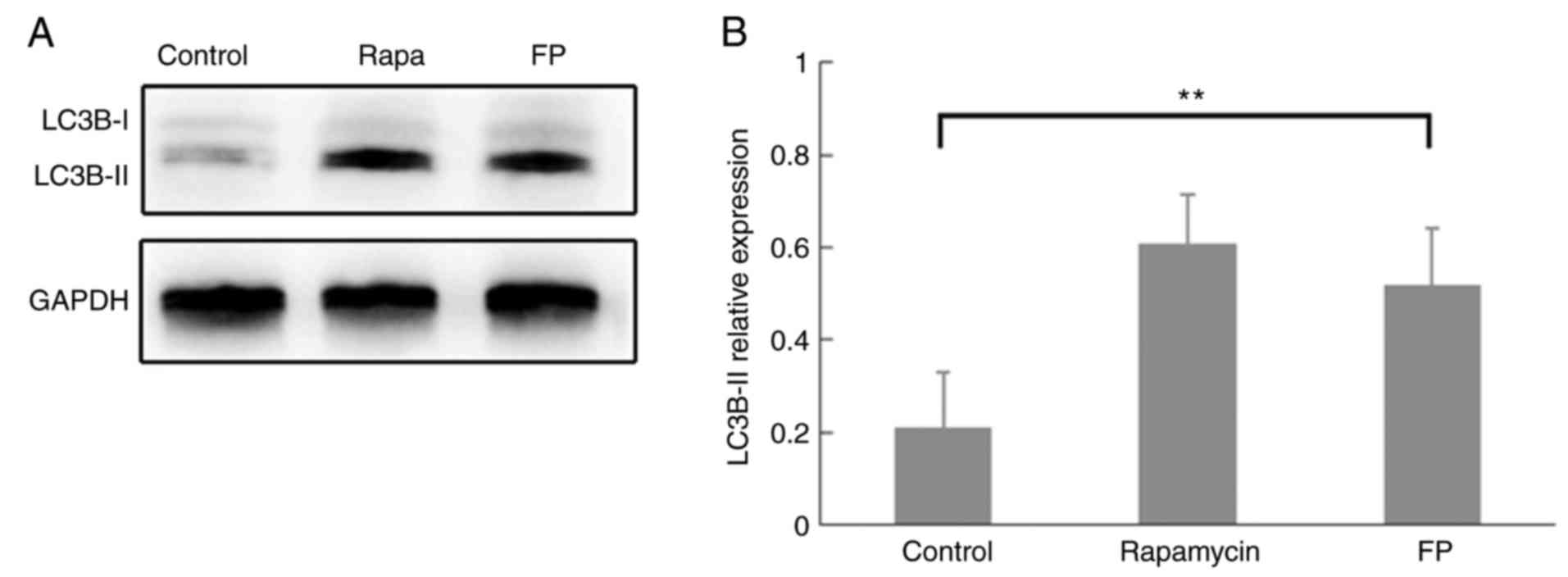
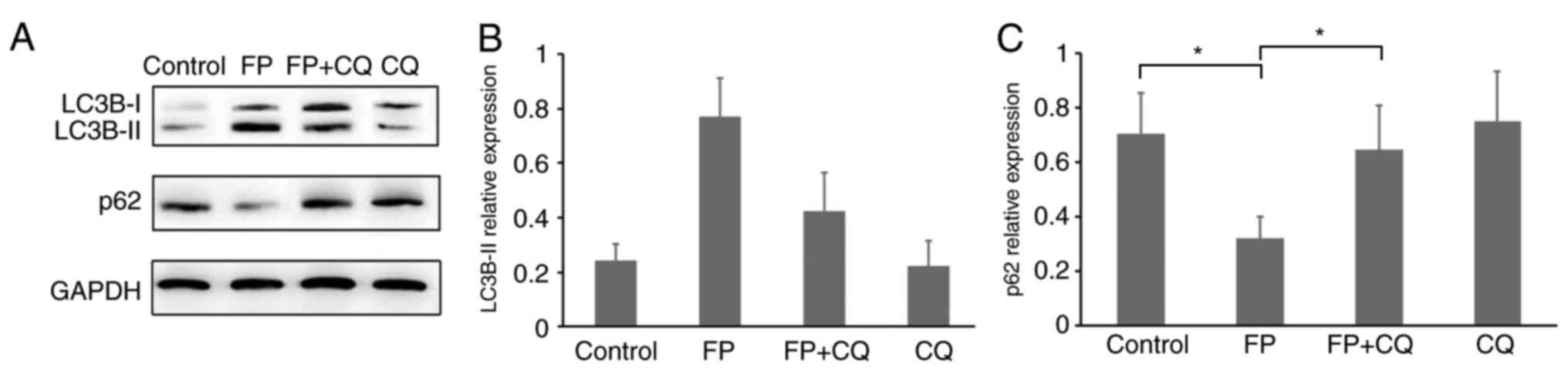
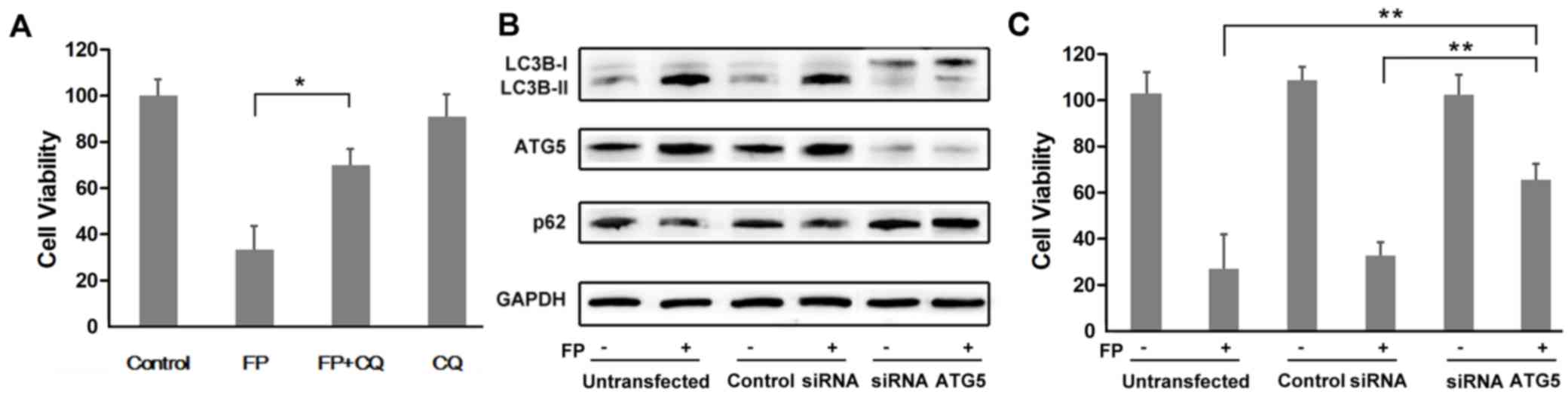
|
1
|
Howell A, Anderson AS, Clarke RB, Duffy
SW, Evans DG, Garcia-Closas M, Gescher AJ, Key TJ, Saxton JM and
Harvie MN: Risk determination and prevention of breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res. 16:4462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Austreid E, Lonning PE and Eikesdal HP:
The emergence of targeted drugs in breast cancer to prevent
resistance to endocrine treatment and chemotherapy. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 15:681–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Asghar U, Witkiewicz AK, Turner NC and
Knudsen ES: The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent
kinases in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:130–146. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
DiPippo AJ, Patel NK and Barnett CM:
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors for the treatment of breast
cancer: Past, Present, and Future. Pharmacotherapy. 36:652–667.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Senderowicz AM and Sausville EA:
Preclinical and clinical development of cyclin-dependent kinase
modulators. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:376–387. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sedlacek HH: Mechanisms of action of
flavopiridol. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 38:139–170. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ravishankar D, Rajora AK, Greco F and
Osborn HM: Flavonoids as prospective compounds for anti-cancer
therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2821–2831. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iyer SP, Mejia J, Rosato AE, Grant S and
Rosato RR: Flavopiridol-mediated multiple modulatory effects
synergistically increase sensitivity to TRAIL-induced cell death in
human leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 73(8 Suppl): S29602013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ali S, El-Rayes BF, Aranha O, Sarkar FH
and Philip PA: Sequence dependent potentiation of gemcitabine by
flavopiridol in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
90:25–31. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wittmann S, Bali P, Donapaty S,
Nimmanapalli R, Guo F, Yamaguchi H, Huang M, Jove R, Wang HG and
Bhalla K: Flavopiridol down-regulates antiapoptotic proteins and
sensitizes human breast cancer cells to epothilone B-induced
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 63:93–99. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Bhuiyan M, Alhasan S, Senderowicz AM
and Sarkar FH: Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of c-erbB-2 in
breast cancer cells by flavopiridol. Clin Cancer Res. 6:223–229.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klionsky DJ and Emr SD: Autophagy as a
regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science. 290:1717–1721.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weiner LM and Lotze MT: Tumor-cell death,
