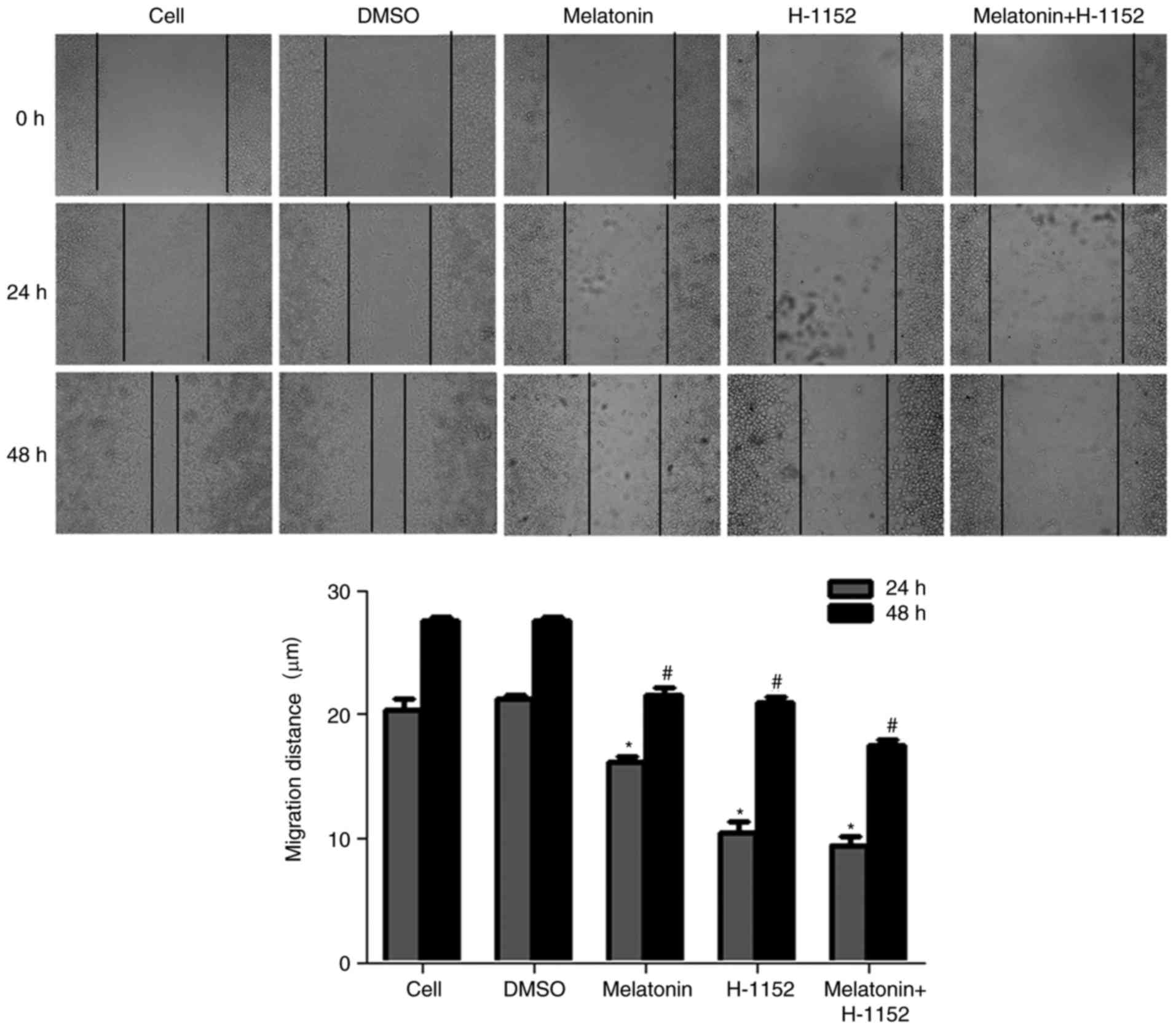
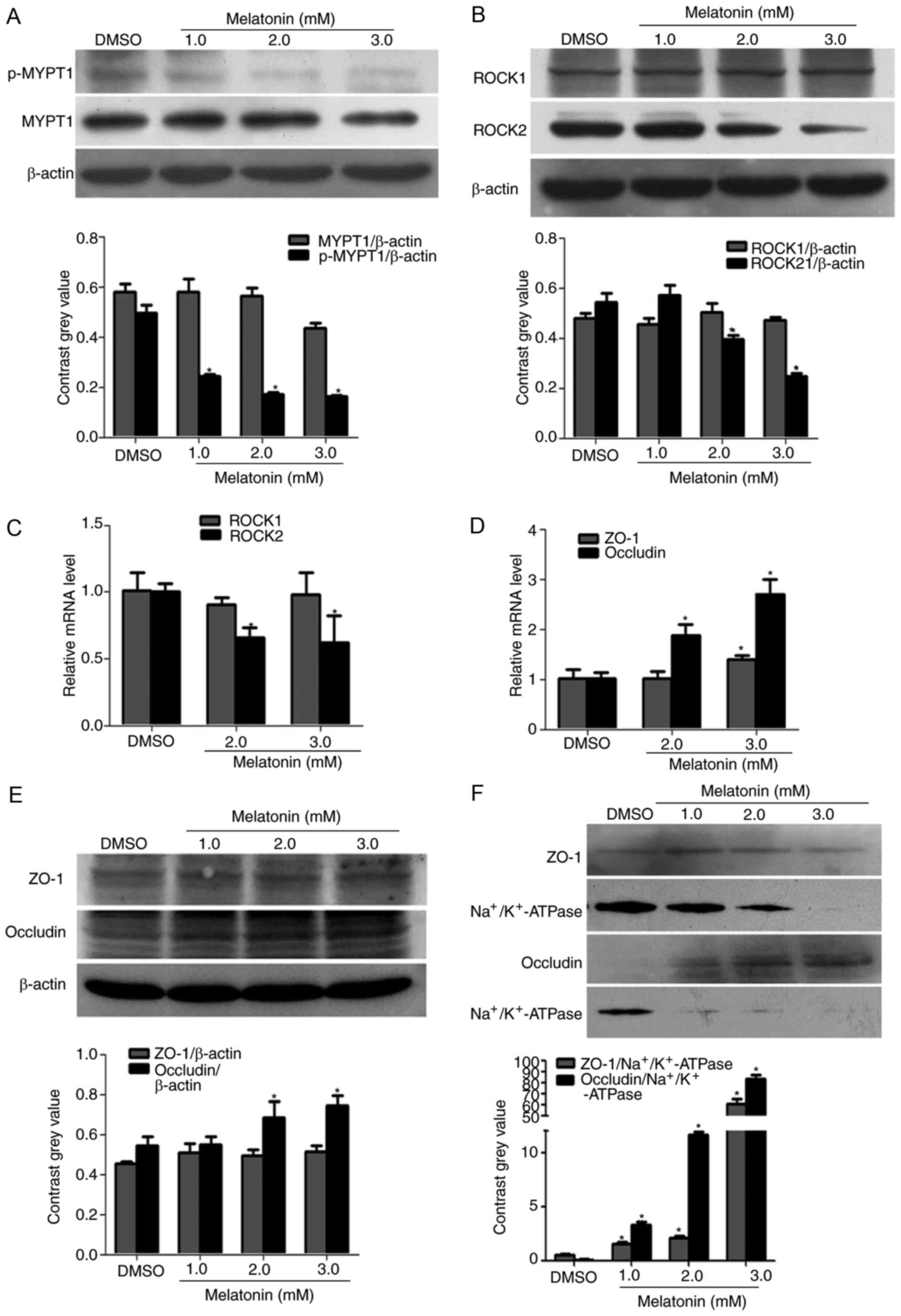
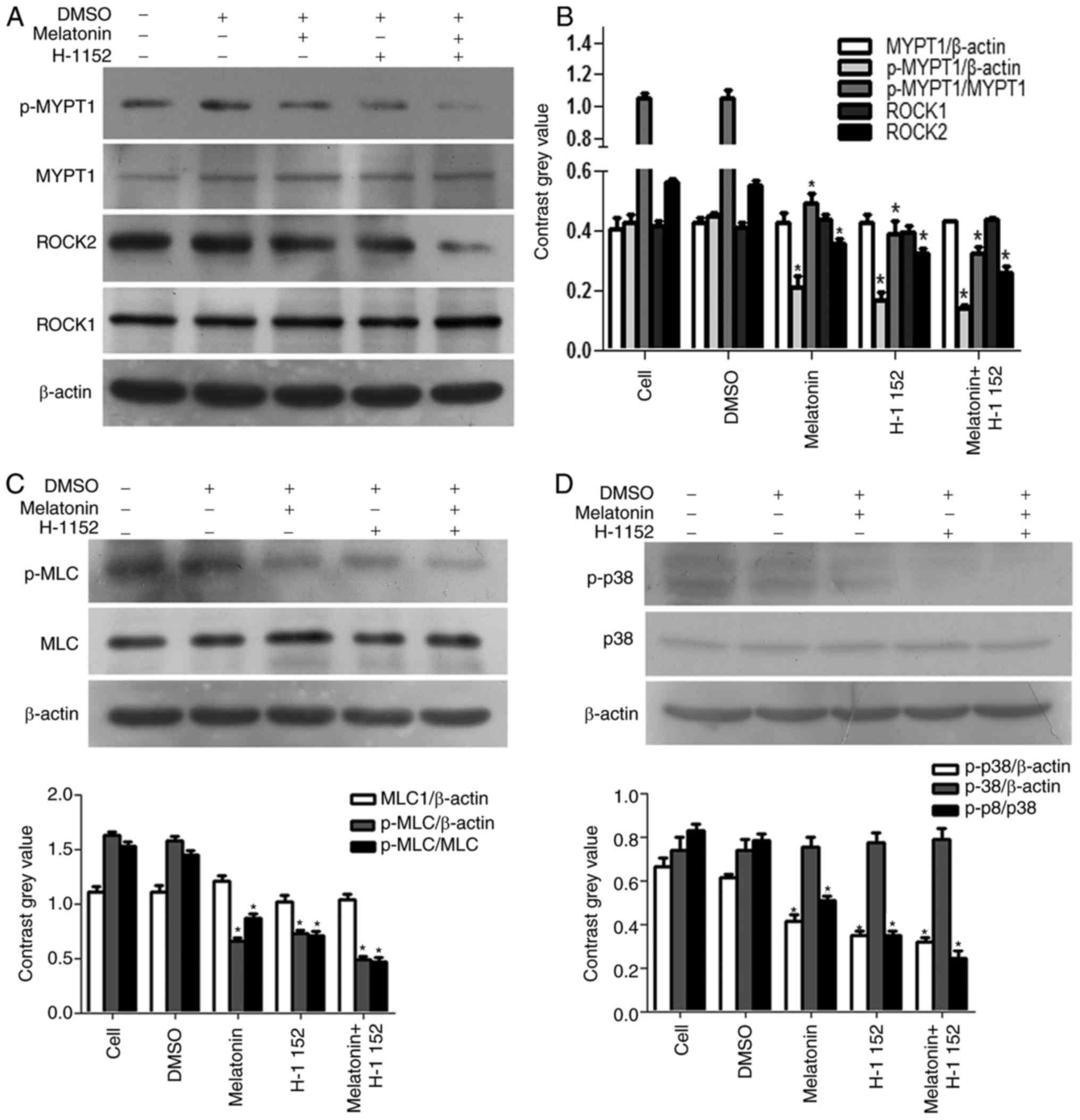
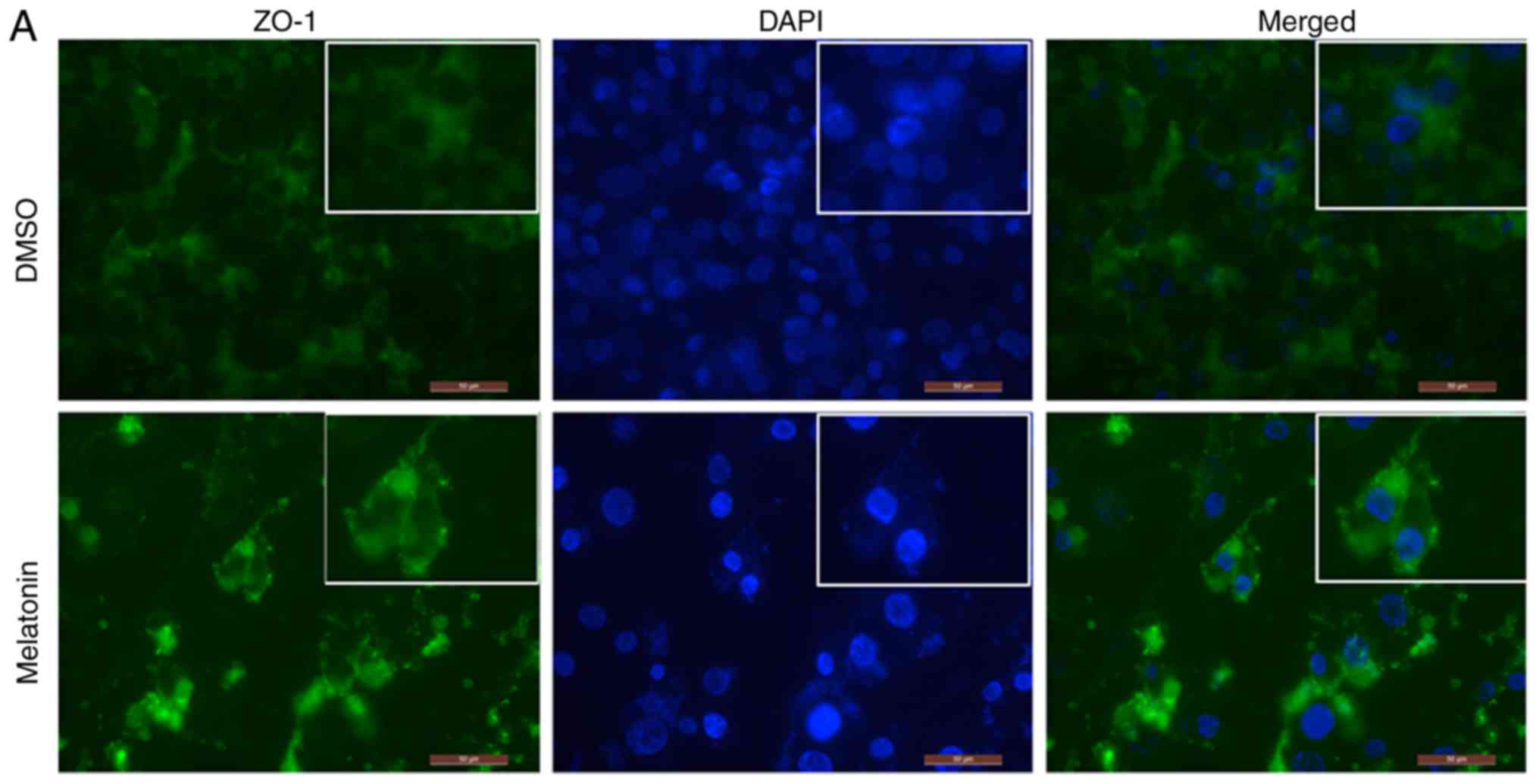
|
1
|
André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L,
Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan
P, Bridgewater J, et al: Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin
as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2343–2351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vellinga TT, Borovski T, de Boer VC,
Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan
P, Bridgewater J, et al: SIRT1/PGC1α dependent increase in
oxidative phosphorylation supports chemotherapy resistance of colon
