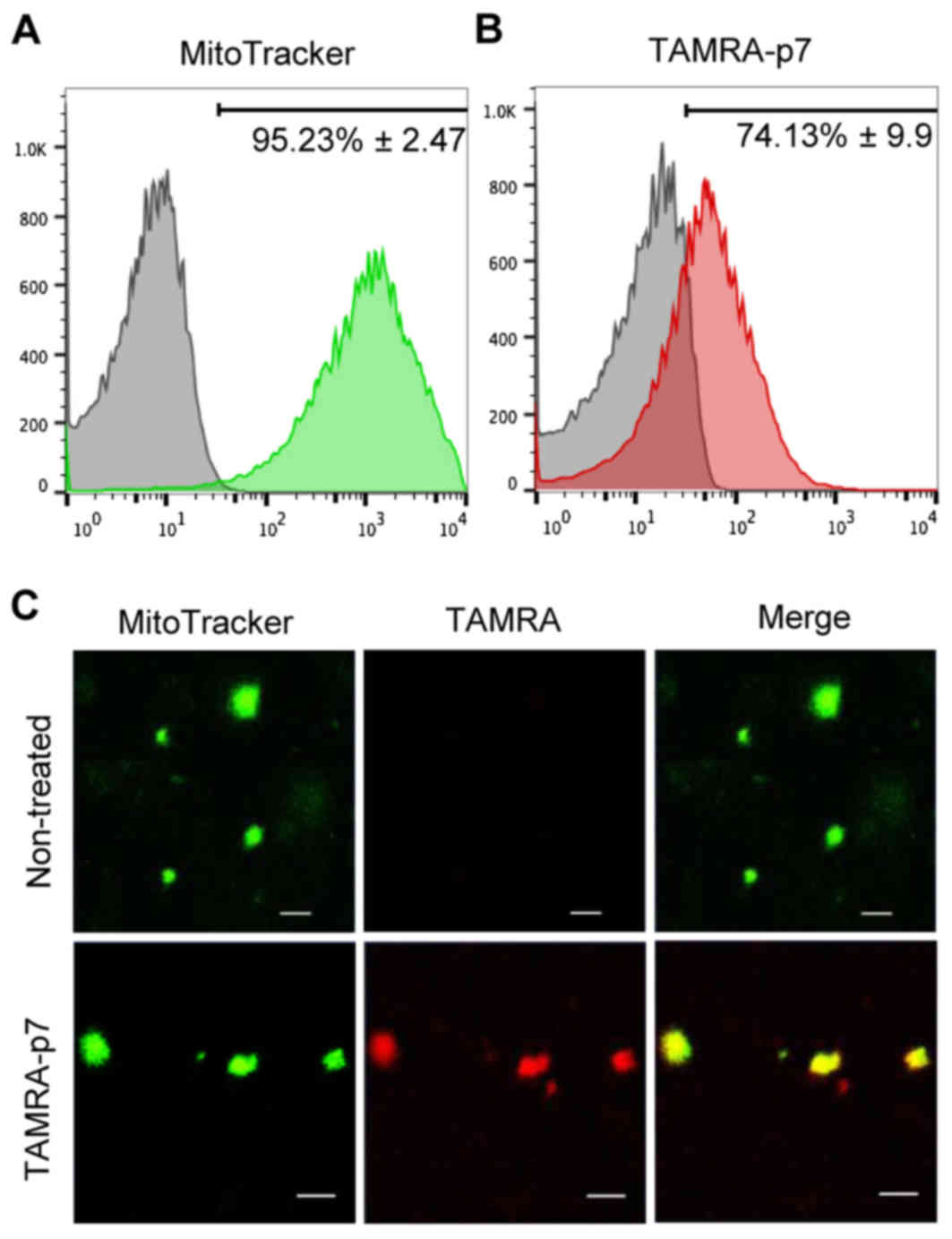
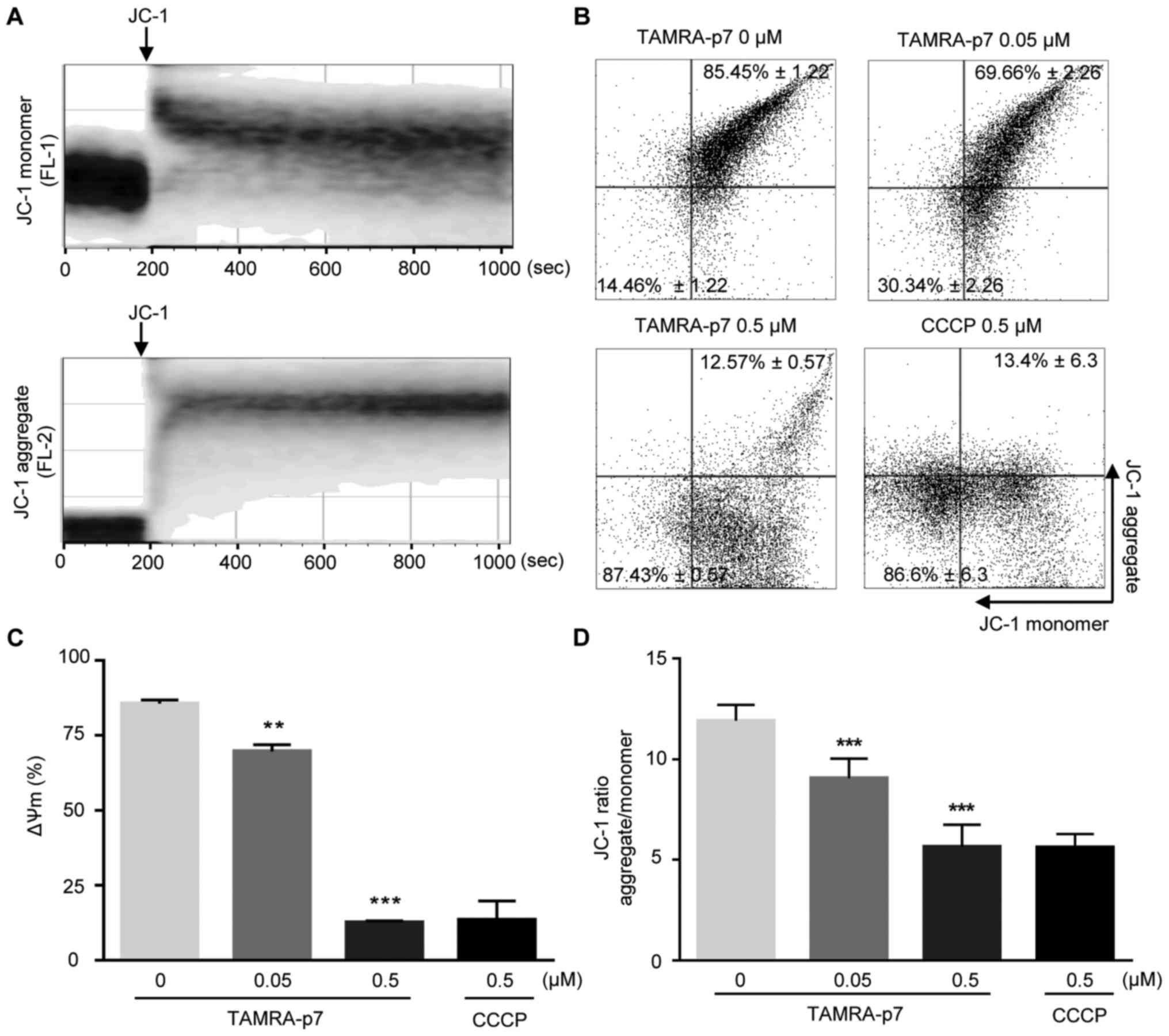
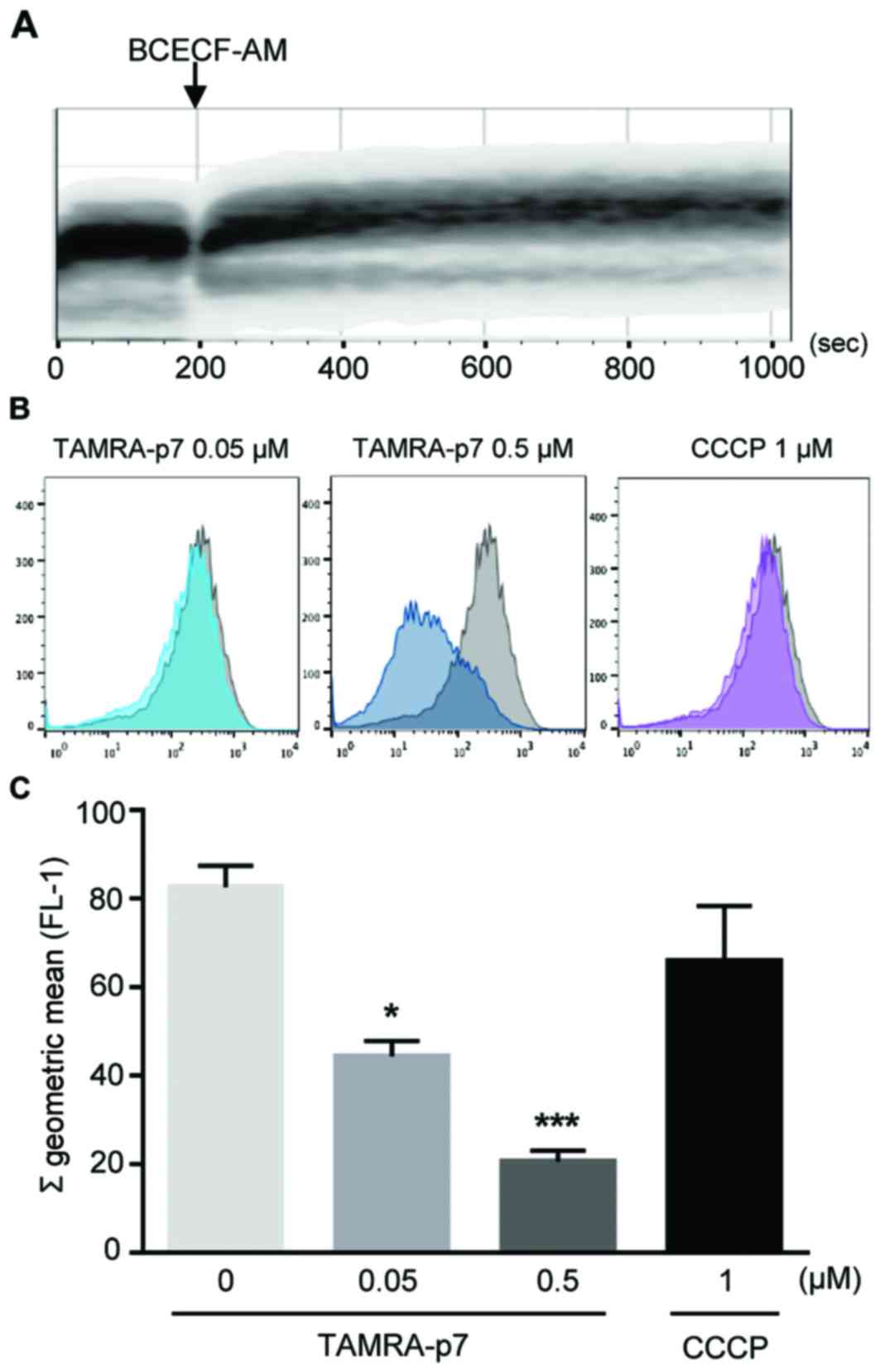
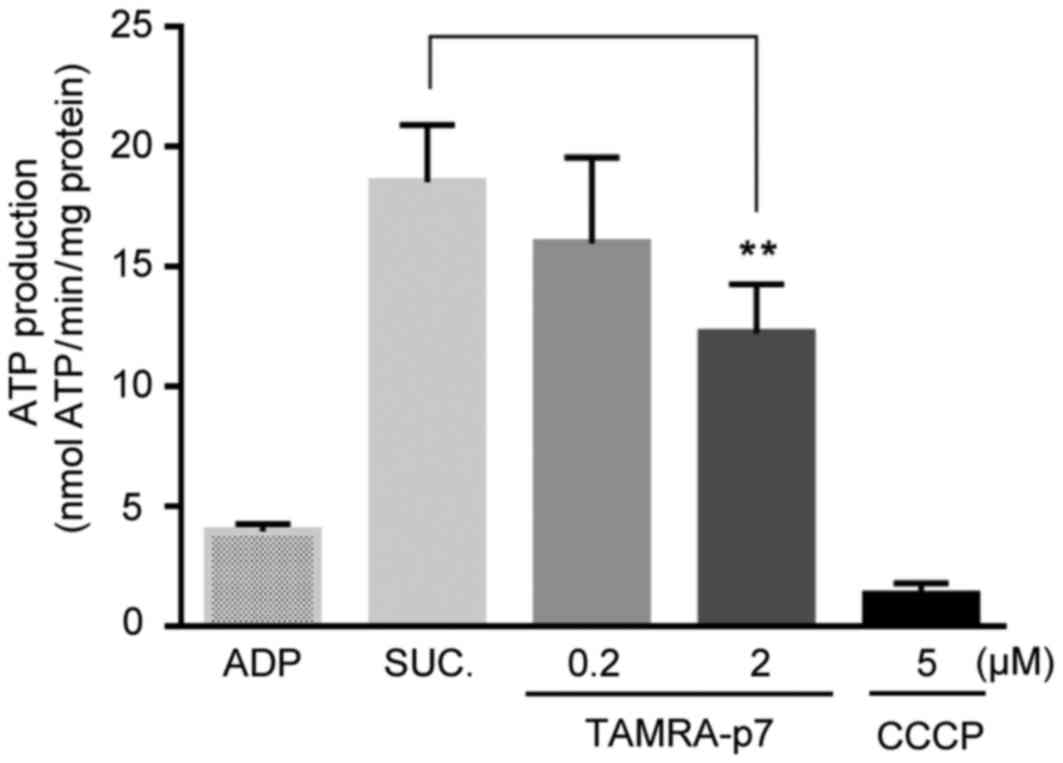
|
1
|
National Institutes of Health, . National
Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement:
Management of hepatitis C: 2002-June 10–12, 2002. Hepatology. 36(5
Suppl 1): S3–S20. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Suzuki T, Ishii K, Aizaki H and Wakita T:
Hepatitis C viral life cycle. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 59:1200–1212.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carrere-Kremer S, Montpellier-Pala C,
