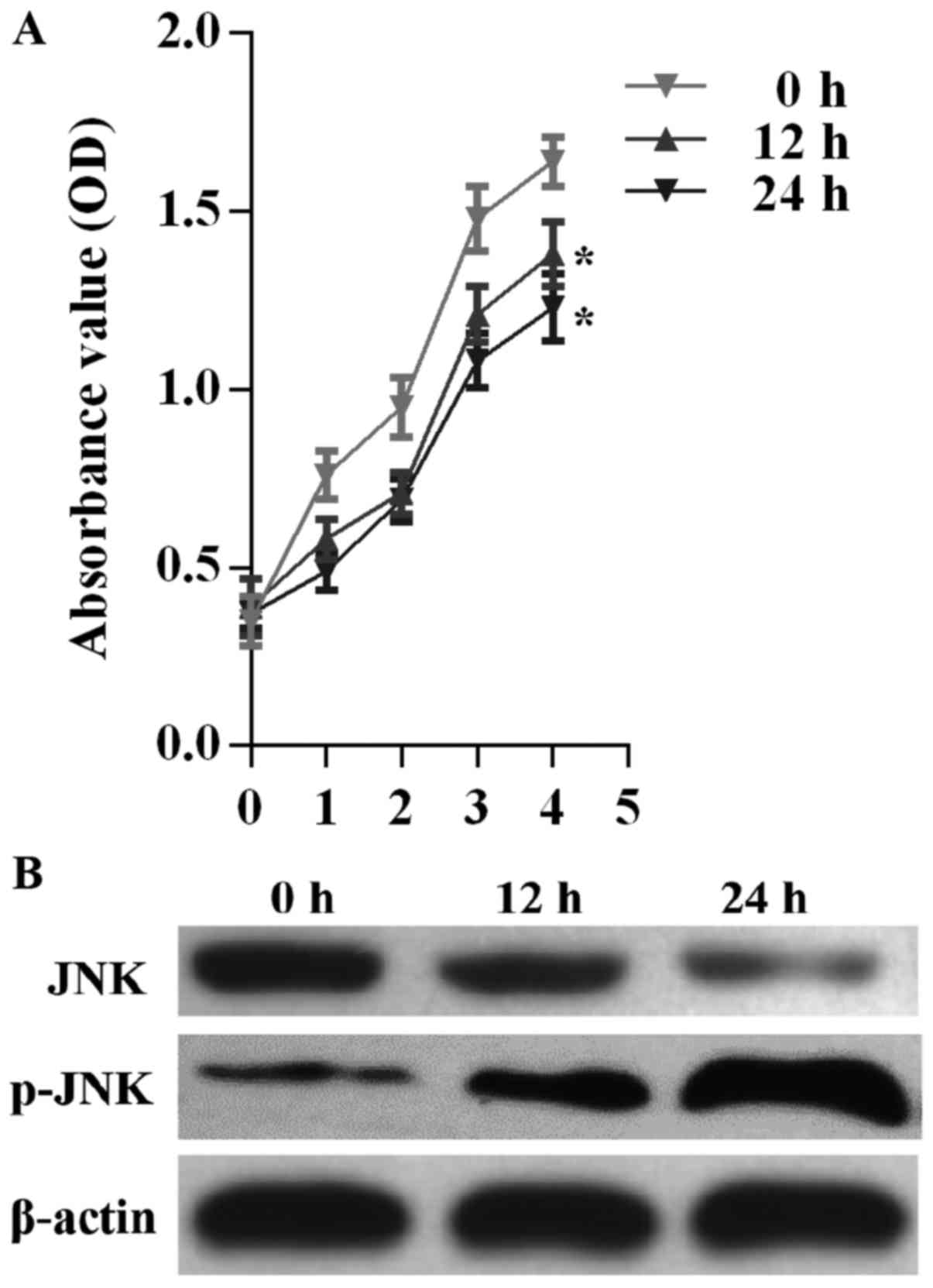
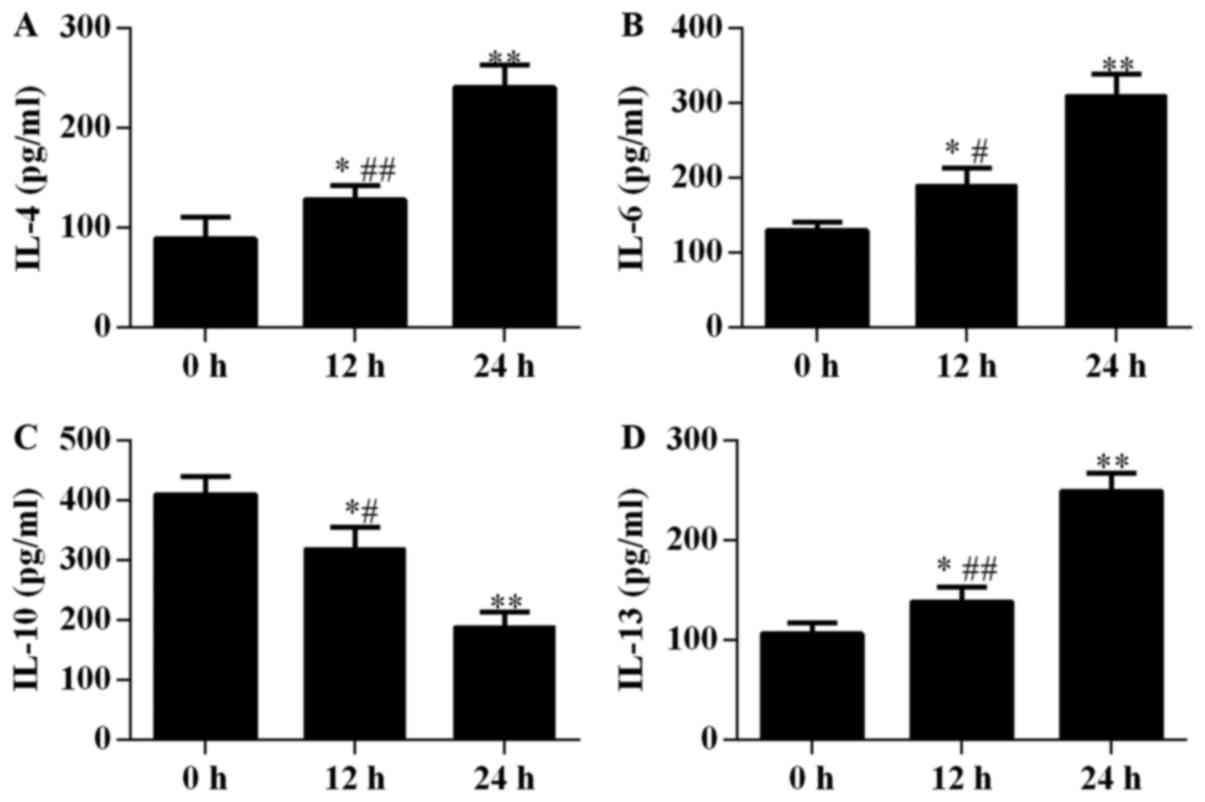
|
1
|
Defilippi A, Silvestri M, Tacchella A,
Giacchino R, Melioli G, Di Marco E, Cirillo C, Di Pietro P and
Rossi GA: Epidemiology and clinical features of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infection in children. Respir Med. 102:1762–1768. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Waites KB and Talkington DF: Mycoplasma
pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev.
17:697–728. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun H, Chen Z, Yan Y, Huang L, Wang M and
Ji W: Epidemiology and clinical profiles of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
infection in hospitalized infants younger than one year. Respir
Med. 109:751–757. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wissel H, Schulz C, Koehne P, Richter E,
Maass M and Rüdiger M: Chlamydophila pneumoniae induces expression
of toll-like receptor 4 and release of TNF-alpha and MIP-2 via an
NF-kappaB pathway in rat type II pneumocytes. Respir Res. 6:512005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sharma AK, Fernandez LG, Awad AS, Kron IL
and Laubach VE: Proinflammatory response of alveolar epithelial
cells is enhanced by alveolar macrophage-produced TNF-alpha during
pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 293:L105–L113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu N, Sun YT, Su XM, He M, Dai B and Kang
J: Melatonin attenuates TGFβ1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in lung alveolar epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep.
14:5567–5572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thakor P, Subramanian RB, Thakkar SS, Ray
A and Thakkar VR: Phytol induces ROS mediated apoptosis by
induction of caspase 9 and 3 through activation of TRAIL FAS and
TNF receptors and inhibits tumor progression factor Glucose 6
phosphate dehydrogenase in lung carcinoma cell line (A549). Biomed
Pharmacother. 92:491–500. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ng PY, Chye SM, Ng ChH, Koh RY, Tiong YL,
Pui LP, Tan YH, Lim CS and Ng KhY: Clinacanthus nutans hexane
extracts induce apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway in
human cancer cell lines. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 18:917–926.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu Y, Zhong Z and Guan Y: The
downregulation of Bcl-xL/Bcl-2-associated death promoter indicates
worse outcomes in patients with small cell lung carcinoma. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13075–13082. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Ha M, Liu J, Li P, Zhang W and
Zhang X: Role of BCL2-associated athanogene in resistance to
platinum-based chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncol
Lett. 11:984–990. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morton HE, Smith PF and Leberman PR:
Investigation of the cultivation of pleuropneumonia-like organisms
from man. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 35:361–369.