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2870–2879. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Akbulut KG, Aktas SH and Akbulut H: The
role of melatonin, sirtuin2 and FoXO1 transcription factor in the
aging process of colon in male rats. Biogerontol. 16:99–108. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xu C, Wu A, Zhu H, Fang H, Xu L, Ye J and
Shen J: Melatonin is involved in the apoptosis and necrosis of
pancreatic cancer cell line SW-1990 via modulating of Bcl-2/Bax
balance. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:133–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Guo W, Chen W, Yu W, Tian Y, Fu L,
Shi D, Tong B, Xiao X, Huang W and Deng W: Melatonin potentiates
the antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of ursolic acid in
colon cancer cells by modulating multiple signaling pathways. J
Pineal Res. 54:406–416. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mao L, Yuan L, Slakey LM, Jones FE, Burow
ME and Hill SM: Inhibition of breast cancer cell invasion by
melatonin is mediated through regulation of the p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Breast Cancer
Res. 12:R1072010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yi C, Zhang Y, Yu Z, Xiao Y, Wang J, Qiu
H, Yu W, Tang R, Yuan Y, Guo W and Deng W: Melatonin enhances the
antitumor effect of fisetin by inhibiting COX-2/iNOS and NF-kB/p300
signaling pathways. PLoS One. 9:999432014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zou DB, Wei X, Hu RL, Yang XP, Zuo L,
Zhang SM, Zhu HQ, Zhou Q, Gui SY and Wang Y: Melatonin inhibits the
