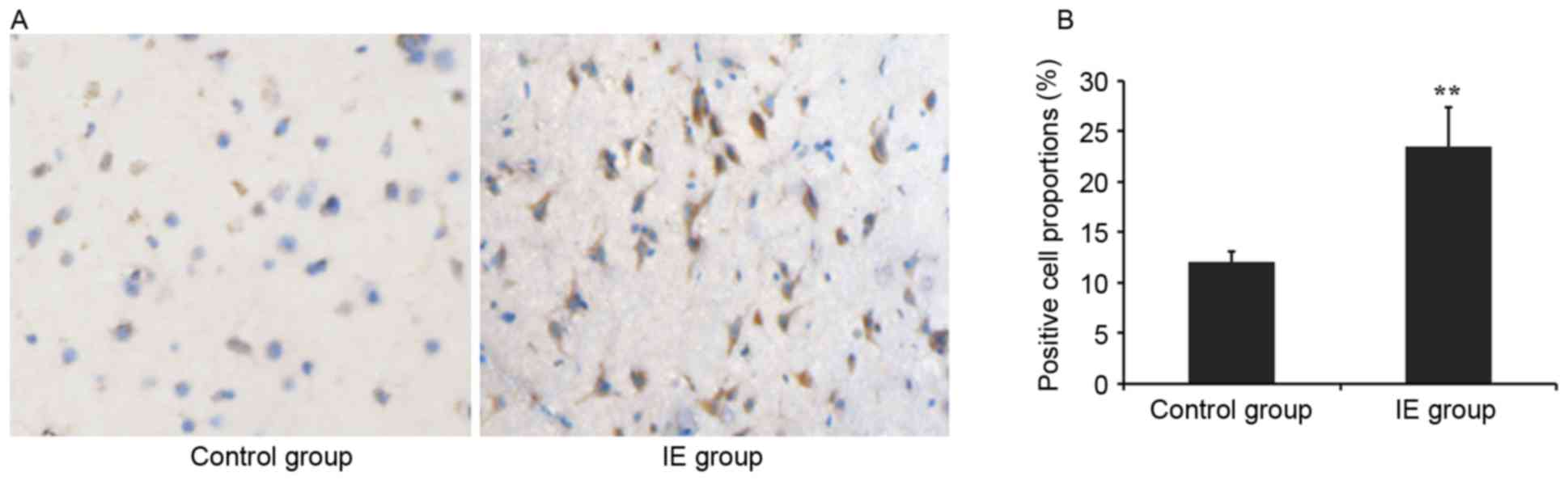
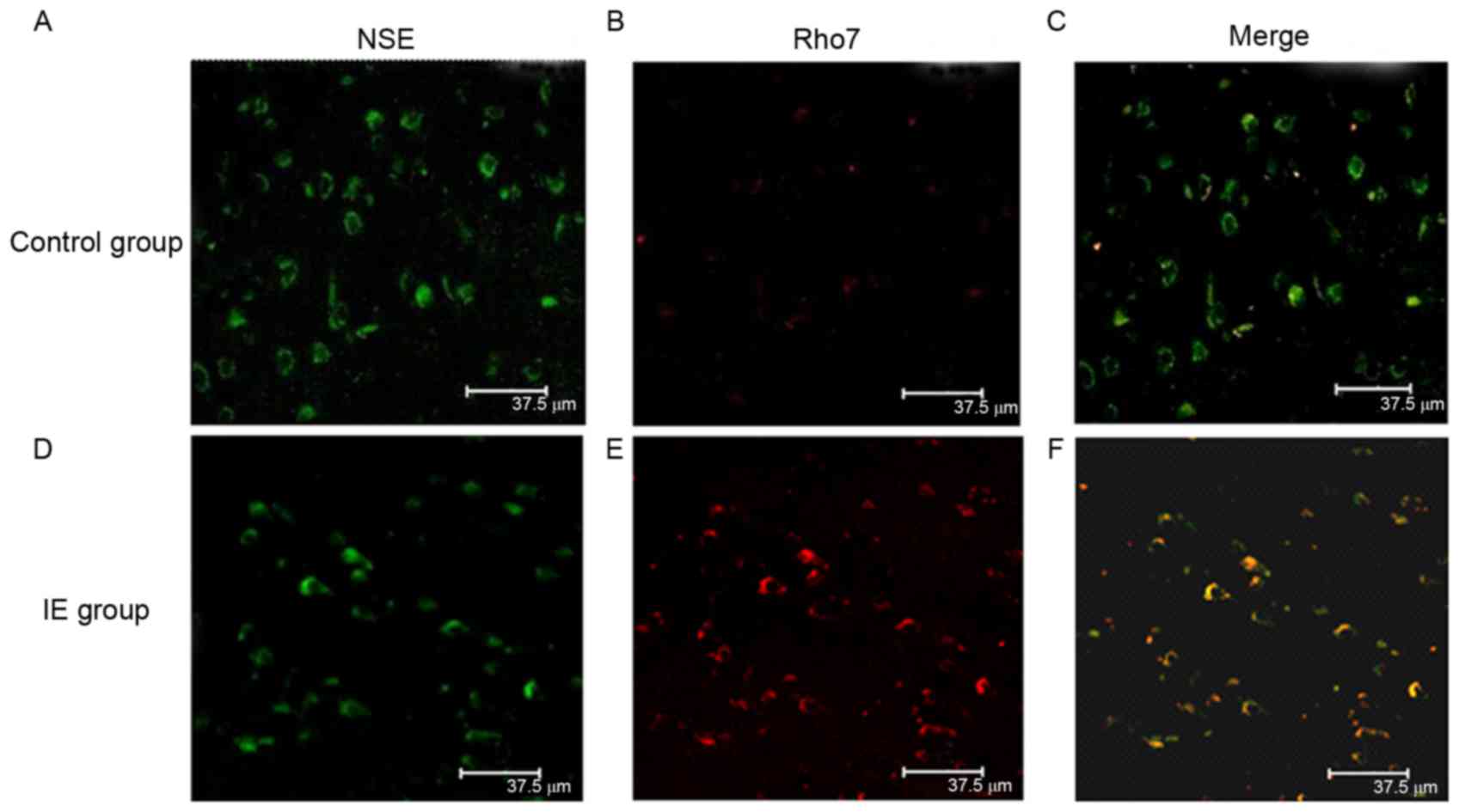
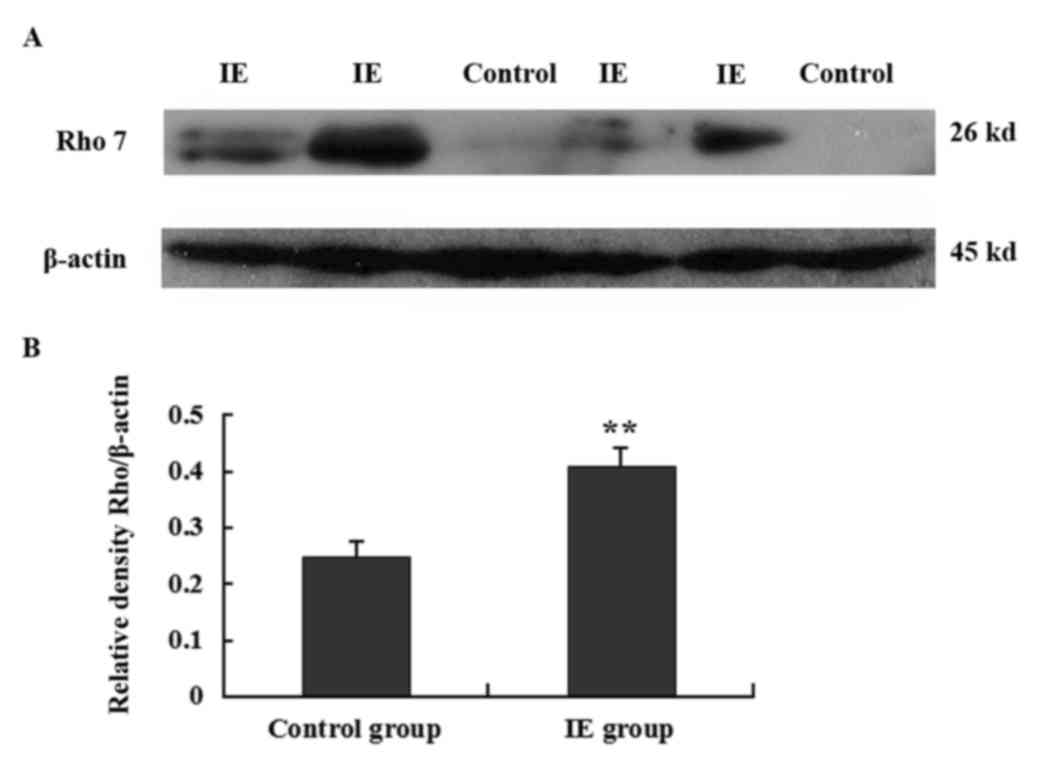
|
1
|
Engel J Jr, McDermott MP, Wiebe S,
Langfitt JT, Stern JM, Dewar S, Sperling MR, Gardiner I, Erba G,
Fried I, et al: Early surgical therapy for drug-resistant temporal
lobe epilepsy: A randomized trial. JAMA. 307:922–930. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Berg AT: Understanding the delay before
epilepsy surgery: Who develops intractable focal epilepsy and when?
