|
1
|
Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA and Ward E:
Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
59:366–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
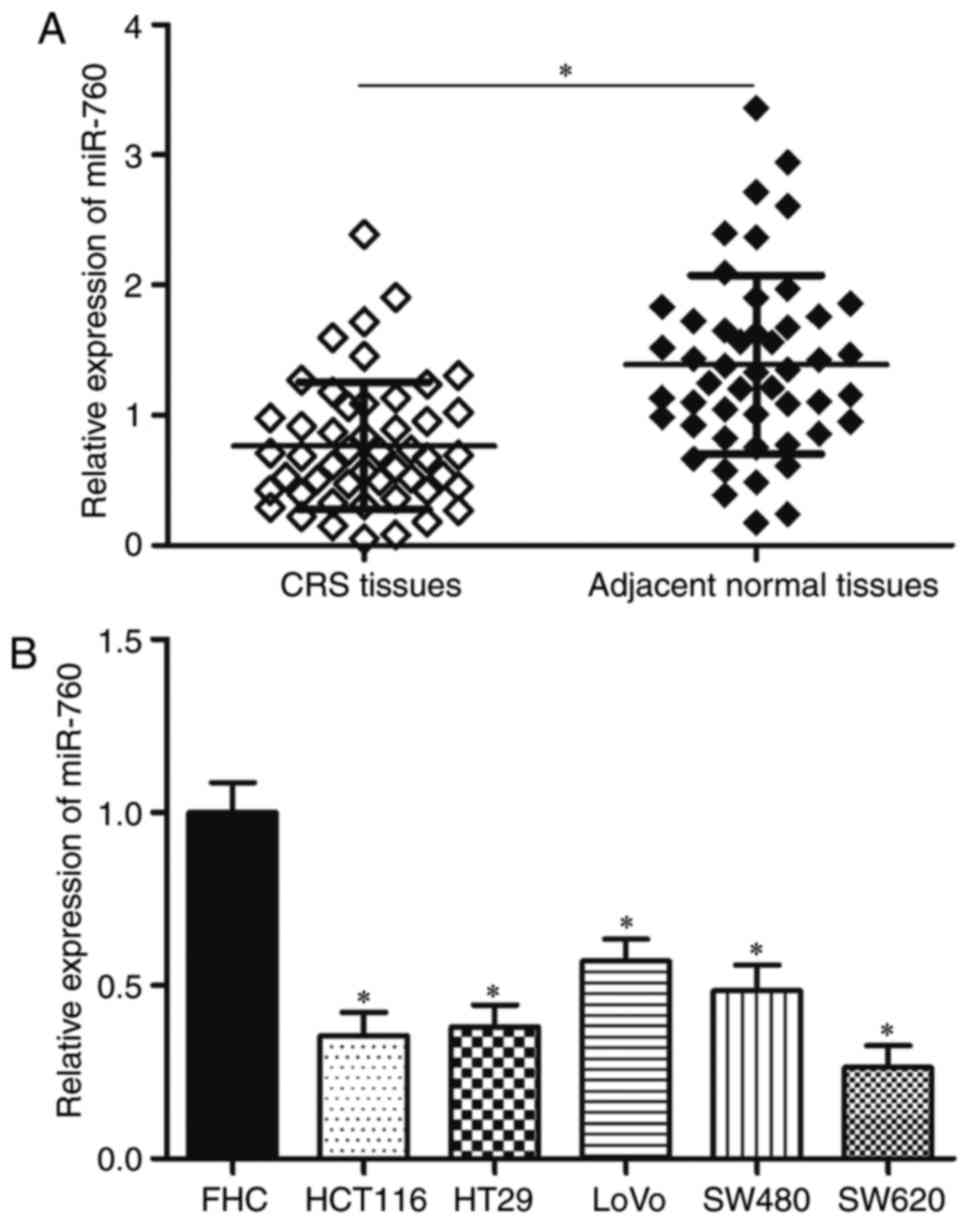
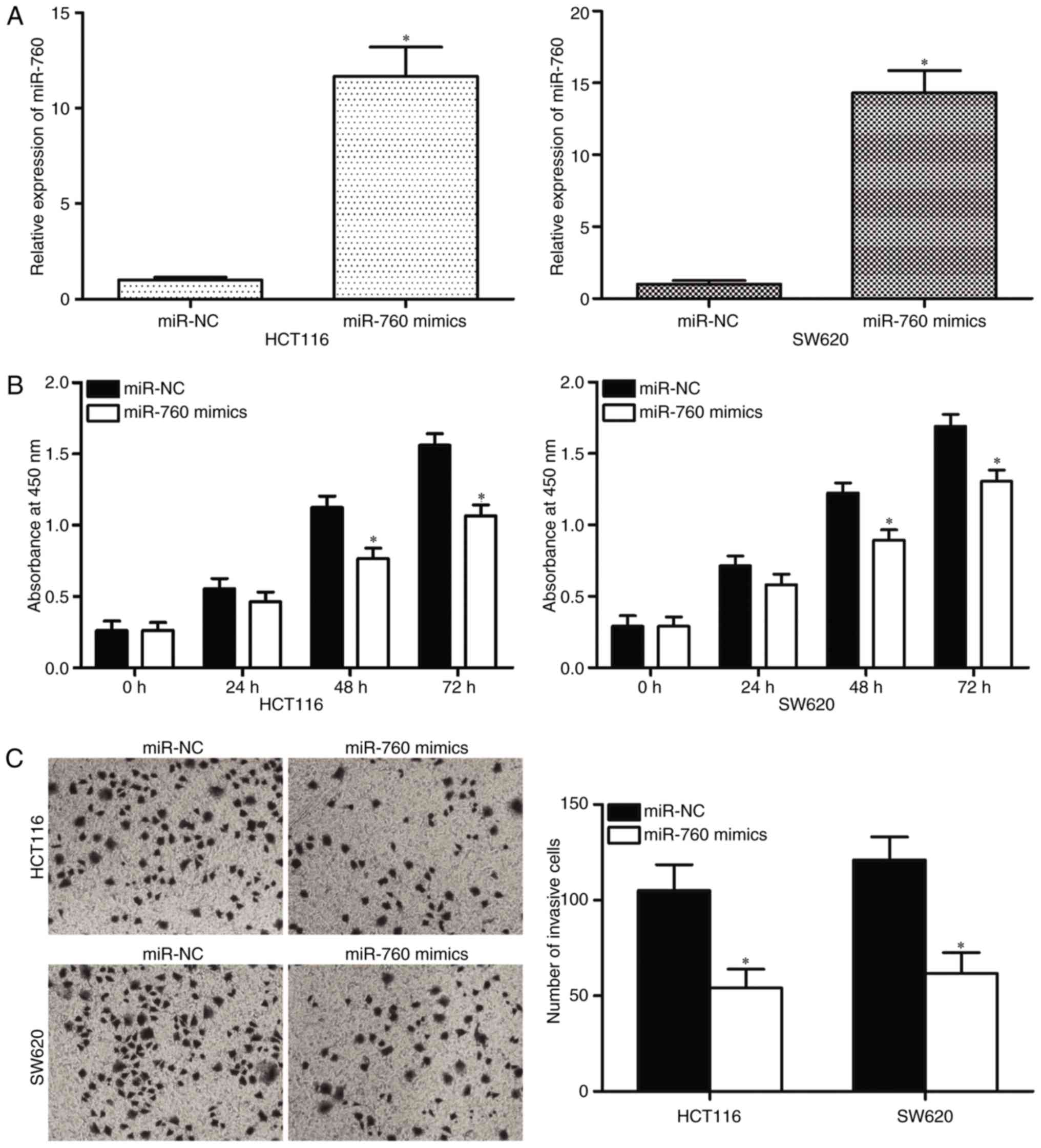
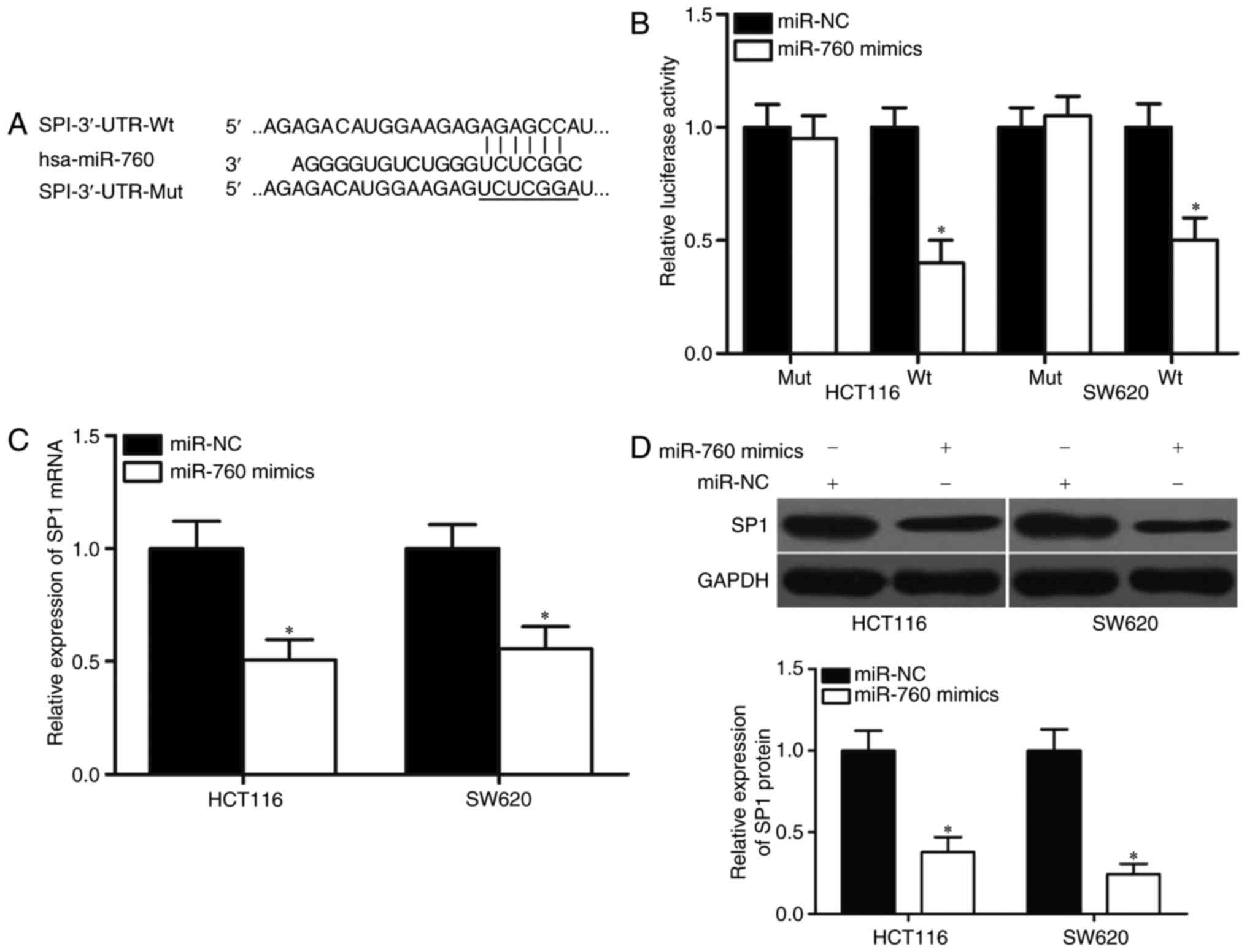
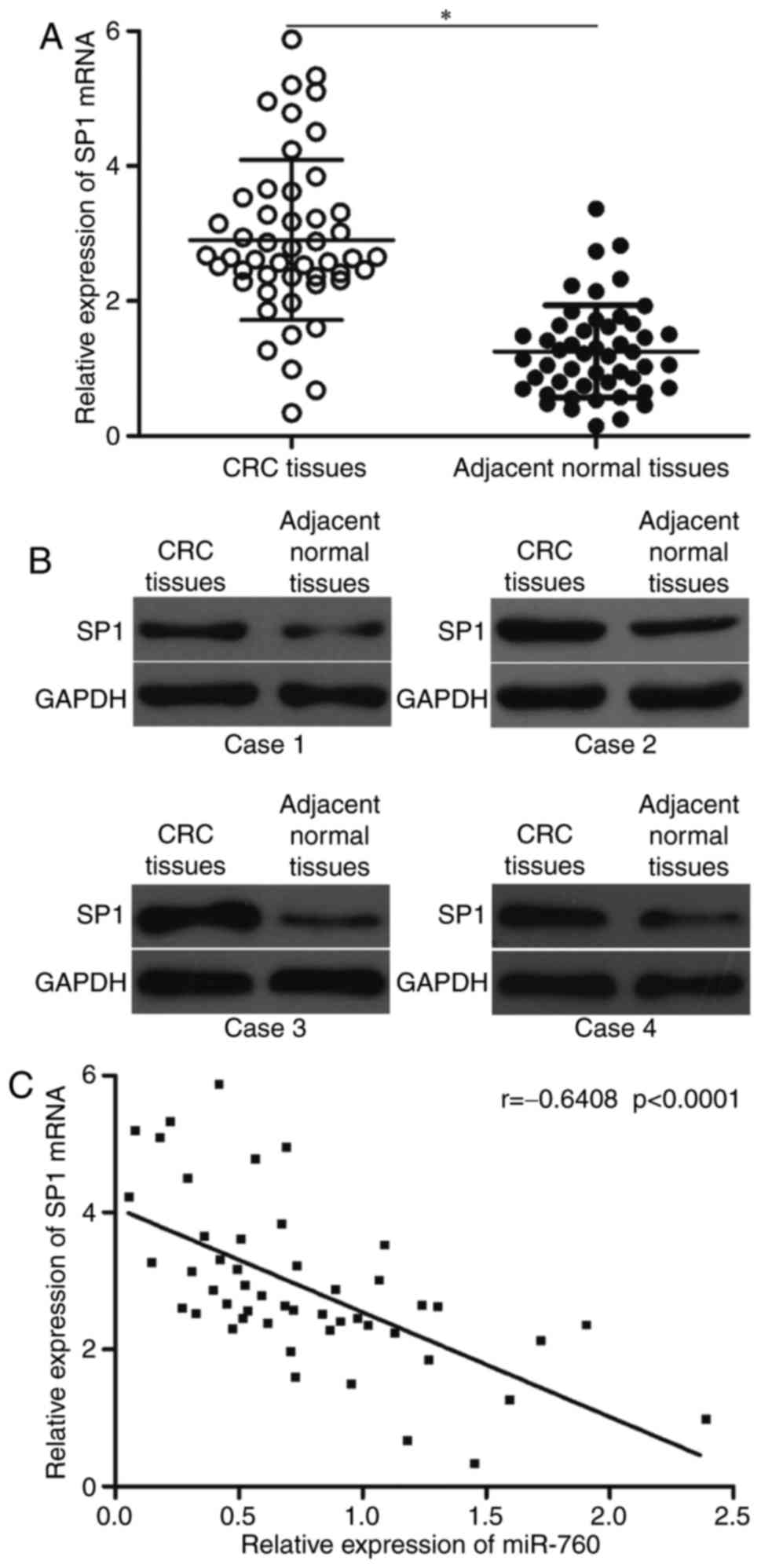
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haggar FA and Boushey RP: Colorectal
cancer epidemiology: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk
factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 22:191–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Manfredi S, Lepage C, Hatem C, Coatmeur O,