autophagy, and immunity. N Engl J Med. 366:1156–1158. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mahoney E, Byrd JC and Johnson AJ:
Autophagy and ER stress play an essential role in the mechanism of
action and drug resistance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
flavopiridol. Autophagy. 9:434–435. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Bravo-San Pedro
JM, Amaravadi RK, Baehrecke EH, Cecconi F, Codogno P, Debnath J,
Gewirtz DA, Karantza V, et al: Autophagy in malignant
transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J. 34:856–880. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rosenfeldt MT and Ryan KM: The multiple
roles of autophagy in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:955–963. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mahoney E, Lucas DM, Gupta SV, Wagner AJ,
Herman SE, Smith LL, Yeh YY, Andritsos L, Jones JA, Flynn JM, et
al: ER stress and autophagy: New discoveries in the mechanism of
action and drug resistance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
flavopiridol. Blood. 120:1262–1273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie ZZ, Li MM, Deng PF, Wang S, Wang L, Lu
XP, Hu LB, Chen Z, Jie HY, Wang YF, et al: Paris saponin-induced
autophagy promotes breast cancer cell apoptosis via the Akt/mTOR
signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 264:1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh A, Chagtoo M, Tiwari S, George N,
Chakrabarti B, Khan S, Lakshmi S and Godbole MM: Inhibition of
inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor induce breast cancer cell
death through deregulated autophagy and cellular bioenergetics. J
Cell Biochem. 118:2333–2346. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shibata M, Yoshimura K, Furuya N, Koike M,
Ueno T, Komatsu M, Arai H, Tanaka K, Kominami E and Uchiyama Y: The
MAP1-LC3 conjugation system is involved in lipid droplet formation.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 382:419–423. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shibata M, Yoshimura K, Tamura H, Ueno T,
Nishimura T, Inoue T, Sasaki M, Koike M, Arai H, Kominami E and
Uchiyama Y: LC3, a microtubule-associated protein1A/B light chain3,
is involved in cytoplasmic lipid droplet formation. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 393:274–279. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Arozena A Acevedo, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Assays
for Monitoring Autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ye H, Chen M, Cao F, Huang H, Zhan R and
Zheng X: Chloroquine, an autophagy inhibitor, potentiates the
radiosensitivity of glioma initiating cells by inhibiting autophagy
and activating apoptosis. BMC Neurol. 16:1782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shao X, Gao D, Wang Y, Jin F, Wu Q and Liu
H: Application of metabolomics to investigate the antitumor
mechanism of flavopiridol in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1025:40–47. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Filippi-Chiela EC, Villodre ES, Zamin LL
