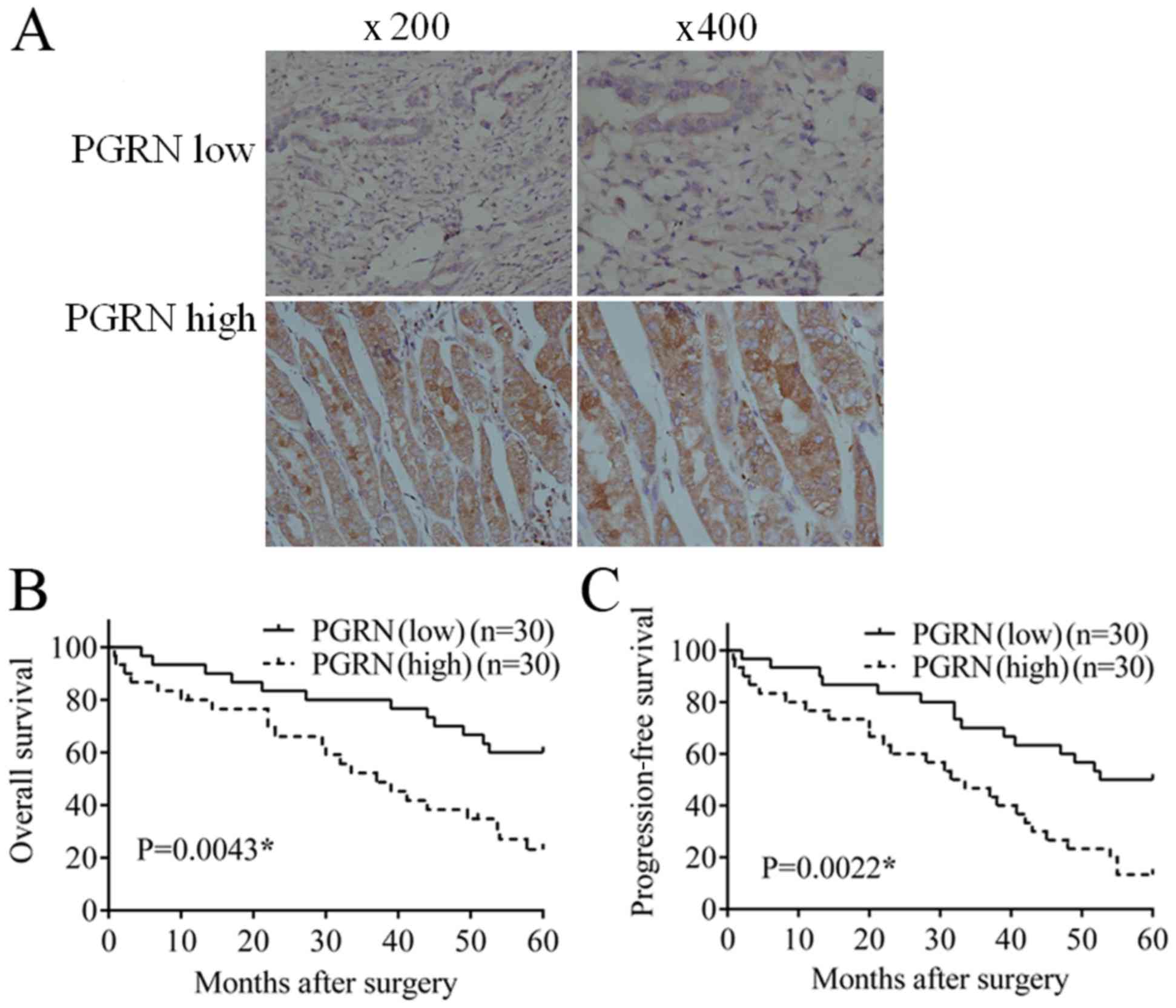
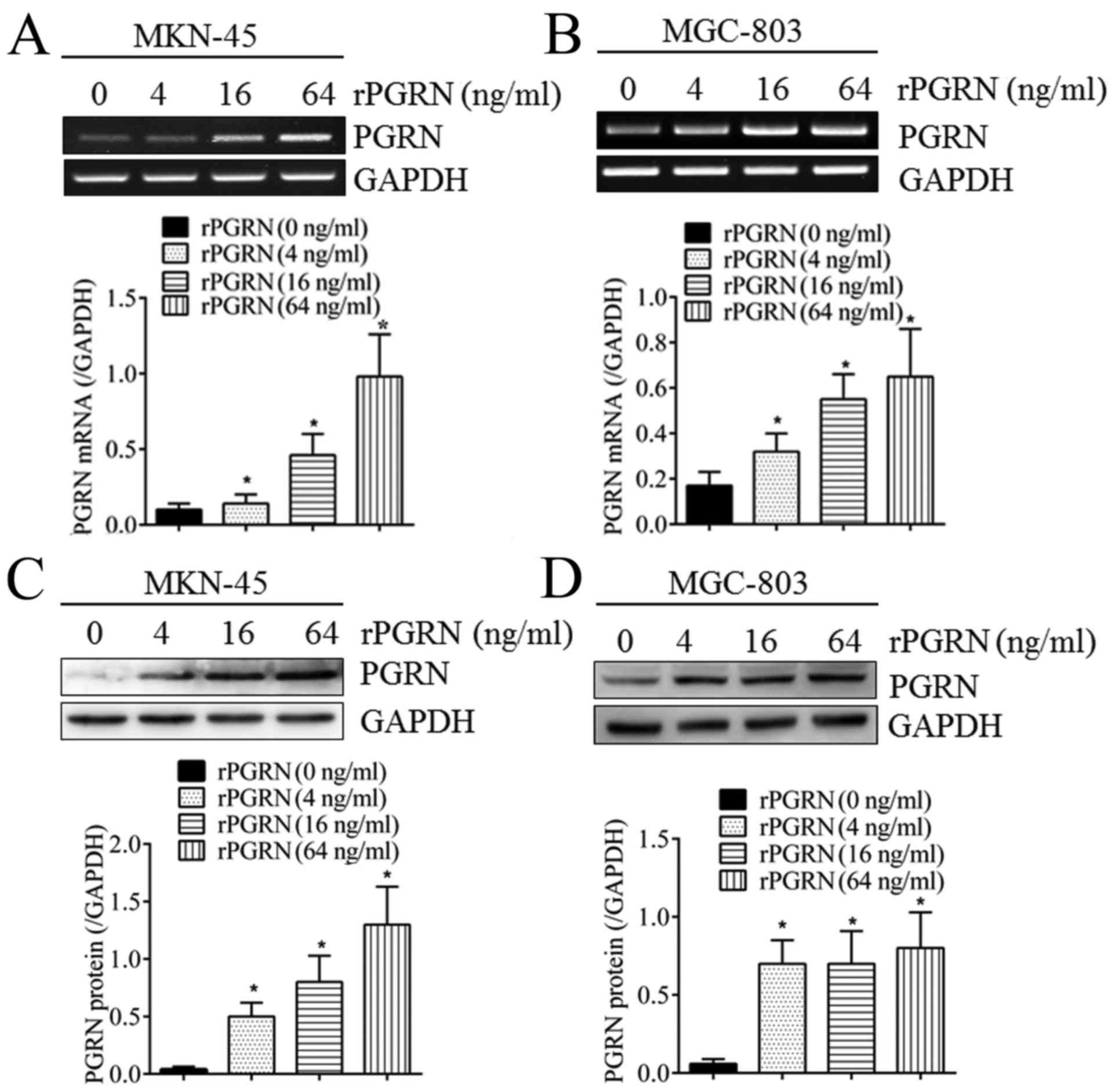
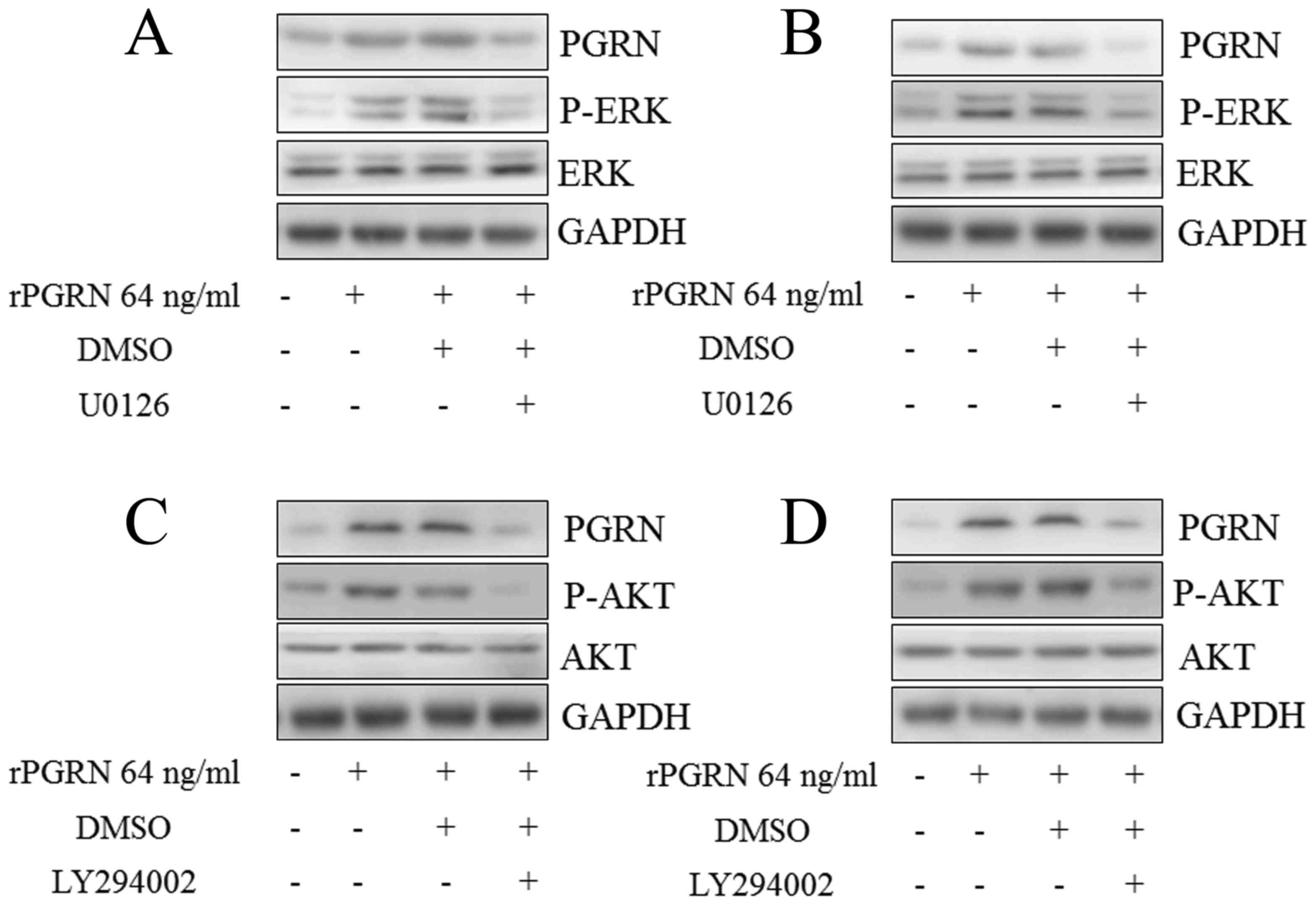
|
1
|
Vohlonen I, Pukkala E, Malila N, Härkönen
M, Hakama M, Koistinen V and Sipponen P: Risk of gastric cancer in
Helicobacter pylori infection in a 15-year follow-up. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 51:1159–1164. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hafez NH and Tahoun NS: Expression of
cyclooxygenase 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric
carcinoma: Relationship with clinicopathological parameters. J
Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 28:149–156. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li P, Sun D, Li X, He Y, Li W, Zhao J,
