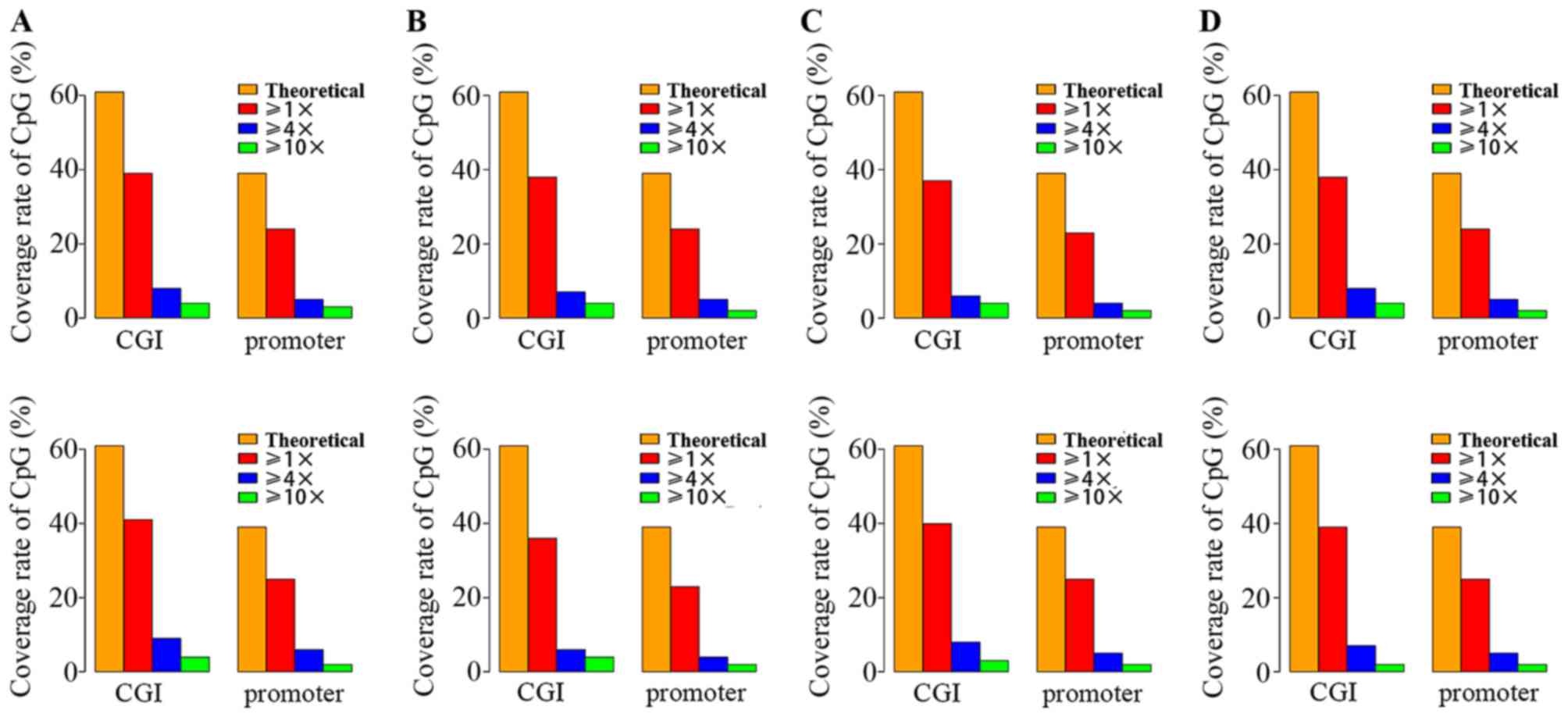
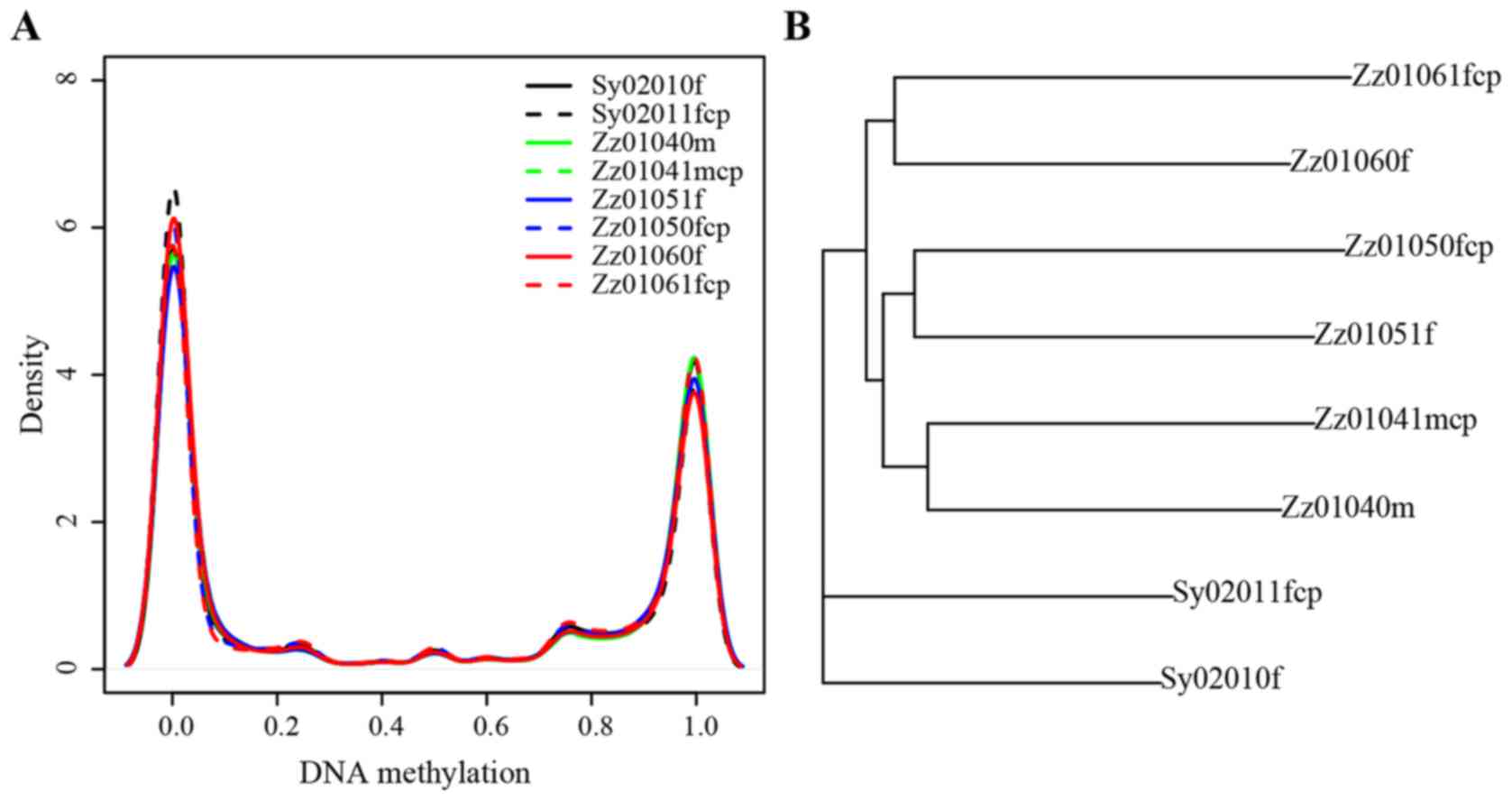
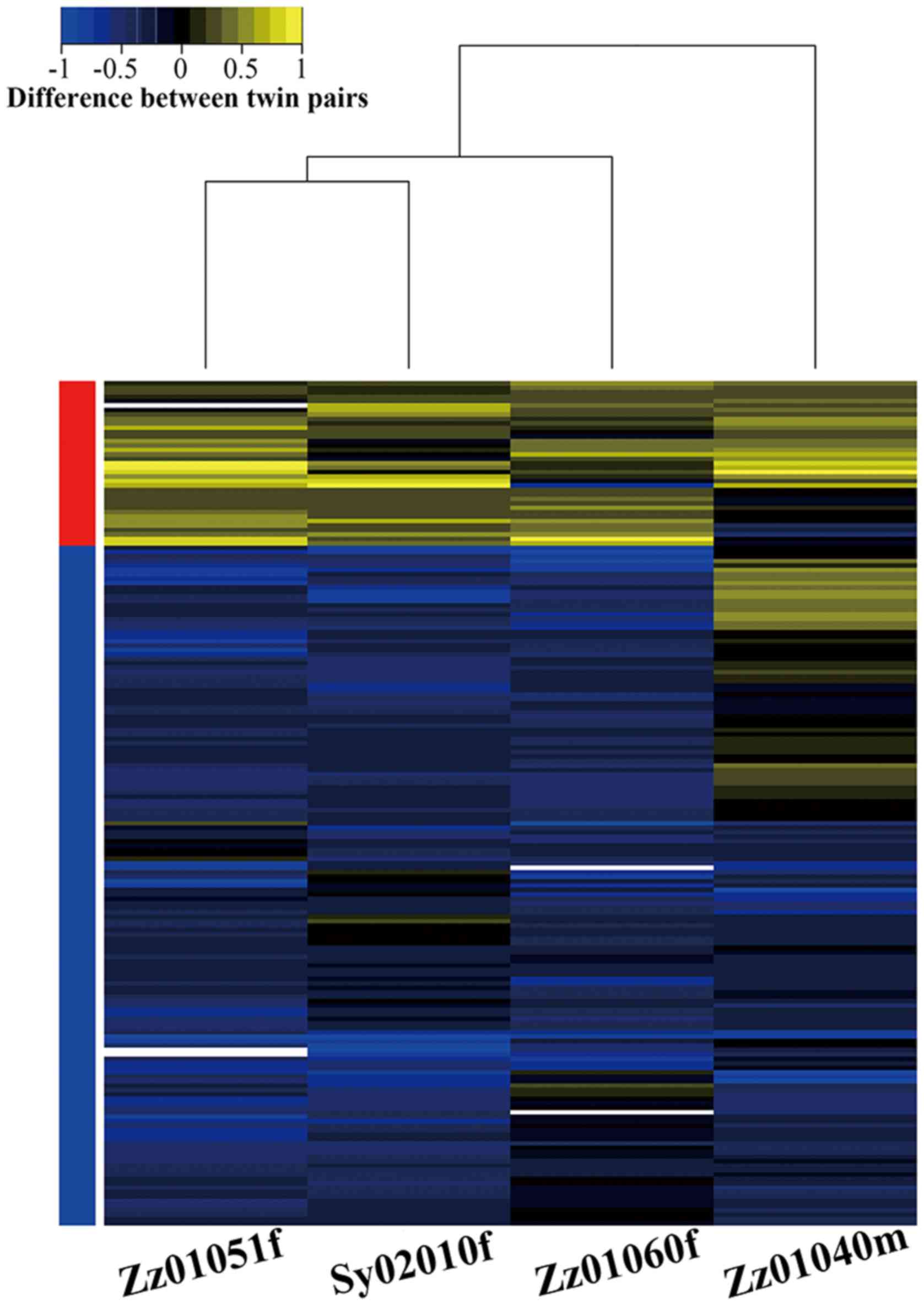