CNS Spectr. 9:136–144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Begley CE, Famulari M, Annegers JF,
Lairson DR, Reynolds TF, Coan S, Dubinsky S, Newmark ME, Leibson C,
So EL and Rocca WA: The cost of epilepsy in the United States: An
estimate from population-based clinical and survey data. Epilepsia.
41:342–351. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hao XT, Wong IS and Kwan P: Interrater
reliability of the international consensus definition of
drug-resistant epilepsy: A pilot study. Epilepsy Behav. 22:388–390.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wassenaar M, Leijten FS, Egberts TC, Moons
KG and Uijl SG: Prognostic factors for medically intractable
epilepsy: A systematic review. Epilepsy Res. 106:301–310. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Engel J Jr; International League Against
Epilepsy (ILAE), : A proposed diagnostic scheme for people with
epileptic seizures and with epilepsy: Report of the ILAE task force
on classification and terminology. Epilepsia. 42:796–803. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang G, Zhou R, He X, Shi Z, Huang M, Yu
J and Wang X: Expression levels of microRNA-199 and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in brain tissue of patients with
intractable epilepsy. Int J Neurosci. 126:326–334. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nazıroğlu M and Yürekli VA: Effects of
antiepileptic drugs on antioxidant and oxidant molecular pathways:
Focus on trace elements. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 33:589–599. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chu H, Zhou X, Liu G, Lv M, Wang Y, Liu L,
Li X, Sun P, Zhu Y, Sun C, et al: Network-based detection of
disease modules and potential drug targets in intractable epilepsy.
Journal. 1–140. 2014.
|
|
10
|
Kawauchi T: Regulation of cell adhesion
and migration in cortical neurons: Not only Rho but also Rab family
small GTPases. Neuron. 2:36–40. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Etienne-Manneville S and Hall A: Rho
GTPases in cell biology. Nature. 420:629–635. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moon SY and Zheng Y: Rho GTPase-activating
proteins in cell regulation. Trends Cell Biol. 13:13–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ridley AJ: Rho GTPases and cell migration.
J Cell Sci. 114:2713–2722. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Negishi M and Katoh H: Rho family GTPases
as key regulators for neuronal network formation. J Biochem.
132:157–166. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Decourt B, Bouleau Y, Dulon D and Hafidi
A: Expression analysis of neuroleukin, calmodulin, cortactin, and
Rho7/Rnd2 in the intact and injured mouse brain. Brain Res Dev
Brain Res. 159:36–54. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakamura K, Yamashita Y, Tamamaki N, Katoh
H, Kaneko T and Negishi M: In vivo function of Rnd2 in the
development of neocortical pyramidal neurons. Neurosci Res.
54:149–153. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Heng JI, Nguyen L, Castro DS, Zimmer C,
Wildner H, Armant O, Skowronska-Krawczyk D, Bedogni F, Matter JM,
Hevner R and Guillemot F: Neurogenin 2 controls cortical neuron
migration through regulation of Rnd2. Nature. 455:114–118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
World Medical Association, . World Medical
Association Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. Bull World Health Organ.
79:373–374. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dreifuss FE, Bancand J, Henriksen O,
Rubio-Donnadieu F, Seino M and Penry JK: Commission on
classification and terminology of the international league against
epilepsy, proposal for revised clinical and electroencephalographic
classification of epileptic seizures. Epilepsia. 1–501.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fang M, Liu GW, Pan YM, Shen L, Li CS, Xi
ZQ, Xiao F, Wang L, Chen D and Wang XF: Abnormal expression and
spatiotemporal change of Slit2 in neurons and astrocytes in
temporal lobe epileptic foci: A study of epileptic patients and
experimental animals. Brain Res. 1324:14–23. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kimiskidis VK, Triantafyllou NI, Kararizou
E, Gatzonis SS, Fountoulakis KN, Siatouni A, Loucaidis P,
Pseftogianni D, Vlaikidis N and Kaprinis GS: Depression and anxiety
in epilepsy: The association with demographic and seizure-related
variables. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 6:282007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanner AM, Soto A and Gross-Kanner H:
Prevalence and clinical characteristics of postictal psychiatric
symptoms in partial epilepsy. Neurology. 62:708–713. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boylan LS, Flint LA, Labovitz DL, Jackson
SC, Starner K and Devinsky O: Depression but not seizure frequency
predicts quality of life in treatment-resistant epilepsy.
Neurology. 62:258–261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Govek EE, Hatten ME and Van Aelst L: The
role of Rho GTPase proteins in CNS neuronal migration. Dev
Neurobiol. 71:528–553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McLoughlin HS, Fineberg SK, Ghosh LL,
Tecedor L and Davidson BL: Dicer is required for proliferation,
viability, migration and differentiation in corticoneurogenesis.