migration of colon cancer RKO cells by down-regulating myosin light
chain kinase expression through cross-talk with p38 MAPK. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 16:5835–5842. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Benítez-King G, Soto-Vega E and
Ramírez-Rodriguez G: Melatonin modulates microfilament phenotypes
in epithelial cells: Implications for adhesion and inhibition of
cancer cell migration. Histol Histopathol. 24:789–799.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ordoñez R, Carbajo-Pescador S,
Prieto-Dominguez N, García-Palomo A, González-Gallego J and Mauriz
JL: Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and nuclear factor
kappa B contribute to melatonin prevention of motility and
invasiveness in HepG2 liver cancer cells. J Pineal Res. 56:20–30.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olson MF and Sahai E: The actin
cytoskeleton in cancer cell motility. Clin Exp Metastasis.
26:273–287. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Runkle EA and Mu D: Tight junction
proteins: From barrier to tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 337:41–48.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou Q, Gui S, Zhou Q and Wang Y:
Melatonin inhibits the migration of human lung adenocarcinoma A549
cell lines involving JNK/MAPK pathway. PLoS One. 9:1011322014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hoover KB, Liao SY and Bryant PJ: Loss of
the tight junction MAGUK ZO-1 in breast cancer: Relationship to
glandular differentiation and loss of heterozygosity. Am J Pathol.