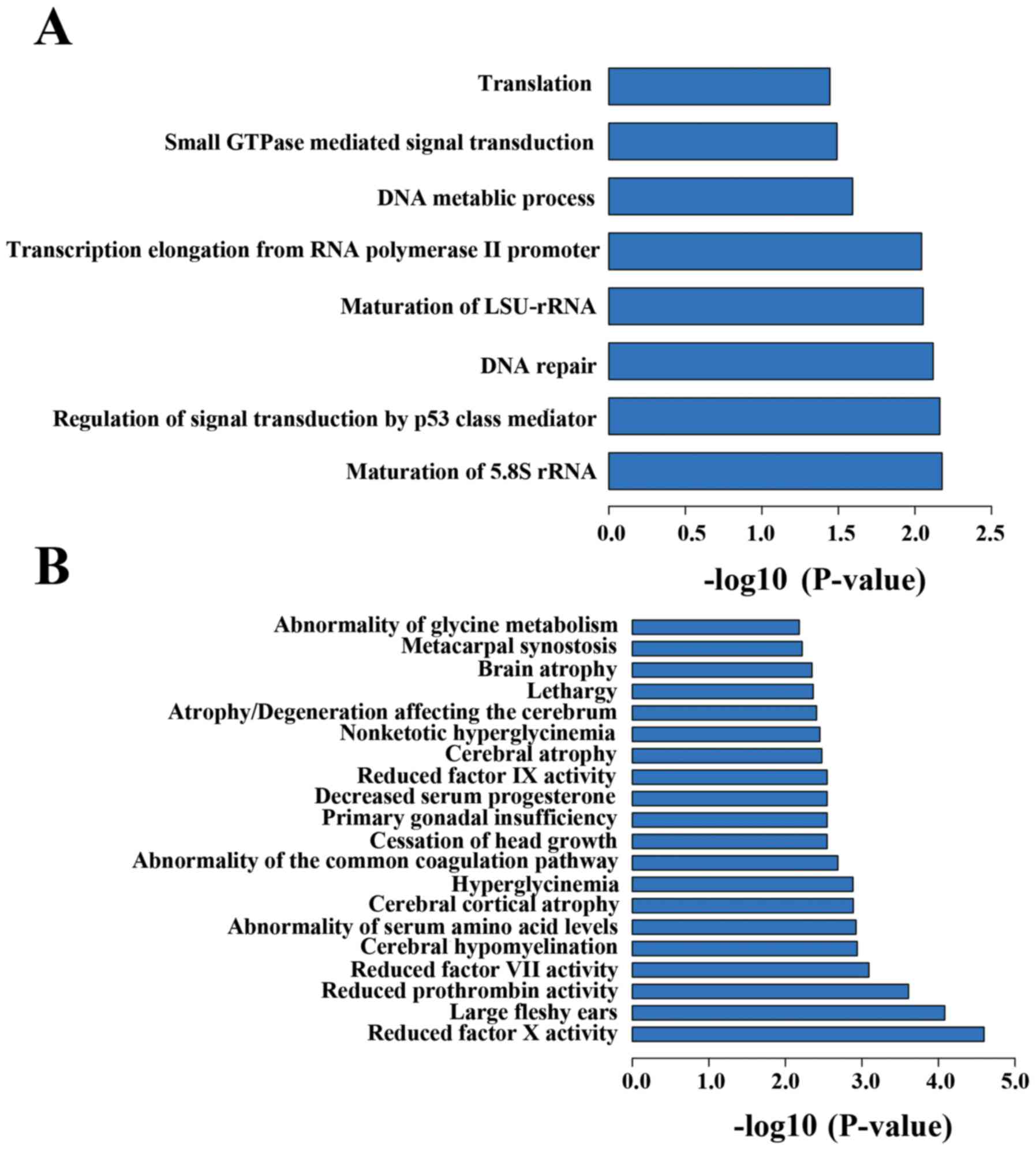
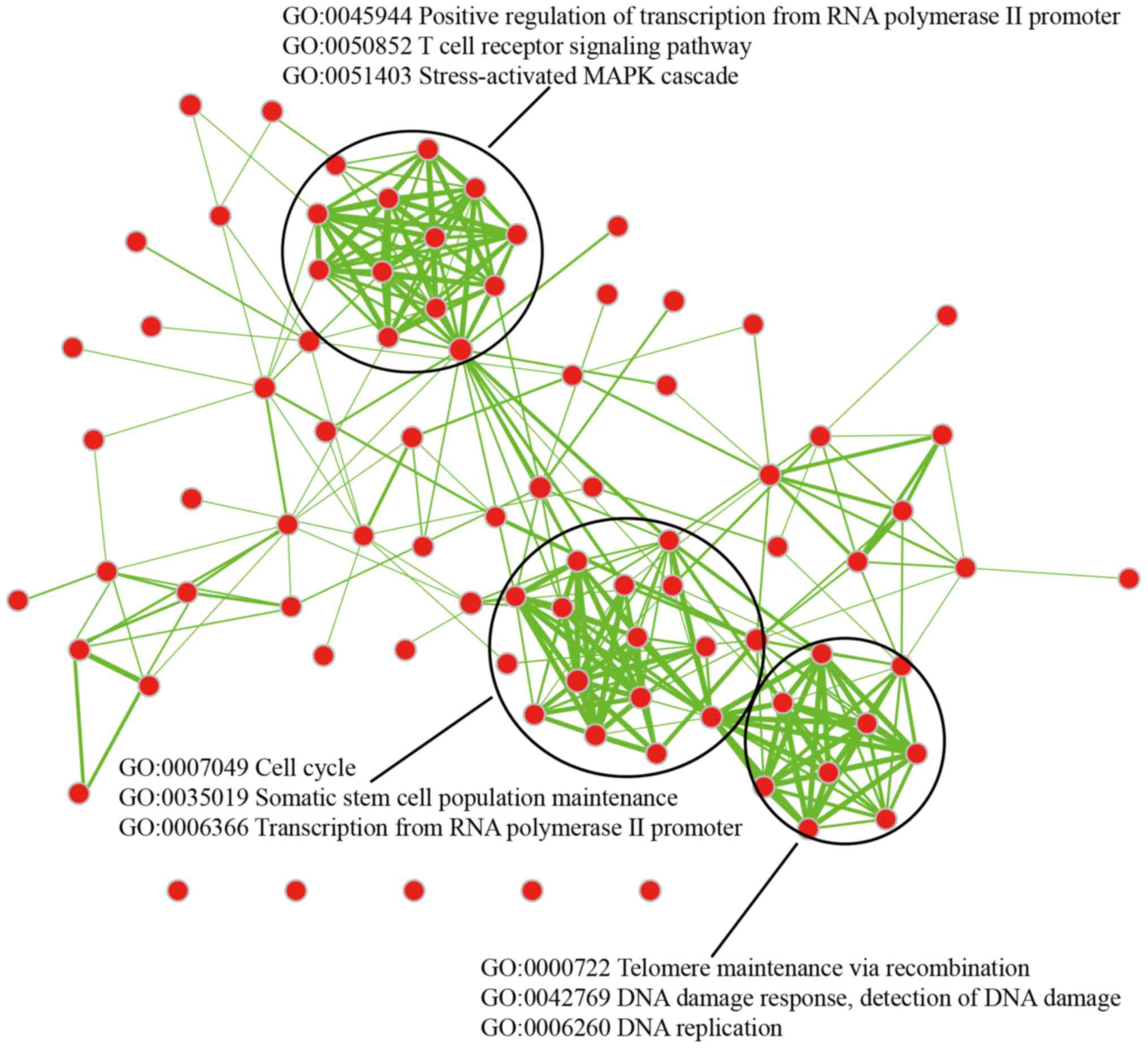
|
1
|
Palisano R, Rosenbaum P, Walter S, Russell