Cocquerel L, Wychowski C, Penin F and Dubuisson J: Subcellular
localization and topology of the p7 polypeptide of hepatitis C
virus. J Virol. 76:3720–3730. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Griffin SD, Harvey R, Clarke DS, Barclay
WS, Harris M and Rowlands DJ: A conserved basic loop in hepatitis C
virus p7 protein is required for amantadine-sensitive ion channel
activity in mammalian cells but is dispensable for localization to
mitochondria. J Gen Virol. 85:451–461. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Griffin S, Clarke D, McCormick C, Rowlands
D and Harris M: Signal peptide cleavage and internal targeting
signals direct the hepatitis C virus p7 protein to distinct
intracellular membranes. J Virol. 79:15525–15536. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sakai A, Claire MS, Faulk K, Govindarajan
S, Emerson SU, Purcell RH and Bukh J: The p7 polypeptide of
hepatitis C virus is critical for infectivity and contains
functionally important genotype-specific sequences. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:pp. 11646–11651. 2003; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Steinmann E, Penin F, Kallis S, Patel AH,
Bartenschlager R and Pietschmann T: Hepatitis C virus p7 protein is
crucial for assembly and release of infectious virions. PLoS
Pathog. 3:e1032007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McBride HM, Neuspiel M and Wasiak S:
Mitochondria: More than just a powerhouse. Curr Biol. 16:R551–R560.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dzbek J and Korzeniewski B: Control over
the contribution of the mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsi)
and proton gradient (DeltapH) to the protonmotive force (Deltap).
