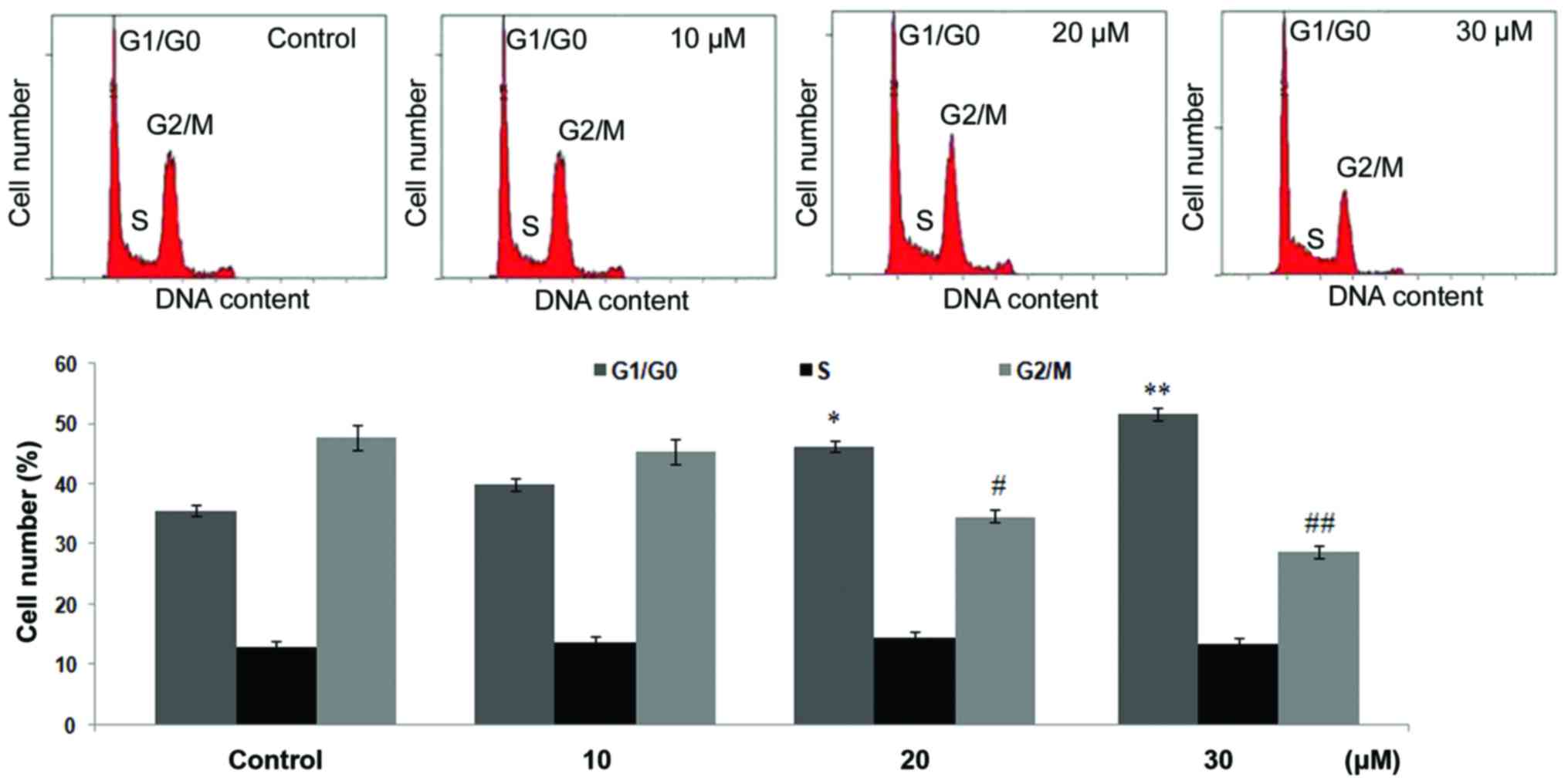
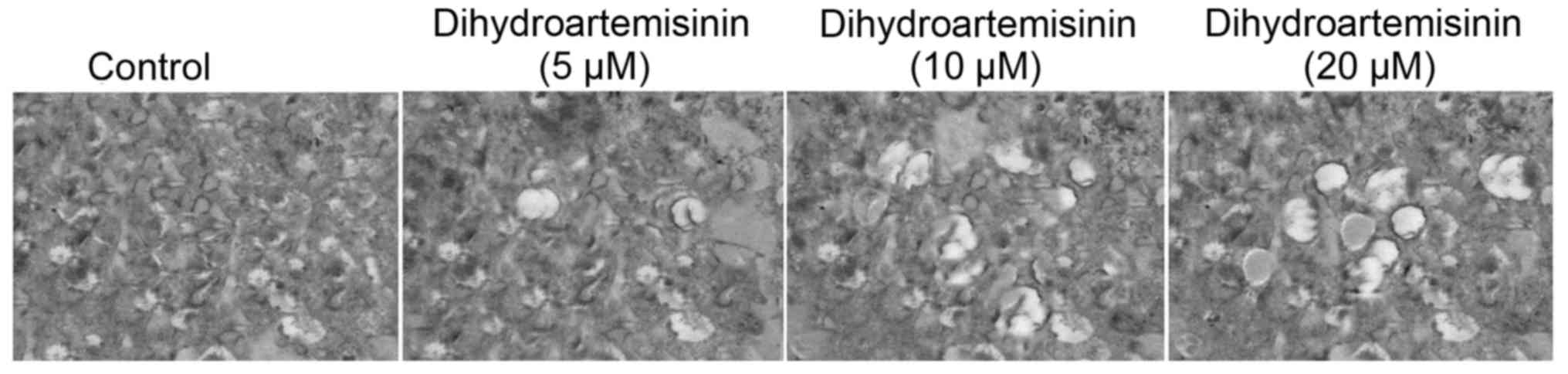
|
1
|
Curran WJ Jr, Scott CB, Horton J, Nelson
JS, Weinstein AS, Fischbach AJ, Chang CH, Rotman M, Asbell SO,
Krisch RE, et al: Recursive partitioning analysis of prognostic
factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group malignant glioma
trials. J Natl Cancer Inst. 85:704–710. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, Rowitch
DH, Louis DN, Cavenee WK and DePinho RA: Malignant glioma: Genetics
and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev. 15:1311–1333. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang SM, Lamborn KR, Malec M, Larson D,
Wara W, Sneed P, Rabbitt J, Page M, Nicholas MK and Prados MD:
Phase II study of temozolomide and thalidomide with radiation
therapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 60:353–357. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fine HA, Wen PY, Maher EA, Viscosi E,
Batchelor T, Lakhani N, Figg WD, Purow BW and Borkowf CB: Phase II
trial of thalidomide and carmustine for patients with recurrent
highgrade gliomas. J Clin Oncol. 21:2299–2304. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marx GM, Pavlakis N, McCowatt S, Boyle FM,
Levi JA, Bell DR, Cook R, Biggs M, Little N and Wheeler HR: Phase
II study of thalidomide in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma
multiforme. J Neurooncol. 54:31–38. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meshnick SR: Artemisinin: Mechanisms of
action, resistance and toxicity. Int J Parasitol. 32:1655–1660.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
O'Neill PM: Medicinal chemistry: A worthy
adversary for malaria. Nature. 430:838–839. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Efferth T, Dunstan H, Sauerbrey A, Miyachi
H and Chitambar CR: The anti-malarial artesunate is also active
against cancer. Int J Oncol. 18:767–773. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang XJ, Ma ZQ, Zhang WP, Lu YB and Wei
EQ: Dihydroartemisinin exerts cytotoxic effects and inhibits
hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha activation in C6 glioma cells. J
Pharm Pharmacol. 59:849–856. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nam W, Tak J, Ryu JK, Jung M, Yook JI, Kim
HJ and Cha IH: Effects of artemisinin and its derivatives on growth
inhibition and apoptosis of oral cancer cells. Head Neck.
29:335–340. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Singh NP and Lai H: Selective toxicity of
dihydroartemisinin and holotransferrin toward human breast cancer
cells. Life Sci. 70:49–56. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen T, Li M, Zhang R and Wang H:
Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis and sensitizes human ovarian
cancer cells to carboplatin therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 13:1358–1370.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
O'Reilly T, Wartmann M, Maira SM,
Hattenberger M, Vaxelaire J, Muller M, Ferretti S, Buchdunger E,
