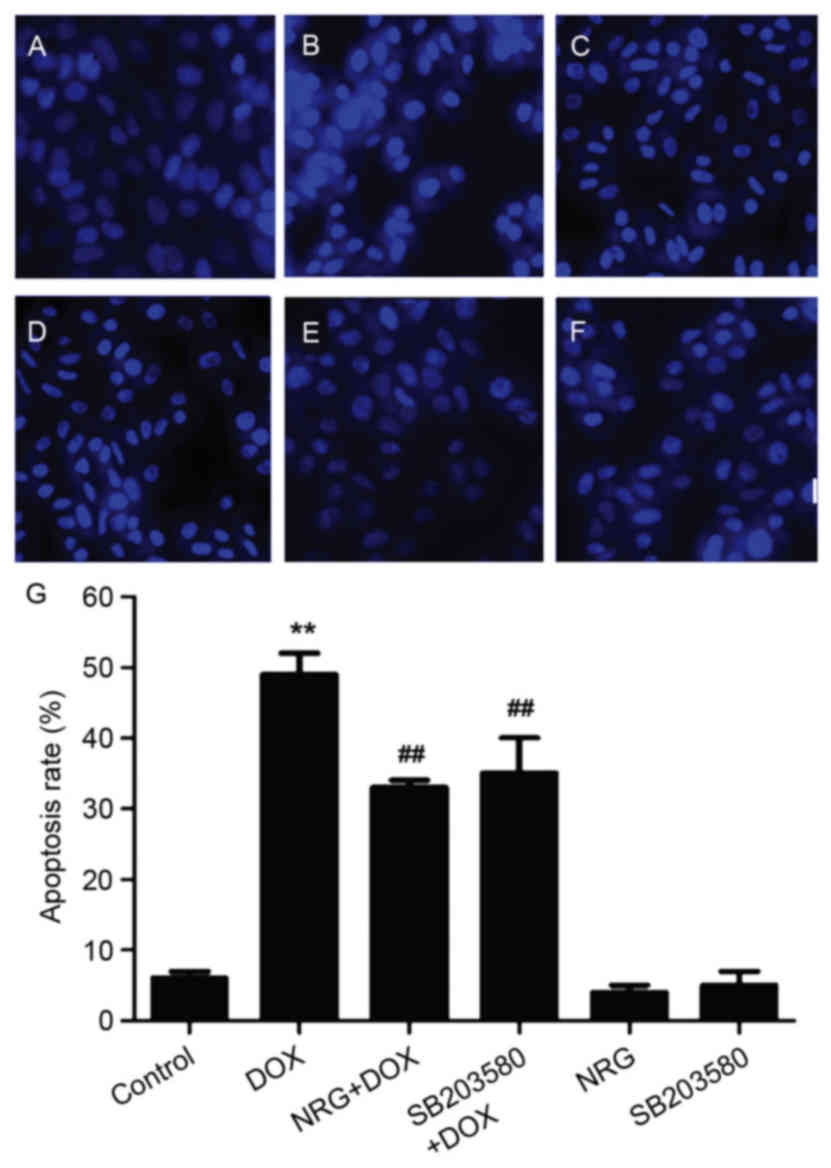
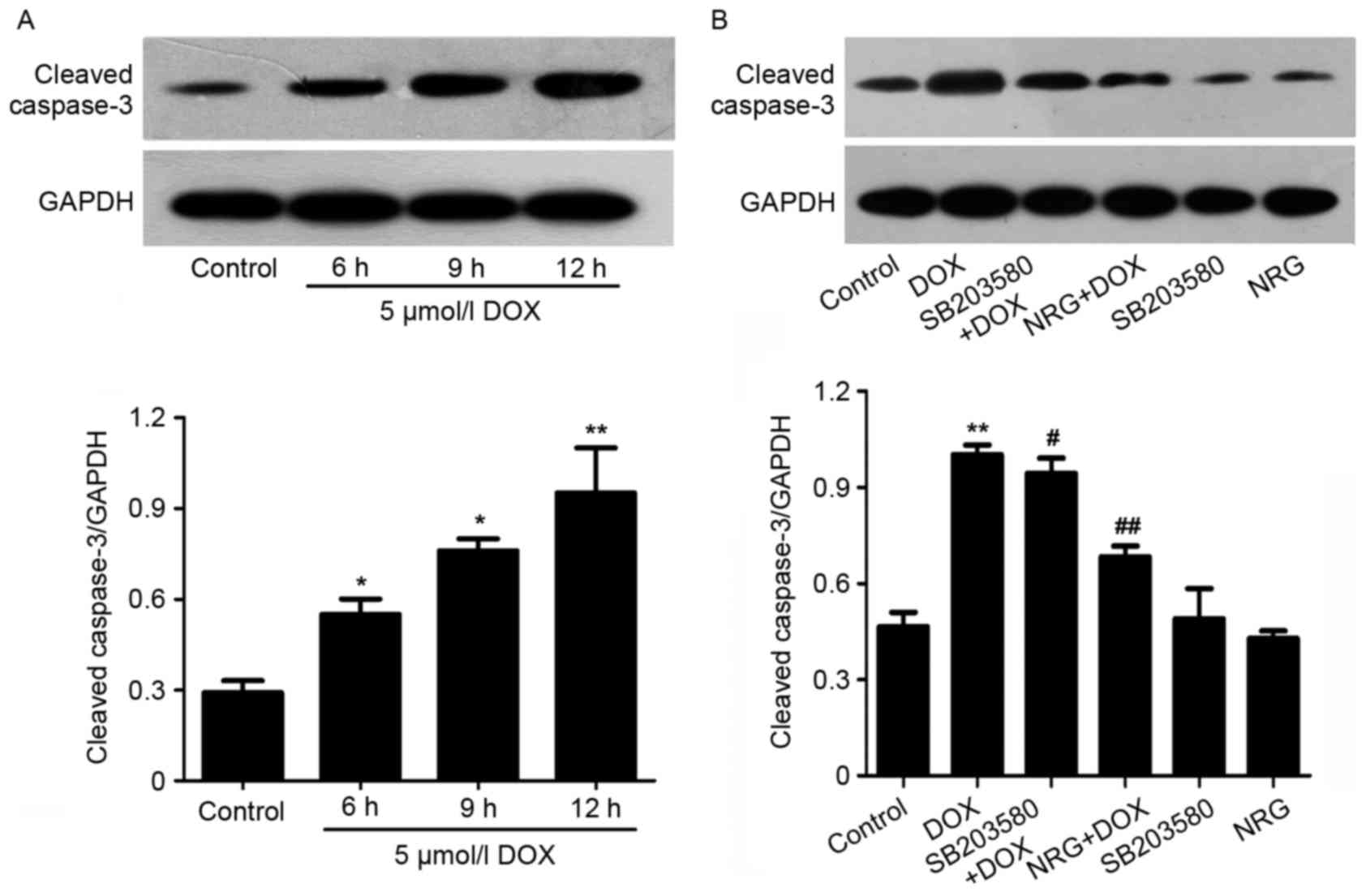
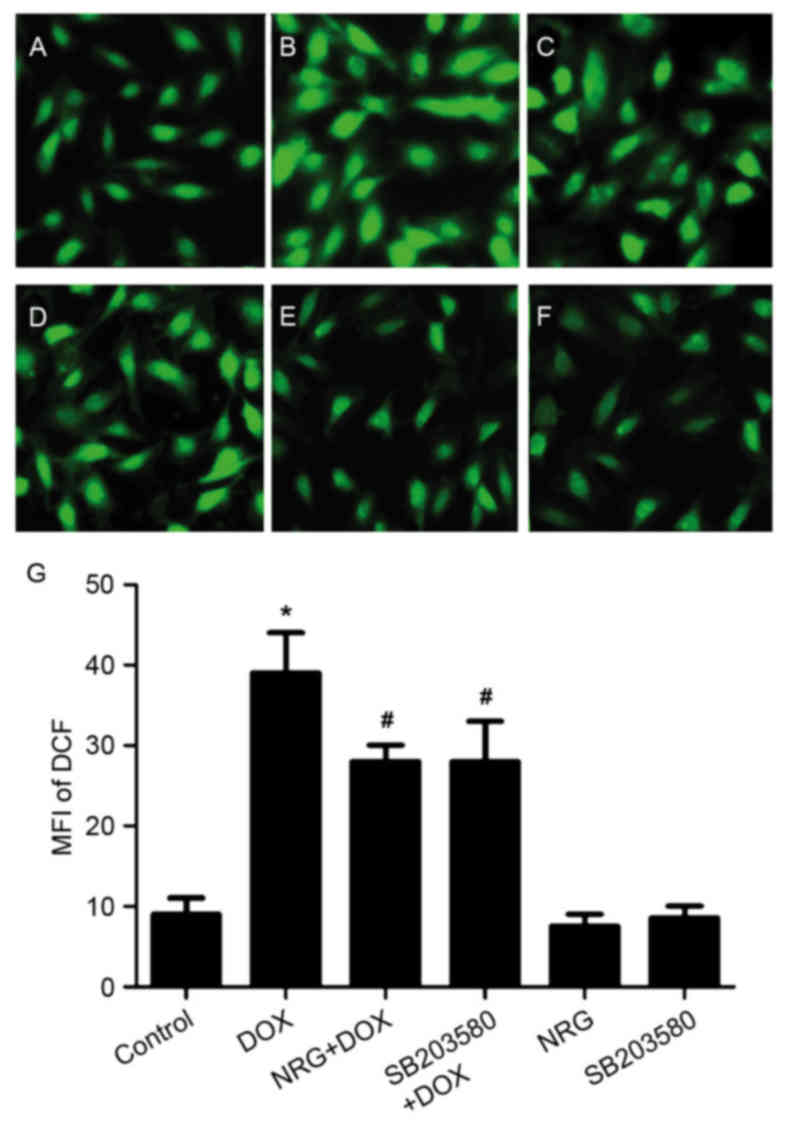
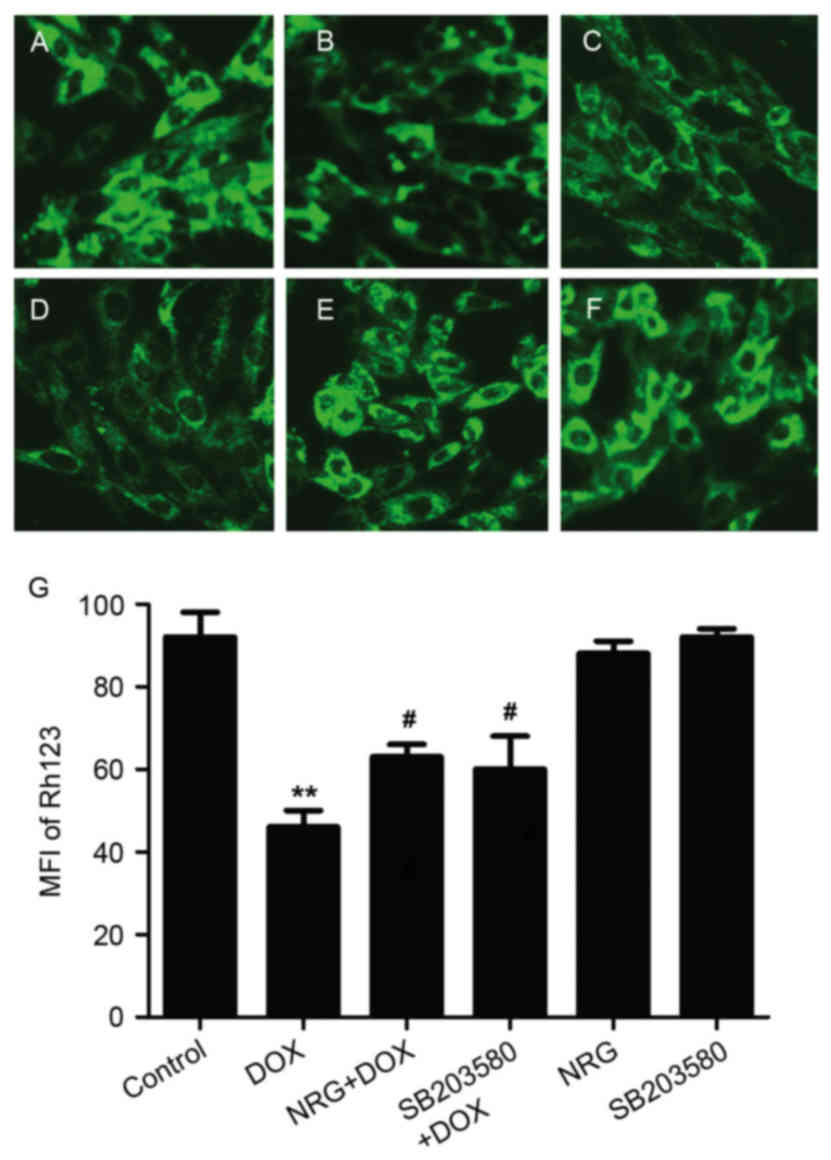
|
1
|
Bai J, Ma M, Cai M, Xu F, Chen J, Wang G,
Shuai X and Tao K: Inhibition enhancer of zeste homologue 2
promotes senescence and apoptosis induced by doxorubicin in p53
mutant gastric cancer cells. Cell Prolif. 47:211–218. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hrdina R, Gersl V, Klimtová I, Simůnek T,
Machácková J and Adamcová M: Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity.