Neuroscience. 223:285–295. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fujita H, Katoh H, Ishikawa Y, Mori K and
Negishi M: Rapostlin is a novel effector of Rnd2 GTPase inducing
neurite branching. J Biol Chem. 277:45428–45434. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kakimoto T, Katoh H and Negishi M:
Identification of splicing variants of Rapostlin, a novel RND2
effector that interacts with neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
protein and induces neurite branching. J Biol Chem.
279:14104–14110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsuchiya D, Kitamura Y, Takata K, Sugisaki
T, Taniguchi T, Uemura K, Miki H, Takenawa T and Shimohama S:
Developmental expression of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein
(N-WASP) and WASP family verprolin-homologous protein
(WAVE)-related proteins in postnatal rat cerebral cortex and
hippocampus. Neurosci Res. 56:459–469. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li J and Anton E: Rnding up RhoA activity
to link neurogenesis with steps in neuronal migration. Dev Cell.
20:409–410. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Marin O and Rubenstein JL: Cell migration
in the forebrain. Annu Rev Neurosci. 26:441–483. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ayala R, Shu T and Tsai LH: Trekking
across the brain: The journey of neuronal migration. Cell.
128:29–43. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guerrini R and Parrini E: Neuronal
migration disorders. Neurobiol Dis. 38:154–166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chai X, Münzner G, Zhao S, Tinnes S,
Kowalski J, Häussler U, Young C, Haas CA and Frotscher M:
Epilepsy-induced motility of differentiated neurons. Cerebral
Cortex. 24:2130–2140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang DD, Blümcke I, Coras R, Zhou WJ, Lu
DH, Gui QP, Hu JX, Zuo HC, Chen SY and Piao YS: Sturge-weber
syndrome is associated with cortical dysplasia ILAE Type IIIc and
excessive hypertrophic pyramidal neurons in brain resections for
intractable epilepsy. Brain Pathol. 25:248–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roper SN, Gilmore RL and Houser CR:
Experimentally induced disorders of neuronal migration produce an
increased propensity for electrographic seizures in rats. Epilepsy
Res. 21:205–219. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tang J, Ip JP, Ye T, Ng YP, Yung WH, Wu Z,
Fang W, Fu AK and Ip NY: Cdk5-dependent Mst3 phosphorylation and
activity regulate neuronal migration through RhoA inhibition. J
Neurosci. 34:7425–7436. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pacary E, Heng J, Azzarelli R, Riou P,
Castro D, Lebel-Potter M, Parras C, Bell DM, Ridley AJ, Parsons M
and Guillemot F: Proneural transcription factors regulate different
steps of cortical neuron migration through Rnd-mediated inhibition
of RhoA signaling. Neuron. 69:1069–1084. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wimmer VC, Reid CA, So EY, Berkovic SF and
Petrou S: Axon initial segment dysfunction in epilepsy. J Physiol.
588:1829–1840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoshimura T and Rasband MN: Axon initial
segments: Diverse and dynamic neuronal compartments. Curr Opin
Neurobiol. 27:96–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kuba H, Oichi Y and Ohmori H: Presynaptic
activity regulates Na(+) channel distribution at the axon initial
segment. Nature. 465:1075–1078. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Katoh H, Harada A, Mori K and Negishi M:
Socius is a novel Rnd GTPase-interacting protein involved in
disassembly of actin stress fibers. Mol Cell Biol. 22:2952–2964.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wennerberg K, Forget MA, Ellerbroek SM,
Arthur WT, Burridge K, Settleman J, Der CJ and Hansen SH: Rnd
proteins function as RhoA antagonists by activating p190 RhoGAP.
Current Biol. 13:1106–1115. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Goh LL and Manser E: The GTPase-deficient
Rnd proteins are stabilized by their effectors. J Biol Chem.
287:31311–31320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wakita Y, Kakimoto T, Katoh H and Negishi
M: The F-BAR protein Rapostlin regulates dendritic spine formation
in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem. 286:32672–32683. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tanaka H, Katoh H and Negishi M: Pragmin,
a novel effector of Rnd2 GTPase, stimulates RhoA activity. J Biol
Chem. 281:10355–10364. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vaessen MJ, Braakman HM, Heerink JS,
Jansen JF, Debeij-van Hall MH, Hofman PA, Aldenkamp AP and Backes
WH: Abnormal modular organization of functional networks in
cognitively impaired children with frontal lobe epilepsy. Cerebral
Cortex. 23:1997–2006. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guasch RM, Blanco AM, Pérez-Aragó A,
Miñambres R, Talens-Visconti R, Peris B and Guerri C: RhoE
participates in the stimulation of the inflammatory response
induced by ethanol in astrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 313:3779–3788.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Höltje M, Hoffmann A, Hofmann F, Mucke C,
Grosse G, Van Rooijen N, Kettenmann H, Just I and Ahnert-Hilger G:
Role of Rho GTPase in astrocyte morphology and migratory response
during in vitro wound healing. J Neurochem. 95:1237–1248. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|