Altmann KH and McSheehy PM: Patupilone (epothilone B, EPO906) and
imatinib (STI571, Glivec) in combination display enhanced
antitumour activity in vivo against experimental rat C6 glioma.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 55:307–317. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lokker NA, Sullivan CM, Hollenbach SJ,
Israel MA and Giese NA: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
autocrine signaling regulates survival and mitogenic pathways in
glioblastoma cells: Evidence that the novel PDGF-C and PDGF-D
ligands may play a role in the development of brain tumors. Cancer
Res. 62:3729–3735. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaygisiz Z, Erkasap N, Yazihan N, Sayar K,
Ataoglu H, Uyar R and Ikizler M: Erythropoietin changes
contractility, cAMP, and nitrite levels of isolated rat hearts. J
Physiol Sci. 56:247–251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Buchdunger E, Cioffi CL, Law N, Stover D,
Ohno-Jones S, Druker BJ and Lydon NB: Abl protein-tyrosine kinase
inhibitor STI571 inhibits in vitro signal transduction mediated by
c-kit and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 295:139–145. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu C, Krystal G, Dent P and Grant S:
Flavopiridol potentiates STI571-induced mitochondrial damage and
apoptosis in BCR-ABL-positive human leukemia cells. Clin Cancer
Res. 8:2976–2984. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Uziel O, Fenig E, Nordenberg J, Beery E,
Reshef H, Sandbank J, Birenbaum M, Bakhanashvili M, Yerushalmi R,
Luria D and Lahav M: Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec) downregulates
telomerase activity and inhibits proliferation in
telomerase-expressing cell lines. Br J Cancer. 92:1881–1891. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sokołowska P and Nowak JZ: Constitutive
activity of beta-adrenergic receptors in C6 glioma cells. Pharmacol
Rep. 57:659–663. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Grobben B, De Deyn PP and Slegers H: Rat
C6 glioma as experimental model system for the study of
glioblastoma growth and invasion. Cell Tissue Res. 310:257–270.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jaiswal BS and Conti M: Calcium regulation
of the soluble adenylyl cyclase expressed in mammalian spermatozoa.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:pp. 10676–10681. 2003; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baillie GS and Houslay MD: Arrestin times
for compartmentalised cAMP signalling and phosphodiesterase-4
enzymes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:129–134. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Antonsson B and Martinou JC: The Bcl-2
protein family. Exp Cell Res. 256:50–57. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Salvesen GS and Dixit VM: Caspases:
Intracellular signaling by proteolysis. Cell. 91:443–446. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|