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 43:75–82. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Scully RE and Lipshultz SE: Anthracycline
cardiotoxicity in long-term survivors of childhood cancer.
Cardiovasc Toxicol. 7:122–128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ludke AR, Al-Shudiefat AA, Dhingra S,
Jassal DS and Singal PK: A concise description of cardioprotective
strategies in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 87:756–763. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alkreathy H, Damanhouri ZA, Ahmed N,
Slevin M, Ali SS and Osman AM: Aged garlic extract protects against
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
48:951–956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu MF, Tang PL, Qian ZM and Ashraf M:
Effects by doxorubicin on the myocardium are mediated by oxygen
free radicals. Life Sci. 68:889–901. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Simůnek T, Stérba M, Popelová O, Adamcová
M, Hrdina R and Gersl V: Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity:
Overview of studies examining the roles of oxidative stress and
free cellular iron. Pharmacol Rep. 61:154–171. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Singal PK, Li T, Kumar D, Danelisen I and
Iliskovic N: Adriamycin-induced heart failure: Mechanism and
modulation. Mol Cell Biochem. 207:77–86. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Spallarossa P, Garibaldi S, Altieri P,
Fabbi P, Manca V, Nasti S, Rossettin P, Ghigliotti G, Ballestrero
A, Patrone F, et al: Carvedilol prevents doxorubicin-induced free
radical release and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes in vitro. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 37:837–846. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu W, Zou Y, Aikawa R, Harada K, Kudoh S,
Uozumi H, Hayashi D, Gu Y, Yamazaki T, Nagai R, et al: MAPK
superfamily plays an important role in daunomycin-induced apoptosis
of cardiac myocytes. Circulation. 100:2100–2107. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kang YJ, Zhou ZX, Wang GW, Buridi A and
Klein JB: Suppression by metallothionein of doxorubicin-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis through inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 275:13690–13698. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo RM, Xu WM, Lin JC, Mo LQ, Hua XX, Chen
PX, Wu K, Zheng DD and Feng JQ: Activation of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB
pathway contributes to doxorubicin-induced inflammation and
cytotoxicity in H9c2 cardiac cells. Mol Med Rep. 8:603–608. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Zhao Z, Liu J, Huang N, Long D, Wang
J, Li X and Liu Y: MEK/ERK and p38 MAPK regulate chondrogenesis of
rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through delicate interaction
with TGF-beta 1/Smads pathway. Cell Prolif. 43:333–343. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Force T and Bonventre JV: Growth factors
and mitogen-activated protein kinases. Hypertension. 31:152–161.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hussein RH and Khalifa FK: The protective
role of ellagitannins flavonoids pretreatment against
N-nitrosodiethylamine induced-hepatocellular carcinoma. Saudi J
Biol Sci. 21:589–596. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lohani M, Ahuja M, Buabeid MA, Dean S,
Dennis S, Suppiramaniam V, Kemppainen B and Dhanasekaran M:
Anti-oxidative and DNA protecting effects of flavonoids-rich
Scutellaria lateriflora. Nat Prod Commun. 8:1415–1418.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huxley RR and Neil HA: The relation
between dietary flavonol intake and coronary heart disease
mortality: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur J
Clin Nutr. 57:904–908. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bast A, Kaiserová H, den Hartog GJ, Haenen
GR and van der Vijgh WJ: Protectors against doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity: Flavonoids. Cell Biol Toxicol. 23:39–47. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Du Y, Guo H and Lou H: Grape seed
polyphenols protect cardiac cells from apoptosis via induction of
endogenous antioxidant enzymes. J Agric Food Chem. 55:1695–1701.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bagchi D, Sen CK, Ray SD, Das DK, Bagchi
M, Preuss HG and Vinson JA: Molecular mechanisms of
cardioprotection by a novel grape seed proanthocyanidin extract.
