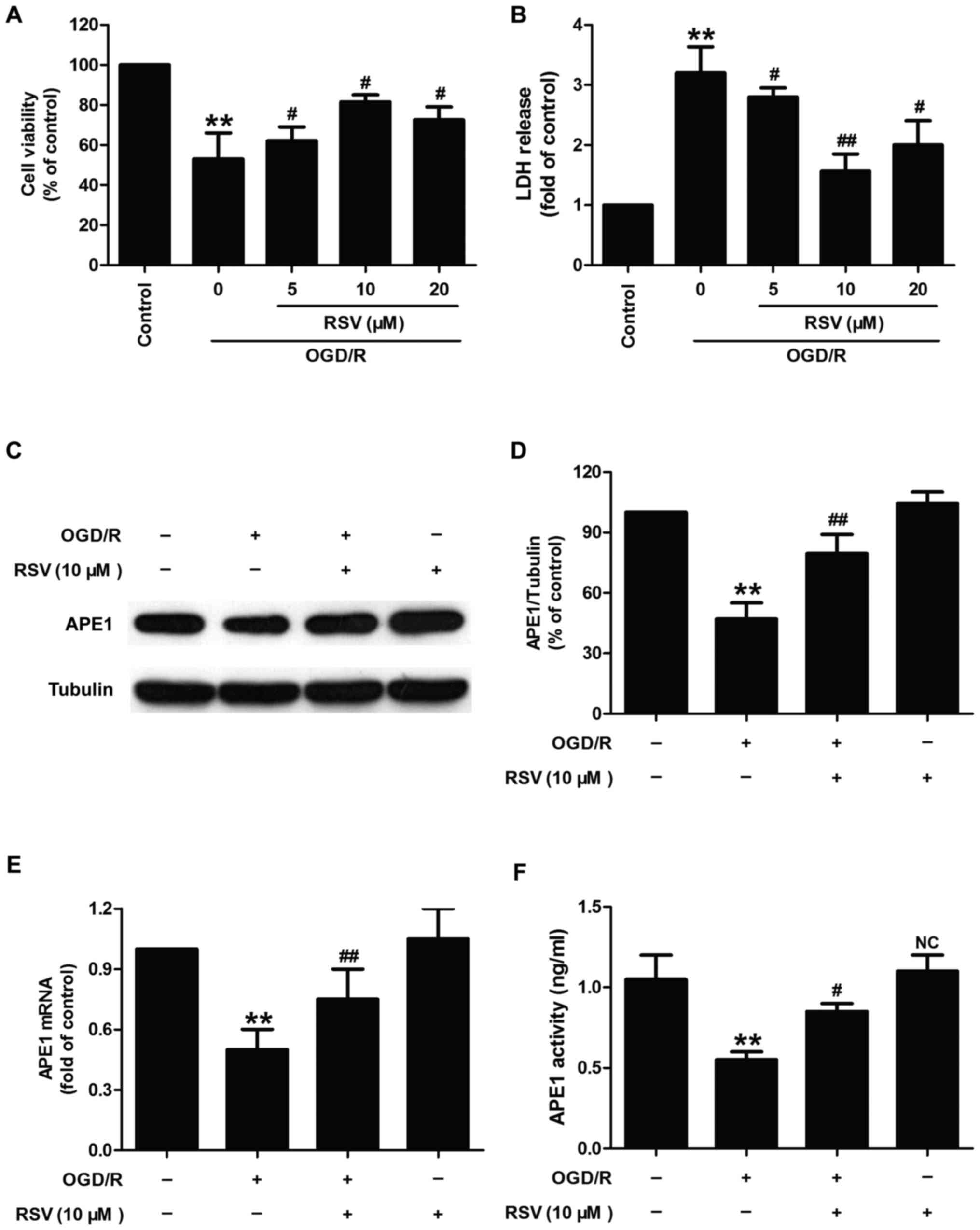
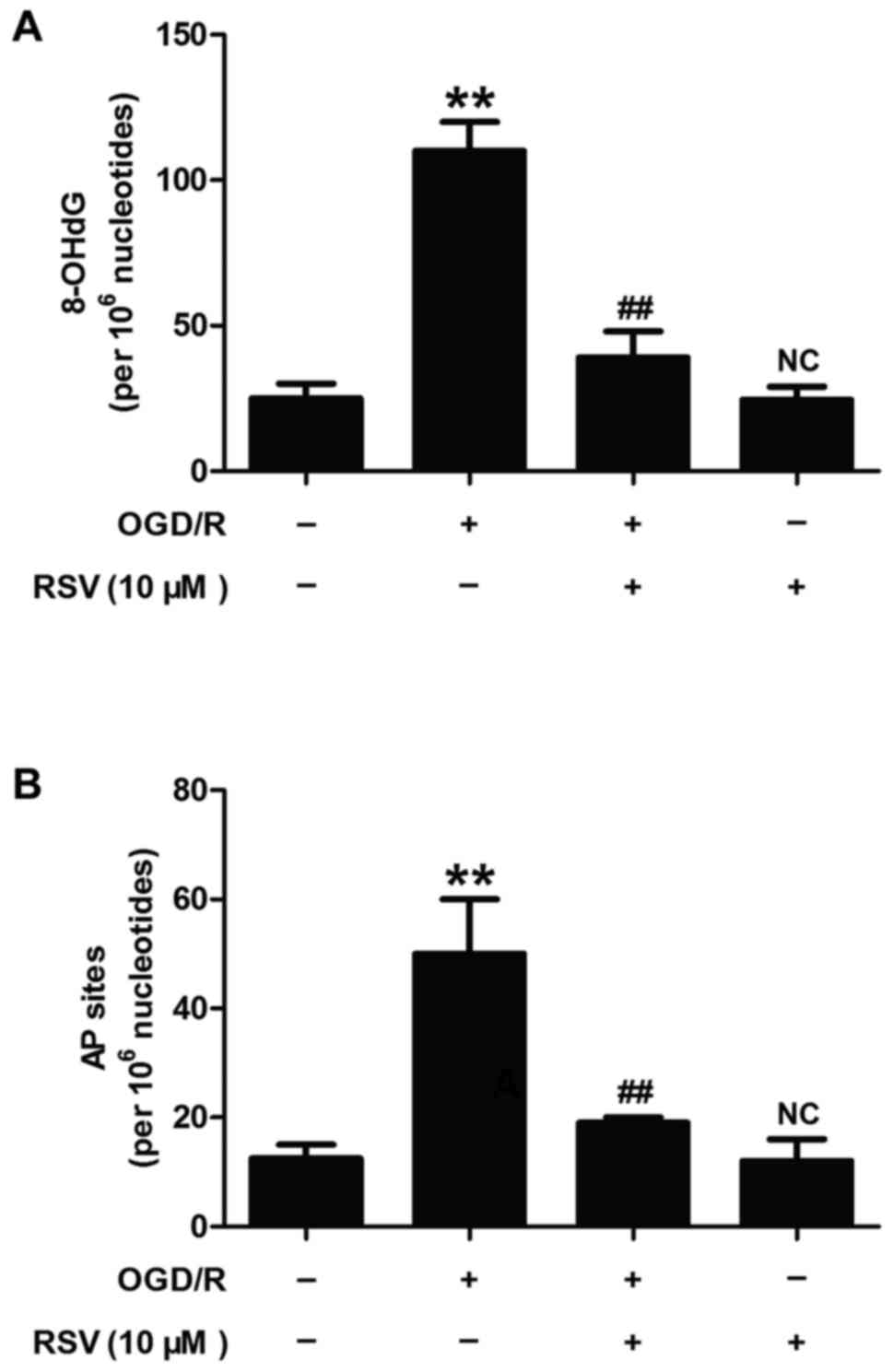
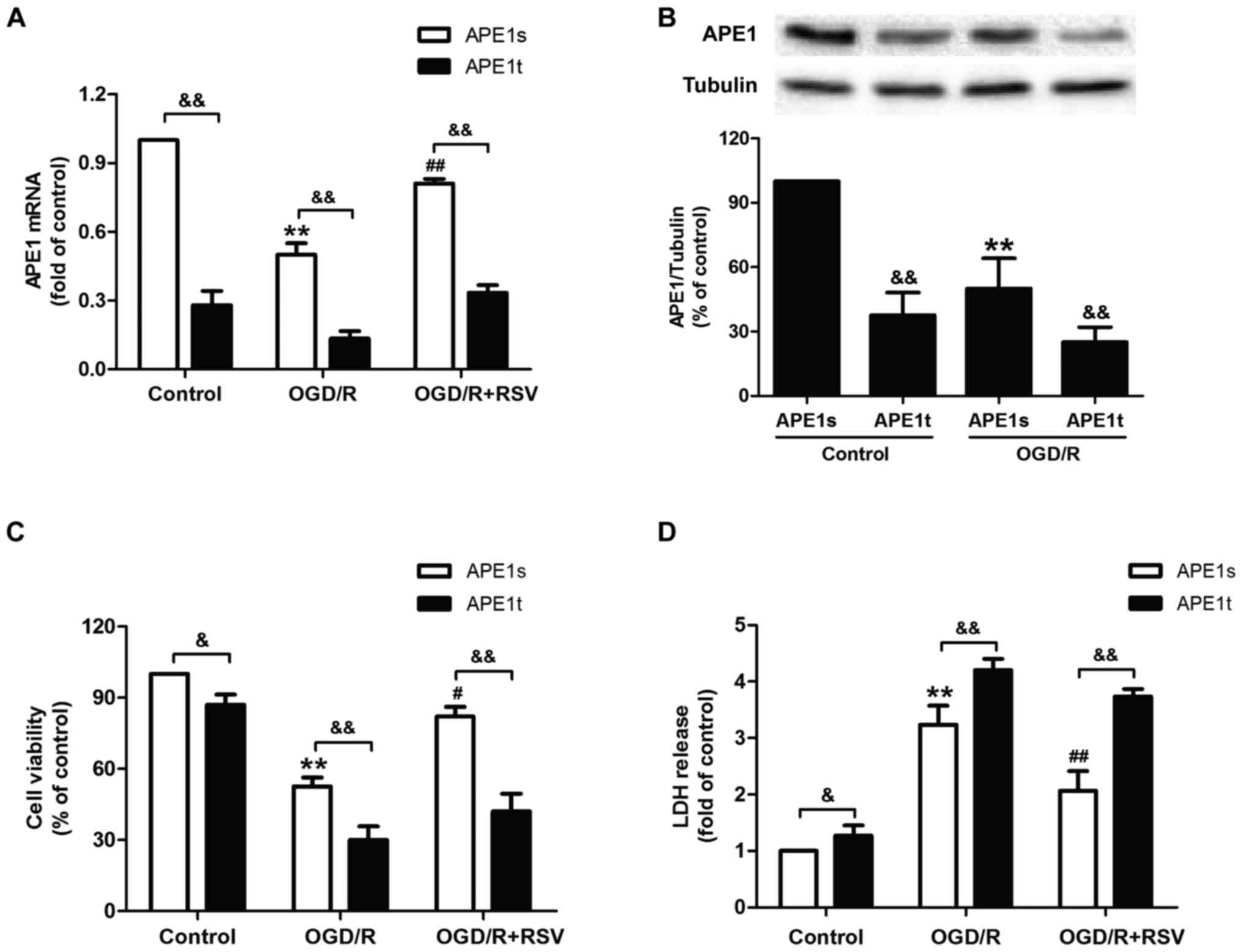
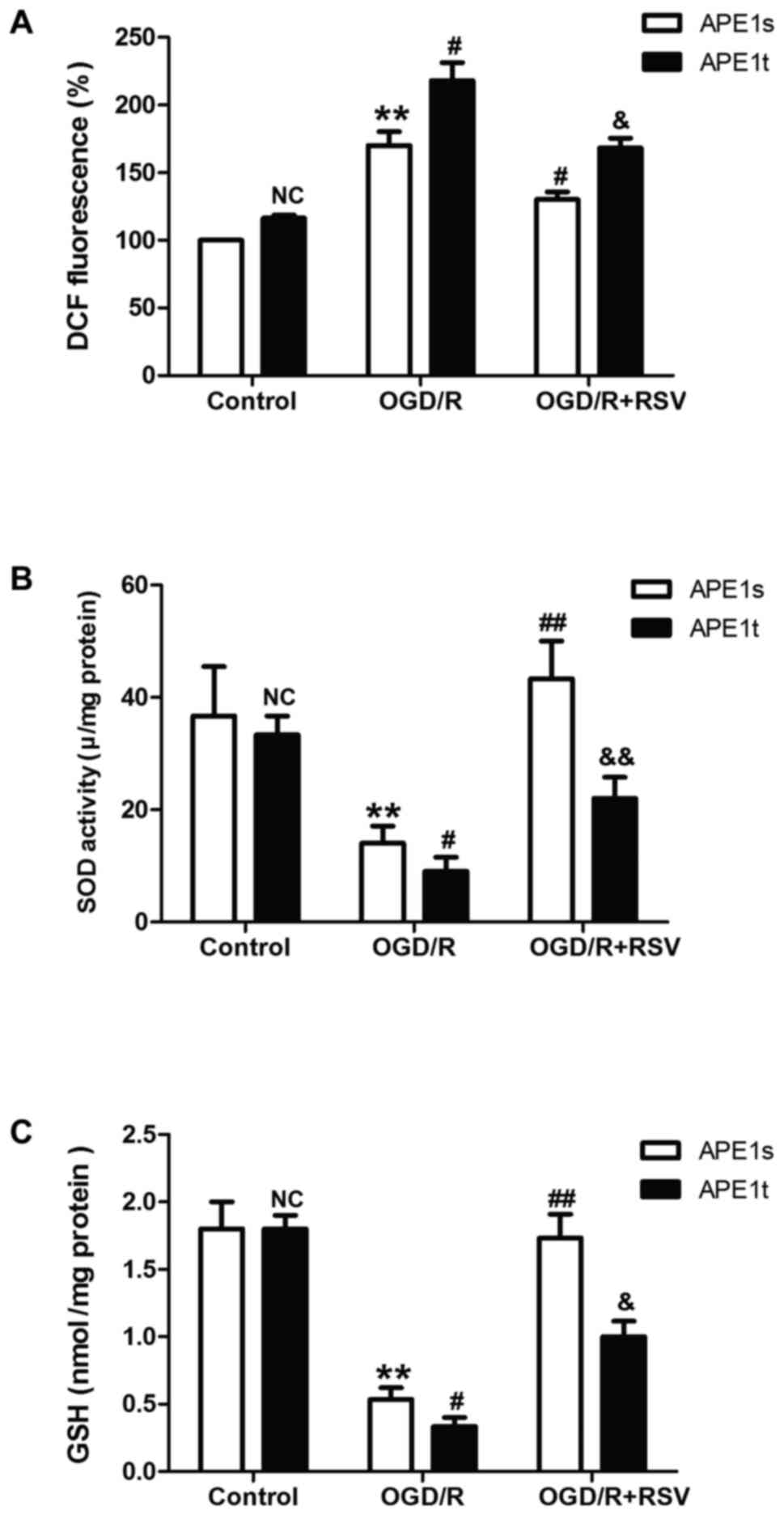
|
1
|
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Adams RJ,
Berry JD, Brown TM, Carnethon MR, Dai S, de Simone G, Ford ES, et
al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2011 update: A report from
the American Heart Association. Circulation. 123:e18–e209. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blakeley JO and Llinas RH: Thrombolytic
therapy for acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. 261:55–62. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li P, Hu X, Gan Y, Gao Y, Liang W and Chen