and Lenz G: Autophagy interplay with apoptosis and cell cycle
regulation in the growth inhibiting effect of resveratrol in glioma
cells. PLoS One. 6:e208492011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Asghar U, Witkiewicz AK, Turner NC and
Knudsen ES: The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent
kinases in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:130–146. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carlson B, Lahusen T, Singh S,
Loaiza-Perez A, Worland PJ, Pestell R, Albanese C, Sausville EA and
Senderowicz AM: Down-regulation of cyclin D1 by transcriptional
repression in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells induced by
flavopiridol. Cancer Res. 59:4634–4641. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Carlson B, Pearlstein R, Naik R, Sedlacek
H, Sausville E and Worland P: Inhibition of CDK2, CDK4 and CDK7 by
flavopiridol and structural analogs. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res.
37:pp. 4241996;
|
|
29
|
Worland PJ, Kaur G, Stetler-Stevenson M,
Sebers S, Sartor O and Sausville EA: Alteration of the
phosphorylation state of p34cdc2 kinase by the flavone L86-8275 in
breast carcinoma cells: Correlation with decreased H1 kinase
activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 46:1831–1840. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim DE, Kim Y, Cho DH, Jeong SY, Kim SB,
Suh N, Lee JS, Choi EK, Koh JY, Hwang JJ and Kim CS: Raloxifene
induces autophagy-dependent cell death in breast cancer cells via
the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Mol Cells.
38:138–144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun WL, Chen J, Wang YP and Zheng H:
Autophagy protects breast cancer cells from epirubicin-induced
apoptosis and facilitates epirubicin-resistance development.
Autophagy. 7:1035–1044. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kimmelman AC: The dynamic nature of
autophagy in cancer. Genes Dev. 25:1999–2010. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Akkoç Y, Berrak Ö, Arısan ED, Obakan
PÇoker-Gürkan A and Palavan-Ünsal N: Inhiition of PI3K signaling
triggered apoptotic potential of curcumin which is hindered by
Bcl-2 through activation of autophagy in MCF-7 cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 71:161–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kelly PN and Strasser A: The role of Bcl-2
and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer
therapy. Cell Death Differ. 18:1414–1424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang XH, Kleeman LK, Jiang HH, Gordon G,
Goldman JE, Berry G, Herman B and Levine B: Protection against
fatal Sindbis virus encephalitis by beclin, a novel
Bcl-2-interacting protein. J Virol. 72:8586–8596. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yu J, Chen C, Xu T, Yan M, Xue B, Wang Y,
Liu C, Zhong T, Wang Z, Meng X, et al: Pseudolaric acid B activates
autophagy in MCF 7 human breast cancer cells to prevent cell death.
Oncol Lett. 11:1731–1737. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|