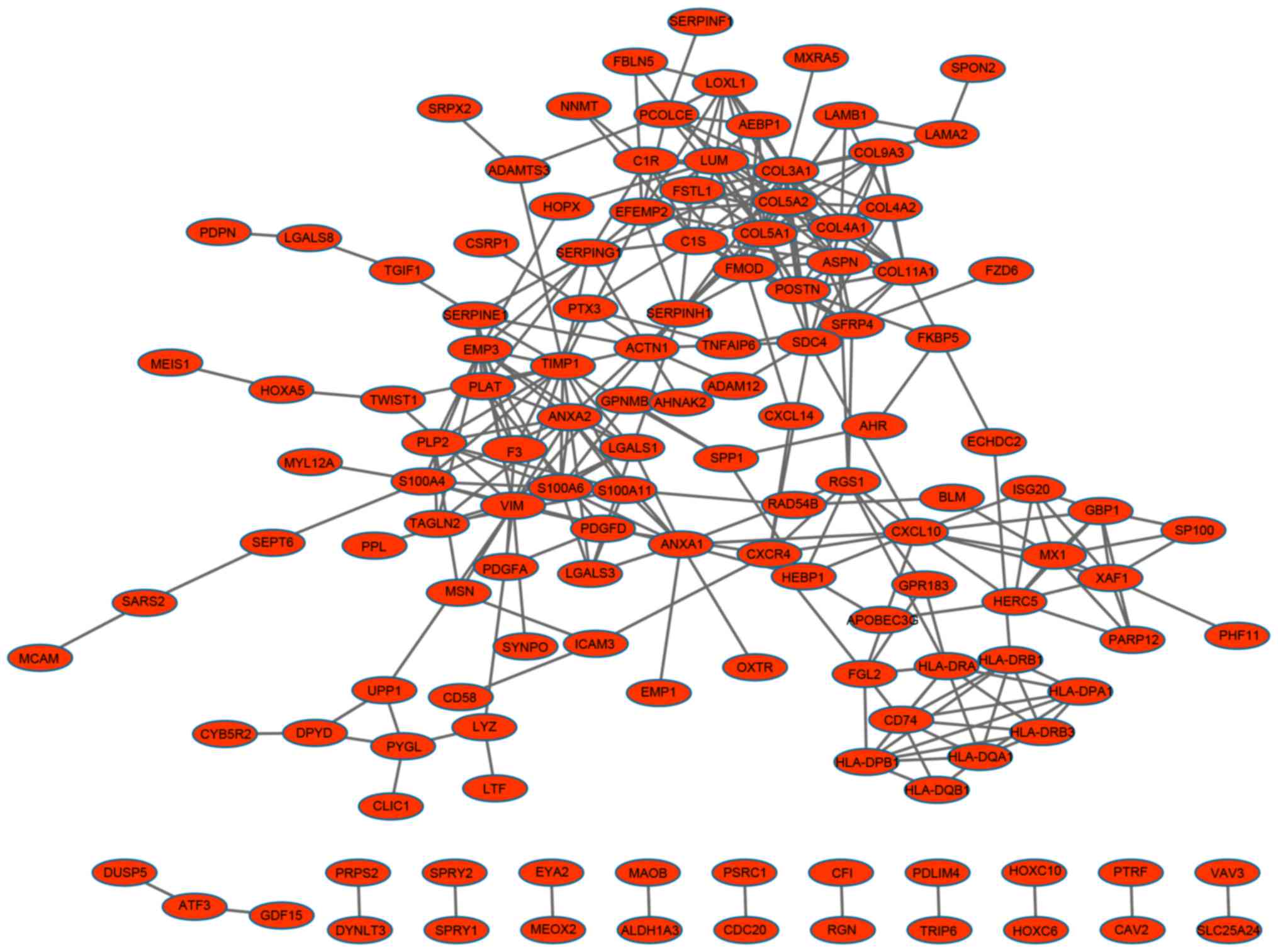
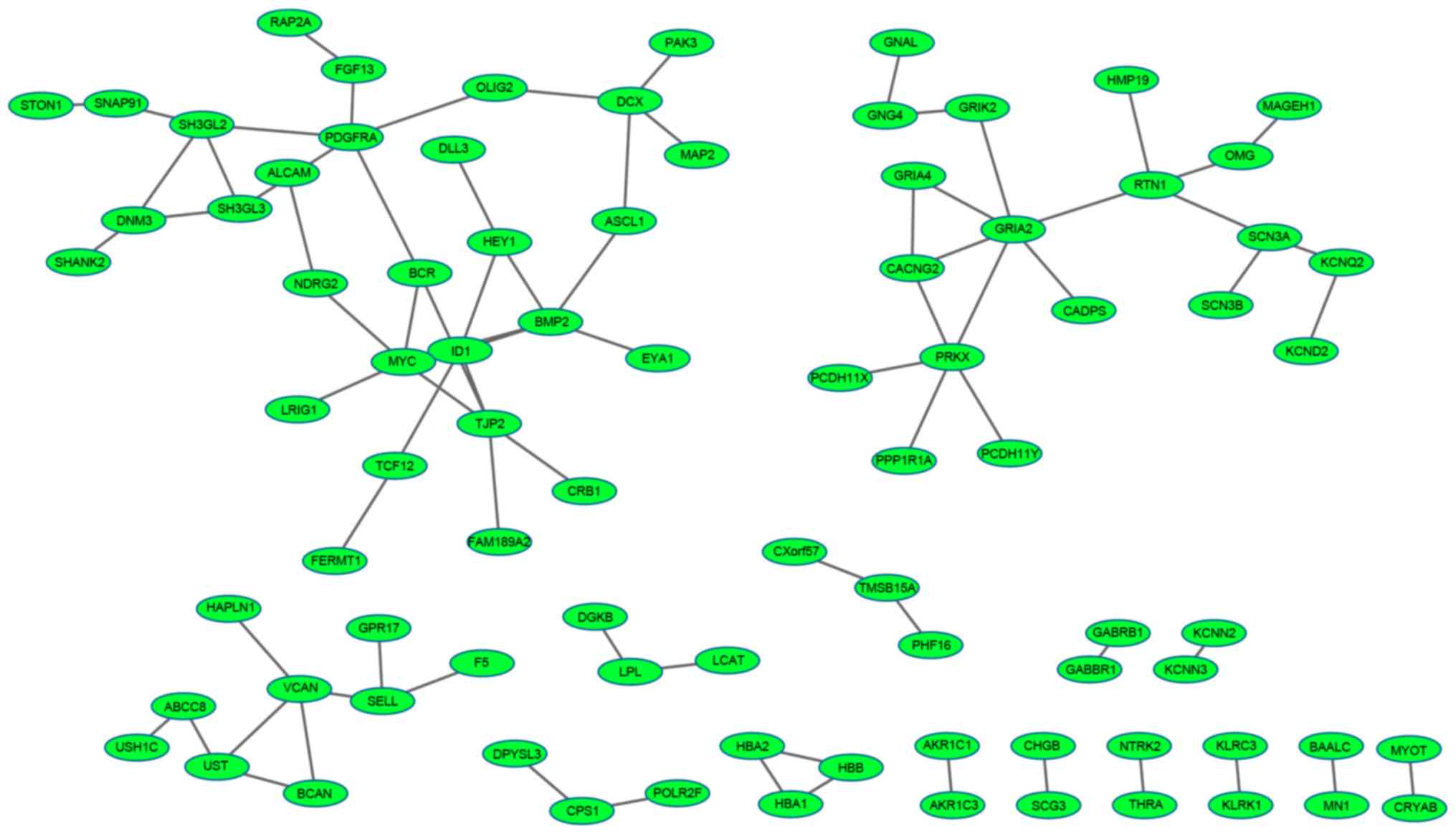
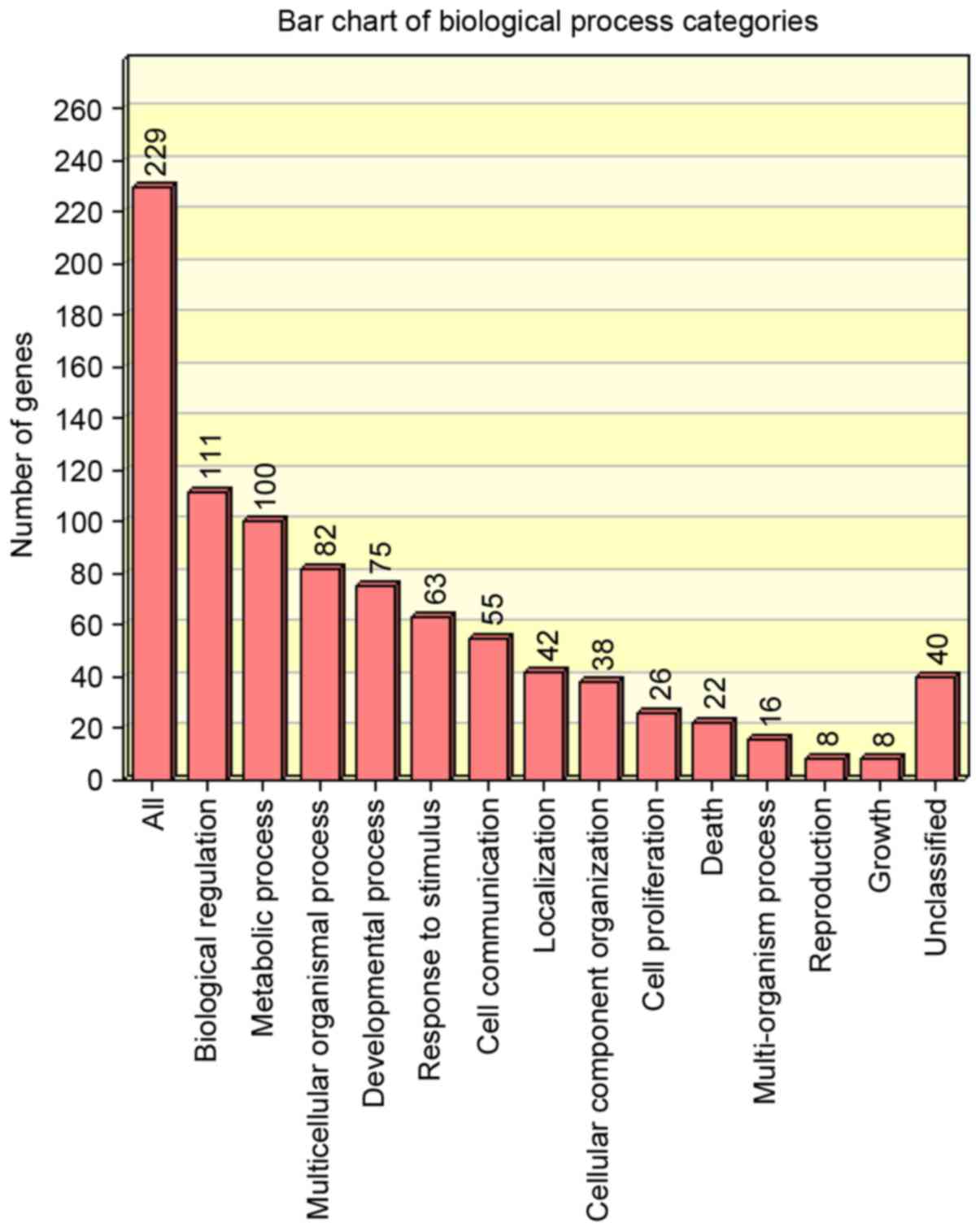
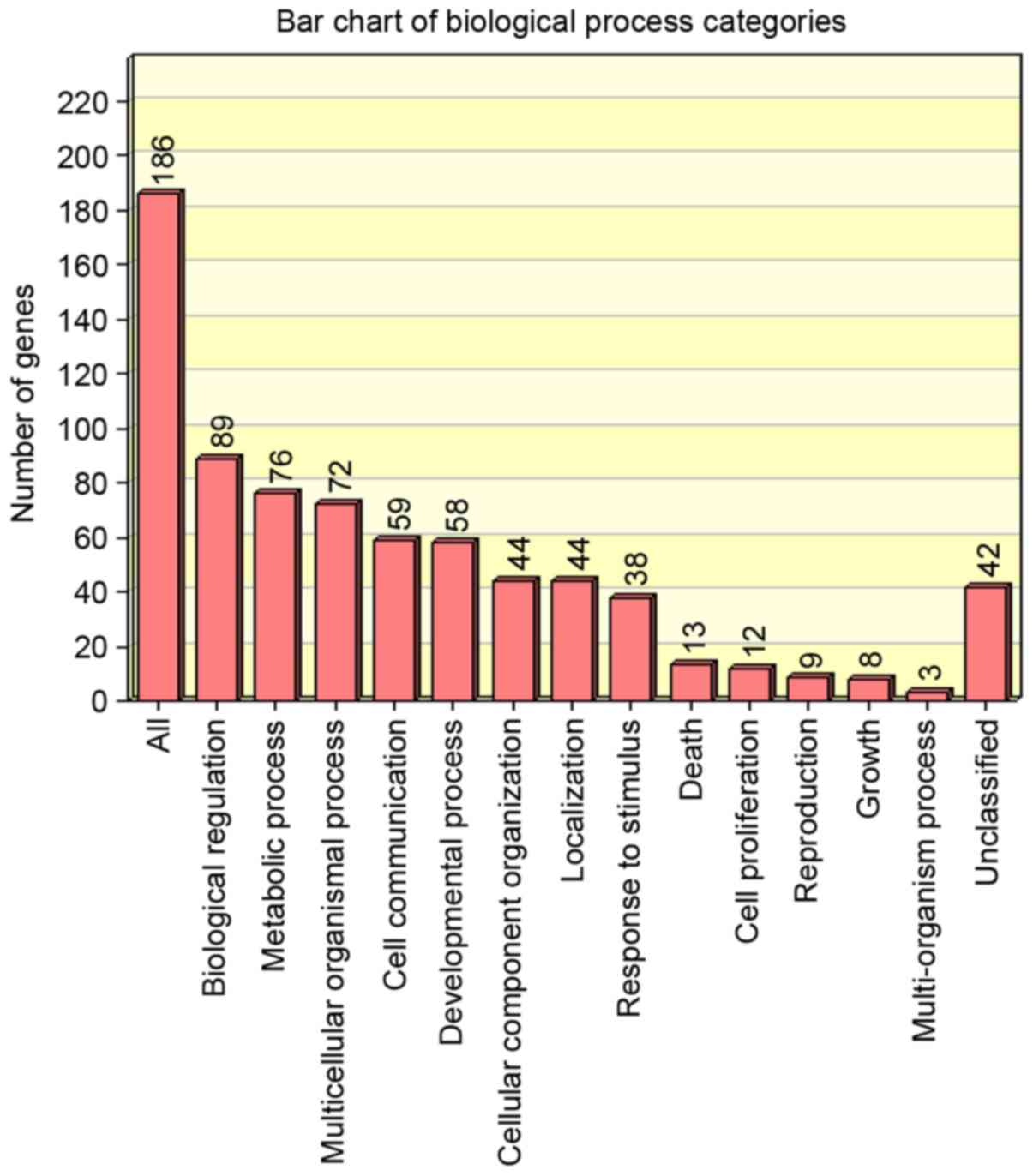
|
1
|
Kim TY, Zhong S, Fields CR, Kim JH and
Robertson KD: Epigenomic profiling reveals novel and frequent
targets of aberrant DNA methylation-mediated silencing in malignant
glioma. Cancer Res. 66:7490–7501. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan D, Wei X, Liu M, Feng S, Tian X, Feng
X and Zhang X: Adenovirus mediated transfer of p53, GM-CSF and B7-1
suppresses growth and enhances immunogenicity of glioma cells.
Neurol Res. 32:502–509. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Christensen BC, Smith AA, Zheng S,
Koestler DC, Houseman EA, Marsit CJ, Wiemels JL, Nelson HH, Karagas
MR, Wrensch MR, et al: DNA methylation, isocitrate dehydrogenase
mutation, and survival in glioma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:143–153.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Noushmehr H, Weisenberger DJ, Diefes K,
Phillips HS, Pujara K, Berman BP, Pan F, Pelloski CE, Sulman EP,
Bhat KP, et al: Identification of a CpG island methylator phenotype
that defines a distinct subgroup of glioma. Cancer Cell.