J: Mechanistic insight into DNA damage and repair in ischemic
stroke: Exploiting the base excision repair pathway as a model of
neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal. 14:1905–1918. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen J, Jin K, Chen M, Pei W, Kawaguchi K,
Greenberg DA and Simon RP: Early detection of DNA strand breaks in
the brain after transient focal ischemia: Implications for the role
of DNA damage in apoptosis and neuronal cell death. J Neurochem.
69:232–245. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen H, Yoshioka H, Kim GS, Jung JE, Okami
N, Sakata H, Maier CM, Narasimhan P, Goeders CE and Chan PH:
Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: Mechanisms of cell death
and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 14:1505–1517. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lan J, Li W, Zhang F, Sun FY, Nagayama T,
O'Horo C and Chen J: Inducible repair of oxidative DNA lesions in
the rat brain after transient focal ischemia and reperfusion. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 23:1324–1339. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dyrkheeva NS, Lebedeva NA and Lavrik OI:
AP Endonuclease 1 as a key enzyme in repair of
apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Biochemistry (Mosc). 81:951–967. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Laev SS, Salakhutdinov NF and Lavrik OI:
Inhibitors of nuclease and redox activity of apurinic/apyrimidinic
endonuclease 1/redox effector factor 1 (APE1/Ref-1). Bioorg Med
Chem. 25:2531–2544. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu PK: DNA damage and repair in the brain
after cerebral ischemia. Curr Top Med Chem. 1:483–495. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vasko MR, Guo C and Kelley MR: The
multifunctional DNA repair/redox enzyme Ape1/Ref-1 promotes
survival of neurons after oxidative stress. DNA Repair (Amst).