Wang Y, Wang H and Xin Y: Elevated expression of Nodal and YAP1 is
associated with poor prognosis of gastric adenocarcinoma. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 142:1765–1773. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoshino S, Nishikawa K, Morita S,
Takahashi T, Sakata K, Nagao J, Nemoto H, Murakami N, Matsuda T,
Hasegawa H, et al: Randomised phase III study of S-1 alone versus
S-1 plus lentinan for unresectable or recurrent gastric cancer
(JFMC36-0701). Eur J Cancer. 65:164–171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suzuki M and Nishiahara M: Granulin
precursor gene: A sex steroid-inducible gene involved in sexual
differentiation of the rat brain. Mol Genet Metab. 75:31–37. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu J, Nathan C, Jin W, Sim D, Ashcroft
GS, Wahl SM, Lacomis L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Wright CD
and Ding A: Conversion of proepithelin to epithelins: Roles of SLPI
and elastase in host defense and wound repair. Cell. 111:867–878.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang W, Lu Y, Tian QY, Zhang Y, Guo FJ,
Liu GY, Syed NM, Lai Y, Lin EA, Kong L, et al: The growth factor
progranulin binds to TNF receptors and is therapeutic against
inflammatory arthritis in mice. Science. 332:478–484. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
De Muynck L and Van Damme P: Cellular
effects of progranulin in health and disease. J Mol Neurosci.