Faivre J and Bouvier AM: Epidemiology and management of liver
metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 244:254–259. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lim LP, Glasner ME, Yekta S, Burge CB and
Bartel DP: Vertebrate microRNA genes. Science. 299:15402003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oliveto S, Mancino M, Manfrini N and Biffo
S: Role of microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J
Biol Chem. 8:45–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Manikandan J, Aarthi JJ, Kumar SD and
Pushparaj PN: Oncomirs: The potential role of non-coding microRNAs
in understanding cancer. Bioinformation. 2:330–334. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li W, Chen A, Xiong L, Chen T, Tao F, Lu
Y, He Q, Zhao L, Ou R and Xu Y: miR-133a acts as a tumor suppressor
in colorectal cancer by targeting eIF4A1. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176983892017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ding L, Yu LL, Han N and Zhang BT: miR-141
promotes colon cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting MAP2K4.
Oncol Lett. 13:1665–1671. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Quan Y, Song Q, Wang J, Zhao L, Lv J and
Gong S: MiR-1202 functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma cells by
targeting Rab1A. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176975652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Han ML, Wang F, Gu YT, Pei XH, Ge X, Guo
GC, Li L, Duan X, Zhu MZ and Wang YM: MicroR-760 suppresses cancer
stem cell subpopulation and breast cancer cell proliferation and
metastasis: By down-regulating NANOG. Biomed Pharmacother.
80:304–310. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liao Y, Deng Y, Liu J, Ye Z, You Z, Yao S
and He S: MiR-760 overexpression promotes proliferation in ovarian
cancer by downregulation of PHLPP2 expression. Gynecol Oncol.