In silico studies. J Biol Chem. 283:33232–33239. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Okuda M, Li K, Beard MR, Showalter LA,
Scholle F, Lemon SM and Weinman SA: Mitochondrial injury, oxidative
stress and antioxidant gene expression are induced by hepatitis C
virus core protein. Gastroenterology. 122:366–375. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Boya P, Pauleau AL, Poncet D,
Gonzalez-Polo RA, Zamzami N and Kroemer G: Viral proteins targeting
mitochondria: Controlling cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1659:178–189. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Piccoli C, Scrima R, D'Aprile A, Ripoli M,
Lecce L, Boffoli D and Capitanio N: Mitochondrial dysfunction in
hepatitis C virus infection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1757:1429–1437.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang T, Campbell RV, Yi MK, Lemon SM and
Weinman SA: Role of hepatitis C virus core protein in viral-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction. J Viral Hepat. 17:784–793. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brault C, Levy PL and Bartosch B:
Hepatitis C virus-induced mitochondrial dysfunctions. Viruses.
5:954–980. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Silic-Benussi M, Marin O, Biasiotto R,
D'Agostino DM and Ciminale V: Effects of human T-cell leukemia
virus type 1 (HTLV-1) p13 on mitochondrial K+ permeability: A new
member of the viroporin family? FEBS Lett. 584:2070–2075. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su YC and Hong JR: Betanodavirus B2 causes
ATP depletion-induced cell death via mitochondrial targeting and
complex II inhibition in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem.
285:39801–39810. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deng L, Adachi T, Kitayama K, Bungyoku Y,
Kitazawa S, Ishido S, Shoji I and Hotta H: Hepatitis C virus
infection induces apoptosis through a Bax-triggered,
mitochondrion-mediated, caspase 3-dependent pathway. J Virol.
82:10375–10385. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wieckowski MR, Giorgi C, Lebiedzinska M,
Duszynski J and Pinton P: Isolation of mitochondria-associated
membranes and mitochondria from animal tissues and cells. Nat
Protoc. 4:1582–1590. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brierley GP, Davis MH, Cragoe EJ and Jung
DW: Kinetic properties of the sodium/hydrogen ion antiport of heart
mitochondria. Biochemistry. 28:4347–4354. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jung DW, Davis MH and Brierley GP:
Estimation of matrix pH in isolated heart mitochondria using a
fluorescent probe. Anal Biochem. 178:348–354. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tardif KD, Waris G and Siddiqui A:
Hepatitis C virus, ER stress, and oxidative stress. Trends
Microbiol. 13:159–163. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
StGelais C, Foster TL, Verow M, Atkins E,
Fishwick CW, Rowlands D, Harris M and Griffin S: Determinants of
hepatitis C virus p7 ion channel function and drug sensitivity
identified in vitro. J Virol. 83:7970–7981. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Piccoli C, Scrima R, Quarato G, D'Aprile
A, Ripoli M, Lecce L, Boffoli D, Moradpour D and Capitanio N:
Hepatitis C virus protein expression causes calcium-mediated
mitochondrial bioenergetic dysfunction and nitro-oxidative stress.
Hepatology. 46:58–65. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ando T, Imamura H, Suzuki R, Aizaki H,
Watanabe T, Wakita T and Suzuki T: Visualization and measurement of
ATP levels in living cells replicating hepatitis C virus genome
RNA. PLoS Pathog. 8:e10025612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|