D, Wood E and Galuppi B: Development and reliability of a system to
classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev
Med Child Neurol. 39:214–223. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mutch L, Alberman E, Hagberg B, Kodama K
and Perat MV: Cerebral palsy epidemiology: Where are we now and
where are we going. Dev Med Child Neurol. 34:547–551. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yokoyama Y, Shimizu T and Hayakawa K:
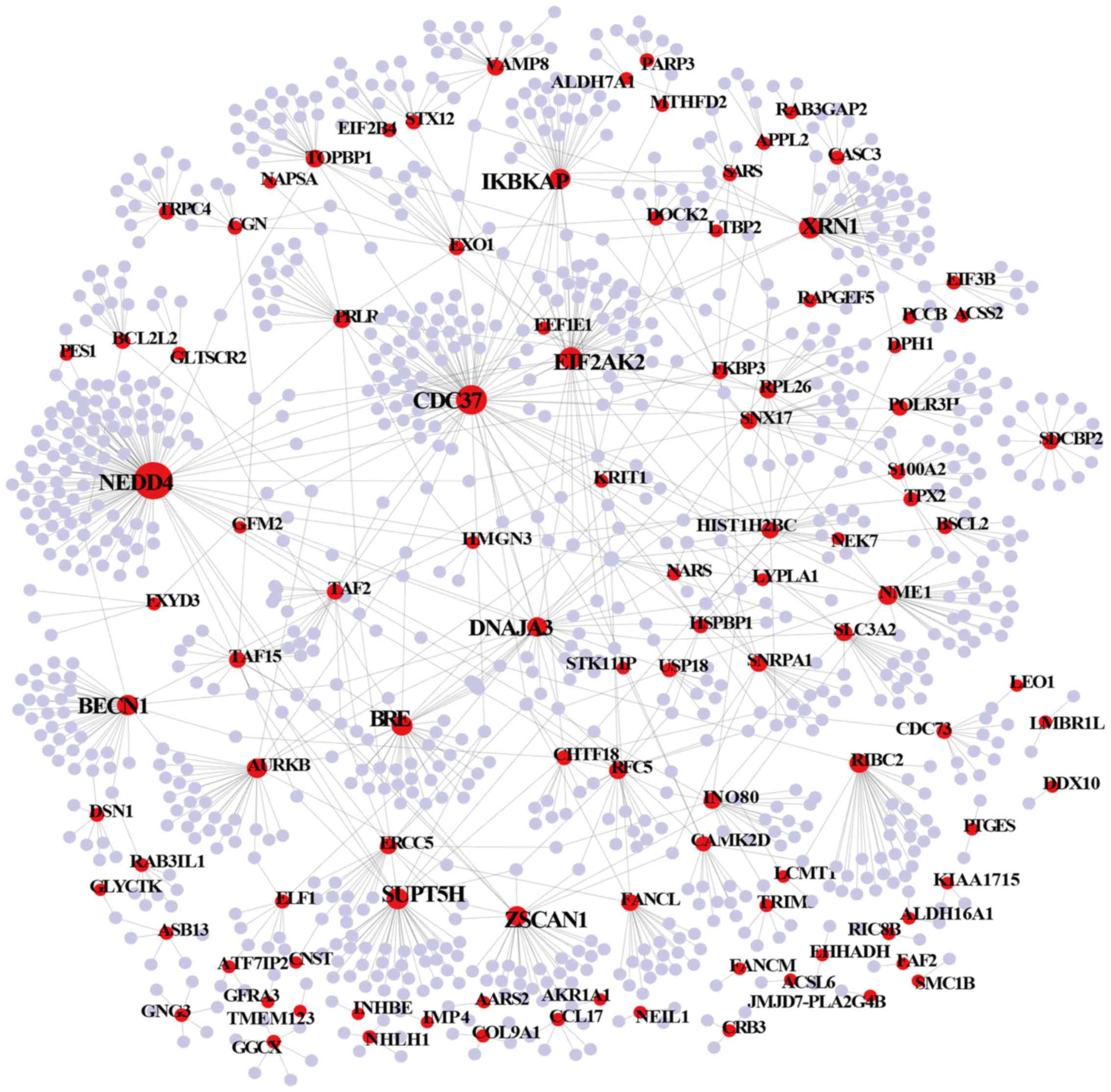
Prevalence of cerebral palsy in twins, triplets and quadruplets.