Mutat Res 523–524. 1–97. 2003.
|
|
21
|
Kong X, Qiu D, Ye X, Bao J, Sui Z, Fan J
and Xiang W: Physicochemical and crystalline properties of
heat-moisture-treated rice starch: Combined effects of moisture and
duration of heating. J Sci Food Agric. 95:2874–2879. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ahmad SF, Attia SM, Bakheet SA, Zoheir KM,
Ansari MA, Korashy HM, Abdel-Hamied HE, Ashour AE and Abd-Allah AR:
Naringin attenuates the development of carrageenan-induced acute
lung inflammation through inhibition of NF-κb, STAT3 and
pro-inflammatory mediators and enhancement of IκBα and
anti-inflammatory cytokines. Inflammation. 38:846–857. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choe SC, Kim HS, Jeong TS, Bok SH and Park
YB: Naringin has an antiatherogenic effect with the inhibition of
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in hypercholesterolemic rabbits.
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 38:947–955. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ali MM and El Kader MA: The influence of
naringin on the oxidative state of rats with streptozotocin-induced
acute hyperglycaemia. Z Naturforsch C. 59:726–733. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang XY, Yang CT, Zheng DD, Mo LQ, Lan AP,
Yang ZL, Hu F, Chen PX, Liao XX and Feng JQ: Hydrogen sulfide
protects H9c2 cells against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell
Biochem. 363:419–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ozyürek M, Akpinar D, Bener M, Türkkan B,
Güçlü K and Apak R: Novel oxime based flavanone, naringin-oxime:
Synthesis, characterization and screening for antioxidant activity.
Chem Biol Interact. 212:40–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu J, Mao W, Ding B and Liang CS:
ERKs/p53 signal transduction pathway is involved in
doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells and cardiomyocytes. Am
J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H1956–H1965. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ozcelik B, Kartal M and Orhan I:
Cytotoxicity, antiviral and antimicrobial activities of alkaloids,
flavonoids, and phenolic acids. Pharm Biol. 49:396–402. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tan TW, Chou YE, Yang WH, Hsu CJ, Fong YC
and Tang CH: Naringin suppress chondrosarcoma migration through
inhibition vascular adhesion molecule-1 expression by modulating
miR-126. Int Immunopharmacol. 22:107–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rajadurai M and Prince PS: Preventive
effect of naringin on cardiac mitochondrial enzymes during
isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats: A transmission
electron microscopic study. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 21:354–361.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rajadurai M and Prince PS: Naringin
ameliorates mitochondrial lipid peroxides, antioxidants and lipids
in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats.
Phytother Res. 23:358–362. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li W, Wang C, Peng J, Liang J, Jin Y, Liu
Q, Meng Q, Liu K and Sun H: Naringin inhibits TNF-a induced
oxidative stress and inflammatory response in HUVECs via Nox4/NF-κB
and PI3K/Akt pathways. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 15:1173–1182. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kanno S, Tomizawa A, Hiura T, Osanai Y,
Shouji A, Ujibe M, Ohtake T, Kimura K and Ishikawa M: Inhibitory
effects of naringenin on tumor growth in human cancer cell lines
and sarcoma S-180-implanted mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:527–530.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takemura G and Fujiwara H:
Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy from the cardiotoxic mechanisms
to management. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 49:330–352. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maejima Y, Adachi S, Morikawa K, Ito H and
Isobe M: Nitric oxide inhibits myocardial apoptosis by preventing
caspase-3 activity via S-nitrosylation. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
38:163–174. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Christiansen S and Autschbach R:
Doxorubicin in experimental and clinical heart failure. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 30:611–616. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen M, Fan ZC, Liu XJ, Deng JL, Yang Q
and Huang DJ: Cell transplantation with a catheter-based approach:
An efficient method for the treatment of heart failure with
multiple lesions. Cell Prolif. 39:471–477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|