4:367–379. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ludwig DL, MacInnes MA, Takiguchi Y,
Purtymun PE, Henrie M, Flannery M, Meneses J, Pedersen RA and Chen
DJ: A murine AP-endonuclease gene-targeted deficiency with
post-implantation embryonic progression and ionizing radiation
sensitivity. Mutat Res. 409:17–29. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Singh S and Englander EW: Nuclear
depletion of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (Ape1/Ref-1) is
an indicator of energy disruption in neurons. Free Radic Biol Med.
53:1782–1790. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stetler RA, Gao Y, Zukin RS, Vosler PS,
Zhang L, Zhang F, Cao G, Bennett MV and Chen J:
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease APE1 is required for
PACAP-induced neuroprotection against global cerebral ischemia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp. 3204–3209. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nakata R, Takahashi S and Inoue H: Recent
advances in the study on resveratrol. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:273–279.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yin K, Zhao L, Feng D, Ma W, Liu Y, Wang
Y, Liang J, Yang F, Bi C, Chen H, et al: Resveratrol attenuated low
ambient temperature-induced myocardial hypertrophy via inhibiting
cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:2451–2462. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nie P, Hu W, Zhang T, Yang Y, Hou B and
Zou Z: Synergistic induction of erlotinib-mediated apoptosis by
resveratrol in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells by
down-regulating survivin and up-regulating PUMA. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 35:2255–2271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mokni M, Elkahoui S, Limam F, Amri M and
Aouani E: Effect of resveratrol on antioxidant enzyme activities in
the brain of healthy rat. Neurochem Res. 32:981–987. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hung LM, Su MJ and Chen JK: Resveratrol
protects myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through both
No-dependent and NO-independent mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med.
36:774–781. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eybl V, Kotyzova D, Cerná P and Koutensky
J: Effect of melatonin, curcumin, quercetin, and resveratrol on
acute ferric nitrilotriacetate (Fe-NTA)-induced renal oxidative
damage in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 27:347–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pan S, Li S, Hu Y, Zhang H, Liu Y, Jiang
H, Fang M, Li Z, Xu K, Zhang H, et al: Resveratrol post-treatment
protects against neonatal brain injury after hypoxia-ischemia.
Oncotarget. 7:79247–79261. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Abdel-Aleem GA, Khaleel EF, Mostafa DG and
Elberier LK: Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol against brain
ischemia reperfusion injury in rats entails reduction of DJ-1
protein expression and activation of PI3K/Akt/GSK3b survival
pathway. Arch Physiol Biochem. 122:200–213. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Feng Y, Cui Y, Gao JL, Li MH, Li R, Jiang
XH, Tian YX, Wang KJ, Cui CM and Cui JZ: Resveratrol attenuates
neuronal autophagy and inflammatory injury by inhibiting the
TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in experimental traumatic brain
injury. Int J Mol Med. 37:921–930. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hua C, Ju WN, Jin H, Sun X and Zhao G:
Molecular chaperones and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neural
Regen Res. 12:153–160. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu Q, Chen W, Sinha B, Tu Y, Manning S,
Thomas N, Zhou S, Jiang H, Ma H, Kroessler DA, et al:
Neuroprotective agents for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.
Drug Discov Today. 20:1372–1381. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Silveira RC and Procianoy RS: Hypothermia
therapy for newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J
Pediatr (Rio J). 91(6 Suppl 1): S78–S83. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stetler RA, Gao Y, Leak RK, Weng Z, Shi Y,
Zhang L, Pu H, Zhang F, Hu X, Hassan S, et al: APE1/Ref-1
facilitates recovery of gray and white matter and neurological
function after mild stroke injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:pp.
E3558–E3567. 2016; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leak RK, Li P, Zhang F, Sulaiman HH, Weng
Z, Wang G, Stetler RA, Shi Y, Cao G, Gao Y and Chen J:
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 upregulation reduces oxidative
DNA damage and protects hippocampal neurons from ischemic injury.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:135–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lopez MS, Dempsey RJ and Vemuganti R:
Resveratrol neuroprotection in stroke and traumatic CNS injury.