143:655–663. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Q, Huang Z, Ni S, Xiao X, Xu Q, Wang
L, Huang D, Tan C, Sheng W and Du X: Plasma miR-601 and miR-760 are
novel biomarkers for the early detection of colorectal cancer. PLoS
One. 7:e443982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bajpai R and Nagaraju GP: Specificity
protein 1: Its role in colorectal cancer progression and
metastasis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 113:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Wang J, Lin S, Geng Y, Wang J and
Jiang B: Sp1 is involved in H2O2-induced PUMA gene expression and
apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
27:442008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dong W, Shen R, Wang Q, Gao Y, Qi X, Jiang
H, Yao J, Lin X, Wu Y and Wang L: Sp1 upregulates expression of
TRF2 and TRF2 inhibition reduces tumorigenesis in human colorectal
carcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:2166–2174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao Y, Zhang W, Guo Z, Ma F, Wu Y, Bai Y,
Gong W, Chen Y, Cheng T, Zhi F, et al: Inhibition of the
transcription factor Sp1 suppresses colon cancer stem cell growth
and induces apoptosis in vitro and in nude mouse xenografts. Oncol
Rep. 30:1782–1792. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu MH and Zhang W: TEAD1 enhances
proliferation via activating SP1 in colorectal cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 83:496–501. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hosoi Y, Watanabe T, Nakagawa K, Matsumoto
Y, Enomoto A, Morita A, Nagawa H and Suzuki N: Up-regulation of
DNA-dependent protein kinase activity and Sp1 in colorectal cancer.
Int J Oncol. 25:461–468. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kou XX, Hao T, Meng Z, Zhou YH and Gan YH:
Acetylated Sp1 inhibits PTEN expression through binding to PTEN
core promoter and recruitment of HDAC1 and promotes cancer cell
migration and invasion. Carcinogenesis. 34:58–67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xia SS, Zhang GJ, Liu ZL, Tian HP, He Y,
Meng CY, Li LF, Wang ZW and Zhou T: MicroRNA-22 suppresses the
growth, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through a
Sp1 negative feedback loop. Oncotarget. 8:36266–36278.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 96
Suppl:R40–R44. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:pp. 2257–2261.
2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu SH, Wang CH, Huang ZJ, Liu F, Xu CW, Li
XL and Chen GQ: miR-760 mediates chemoresistance through inhibition
of epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:5002–5008. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lv J, Fu Z, Shi M, Xia K, Ji C, Xu P, Lv
M, Pan B, Dai L and Xie H: Systematic analysis of gene expression
pattern in has-miR-760 overexpressed resistance of the MCF-7 human
breast cancer cell to doxorubicin. Biomed Pharmacother. 69:162–169.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chang WC and Hung JJ: Functional role of
post-translational modifications of Sp1 in tumorigenesis. J Biomed
Sci. 19:942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu Y, Zhao F, Wang Z, Song Y, Luo Y, Zhang
X, Jiang L, Sun Z, Miao Z and Xu H: MicroRNA-335 acts as a
metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Bcl-w and
specificity protein 1. Oncogene. 31:1398–1407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yin P, Zhao C, Li Z, Mei C, Yao W, Liu Y,
Li N, Qi J, Wang L, Shi Y, et al: Sp1 is involved in regulation of
cystathionine γ-lyase gene expression and biological function by
PI3K/Akt pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cell
Signal. 24:1229–1240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sankpal UT, Goodison S, Abdelrahim M and
Basha R: Targeting Sp1 transcription factors in prostate cancer
therapy. Med Chem. 7:518–525. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bonofiglio D, Qi H, Gabriele S, Catalano
S, Aquila S, Belmonte M and Ando S: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma inhibits follicular and
anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells growth by upregulating
p21Cip1/WAF1 gene in a Sp1-dependent manner. Endocr Relat Cancer.
15:545–557. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yue L, Li L, Liu F, Hu N, Zhang W, Bai X,
Li Y, Zhang Y, Fu L, Zhang X and Ye L: The oncoprotein HBXIP
activates transcriptional coregulatory protein LMO4 via Sp1 to
promote proliferation of breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
34:927–935. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang C and Xie K: Crosstalk of Sp1 and
Stat3 signaling in pancreatic cancer pathogenesis. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 23:25–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsu TI, Wang MC, Chen SY, Yeh YM, Su WC,
Chang WC and Hung JJ: Sp1 expression regulates lung tumor
progression. Oncogene. 31:3973–3988. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|