45:549–560. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu CJ and Bosch X: Progranulin: A growth
factor, a novel TNFR ligand and a drug target. Pharmacol Ther.
133:124–132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Swamydas M, Nguyen D, Allen LD, Eddy J and
Dréau D: Progranulin stimulated by LPA promotes the migration of
aggressive breast cancer cells. Cell Commun Adhes. 18:119–130.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abrhale T, Brodie A, Sabnis G, Macedo L,
Tian C, Yue B and Serrero G: GP88 (PC-Cell derived growth factor,
progranulin) stimulates proliferation and confers letrozole
resistance to aromatase overexpressing breast cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 11:2312011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Diaz-Cueto L, Arechavaleta-Velasco F,
Diaz-Arizaga A, Dominguez-Lopez P and Robles-Flores M: PKC
signaling is involved in the regulation of progranulin
(acrogranin/PC-cell-derived growth factor/granulin-epithelin
precursor) protein expression in human ovarian cancer cell lines.
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 22:945–950. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carlson AM, Maurer MJ, Goergen KM, Kalli
KR, Erskine CL, Behrens MD, Knutson KL and Block MS: Utility of
progranulin and serum leukocyte protease inhibitor as diagnostic
and prognostic biomarkers in ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 22:1730–1735. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cheung PF, Cheng CK, Wong NC, Ho JC, Yip
CW, Lui VC, Cheung AN, Fan ST and Cheung ST: Granulin-epithelin
precursor is an oncofetal protein defining hepatic cancer stem
cells. PLoS One. 6:e282462011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao J, Liu D, Li J, Song Q and Wang Q:
Effect of STK17A on the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to
paclitaxel and carboplatin. Oncol Lett. 12:1107–1112.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu Y, Xiao H, Shi T, Oppenheim JJ and Chen
X: Progranulin promotes tumour necrosis factor-induced
proliferation of suppressive mouse CD4+
Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Immunology. 142:193–201.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Edelman MJ, Feliciano J, Yue B, Bejarano
P, Ioffe O, Reisman D, Hawkins D, Gai Q, Hicks D and Serrero G:
GP88 (progranulin): A novel tissue and circulating biomarker for
non-small cell lung carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 45:1893–1899. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dong T, Yang D, Li R, Zhang L, Zhao H,
Shen Y, Zhang X, Kong B and Wang L: PGRN promotes migration and
invasion of epithelial ovarian cancer cells through an epithelial
mesenchymal transition program and the activation of cancer
associated fibroblasts. Exp Mol Pathol. 100:17–25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang H, Sun Y, Liu S, Yu H, Li W, Zeng J,
Chen C and Jia J: Upregulation of progranulin by helicobacter
pylori in human gastric epithelial cells via p38MAPK and MEK1/2
signaling pathway: Role in epithelial cell proliferation and
migration. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 63:82–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu F, Zhang W, Yang F, Feng T, Zhou M, Yu
Y, Yu X, Zhao W, Yi F, Tang W and Lu Y: Interleukin-6-stimulated
progranulin expression contributes to the malignancy of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating mTOR signaling. Sci
Rep. 6:212602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang D, Wang LL, Dong TT, Shen YH, Guo XS,
Liu CY, Liu J, Zhang P, Li J and Sun YP: Progranulin promotes
colorectal cancer proliferation and angiogenesis through TNFR2/Akt
and ERK signaling pathways. Am J Cancer Res. 5:3085–3097.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tkaczuk KR, Yue B, Zhan M, Tait N,
Yarlagadda L, Dai H and Serrero G: Increased circulating level of
the survival factor GP88 (progranulin) in the serum of breast
cancer patients when compared to healthy subjects. Breast Cancer
(Auckl). 5:155–162. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He Z, Ismail A, Kriazhev L, Sadvakassova G
and Bateman A: Progranulin (PC-cell-derived growth
factor/acrogranin) regulates invasion and cell survival. Cancer
Res. 62:5590–5596. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kamrava M, Simpkins F, Alejandro E,
Michener C, Meltzer E and Kohn EC: Lysophosphatidic acid and
endothelin-induced proliferation of ovarian cancer cell lines is
mitigated by neutralization of granulin-epithelin precursor (GEP),
a prosurvival factor for ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 24:7084–7093.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ong CH and Bateman A: Progranulin
(granulin-epithelin precursor, PC-cell derived growth factor,
acrogranin) in proliferation and tumorigenesis. Histol Histopathol.
18:1275–1288. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|