17:510–522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fang F, Turcan S, Rimner A, Kaufman A,
Giri D, Morris LG, Shen R, Seshan V, Mo Q, Heguy A, et al: Breast
cancer methylomes establish an epigenomic foundation for
metastasis. Sci Transl Med. 3:75ra252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng YW, Pincas H, Bacolod MD, Schemmann
G, Giardina SF, Huang J, Barral S, Idrees K, Khan SA, Zeng Z, et
al: CpG island methylator phenotype associates with low-degree
chromosomal abnormalities in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
14:6005–6013. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weller M, Stupp R, Reifenberger G, Brandes
AA, van den Bent MJ, Wick W and Hegi ME: MGMT promoter methylation
in malignant gliomas: Ready for personalized medicine? Nat Rev
Neurol. 6:39–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hegi ME, Liu L, Herman JG, Stupp R, Wick
W, Weller M, Mehta MP and Gilbert MR: Correlation of
O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter
methylation with clinical outcomes in glioblastoma and clinical
strategies to modulate MGMT activity. J Clin Oncol. 26:4189–4199.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bruna A, Darken RS, Rojo F, Ocaña A,
Peñuelas S, Arias A, Paris R, Tortosa A, Mora J, Baselga J and
Seoane J: High TGFbeta-Smad activity confers poor prognosis in
glioma patients and promotes cell proliferation depending on the
methylation of the PDGF-B gene. Cancer Cell. 11:147–160. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wiencke JK, Zheng S, Jelluma N, Tihan T,
Vandenberg S, Tamgüney T, Baumber R, Parsons R, Lamborn KR, Berger
MS, et al: Methylation of the PTEN promoter defines low-grade
gliomas and secondary glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 9:271–279. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mueller W, Nutt CL, Ehrich M,
Riemenschneider MJ, Von Deimling A, Van Den Boom D and Louis DN:
Downregulation of RUNX3 and TES by hypermethylation in
glioblastoma. Oncogene. 26:583–593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yi JM, Tsai HC, Glöckner SC, Lin S, Ohm
JE, Easwaran H, James CD, Costello JF, Riggins G, Eberhart CG, et
al: Abnormal DNA methylation of CD133 in colorectal and
glioblastoma tumors. Cancer Res. 68:8094–8103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Amatya VJ, Naumann U, Weller M and Ohgaki
H: TP53 promoter methylation in human gliomas. Acta Neuropathol.
110:178–184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Turcan S, Rohle D, Goenka A, Walsh LA,
Fang F, Yilmaz E, Campos C, Fabius AW, Lu C, Ward PS, et al: IDH1
mutation is sufficient to establish the glioma hypermethylator
phenotype. Nature. 483:479–483. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baysan M, Bozdag S, Cam MC, Kotliarova S,
Ahn S, Walling J, Killian JK, Stevenson H, Meltzer P and Fine HA:
G-cimp status prediction of glioblastoma samples using mRNA
expression data. PLoS One. 7:e478392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Diboun I, Wernisch L, Orengo CA and
Koltzenburg M: Microarray analysis after RNA amplification can
detect pronounced differences in gene expression using limma. BMC
Genomics. 7:2522006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gene Ontology Consortium, ; Blake JA,
Dolan M, Drabkin H, Hill DP, Li N, Sitnikov D, Bridges S, Burgess
S, Buza T, et al: Gene Ontology annotations and resources. Nucleic
Acids Res. 41(Database issue): D530–D535. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39(Database issue): D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang B, Kirov S and Snoddy J: WebGestalt:
An integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological
contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 33(Web server issue): W741–W748. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yao ZQ and Lu YC: Research on molecular
mechanism of human glioma and its clinical application. Chin J
Cancer Biother. 15:90–94. 2008.
|
|
24
|
Huse JT and Holland EC: Targeting brain
cancer: Advances in the molecular pathology of malignant glioma and
medulloblastoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:319–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Clubb BH and Shivers RR: Extracellular
matrix regulates microfilament and vinculin organization in
C6-glioma cells. Acta Neuropathol. 91:31–40. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bauke AC, Sasse S, Matzat T and Klämbt C:
A transcriptional network controlling glial development in the
Drosophila visual system. Development. 142:2184–2193. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ulrich TA, de Juan Pardo EM and Kumar S:
The mechanical rigidity of the extracellular matrix regulates the
structure, motility, and proliferation of glioma cells. Cancer Res.
69:4167–4174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee SJ, Yoo HJ, Bae YS, Kim HJ and Lee ST:
TIMP-1 inhibits apoptosis in breast carcinoma cells via a pathway
involving pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein and c-Src. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 312:1196–1201. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Groft LL, Muzik H, Rewcastle NB, Johnston
RN, Knäuper V, Lafleur MA, Forsyth PA and Edwards DR: Differential
expression and localization of TIMP-1 and TIMP-4 in human gliomas.