1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hao Y, Kuang Z, Jing J, Miao J, Mei LY,
Lee RJ, Kim S, Choe S, Krause DC and Lau GW: Mycoplasma pneumoniae
modulates STAT3-STAT6/EGFR-FOXA2 signaling to induce overexpression
of airway mucins. Infect Immun. 82:5246–5255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Waites KB, Balish MF and Atkinson TP: New
insights into the pathogenesis and detection of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infections. Future Microbiol. 3:635–648. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Li S, Yang D, Wu X and
Chen Z: The clinical characteristics and predictors of refractory
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. PLoS One.
11:e01564652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Atkinson TP, Balish MF and Waites KB:
Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, pathogenesis and laboratory
detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. FEMS Microbiol Rev.
32:956–973. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martin RJ, Kraft M, Chu HW, Berns EA and
Cassell GH: A link between chronic asthma and chronic infection. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 107:595–601. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tamura A, Matsubara K, Tanaka T, Nigami H,
Yura K and Fukaya T: Methylprednisolone pulse therapy for
refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. J Infect.
57:223–228. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fernald GW: Immunologic mechanisms
suggested in the association of M. pneumoniae infection and
extrapulmonary disease: A review. Yale J Biol Med. 56:475–479.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang M, Wang Y, Yan Y, Zhu C, Huang L,
Shao X, Xu J, Zhu H, Sun X, Ji W and Chen Z: Clinical and
laboratory profiles of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
in children. Int J Infect Dis. 29:18–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Naikawadi RP, Disayabutr S, Mallavia B,
Donne ML, Green G, La JL, Rock JR, Looney MR and Wolters PJ:
Telomere dysfunction in alveolar epithelial cells causes lung
remodeling and fibrosis. JCI Insight. 1:e867042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ruenraroengsak P and Tetley TD:
Differential bioreactivity of neutral, cationic and anionic
polystyrene nanoparticles with cells from the human alveolar
compartment: Robust response of alveolar type 1 epithelial cells.
Part Fibre Toxicol. 12:192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang L, Zhao S, Yuan LJ, Wu HM, Jiang H,
Zhao SM, Luo G and Xue XD: Autophagy regulates hyperoxia-induced
intracellular accumulation of surfactant protein C in alveolar type
II cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 408:181–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang C, Dong WB, Zhao S, Li QP, Kang L,
Lei XP, Guo L and Zhai XS: Construction of p66Shc gene interfering
lentivirus vectors and its effects on alveolar epithelial cells
apoptosis induced by hyperoxia. Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:2611–2622.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Larsen BD and Sørensen CS: The
caspase-activated DNase: Apoptosis and beyond. FEBS J.
284:1160–1170. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koff JL, Ramachandiran S and
Bernal-Mizrachi L: A time to kill: Targeting apoptosis in cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:2942–2955. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li M, Li X and Li JC: Possible mechanisms
of trichosanthin-induced apoptosis of tumor cells. Anat Rec
(Hoboken). 293:986–992. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Williams AE, José RJ, Brown JS and
Chambers RC: Enhanced inflammation in aged mice following infection
with Streptococcus pneumoniae is associated with decreased IL-10
and augmented chemokine production. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 308:L539–L549. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu W and Shou C: Mycoplasma hyorhinis and
Mycoplasma fermentans induce cell apoptosis and changes in gene
expression profiles of 32D cells. Biol Res. 44:383–391. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kumari N, Dwarakanath BS, Das A and Bhatt
AN: Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic
resistance. Tumour Biol. 37:11553–11572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lou L, Zhou J, Liu Y, Wei YI, Zhao J, Deng
J, Dong B, Zhu L, Wu A, Yang Y and Chai L: Chlorogenic acid induces
apoptosis to inhibit inflammatory proliferation of IL-6-induced
fibroblast-like synoviocytes through modulating the activation of
JAK/STAT and NF-κB signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med. 11:2054–2060.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|