Int J Epidemiol. 24:943–948. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McMichael G, Bainbridge MN, Haan E,
Corbett M, Gardner A, Thompson S, van Bon BW, van Eyk CL, Broadbent
J, Reynolds C, et al: Whole-exome sequencing points to considerable
genetic heterogeneity of cerebral palsy. Mol Psychiatry.
20:176–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McMichael G, Girirajan S, Moreno-De-Luca
A, Gecz J, Shard C, Nguyen LS, Nicholl J, Gibson C, Haan E, Eichler
E, et al: Rare copy number variation in cerebral palsy. Eur J Hum
Genet. 22:40–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Smith ZD and Meissner A: DNA methylation:
Roles in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet. 14:204–220. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bird A: DNA methylation patterns and
epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 16:6–21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wen Y, Wei Y, Zhang S, Li S, Liu H, Wang
F, Zhao Y, Zhang D and Zhang Y: Cell subpopulation deconvolution
reveals breast cancer heterogeneity based on DNA methylation
signature. Brief Bioinform. 18:426–440. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Das PM and Singal R: DNA methylation and
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:4632–4642. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Timp W and Feinberg AP: Cancer as a
dysregulated epigenome allowing cellular growth advantage at the
expense of the host. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:497–510. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu H, Li S, Wang X, Zhu J, Wei Y, Wang Y,
Wen Y, Wang L, Huang Y, Zhang B, et al: DNA methylation dynamics:
Identification and functional annotation. Brief Funct Genomics.
15:470–484. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ziller MJ, Gu H, Müller F, Donaghey J,
Tsai LT, Kohlbacher O, De Jaqer PL, Rosen ED, Bennett DA, Bernstein
BE, et al: Charting a dynamic DNA methylation landscape of the
human genome. Nature. 500:477–481. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Varley KE, Gertz J, Bowling KM, Parker SL,
Reddy TE, Pauli-Behn F, Cross MK, Williams BA, Stamatoyannopoulos
JA, Crawford GE, et al: Dynamic DNA methylation across diverse
human cell lines and tissues. Genome Res. 23:555–567. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meissner A, Gnirke A, Bell GW, Ramsahoye
B, Lander ES and Jaenisch R: Reduced representation bisulfite
sequencing for comparative high-resolution DNA methylation
analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:5868–5877. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xi Y and Li W: BSMAP: Whole genome
bisulfite sequence MAPping program. BMC Bioinformatics. 10:2322009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Desper R and Gascuel O: Fast and accurate
phylogeny reconstruction algorithms based on the minimum-evolution
principle. J Comput Biol. 9:687–705. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
National Institute of Allergy and
Infectious Diseases (NIAID), NIH, . Database for Annotation,
Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID). 2006.https://david.ncifcrf.gov/ease/ease.jsp
|
|
18
|
McLean CY, Bristor D, Hiller M, Clarke SL,
Schaar BT, Lowe CB, Wenger AM and Bejerano G: GREAT improves
functional interpretation of cis-regulatory regions. Nature
Biotechnol. 28:495–501. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang C, Zhao H, Li J, Liu H, Wang F, Wei
Y, Su J, Zhang D, Liu T and Zhang Y: The identification of specific
methylation patterns across different cancers. PLoS One.
10:e01203612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meissner A, Mikkelsen TS, Gu H, Wernig M,
Hanna J, Sivachenko A, Zhang X, Bernstein BE, Nusbaum C, Jaffe DB,
et al: Genome-scale DNA methylation maps of pluripotent and
differentiated cells. Nature. 454:766–770. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bell JT and Spector TD: DNA methylation
studies using twins: What are they telling us? Genome Biol.
13:1722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wong CC, Meaburn EL, Ronald A, Price TS,
Jeffries AR, Schalkwyk LC, Plomin R and Mill J: Methylomic analysis
of monozygotic twins discordant for autism spectrum disorder and
related behavioural traits. Mol Psychiatry. 19:495–503. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nelson KB, Dambrosia JM, Iovannisci DM,
Cheng S, Grether JK and Lammer E: Genetic polymorphisms and
cerebral palsy in very preterm infants. Pediatr Res. 57:494–499.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|