153:1767–1773. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vicente-Manzanares M, Ma X, Adelstein RS
and Horwitz AR: Non-muscle myosin II takes centre stage in cell
adhesion and migration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:778–790. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
González-Marisca L, Tapia R and Chamorro
D: Crosstalk of tight junction components with signaling pathways.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1778:729–756. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ito M, Nakano T, Erdodi F and Hartshorne
DJ: Myosin phosphatase: Structure, regulation and function. Mol
Cell Biochem. 259:197–209. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pellegrin S and Mellor H: Actin stress
fibres. J Cell Sci. 120:3491–3499. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsuji T, Ishizaki T, Okanoto M, Higashida
C, Kimura K, Furuyashiki T, Arakawa Y, Birge RB, Nakamoto T, Hirai
H and Narumiya S: ROCK and mDia1 antagonize in Rho-dependent Rac
activation in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 157:819–830.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wojciak-Stothard B and Ridley AJ: Shear
stress-induced endothelial cell polarization is mediated by Rho and
Rac but not Cdc42 or PI 3-kinases. J Cell Biol. 161:429–439. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Totsukawa G, Wu Y, Sasaki Y, Hartshorne
DJ, Yamakita Y, Yamashiro S and Matsumura F: Distinct roles of MLCK
and ROCK in the regulation of membrane protrusions and focal
adhesion dynamics during cell migration of fibroblasts. J Cell
Biol. 164:427–439. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Banerjee S and McGee DW: ROCK activity
affects IL-1-induced signaling possibly through MKK4 and p38 MAPK
in Caco-2 cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 52:878–884. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chang L and Karin M: Mammalian MAP kinase
signaling cascades. Nature. 410:37–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cumaoglu A, Dayan S, Agkaya AO, Ozkul Z
and Ozpozan NK: Synthesis and pro-apoptotic effects of new
sulfonamide derivatives via activating p38/ERK phosphorylation in
cancer cells. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 30:413–419. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grossi V, Peserico A, Tezil T and Simone
C: p38α MAPK pathway: A key factor in colorectal cancer therapy and
chemoresistance. World J Gastroenterol. 20:9744–9758. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hill SM, Belancio VP, Dauchy RT, Xiang S,
Brimer S, Mao L, Hauch A, Lundberg PW, Summers W, Yuan L, et al:
Melatonin: An inhibitor of breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer.
22:R183–R204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakagawa O, Fujisawa K, Ishizaki T, Saito
Y, Nakao K and Narumiya S: ROCK-I and ROCK-II, two isoforms of
Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein serine/threonine kinase
in mice. FEBS Lett. 392:189–193. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hahmann C and Schroeter T: Rho-kinase
inhibitors as therapeutics: From pan inhibition to isoform
selectivit. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:171–177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matsuoka T, Yashiro M, Kato Y, Shinto O,
Kashiwagi S and Hirakawa K: RhoA/ROCK signaling mediates plasticity
of scirrhous gastric carcinoma motility. Clin Exp Metastasis.
28:627–636. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu N, Bi F, Pan Y, Sun L, Xue Y, Shi Y,
Yao X, Zheng Y and Fan D: Reversal of the malignant phenotype of
gastric cancer cells by inhibition of RhoA expression and activity.
Clin Cancer Res. 10:6239–6247. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zucchini C, Martinelli M, De Sanctis P,
Rodia MT, Mattei G, Ugolini G, Montroni I, Ghignone F and Solmi R:
Possible gender-related modulation by the ROCK1 gene in colorectal
cancer susceptibility. Pathobiology. 82:252–258. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsu HH, Kuo WW, Day CH, Shibu MA, Li SY,
Chang SH, Shih HN, Chen RJ, Viswanadha VP, Kuo YH and Huang CY:
Taiwanin E inhibits cell migration in human LoVo colon cancer cells
by suppressing MMP-2/9 expression via p38 MAPK pathway. Environ
Toxicol. 32:2021–2031. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shin I, Kim S, Song H, Kim HR and Moon A:
H-Ras-specific activation of Rac-MKK3/6-p38 pathway: Its critical
role in invasion and migration of breast epithelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 280:14675–14683. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mao L, Yuan L, Slakey LM, Jones FE, Burow
ME and Hill SM: Inhibition of breast cancer cell invasion by
melatonin is mediated through regulation of the p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Breast Cancer
Res. 2:R1072010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hill SM, Belancio VP, Dauchy RT, Xiang S,
Brimer S, Mao L, Hauch A, Lundberg PW, Summers W, Yuan L, et al:
Melatonin: An inhibitor of breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer.
22:R183–R204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lai JM, Hsieh CL and Chang ZF: Caspase
activation during phorbol ester-induced apoptosis requires ROCK
dependent myosin-mediated contraction. J Cell Sci. 116:3491–3501.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|