Br J Cancer. 85:55–63. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aaberg-Jessen C, Christensen K, Offenberg
H, Bartels A, Dreehsen T, Hansen S, Schrøder HD, Brünner N and
Kristensen BW: Low expression of tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) in glioblastoma predicts longer
patient survival. J Neurooncol. 95:117–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Crocker M, Ashley S, Giddings I, Petrik V,
Hardcastle A, Aherne W, Pearson A, Bell BA, Zacharoulis S and
Papadopoulos MC: Serum angiogenic profile of patients with
glioblastoma identifies distinct tumor subtypes and shows that
TIMP-1 is a prognostic factor. Neuro Oncol. 13:99–108. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yamasaki T, Seki N, Yamada Y, Yoshino H,
Hidaka H, Chiyomaru T, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M and
Enokida H: Tumor suppressive microRNA-138 contributes to cell
migration and invasion through its targeting of vimentin in renal
cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 41:805–817. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Satelli A and Li S: Vimentin in cancer and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 68:3033–3046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee J, Son MJ, Woolard K, Donin NM, Li A,
Cheng CH, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Walling J, Ahn S, et al:
Epigenetic-mediated dysfunction of the bone morphogenetic protein
pathway inhibits differentiation of glioblastoma-initiating cells.
Cancer Cell. 13:69–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu C, Tian G, Tu Y, Fu J, Lan C and Wu N:
Expression pattern and clinical prognostic relevance of bone
morphogenetic protein-2 in human gliomas. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
39:625–631. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang J, Wang H, Li Z, Wu Q, Lathia JD,
McLendon RE, Hjelmeland AB and Rich JN: c-Myc is required for
maintenance of glioma cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 3:e37692008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jensen NA, Pedersen KM, Lihme F, Rask L,
Nielsen JV, Rasmussen TE and Mitchelmore C: Astroglial c-Myc
overexpression predisposes mice to primary malignant gliomas. J
Biol Chem. 278:8300–8308. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Puputti M, Tynninen O, Sihto H, Blom T,
Mäenpää H, Isola J, Paetau A, Joensuu H and Nupponen NN:
Amplification of KIT PDGFRA, VEGFR2, and EGFR in gliomas. Mol
Cancer Res. 4:927–934. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Giannini C, Sarkaria JN, Saito A, Uhm JH,
Galanis E, Carlson BL, Schroeder MA and James CD: Patient tumor
EGFR and PDGFRA gene amplifications retained in an invasive
intracranial xenograft model of glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro
Oncol. 7:164–176. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Silber J, Lim DA, Petritsch C, Persson AI,
Maunakea AK, Yu M, Vandenberg SR, Ginzinger DG, James CD, Costello
JF, et al: miR-124 and miR-137 inhibit proliferation of
glioblastoma multiforme cells and induce differentiation of brain
tumor stem cells. BMC Med. 6:142008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fowler A, Thomson D, Giles K, Maleki S,
Mreich E, Wheeler H, Leedman P, Biggs M, Cook R, Little N, et al:
miR-124a is frequently down-regulated in glioblastoma and is
involved in migration and invasion. Eur J Cancer. 47:953–963. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kuroda S, Fukata M, Nakagawa M, Fujii K,
Nakamura T, Ookubo T, Izawa I, Nagase T, Nomura N, Tani H, et al:
Role of IQGAP1, a target of the small GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1, in
regulation of E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. Science.
281:832–835. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Noritake J, Watanabe T, Sato K, Wang S and
Kaibuchi K: IQGAP1: A key regulator of adhesion and migration. J
Cell Sci. 118:2085–2092. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li Y, Guessous F, Zhang Y, Dipierro C,
Kefas B, Johnson E, Marcinkiewicz L, Jiang J, Yang Y, Schmittgen
TD, et al: MicroRNA-34a inhibits glioblastoma growth by targeting
multiple oncogenes. Cancer Res. 69:7569–7576. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Duensing A,
Mcgreevey L, Chen CJ, Joseph N, Singer S, Griffith DJ, Haley A,
Town A, et al: PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal
stromal tumors. Science. 299:708–710. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Silber J, Jacobsen A, Ozawa T, Harinath G,
Holland EC, Sander C and Huse JT: Abstract B15: Repression of
PDGFRA-targeting miR-34a promotes tumorigenesis in proneural
malignant gliomas. Cancer Res. 72 Suppl 2:B152012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Swart GW: Activated leukocyte cell
adhesion molecule (CD166/ALCAM): Developmental and mechanistic
aspects of cell clustering and cell migration. Eur J Cell Biol.
81:313–321. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|