Neurochem Int. 89:75–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kizmazoglu C, Aydin HE, Sevin IE, Kalemci
O, Yüceer N and Atasoy MA: Neuroprotective Effect of Resveratrol on
Acute Brain Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Measuring Annexin V,
p53, Bcl-2 Levels in Rats. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 58:508–512.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang R, Liu YY, Liu XY, Jia SW, Zhao J,
Cui D and Wang L: Resveratrol protects neurons and the myocardium
by reducing oxidative stress and ameliorating mitochondria damage
in a cerebral ischemia rat model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:854–864.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li W, Tan C, Liu Y, Liu X, Wang X, Gui Y,
Qin L, Deng F, Yu Z, Hu C and Chen L: Resveratrol ameliorates
oxidative stress and inhibits aquaporin 4 expression following rat
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. 12:7756–7762.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zaky A, Mohammad B, Moftah M, Kandeel KM
and Bassiouny AR: Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 is a key
modulator of aluminum-induced neuroinflammation. BMC Neurosci.
14:262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dietrich AK, Humphreys GI and Nardulli AM:
17β-estradiol increases expression of the oxidative stress response
and DNA repair protein apurinic endonuclease (Ape1) in the cerebral
cortex of female mice following hypoxia. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 138:410–420. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim HW, Cho KJ, Park SC, Kim HJ and Kim
GW: The adenoviral vector-mediated increase in
apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease inhibits the induction of
neuronal cell death after transient ischemic stroke in mice. Brain
Res. 1274:1–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Y and Liu S: The effect of
dexmedetomidine on oxidative stress response following cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion in rats and the expression of intracellular
adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and S100B. Med Sci Monit. 23:867–873.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xiao H, Deng M, Yang B, Hu Z and Tang J:
Pre-treatment of 17β-estradiol attenuates cerebral-ischemia-induced
blood-brain barrier disruption in aged rats: Involvement of
antioxidant signaling. Neuroendocrinology. Feb 15–2017.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Choi S, Joo HK and Jeon BH: Dynamic
regulation of APE1/Ref-1 as a therapeutic target protein. Chonnam
Med J. 52:75–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Howitz KT, Bitterman KJ, Cohen HY, Lamming
DW, Lavu S, Wood JG, Zipkin RE, Chung P, Kisielewski A, Zhang LL,
et al: Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces
cerevisiae lifespan. Nature. 425:191–196. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gurusamy N, Lekli I, Mukherjee S, Ray D,
Ahsan MK, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM and Das DK: Cardioprotection
by resveratrol: A novel mechanism via autophagy involving the
mTORC2 pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 86:103–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Malhotra A, Bath S and Elbarbry F: An
organ system approach to explore the antioxidative,
anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective actions of resveratrol. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2015:8039712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Thakur S, Sarkar B, Cholia RP, Gautam N,
Dhiman M and Mantha AK: APE1/Ref-1 as an emerging therapeutic
target for various human diseases: Phytochemical modulation of its
functions. Exp Mol Med. 46:e1062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu Y, Zhang B, Xie D, Hu Y, Li HL, Zhong
LL, Wang HW, Jiang W, Ke ZP and Zheng DH: Nanoparticle-mediated
dual delivery of resveratrol and DAP5 ameliorates kidney
ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting cell apoptosis and
inflammation. Oncotarget. 8:39547–39558. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kolahdouz Mohammadi R and Arablou T:
Resveratrol and endometriosis: In vitro and animal studies and
underlying mechanisms (Review). Biomed Pharmacother. 91:220–228.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhai L, Liu M, Wang T, Zhang H, Li S and
Guo Y: Picroside II protects the blood-brain barrier by inhibiting
the oxidative signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion
injury. PLoS One. 12:e01744142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sarkar S, Mukherjee A, Das N and Swarnakar
S: Protective roles of nanomelatonin in cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion of aged brain: Matrixmetalloproteinases as
regulators. Exp Gerontol. 92:13–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Su D, Li S, Zhang W, Wang J, Wang J and Lv
M: Structural elucidation of a polysaccharide from Lonicera
japonica flowers and its neuroprotective effect on cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat. Int J Biol Macromol.
99:350–357. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|